Lecture 31 - Na-K-H2O homeostasis
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
diuresis
increased production of urine
where is ADH (vasopressin) made?
in the hypothalamus and secreted by the posterior pituitary gland
what kind of response is ADH
mostly acute response
can be released and cause changes within minutes
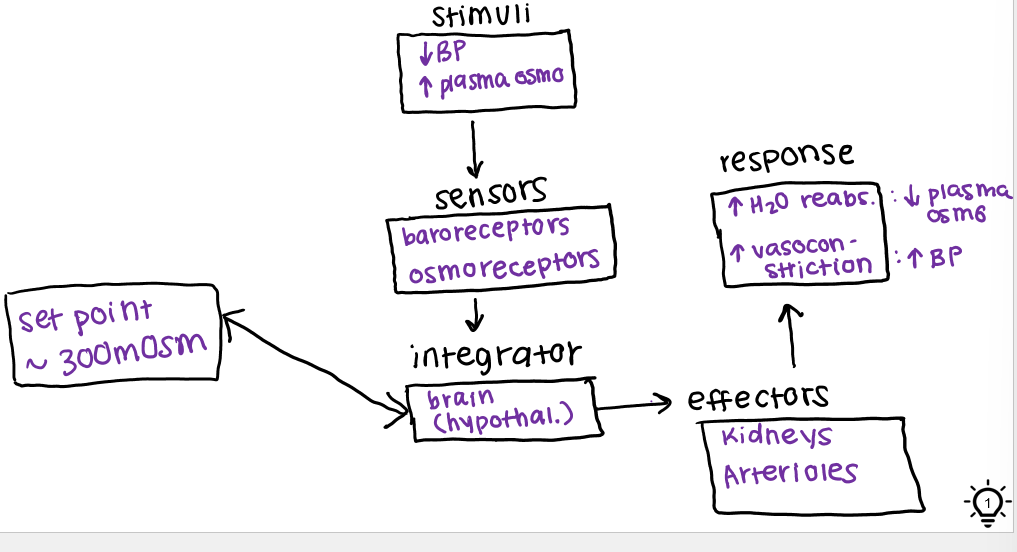
what is the stimuli for ADH
decreased blood pressure
high plasma osmolarity
angiotensin II
sensors for ADH
baroreceptors in blood vessels
osmoreceptors in hypothalamus
draw feedback loop for ADH
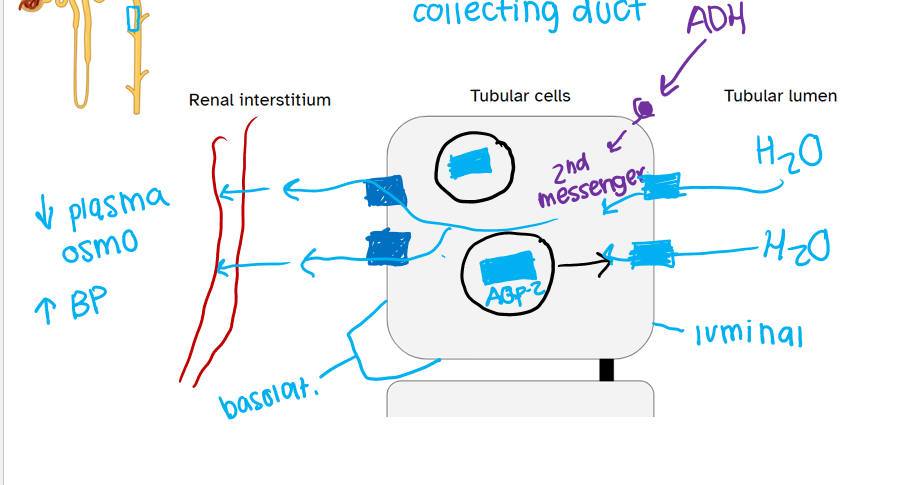
what is the response generated by ADH in the collecting duct?
when dehydrated, plasma osmolarity will
increase
dehydration will ___ the release of ADH, increasing water ____
stimulate; reabsorption
what is the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system?
