LAST VOCAB SET: Asian Transitions in an Age of Global Change
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
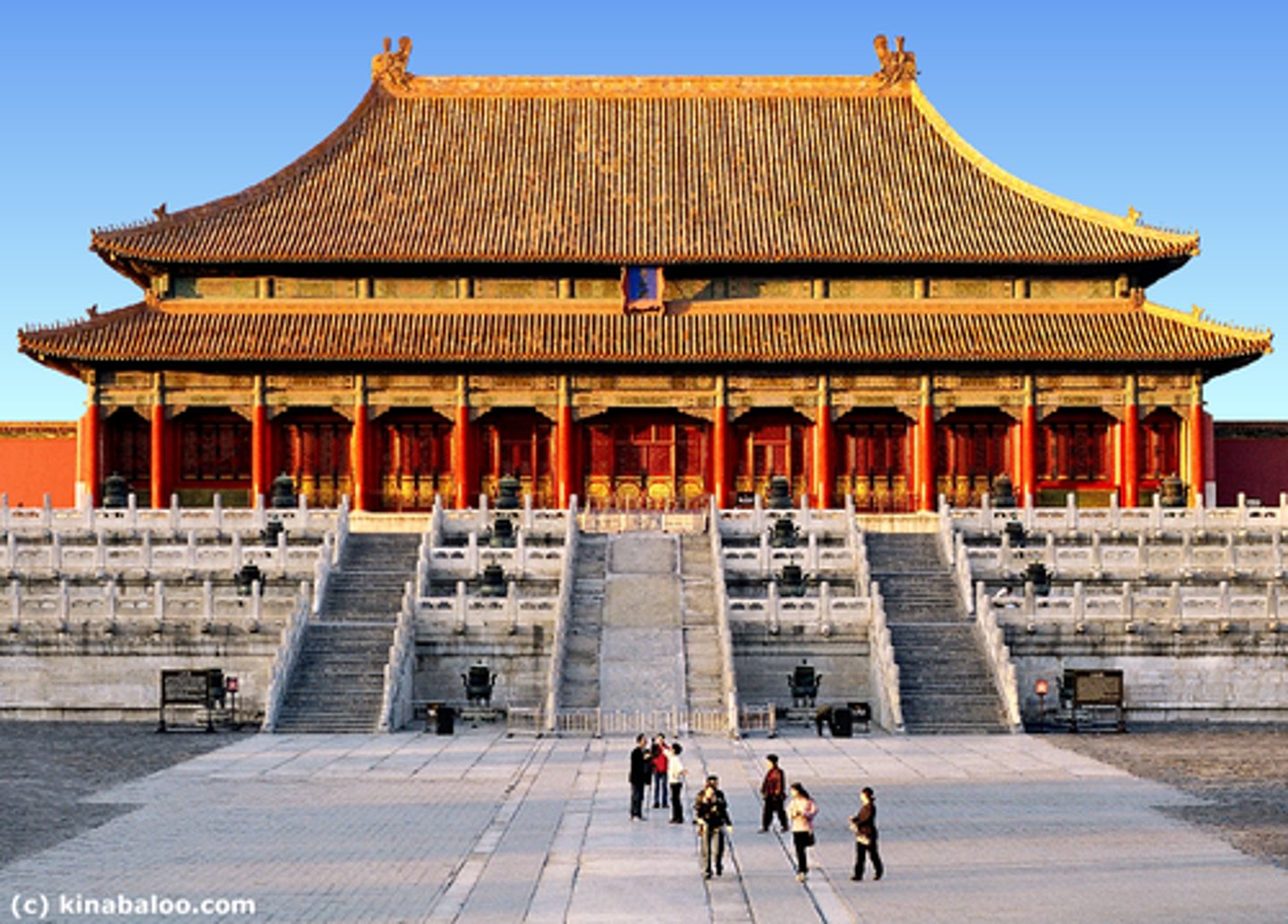
Forbidden City
Built in the Ming Dynasty, was a stunning residence in Beijing for the emperor until 1924.

