Evidence for Nativism
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lesson 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
According to Empiricism
a language learner encounters primary linguistic data in h=their environment, receives instruction/conditioning from caregivers, and uses general cognitive abilities to convert this experience into knowledge of language
According to Nativism
a child encounters primary linguistic data in their environment and uses the Language Acquisition device provided by Universal Grammar to convert that data into knowledge of language
Prediction of Empiricism. We should observe individual differenced in the following in language learning
Some people won’t have any language.
Some people will take longer to learn it.
Different people in a community will have completely different
grammars.
Different children will go through completely different processes in
learning language.
Also, certain languages will be harder for a child to learn.
Predictions of Empiricism
experience is necessary. children who are never exposed to a language will never have a language
(Empiricism) Outcome of language acquisition should bear a relationship to general intelligence:
success at learning language will correlate with success at other mental tasks
learning language will take about the same amount of time as other complex tasks
Nativist response to Emp predictions
Universality, uniformity, rapidity, concistency of stages
Universality
all human societies have (always had language
all children acquire at least on language (aside from pathology)
Uniformity of EASE
Any human child can acquire an human language in about 5 years. That is, all human languages are equally easy for children to learn
Uniformity of SUCCESS
All children acquire a grammar that is virtually indistinguishable from their language models P(parents peers, caretakers)
Rapidity
Children acquire language much more rapidly than other information of similar complexity (algebra, calculus)
Consistency of stages
Children acquiring the same language pass through highly similar acquisition stages
Can children succeed at acquiring language even when they are not exposed to a full language in their primary linguistic data?
Yes, in certain circumstances (nativism)
In Empiricism, what does an individual’s general intelligence (IQ) correlate with?
their success and speed in acquiring language
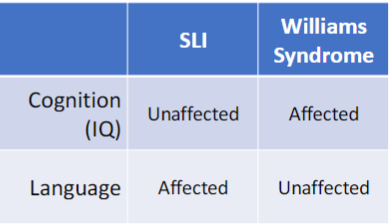
Conditions that indicate developmental double dissociation between intelligence and linguistic abilities
Specific Language Impairment (SLI) and Williams Syndrome
Specific Language Impairment (SLI)
developmental disorder that affects language with no additional cognitive deficits
Children diagnosed with SLI show:
Normal (non-verbal) IQ
Normal socialization
Some areas of language are OK
Severe problems with certain parts of language
What parts of language do children with SLI have problems with?
Delay in producing first words
Problems in articulating speech sounds
Simplified grammatical production (leaving off noun, verb endings)
Comprehension difficulty with complex speech
Examples of production by children with SLI
It’s a Flying finches, they are
They boys eat four cookie
Carol is cry in the church
Cause of SLI
genetic
Evidence for genetic nature of SLI?
comes from twin studies: identical twins are more likely to share a diagnosis than fraternal twins
SLI suggests that there are children of normal intelligence who fail to acquire language in a typical fashion
Intelligence is not sufficient for language acquisition
Williams Syndrome
Developmental disorder that causes broad cognitive deficits but leaves language intact
Children diagnosed with Williams Syndrome show:
Cardiovascular difficulties
An average IQ of 55
Limited motor control
Excessively social
Language preserved
Facial features of Williams Syndrome
elfin or youthful

Who has difficulty with visual-spatial tasks and can see detail but cannot organize them in space?
children with Williams Syndrome

Language production of children with Williams Syndrome is:
fluent, coherent, and free from grammatical errors
Example of language production by a child with Williams Syndrome
They’ve got the habit of doing that. They lose, they’ve lost my
bank book twice in a month, and I think I’ll scream. My mum went
yesterday to the bank for me. She said, “They’ve lost your bank
book again.” I went “Can I scream?”
Cause of Williams Syndrome
Genetic: deletion of ~25 genes on chromosome 7
What might the deleted genes’ function be linked to (Williams Syndrome)
protein production — cardiovascular difficulties — and to visuospatial cognition
Williams Syndrome suggests that:
there are children with impairment of general cognition who nevertheless succeed to acquire language in a typical fashion. General intelligence is not required for language acquisition
Double Dissociation
General (non-verbal) intelligence is entirely independent of linguistic competence
Nativism or Empiricism predicts correlations between linguistic ability and generative cognitive abilities and intelligence.
Empiricism. Nativists found that these are not confirmed.