NEUR305: Auditory
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is sound?
Pressure waves through air evoked by quickly moving objects
Purpose of signaling?
Show presence of objects, prey/predators (avoiding danger), animal communication
Properties of signals?
Frequency - Pitch
Amplitude/Intensity - Loudness
Timing/Phase
Complexity - Timbre
Structure of the ear
Outer ear (pinna & ear canal), middle ear (ossicles), inner ear (cochlea)
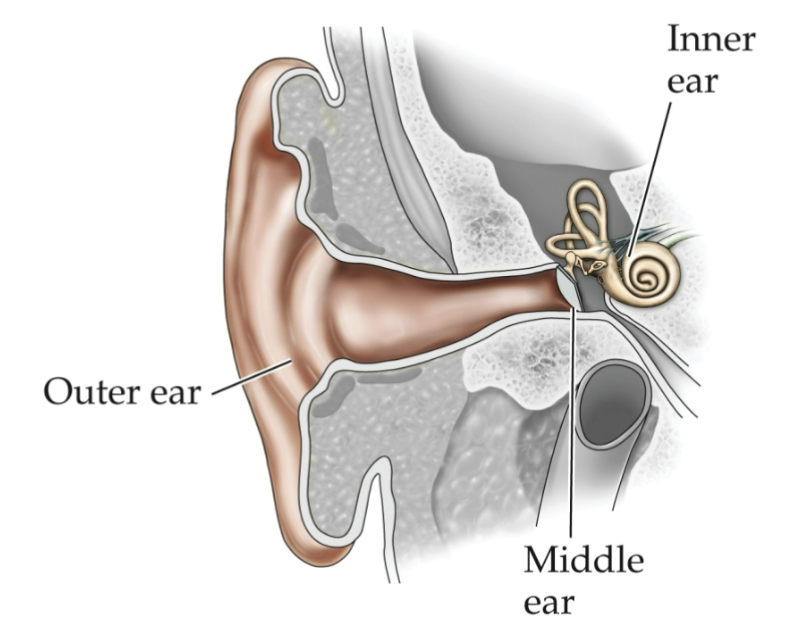
Outer ear function?
Amplifies sound in 3k Hz range (range of human speech)
ex. bats with big ears have ridges that create frequency dependent sound level differences
Middle ear function?
Condenses air waves into signals
Consists of the malleus, incus, stapes, and tympanic membrane
What is impedance matching?
Inner ear is fluid-filled and the rest is air!
Expected loss of signal from the switch of mediums (due to reflection of signal), is accounted for in an amplification of the signal.
How does the middle ear deal with impedance?
Mechanical advantage through tympanic ossicles that act as levers; focuses the force thru the ration between tympanic membrane and oval window
Inner ear function?
Waves enter scala vestibuli through oval window
Waves exit through scala tympani out round window
What is the cochlea + 3 steps?
Transduces mechanical energy into electrical signals!
hair cells detect motion of wave
cilia motion transduces to neurotransmitter release
spiral ganglion cell axons form the cochlear nerve
What converts the stimulus to action potentials in the auditory system?
Spiral ganglion cells!
What’s the tonotopic map of cochlea?
Base = higher frequency
Apex = lower frequency
What’s the auditory pathway?
auditory nerve → cochlear nuclei → superior olivary nucleus → inferior colliculus → thalamus (MGN) → primary auditory cortex
What’s the auditory cortex function?
complex selectivity for sound features; context dependent
What’s the thalamus function?
associating sound w/ reward; attentional modification; shaping to process complex sound
What’s the inferior colliculus function?