critical regulator of blood volume, electrolyte (Ma/L) balance, and blood pressure
involved in acute and long term physiological responses to these variables
extremely clinically relevant
many areas where things can go wrong
many points of pharmacological control
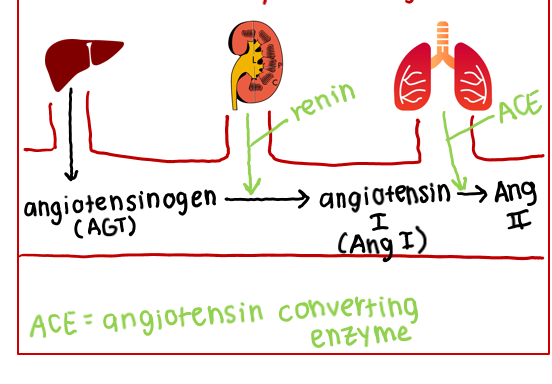
what is the assembly line for angiotensin II
liver = angiotensinogen
kidneys = renin
prod: angiotensin I
lungs = ACE
prod: angiotensin II
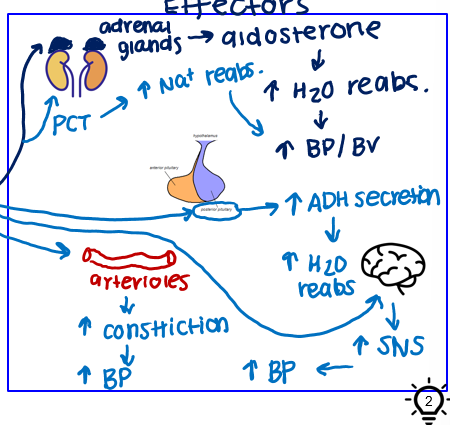
what are the effectors of RAAS?
kidneys
PCT in kidneys→ inc Na+ reabs.+ inc. BP/BV
adrenal glands → aldosterone → inc H20 reabs. and inc. BP/BV
posterior pituitary → ADH secretion → inc. H2O reabs.
arterioles → inc constriction → inc BP
brain → inc SNS → inc. BP
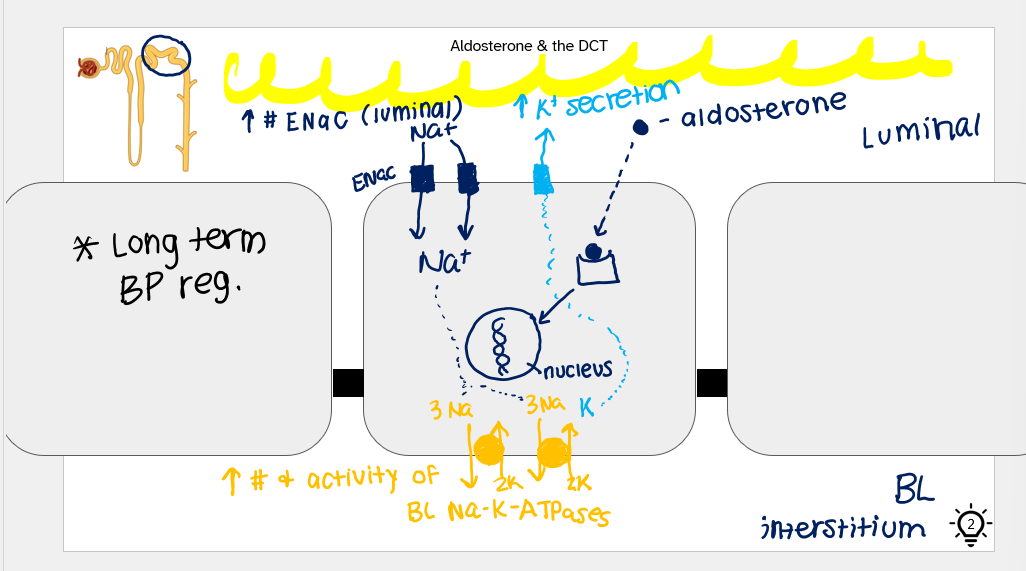
aldosterone and the DCT
aldosterone binds to internal receptors in the cell and it makes changes in the nucleus that lead to the ENaC
inc. in number of ENaC (luminal)
bring in Na+
inc. activity of the Na-K-ATPases
bring sodium out of cell
inc. K+ secretion on luminal side
IMP for LONG TERM BP reg.