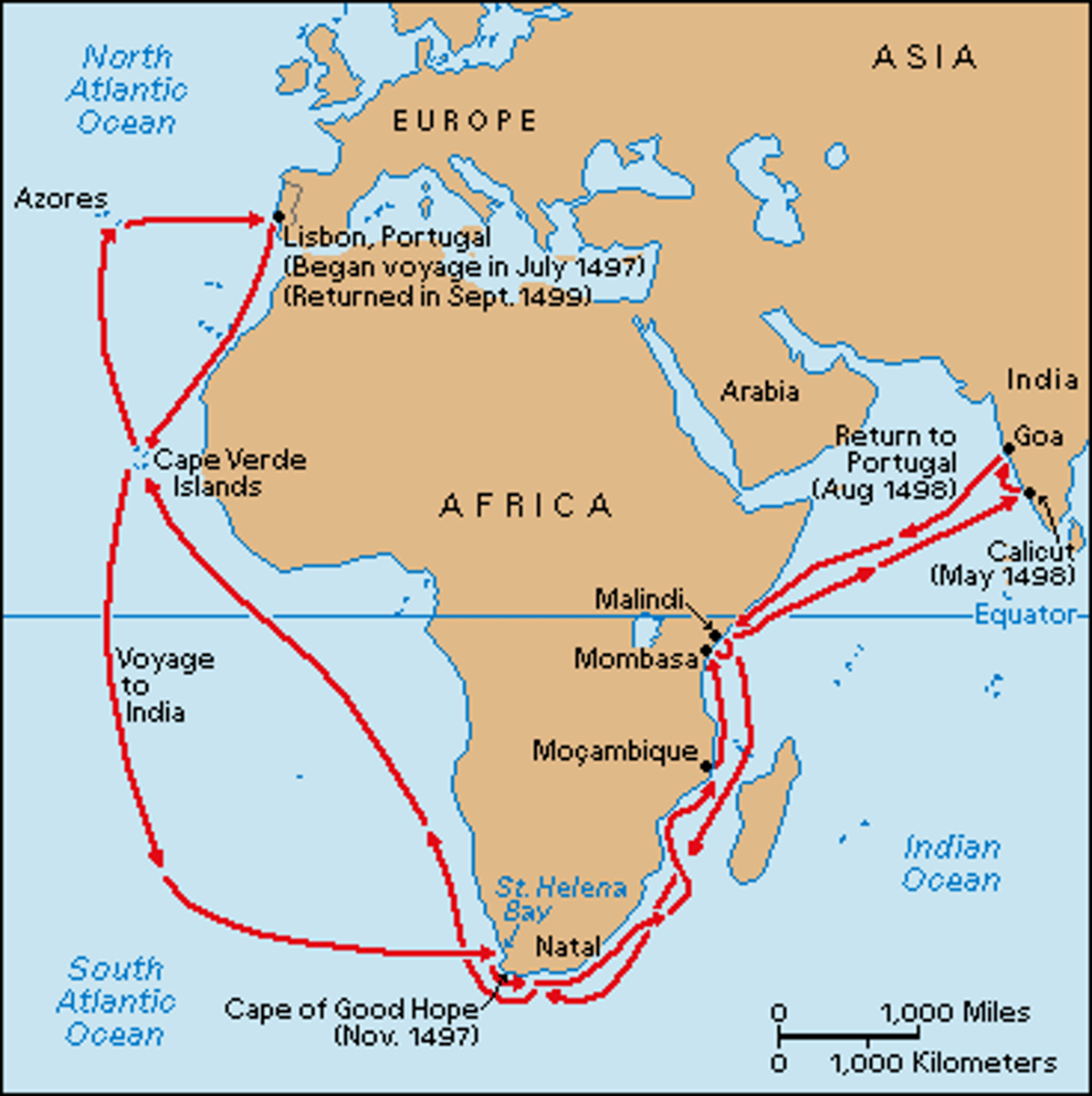
Vasco da Gama
Explorer who gave Portugal a direct sea route to India.