full spatial map of sound location; spectrotemporal processing; motor structures & startle response
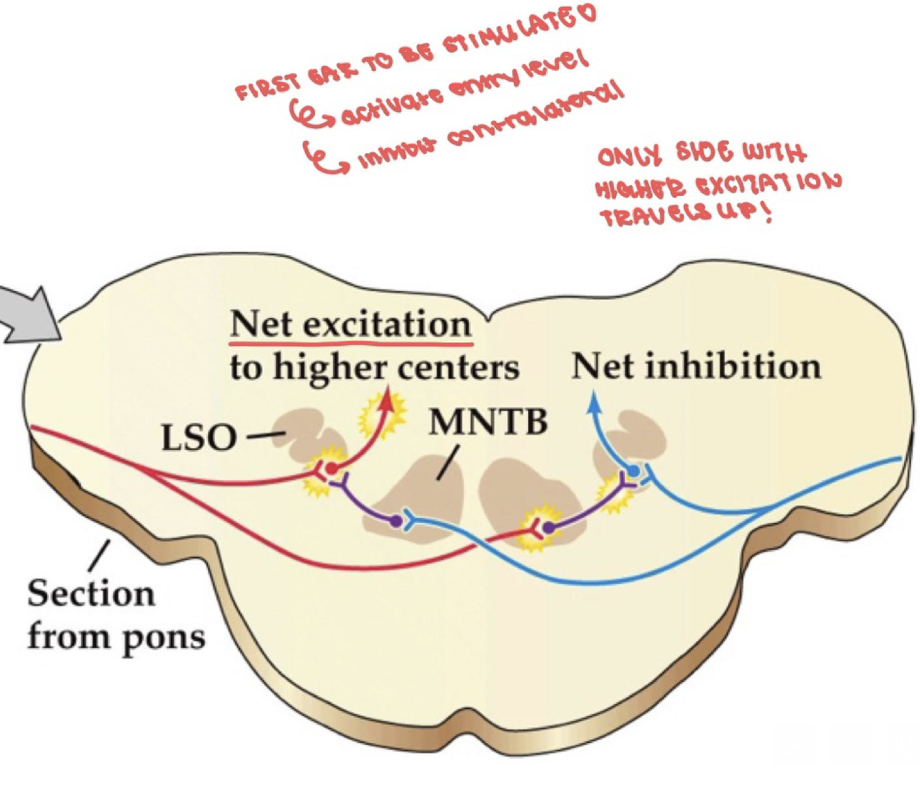
What’s the superior olivary nucleus function?
LOCALIZE SOUND
Medial superior olive is interaural time difference (ITD) or time differences (time to for sound to reach the two ears).
Lateral superior olive is interaural level difference (ILD) loudness differences (difference in sound pressure level reaching two ears)
What’s ITD (Interaural Time Differences)?
ITD look at the time sound reaches the two ears!
Medial Superior Olive
Same distance = no time difference
Smaller heads have small ITDs
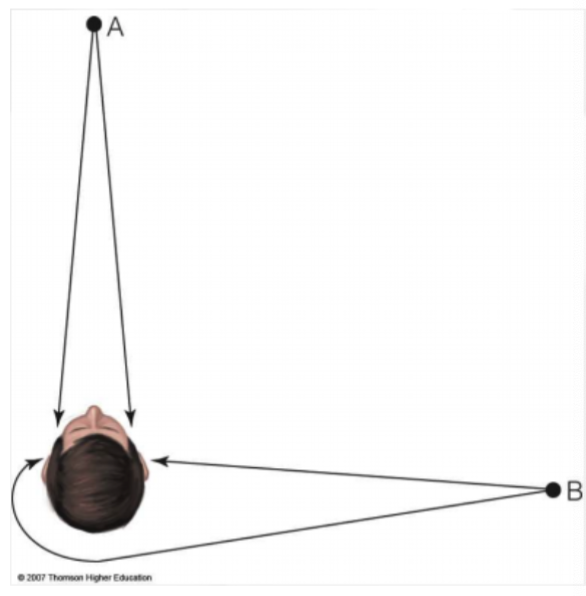
What’s ILD (Interaural Level Differences)?
Looks at the intensity of the sound reaching both ears; greater intensity = louder
First ear to be stimulated activates entry level, which inhibits contralateral; only side with high excitation travels up!
What happens as we move up the auditory “hierarchy”?
Stimulus selectivity increases! It may be multi-dimensional: frequency, bandwidth, intensity, modulation frequency, spatial location
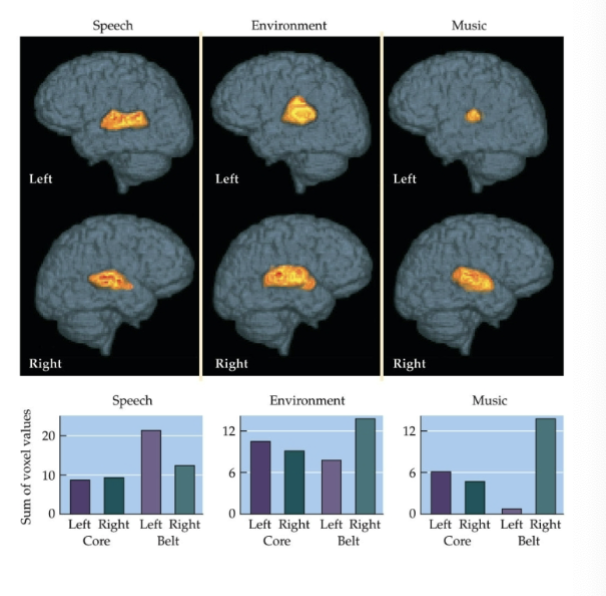
What are secondary auditory areas?
It’s the belt area; prefers complex sounds; what and where streams
How is sound perceived differently based on relevance?
Belt area is more lateralized than the core!
In speech, the left belt is more active.
In music, the right belt area is more active.
What is the auditory processing of barn owl?
Owl’s ears are not symmetrically aligned which leads to differences in sound input.