The History of Life on Earth: Key Concepts and Events
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Fossil Record
Shows macroevolutionary changes over time.
Terrestrial Vertebrates
First vertebrates adapted to land environments.
Photosynthesis Origin
Process that converts light energy into chemical energy.
Mass Extinctions
Significant loss of biodiversity in Earth's history.
Earth's Age
Earth is approximately 4.6 billion years old.
First Life Forms
Appeared around 3.8 billion years ago.
Small Organic Molecules
Basic building blocks for life, synthesized early.
Macromolecules
Complex molecules like proteins and nucleic acids.
Protocells
Membrane-containing droplets that may lead to life.
RNA World
Hypothesis that RNA was the first genetic material.
Ribozymes
RNA molecules that act as biological catalysts.
Oparin-Haldane Hypothesis
Suggests early Earth conditions favored organic compound synthesis.
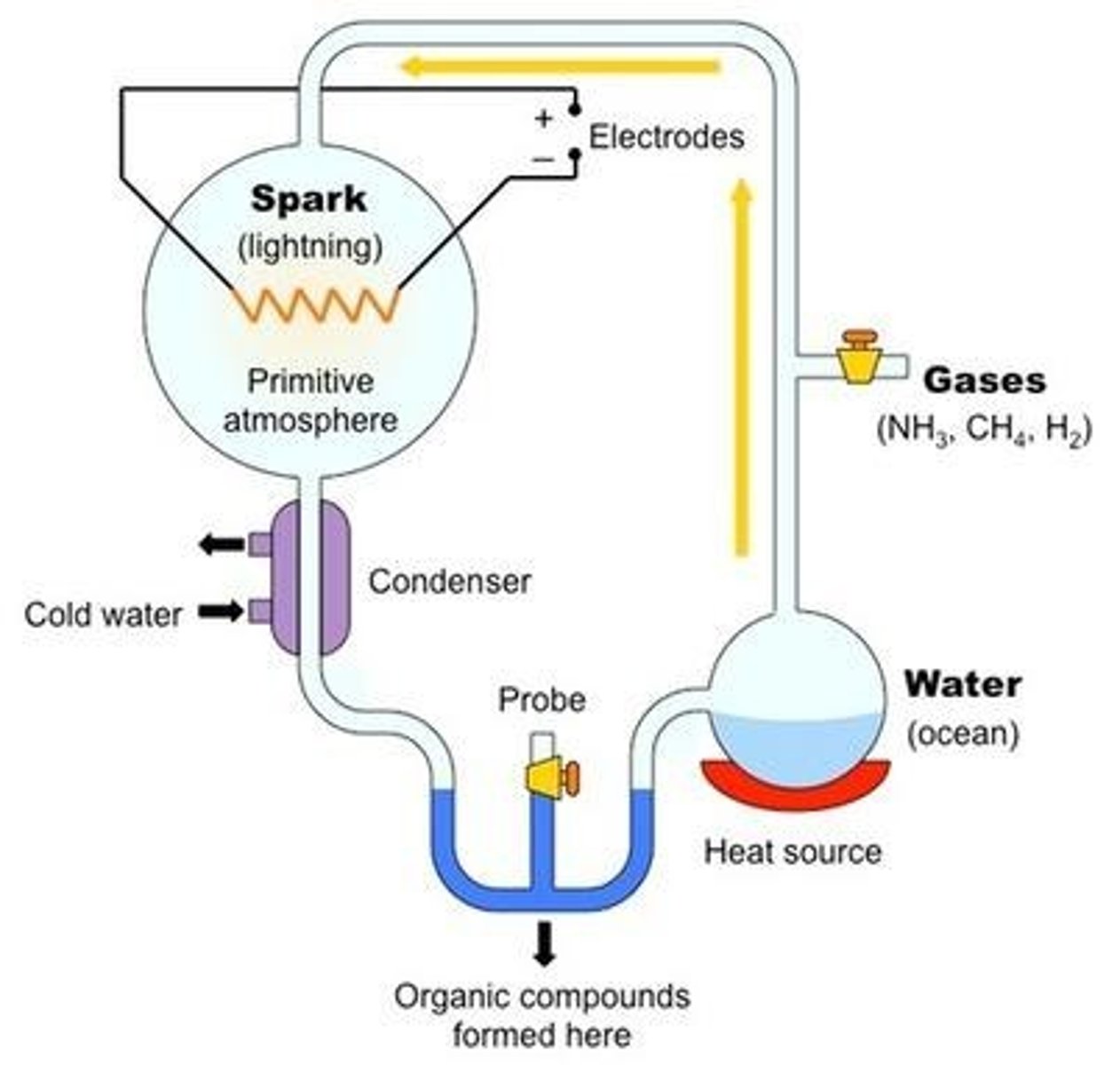
Miller-Urey Experiment
Simulated early Earth conditions to produce amino acids.