Ming Dynasty
Chinese dynasty in which Chinese rule was restored from the Mongols; held power from 1368 to 1644
Bullion
Gold and silver in the form of bars

Asian Sea Trading Network
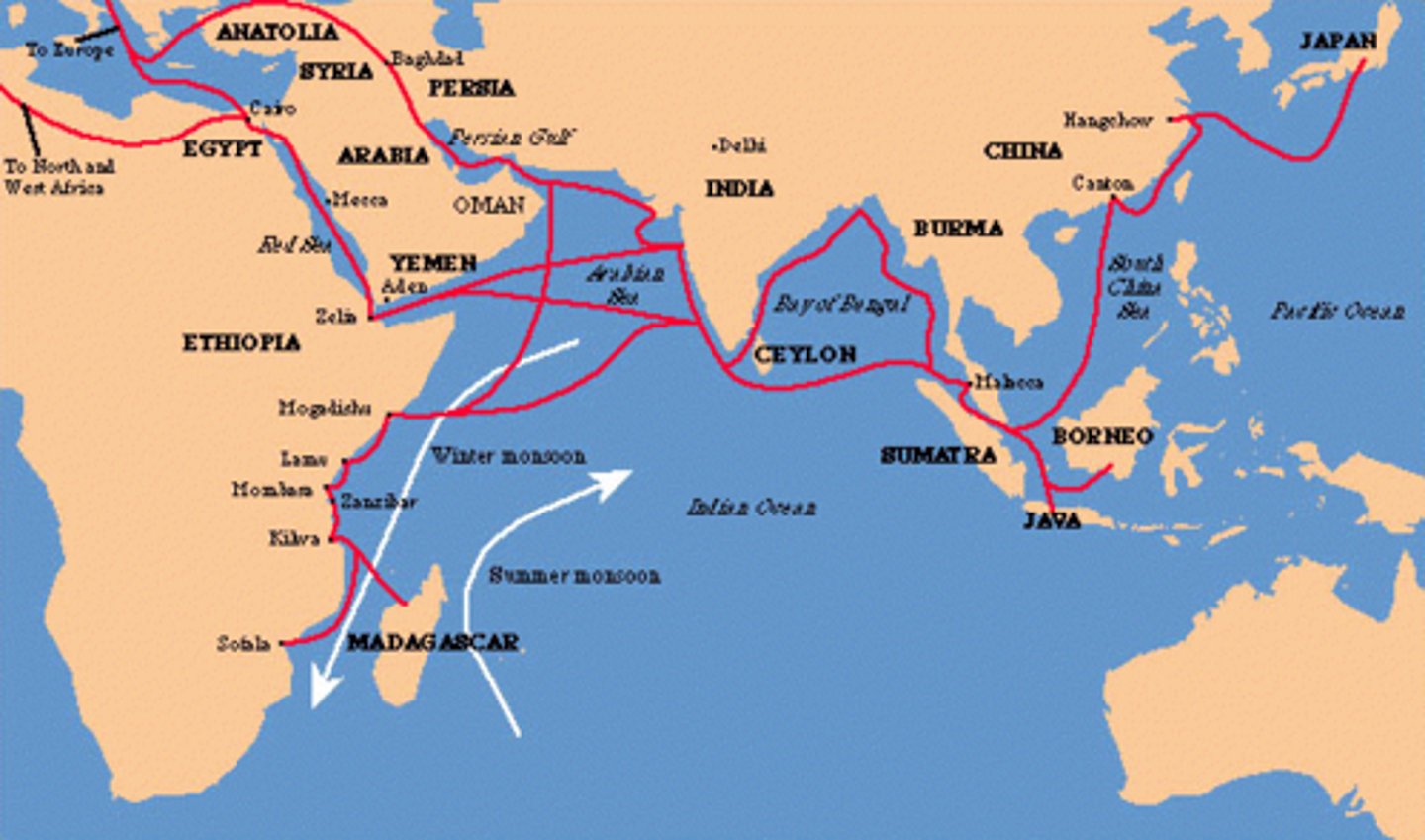
"The Asian trading network was composed of three main zones: an Indian zone, an Arab zone and a Chinese zone. The Arab zone was based on tapestry, glass and carpentry. The Indian zone was focused on the trade of cotton and textiles. The Chinese zone primarily traded porcelain, silks and paper. The merchants who initiated the trade carried their culture to the different geographic regions. As a result, foreign languages, customs, religions, beliefs, technology and art emerged in Asia. Asian culture also spread to other regions through this trade network. The Asian sea trading network also included the Japan, the Southeast Asian islands, as well as parts of East Africa. Arab, Chinese, Southeast Asian, and Indian traders sailed and traded to provide for their own livelihood and also to make profits for the merchants and princes who funded their expeditions."
Hongwu
First Ming emperor from 1368 to 1398; originally of peasant lineage; drove out Mongol influence; restored position of scholar gentry.

