Psychopathy
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Psychopathy
A disorder characterized by:
Shallow emotional responses
Lack of empathy
Impulsivity
Increased likelihood of antisocial behaviour
What is the closest thing to psychopathy in the DSM?
Antisocial personality disorder
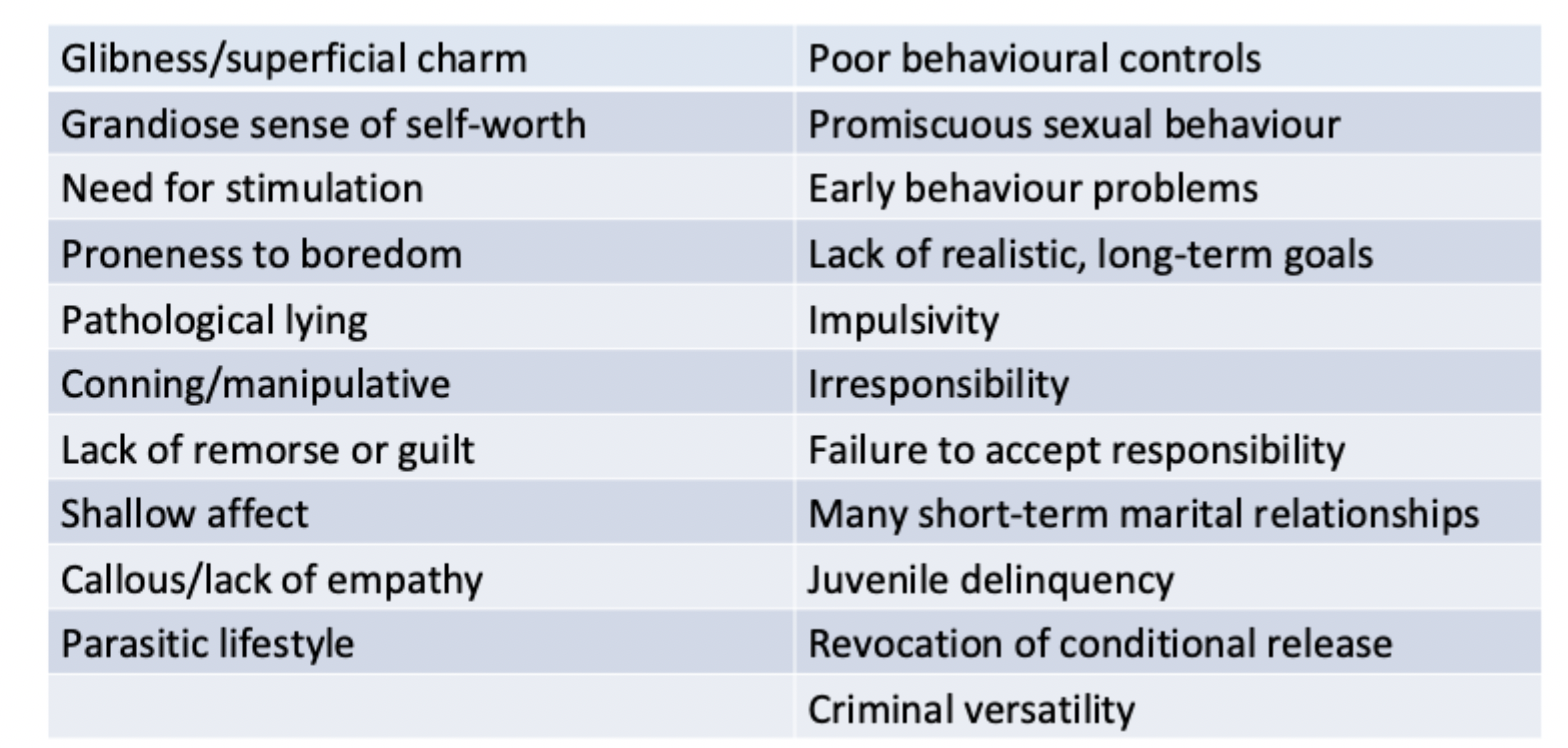
Psychopathy checklist-revised (PCL-R)
This checklist is used to determine whether someone meets criteria for psychopathy
Items are scores:
0 = not applicable
1 = applicable only to a certain extent
2 = applicable
How does recidivism relate to psychopathy (Grann et al., 1999)
Study looked at violent recidivism follow probation, forensic psychiatric discharge, or prison release
Recidivism = committing another crime after being let out of jail
Research Q: Who commits violent crimes again after being let out of jail based on their psychopathy score?