Sedimentary Rock Strata
Layers of rock that contain fossil records.
Relative Dating
Determines age of fossils based on rock layers.
Radiometric Dating
Measures decay of radioactive isotopes to date fossils.
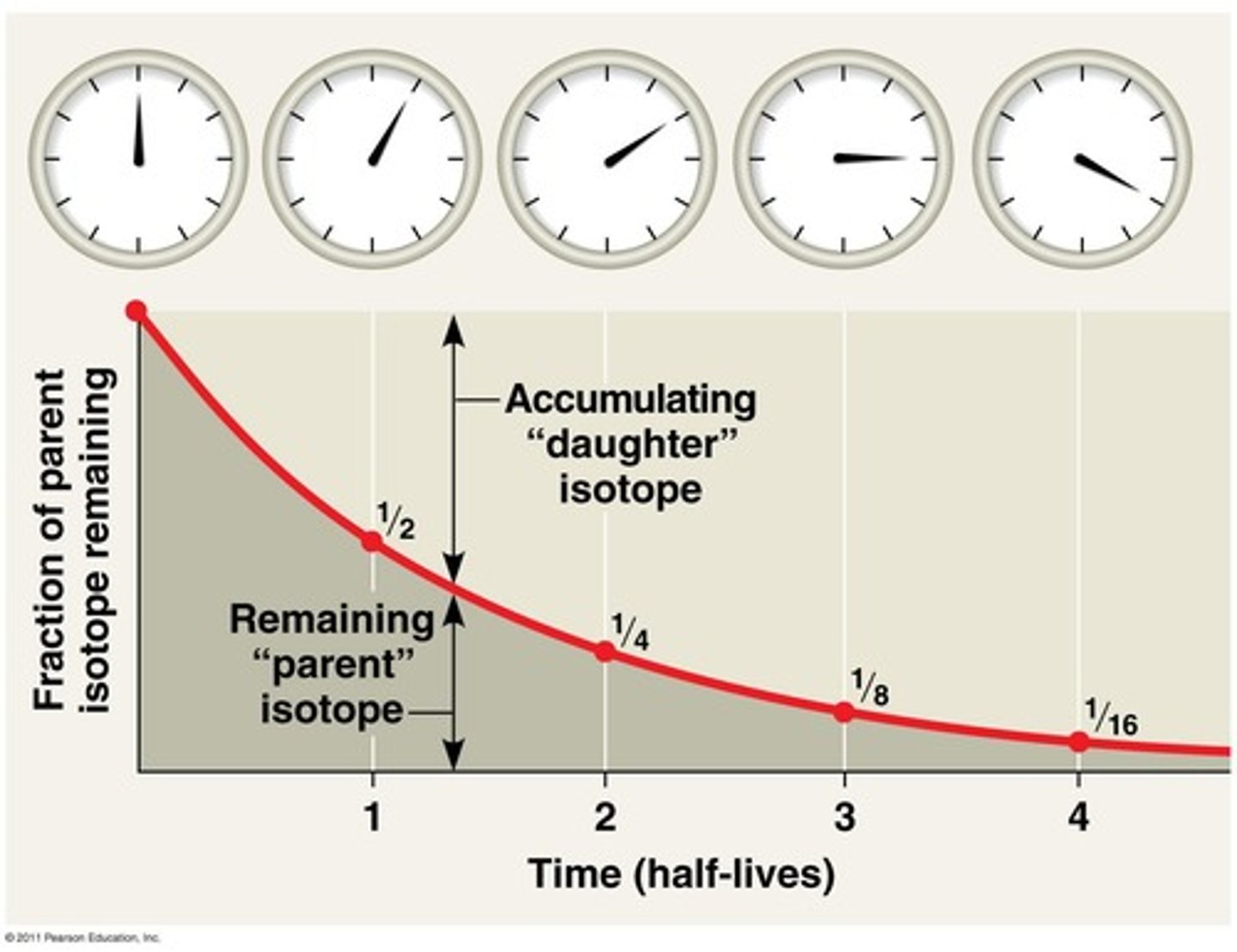
Half-life
Time for half of a radioactive sample to decay.