Zheng he
Chinese Muslim admiral (1371-1433) who commanded a fleet of more than 300 ships in a series of voyages of contact and exploration that began in 1405. Was eventually called back in 1433 by the Chinese because of his growing popularity and his journey was too expensive. This started a period of relative isolation for China.
Shogunates
A government controlled by shoguns. Japan had 3 shogunates during its history: Kamakura, Ashikaga, and Tokugawa.
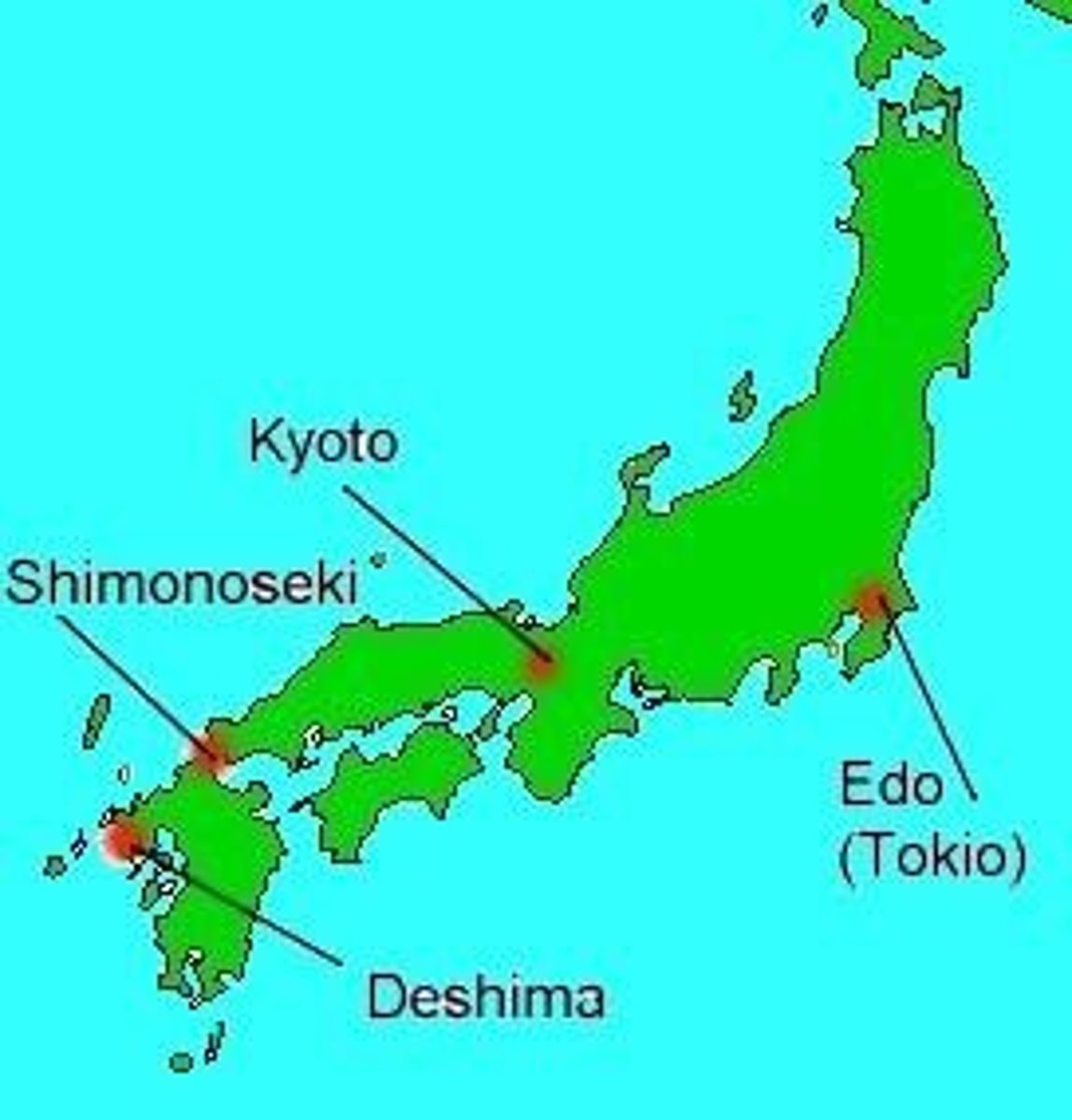
Deshima
Island in Nagasaki Bay; only port open to non-Japanese after closure of the islands in the 1640s; only Chinese and Dutch ships were permitted to enter
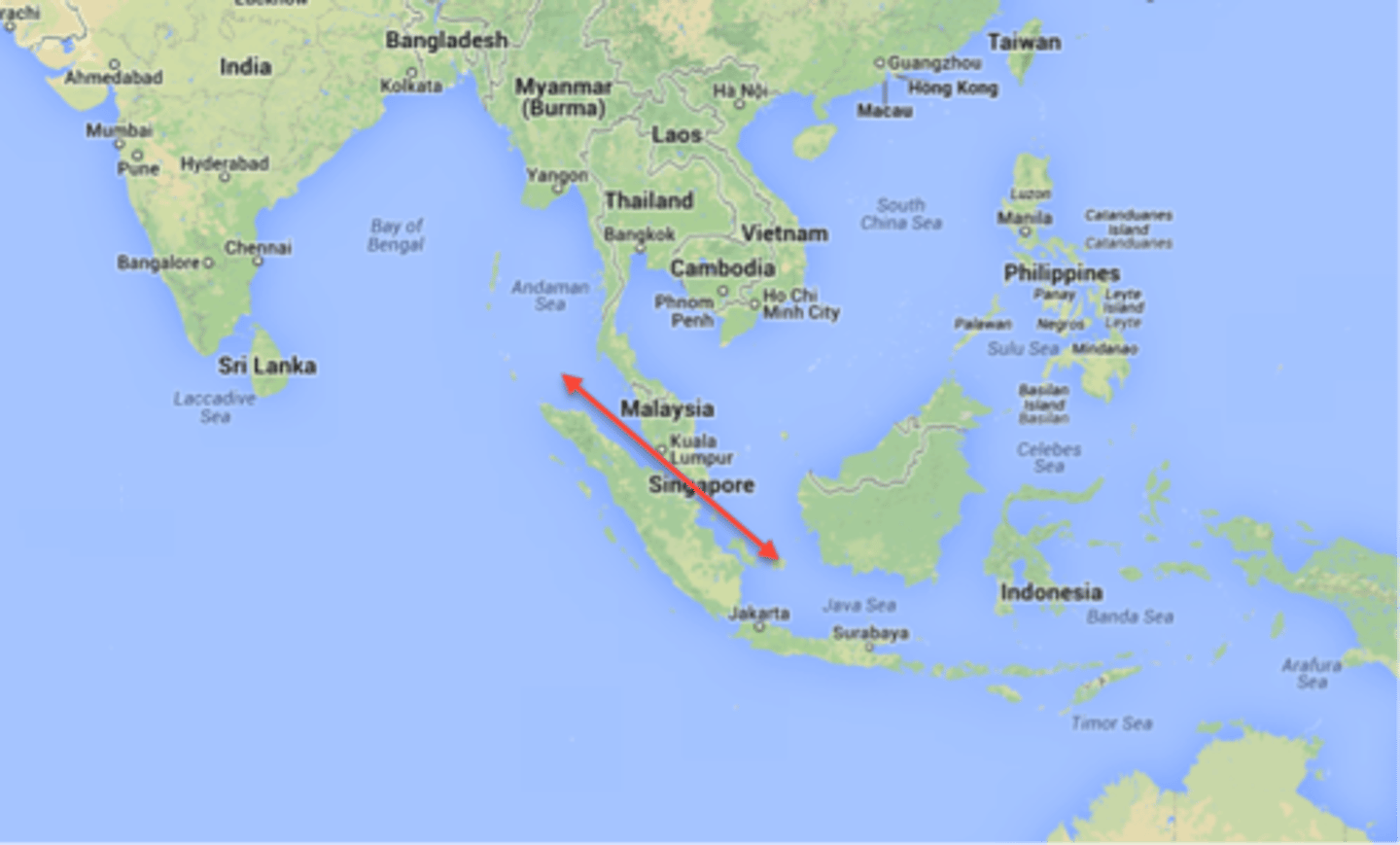
Malacca
Portuguese factory or fortified trade town located on the tip of the Malayan peninsula; traditionally a center for trade among the southeastern Asian islands
Francis Xavier and Robert Di Nobili
Spanish Jesuit missionaries; worked in India in 1540s among the outcaste and lower caste groups; made little headway among elites
Matteo Ricci and Adam Schall
Jesuit scholars in court of Ming emperors; skilled scientists; but won few converts to Christianity in China
Manchu
The people who founded the Qing dynasty that seized control of China in the mid 17th century after the decline of the Ming. Were made up of united tribes to the north that formerly made up the Jin Dynasty. This NOMAD group blended with Chinese.
