13. Wavelength-Division Multiplexing
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] It is easy to understand WDM.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] WDM is just a variation of FDM.
low
FDM uses __-frequency electromagnetic waves.
high
WDM uses __-frequency electromagnetic waves.
prism
The colors are transmitted thru the air together and may mix, but they can be easily separated using a simple device like a _____.
optical coupler/optical amplifier
one of the components used in WDM.
optical fiber cable
kind of cable used in WDM
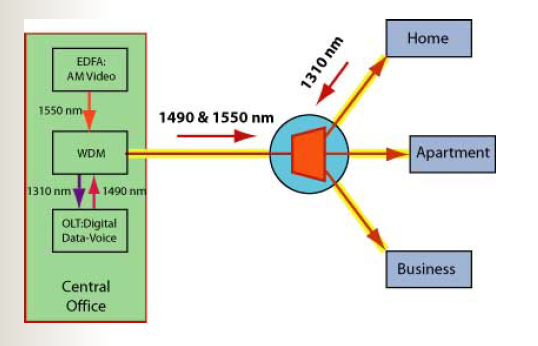
Fiber to the Home (FTTH) Passive Optical Networks
It uses a simple version of WDM to allow bidirectional communications over a single fiber to reduce costs.
different wavelengths
In FTTH passive optical networks, the signals downstream and upstream are at _____ to prevent interference.
1490nm and 1550nm
PON standards’ wavelength used for downstream?
1310nm
PON standards’ wavelength used for upstream?
FTTH Passive Optical Network
CWDM vs. DWDM
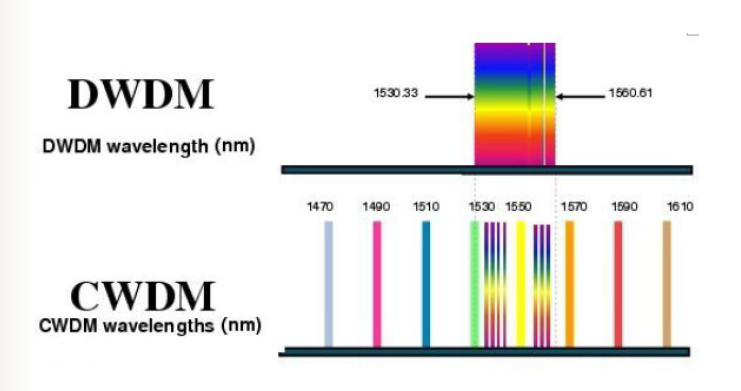
coarse WDM and dense WDM (CWDM and DWDM)
2 types of WDM (HINT: CD)
coarse WDM (CWDM)
It is defined by WDM systems with fewer than 8 active wavelengths per fiber.
8
CWDM is defined by WDM systems with fewer than __ active wavelengths per fiber.
CWDM
It is used for short-range communications, so it employs wide-range frequencies with wavelengths that are spread far apart.
wavelength drift
[CWDM] Standardized channel spacing permits room for _____ as lasers heat up and cool down during operation.
CWDM
It is a compact and cost-effective option when spectral efficiency is not an important requirement.
spectral efficiency
CWDM is a compact and cost-effective option when _______ is not an important requirement.
dense WDM (DWDM)
It is defined in terms of frequencies.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] DWDM’s tighter wavelength spacing fits more channels onto a single fiber, but costs more to implement and operate.
DWDM
It is for systems with more than 8 active wavelengths per fiber.
DWDM
It dices spectrum finely, fitting 40-plus channels into the C-band frequency range.
40-plus
DWDM dices spectrum finely, fitting ____ channels into the C-band frequency range.
C-band
DWDM dices spectrum finely, fitting 40-plus channels into the ____ frequency range.
13nm
channel width: CWDM
1nm
channel width: DWDM
20nm
channel spacing: CWDM
0.8nm
channel spacing: DWDM
4-18
number of channels: CWDM
up to 160
number of channels: DWDM
CWDM
does not use an optical amplifier
DWDM
uses an optical amplifier
up to 120km
CWDM range
up to 500km
DWDM range
DWDM
It transmits multiple data signals using different wavelengths of light thru a single fiber.
incoming optical signals
In DWDM, _____ are assigned to specific frequencies within a designated frequency band.
increased
The capacity of fiber is ______ when these signals are multiplexed onto one fiber.
4-8 times
Transmission capabilities is ___ of TDM Systems with the help of Erbium doped optical amplifier.
Erbium doped optical amplifier
Transmission capabilities is 4-8 times of TDM Systems with the help of ______.
Erbium doped fiber amplifier (EDFA)
other term for Erbium doped optical amplifier
EDFA
It increases the optical signal and do not have to regenerate signal to boost its strength.
300km
DWDM lengthens the distances of transmission to more than ____ before regeneration.
O band
E-band
S-band
C-band
L-band
U-band
DWDM Bands (HINT: OESCLU)
O-band
original band, PON upstream
E-band
water peak band
S-band
PON downstream
C-band
lowest attenuation, original DWDM band, compatible with fiber amplifiers, CATV
L-band
low attenuation, expanded DWDM band
U-band
ultra-long wavelength
1260-1360nm
O-band wavelength
1360-1460nm
E-band wavelength
1460-1530nm
S-band wavelength
1530-1565nm
C-band wavelength
1565-1625nm
L-band wavelength
1625-1675nm
U-band wavelength
C-band, L-band
DWDM’s range starts from ___ until ____.
