Epigenetics
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
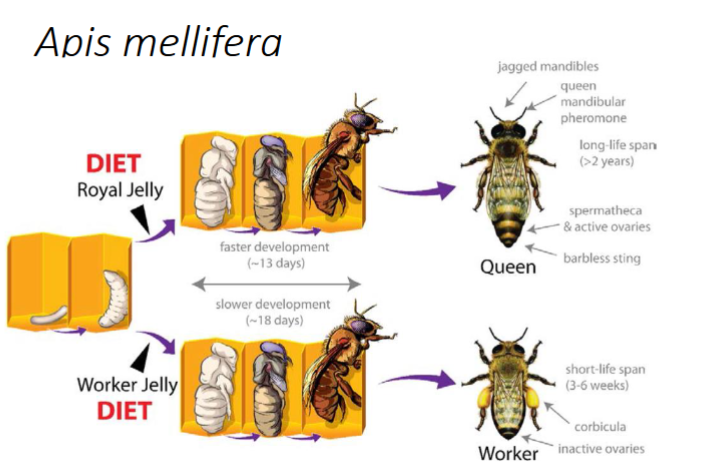
In Apis mellifera bees, what determines if a bee becomes a worker bee or a queen
Their diet
What is a mosaic
A mosaic is an individual who arose from a single fertilized egg, but who has 2 or more populations of cells each with different genotypes
Are both X chromosomes in females active
No

What makes this cat 2 different colours
Random exon activation
Random X-chromosome inactivation explains tortoiseshell or calico (3+ colors) in females
Turner Syndrome traits/symptoms
• Coarctation of aorta or bicuspid aortic valve
• Webbed neck and lymphedema (sometimes)
• Kidney problems – horseshoe kidney
• Amenorrhea
• Non-functional ovaries (streak gonads) – infertile
• Non verbal learning disabilities and behavioural problems - variable
Turner Syndrome cause
Turner syndrome occurs due to anaphase lag – where one sex chromosome moves too slowly to the pole of the daughter cell during division
It can happen:
• During gametogenesis - classical monosomy X – 45,X
• During early mitotic division - Turner Mosaicism – 45X/46XX or 45X/46XY
Is turner syndrome / Turner Mosaicism inherited
No - neither
Treatment options & priorities for Turner Syndrome
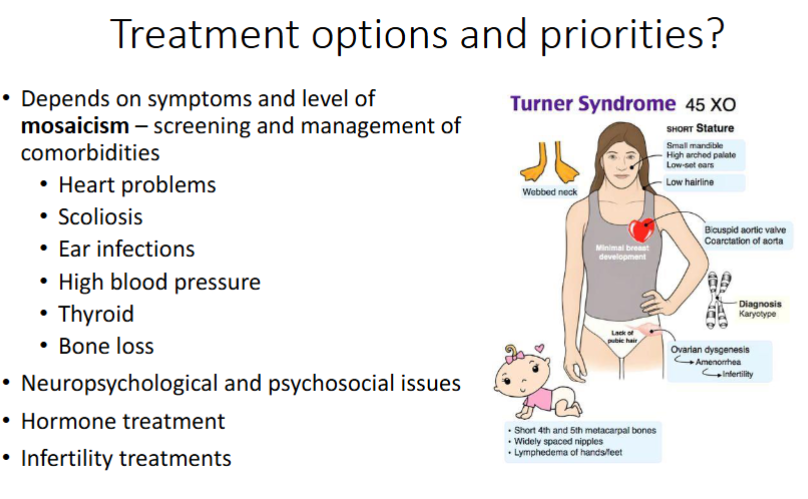
What would be 4 key tests/investigations to assess people diagnosed with Turner syndrome
Karyotype – translocation?
Cardiac function tests
Cardiac imaging - CT, MRI, MRA
Y chromosome PCR
Why would 45,X be a problem for women but men can live with just 1 X chromosome
There are genes that are on both the X and Y chromosomes that need to be expressed twice to function.