Tetrapods
Four-limbed vertebrates, evolved from ancestral synapsids.
Geologic Time Scale
Chronological dating of Earth's history in eons.
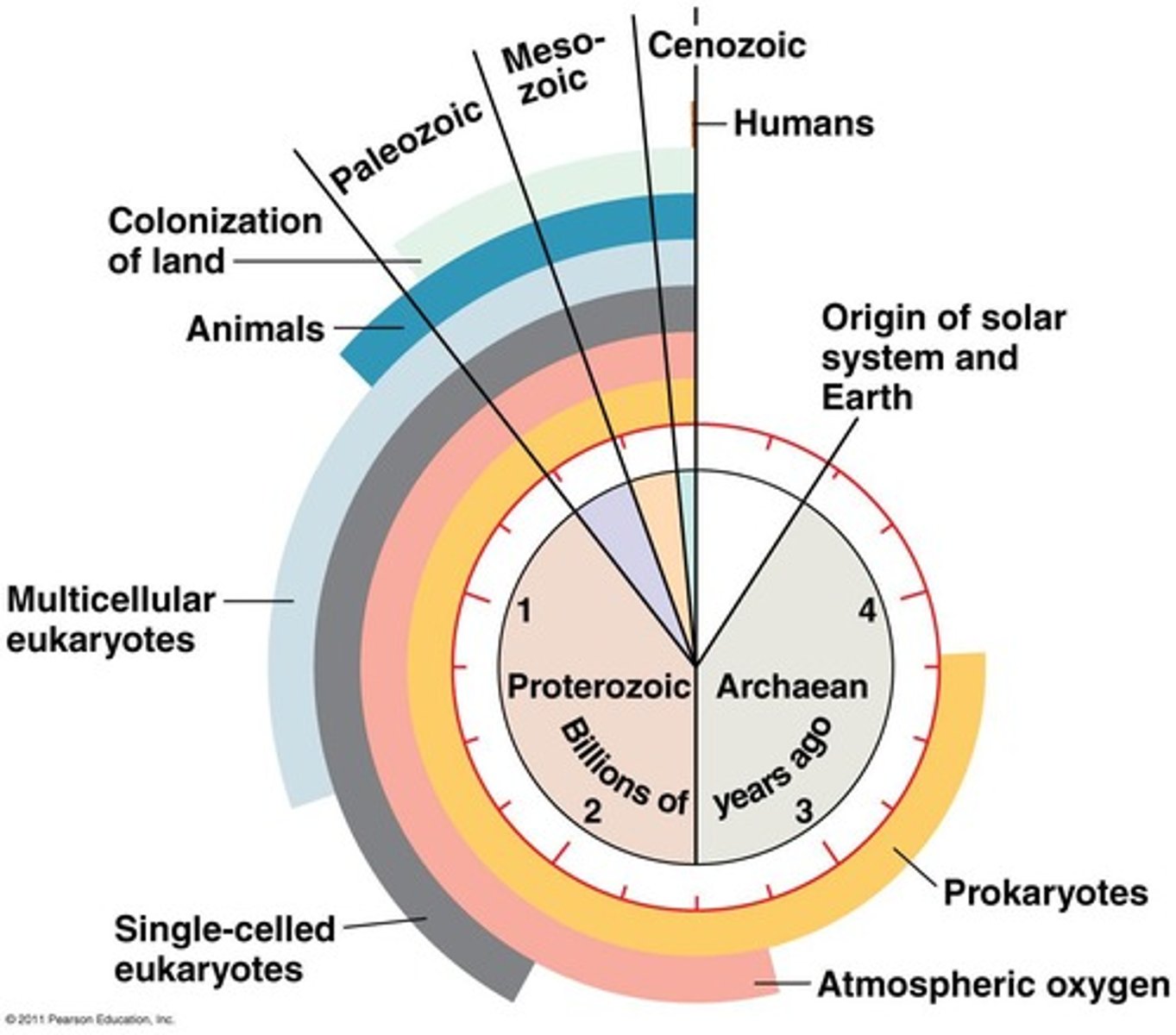
Phanerozoic Eon
Current eon characterized by abundant fossil records.