O-band, L-band
CWDM’s range starts from _____ until ____.
unlimited transmission capacity
scalability
transparency
dynamic provisioning
Why DWDM? (HINT: USTD)
independent
DWDM is a protocal and bit rate ______ hence, data signals such as ATM, SONET, and IP can be transmitted thru same stream regardless their speed difference.
optical layer
DWDM signals are never terminated within the _____ allows the independence of bit rate and protocols, allowing DWDM technology to be integrated with existing equipment in network.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] DWDM has a flexibility to expand capacity within any portion of their networks.
Mike Flynn
“DWDM technology gives us the ability to expand out fiber network rapidly to meet growing demands of our customer,” said _____, group Prresident for ALLTEL’s comms operations.
ATM
DWDM coupled with ____ simplifies the network, reduce network costs and provide new services.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] They can add current and new TDM systems to their existing technology to create a system with virtually endless capacity expansion.
DWDM system
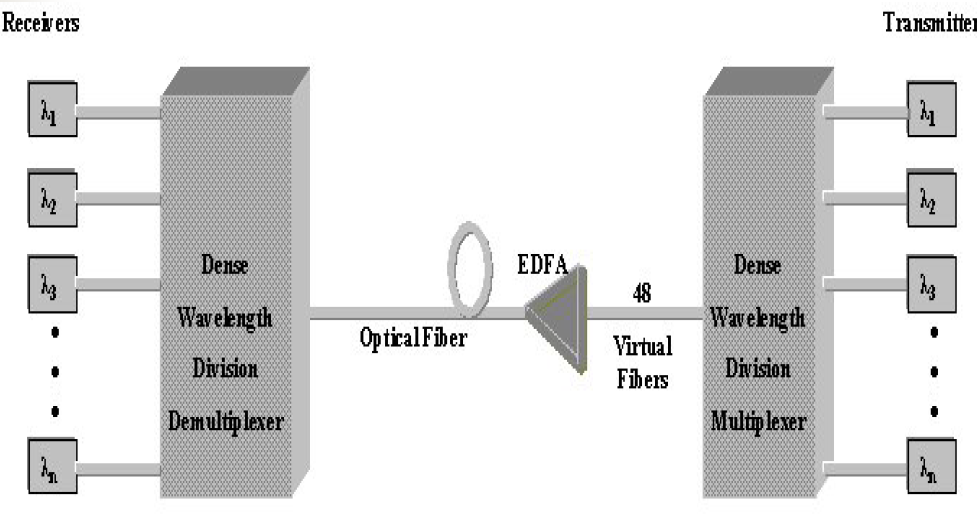
channel spacing
signal direction: uni and bidirectional
signal trace
optical transmission principles (HINT: CSS)
ring topology vs. mesh topology
single hop vs. multi-hop networks
network classificaitons (HINT: RS)
transmitter
link
receiver
optical add/drop multiplexers and optical cross connect components
DWDM components (HINT: TLRO)
transmitter
laser with precise stable wavelength
link
optical fiber that exhibits low loss and transmission performance in relevant wavelength spectra.
receiver
photo detectors and optical demultiplexers using thin film filters or diffractive elements
optical add/drop multiplexers and optical cross connect components
enables new signals to come in and existing signals to come out
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] Well-engineered DWDM systems offer component reliability, system availability, and system margin.
humidity
Although filters were often susceptible to ____, this is no longer the case.
optical fiber doped with erbium
amplifier
2 key elements of an optical amplifier (HINT: OA)
optimal system performance
Automatic adjustment of the optical amplifiers when channels are added or removed achieves ______.
1530-1565nm
Silica-based optical amplifiers with filters and Fluoride-based optical amplifiers perform equally well in this range.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] The system wavelength and bit rate can be upgraded but planning for this is critical.
attenuation
rayleigh scattering
attenuation due to absorption
dispersion
transmission challenges (HINT: ARAD)
attenuation
This is caused by intrinsic factors (primarily scattering and absoprtion) and extrinsic factors (stress from the manufacturing process, the envi, and physical bending)
rayleigh scattering
An issue at shorter wavelengths.
attenuation due to absorption
An issue at longer wavelengths.
attenuation due to absorption
Includes: the intrinsic properties of the material, the impurities in the glass, and any atomic defects.
dimmer
In attenuation due to absorption, the impurities absorb the optical energy, causing the light to become _____.
dispersion
It is the spreading of light pulses as they travel down optical fiber.
distortion
Dispersion results in ____ of the signal, which limits the bandwidth of the fiber.
chromatic dispersion and polarization mode dispersion
2 General Types of Dispersion
linear
Chromatic dispersion is _____.
chromatic dispersion
It occurs because different wavelengths propagate at different speeds.
square of the bit rate
chromatic dispersion increases as the _______.
nonlinear
Polarization Mode Dispersion is ______.
Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD)
It is caused by ovality of the fiber shape as a result of the manufacturing process or from external stressors.
ovality
Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD) is caused by ___ of the fiber shape as a result of the manufacturing process or from external stressors.
DWDM
It is ready made for long-distance telecomms operators that use either point-to-point or ring topologies.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] DWDM is used for building or expanding networks.
TRUE
[DWDM] Network wholesalers can lease capacity, rather than entire fibers. True or False?
transparency
The ______ of DWDM systems to various bit rates and protocols.
thin fiber
Applications of DWDM: utilize the existing ____.