Findings:
Low psychopathy scores = not many committed again…
High psychopathy score = more than half committed again
These findings can have practical implications (e.g., determining who gets parole)
What is the difference between psychopathy vs. sociopathy?
Sociopaths:
Can form some deep bonds (e.g., with family)
Have a less severe lack of empathy and lack of guilt
May feel guilt and remorse over hurting someone with whom they share a bond
Anti-social behaviour may lessen over time as they learn to avoid consequences of their actions
Not able to move through society committing callous crimes as easily
The same cannot be said for psychopaths…
Callous yet charming
Will manipulate others with charisma and intimidation
Can effectively mimic feelings to present as "normal to society"
Displays little emotion in situations that normal people would find threatening or horrifying
Aware what they are doing is wrong, but do not care
Dark triad
Psychopathy
Traits = Impulsive, emotionally cold, remorseless
Body language = inappropriate emotional expression (or lack thereof)
Machiavellianism
Traits = manipulative, self-interested, domineering
Body language = dominant, expansive posture
Narcissism
Traits = Grandiosity, perceived superiority, entitlement
Body language = 1st person pronouns, self-focused in conversations
Etiological factors
Behavioural Inhibition System (BIS) deficits
Difficulty avoiding/inhibiting responses to previously punished stimuli
Low electrodermal response in anticipation of an aversive event
Low eye-blink startle in response to an aversive stimulus
Impaired aversive conditioning
The BIS is a temperamental system that inhibits behaviour out of fear of being punished (but this is impaired in psychopaths)
An overall fearlessness and insensitivity to punishment
Psychopaths show deficits in conditioned fear (Birmbauer et al., 2005)
Study included incarcerated psychopathic men + healthy men from the community
Conditions:
Paired conditioned stimulus -> shown mustached man
Impaired conditioned stimulus -> shown non-mustached man
Unconditioned stimulus -> painful pressure
*Seeing the moustache face was paired with painful pressure
Research Q: Do psychopathic men vs. healthy men show differential responses?
Findings:
Healthy men = seeing moustache man induced higher arousal + greater skin conductance + greater brain activation in anterior cingulate, anterior insula, and amygdala
Psychopathic men = showed no difference in arousal + skin conductance + brain activation between seeing moustache man vs. non-moustache man
Specifically: lower levels of arousal + no differences in skin conductance
These findings suggest that psychopathic men did not develop a conditioned fear response
What is the association between empathy and psychopathy?
Study included 53 men from the community
Participants were shown pictures of people being victimized while in the MRI
Assumption is that normal people would show an empathetic response to these photos
RQ: How does brain response (anterior insula, inferior frontal gyrus, midcingulate cortex) differ based on psychopathy score?
Findings:
There was a significant negative correlation
Increased psychopathy scores = decreased brain activation in empathy brain regions
Psychopathy in women
Rates of women incarcerated in maximum-security prison who meet diagnostic criteria for psychopathy using the PCL-T (30 score cut-off) are compared to men
Women = 17%
Men = 15-25%
PCL-R had a similar factor structure in women as in men
Depression, anxiety, and borderline personality disorder are more strongly related to psychopathy in women
Blink startle response in psychopathic women (Verona et al., 2013)
Study included 48 women inmates assessed for psychopathy
Study aimed to assess participant's ability to learn from punishment
Participants shown pleasant, neutral, and unpleasant/upsetting pictures
Throughout the picture-viewing trials, blink-eliciting noises would go off randomly
Findings:
Low-psychopathy group = showed larger (healthy/normal) blink-startle response in the unpleasant photos
High-psychopathy group = showed lower blink-startle response to unpleasant photos + victim threat-related photos
Psychopathic women showed deficits in the response to the distress of others