The inactivation of the 2nd X chromosome is incomplete - it still has a few active gene. (Up to 25% of X chromosome genes partially or totally escape (including PAR genes e.g. SHOX))
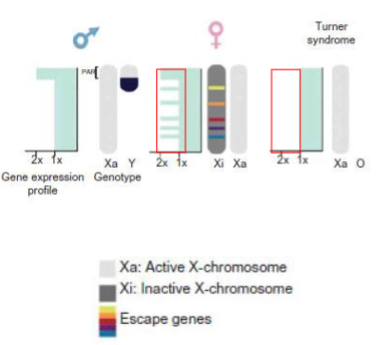
Escape genes expressed in higher/lower levels in normal women versus Turner women
Higher
Function of genes outside PARs
Genes outside PARs may contribute to female phenotype
Tetragametic Chimerism
2 Oocytes + 2 Sperm
2 Zygotes that Merge into one Organism
Chimaerism vs Mosaicism
Chimaera = an individual with 2 or more populations of cells with different genotypes who arose by fusion of more than one fertilised zygote during embryogenesis
Mosaic = an individual with 2 or more populations of cells with different genotypes who arose from a single fertilised egg
Mosaic usually results from what
somatic change during early replication
What can Germline mosaicism result in
Germline mosaicism occur early in germ cell development, resulting in a significant no. of gametes that carry the mutation and thus can affect >1 child
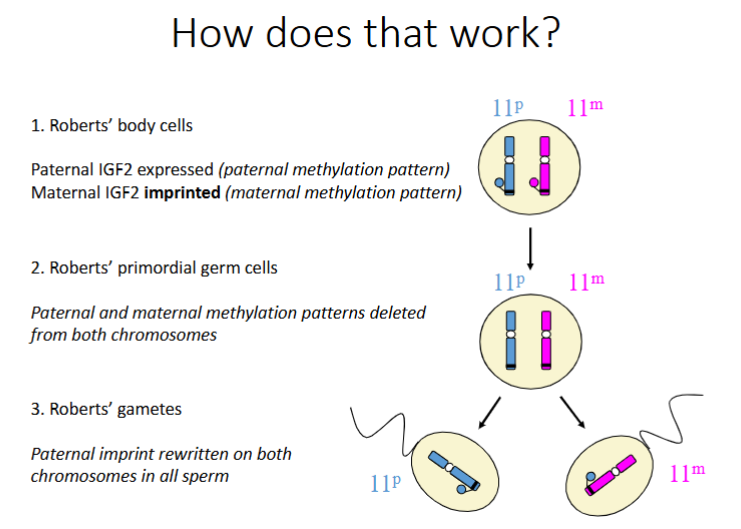
Robert has an allele of Insulin Like Growth Factor 2 (IGF2) from Don – which works
He has an allele of Insulin Like Growth Factor 2 from Betty that is switched off (imprinted)
If Robert Draper has a child, which allele of the IGF2 gene will work?
If Robert (the father) has a child, whichever version of the allele (from Don or from Betty) that is present in his sperm will be switched on
Explain the mechanism behind this
Role of IGF2 in gestation
Regulate growth
Give an example of what can occur as a result of loss of imprinting (LOI) of maternal IGF2
Wilms’ tumour is an embryonic kidney cancer associated with loss of imprinting (LOI) of maternal IGF2
If both IGF2 alleles should begin to be expressed in a cell, what can be the result
That cell may develop into cancer
What deletion is associated with Prader Willi
Deletion from paternal Chr 15 (15q11-q13)
What deletion is associated with Angelman syndrome
Deletion from maternal Chr 15 (15q11-q13)
What would a child with paternal uniparental disomy for Ch 15 have ?
Child is missing a maternal Ch15 – therefore Angelman’s syndrome (vice versa for Prader Willi)
Is it possible for an individual with Prada Willi syndrome to have BOTH maternal and paternal chromosomes
Yes - the paternal chromosome may have maternal pattern of methylation (effectively no paternal chromosome) due to:
• Epigenetic (imprinting) error
• Mutations in the imprinting control centre
Is it possible for an individual with Angelman syndrome to have BOTH maternal and paternal chromosomes
The maternal chromosome may have the paternal pattern or methylation due to:
• Epigenetic (imprinting) error
• Mutations in the imprinting control centre
X-inactivation is incomplete - up to 25% of X chromosome genes partially or totally escape (including PAR genes), which has implications for what
gene dosing
Diseases related to imprinting can occur due to what 4 causes
Diseases related to imprinting can occur due to UPD or a mutation in the imprinting control centre, as well as deletion/mutation of the genes themselves on the relevant Chr