Endosymbiosis
Theory that eukaryotic cells originated from prokaryotes.
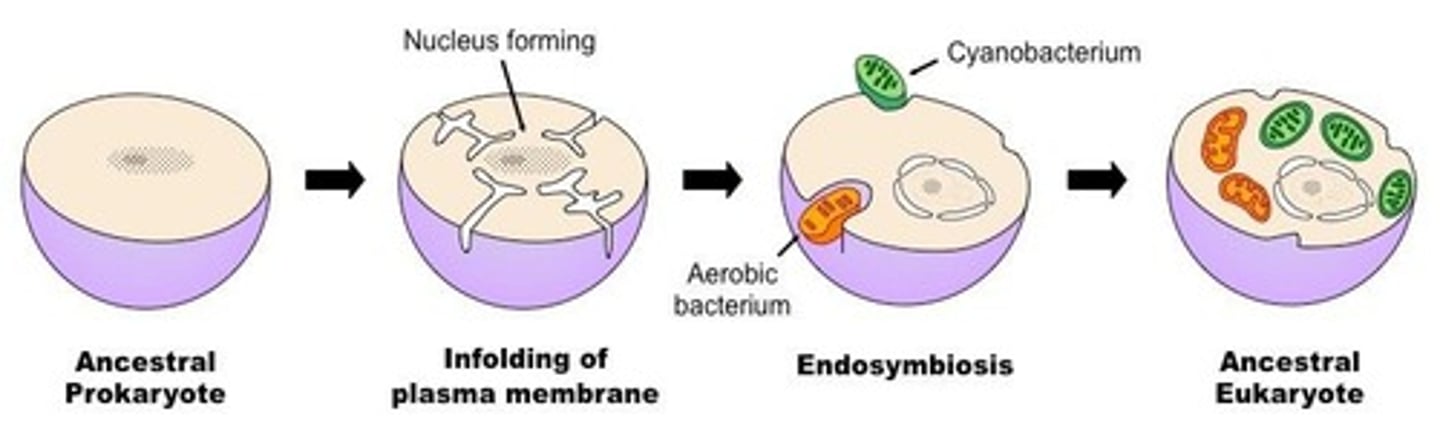
Endosymbiont Theory Evidence
Includes replication by binary fission and circular DNA.
Origin of Multicellularity
Occurred approximately 1.2 billion years ago.
Snowball Earth Hypothesis
Extreme glaciation that confined life to equatorial regions.
Cambrian Explosion
Rapid diversification of life forms 535-525 million years ago.
Colonization of Land
Fungi, plants, and animals moved onto land 500 million years ago.
Continental Drift
Movement of Earth's continents over geological time.
Pangaea
Supercontinent that existed around 250 million years ago.
Adaptive Radiation
Rapid evolution of species to fill ecological niches.
Heterochrony
Evolutionary change in the timing of developmental events.
Paedomorphosis
Retention of juvenile traits in adult organisms.
Homeotic Genes
Regulatory genes that control body plan development.
Hox Genes
Specific homeotic genes influencing body structure organization.
Exaptations
Structures evolved for one function but adapted for another.
Complex Eyes Evolution
Evolved independently from simple light-sensitive cells.