Batavia
Dutch fortress located after 1620 on the island of Java. Known as Jakarta today.
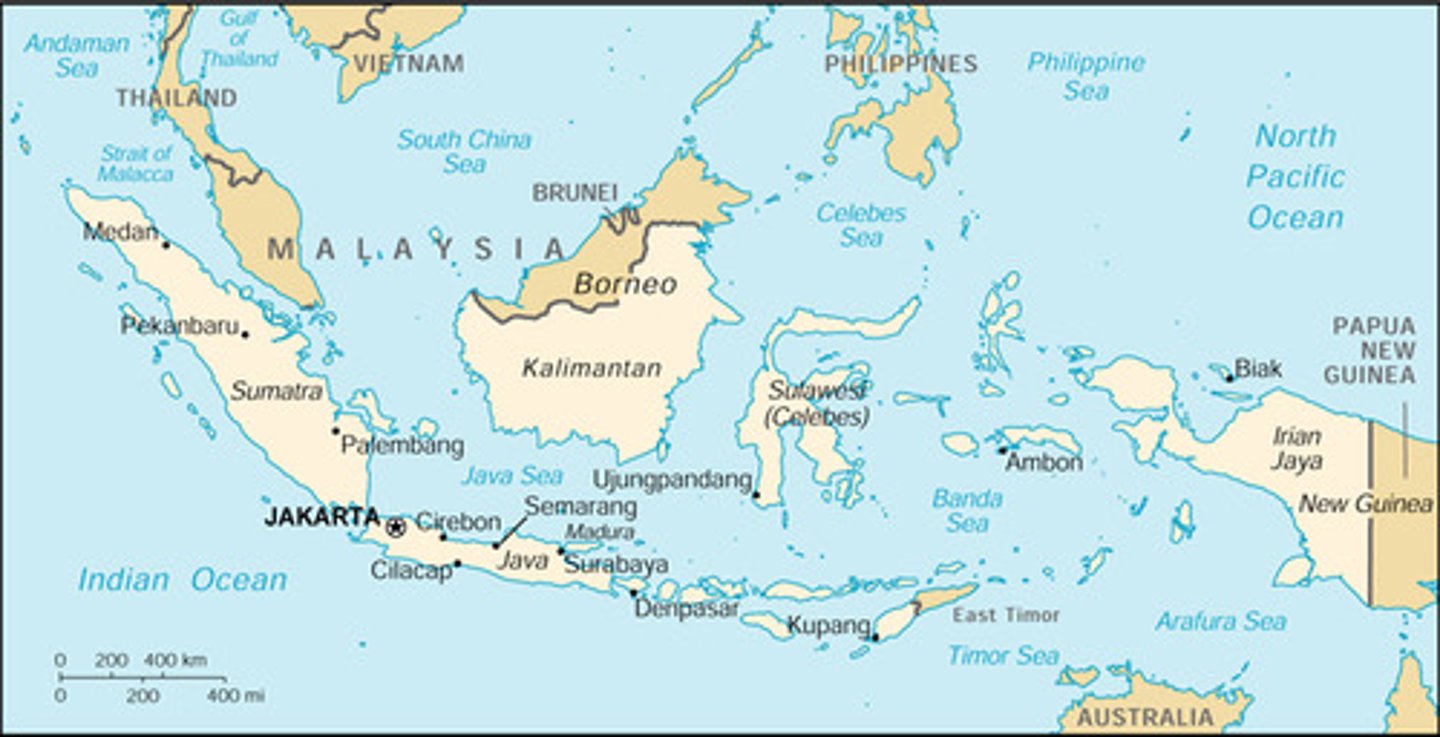
Luzon
Northern island of Philippines; conquered by Spain during the 1560s; site of major Catholic missionary effort
Canton
One of two port cities in which Europeans were permitted to trade in China during the Ming dynasty.
Mindanao
Southern island of Philippines; a Muslim kingdom that was able to successfully resist Spanish conquest.
Single Whip Tax System
A policy put forth by the Ming in the 1570s requiring a single national tax and that all taxes be paid in the form of silver, including those taxes paid by tributary states.
• This change in policy had global implications, as people now now had to fulfill the demand for silver.
• Silver made its way into China from both Japan and the Americas, resulting in enormous profits for both Spain and Japan.
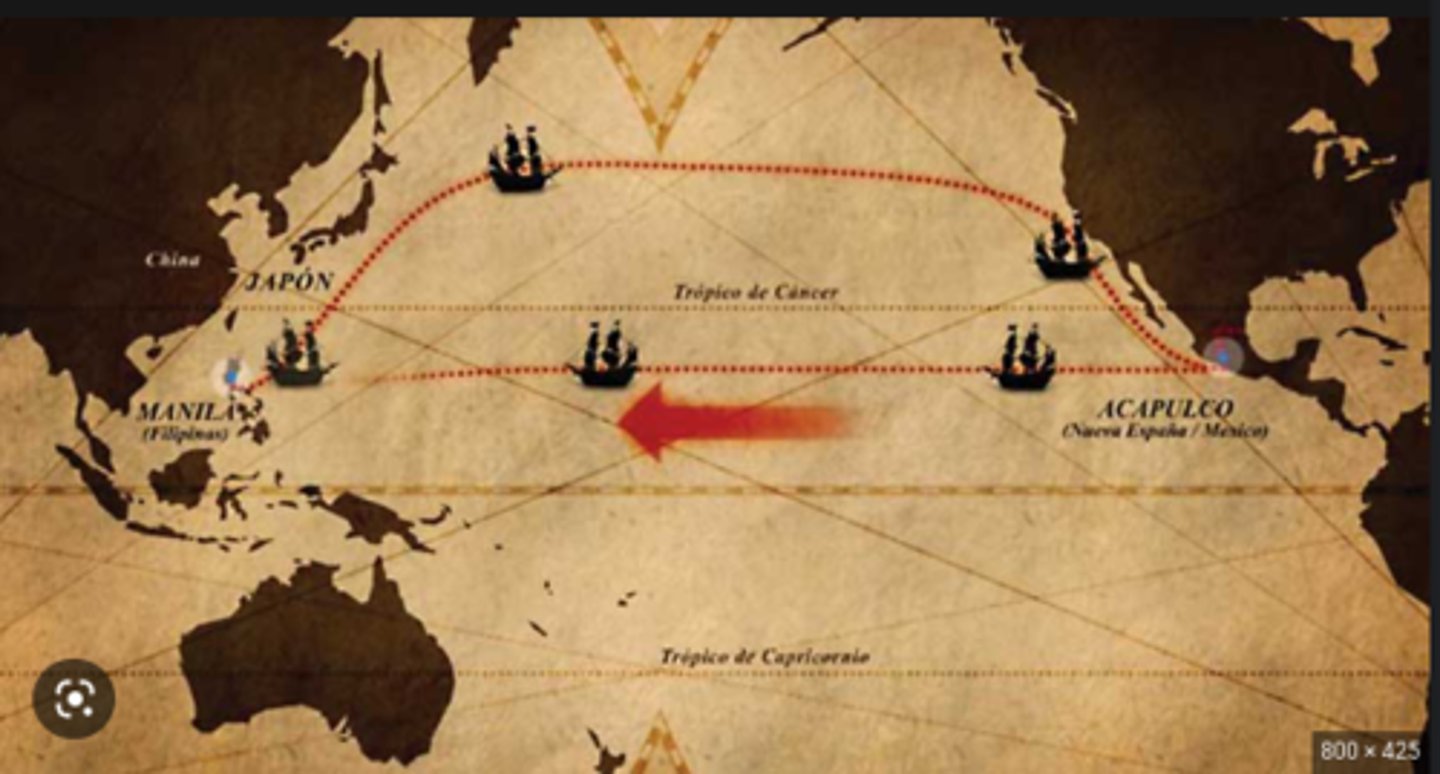
Manilla Galleon Trade
The very profitable trade between Manila in the Philippines and the west coast of the Americas during the 1500- 1700s.
Factories
European trading fortresses and compounds with resident merchants; utilized throughout Portuguese trading empire to assure secure landing places and commerce.