Neuroanatomy (L1)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
The nervous system
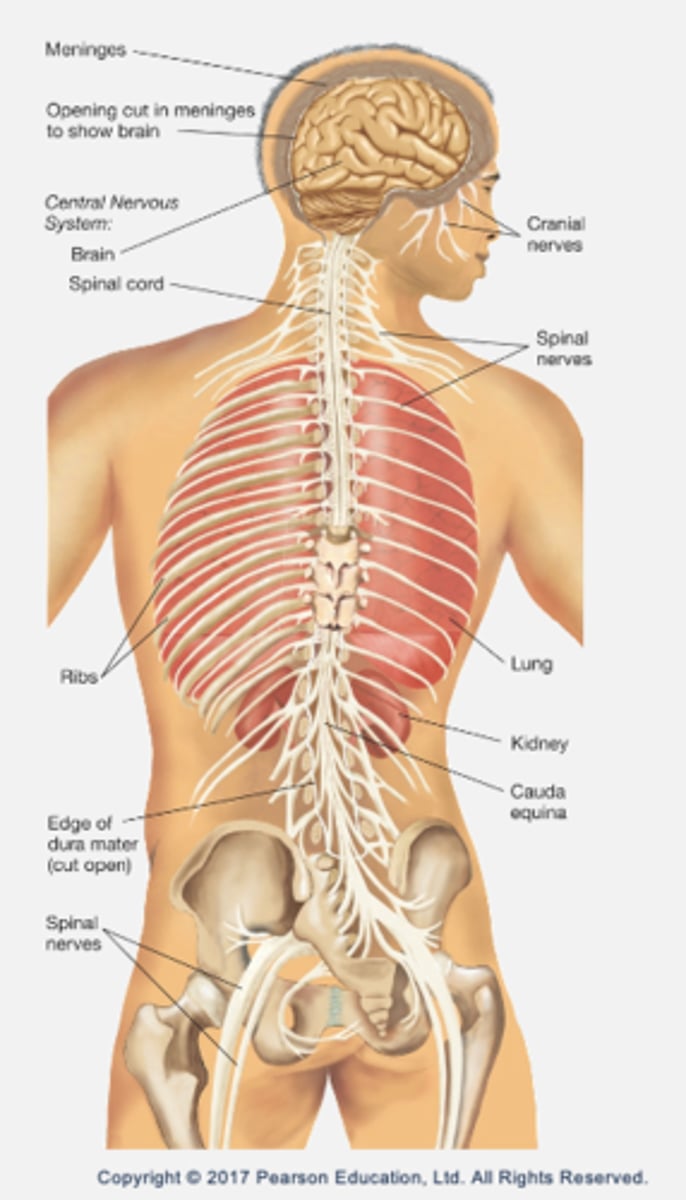
Central nervous system (CNS):
- Brain (encased in skull).
- Spinal cord (encased in vertebral column).
Peripheral nervous system (PNS):
- All other nerves.
- Motor pathways send information to muscles or tissue from CNS.
- Sensory pathways bring information from sensory surfaces into CNS.
The brain
1. Cerebrum
2. Cerebellum
3. Brain stem
Split into two hemispheres: left and right.
- Left controls right side of the body.
- Right controls left side of the body (contralateral = opposite side).
- Ipsilateral: same side of the brain controls a function.
The brain receives a constant flow of blood (approx. 20% flow from the heart) in order to maintain oxygen levels.
- If deprived = unconsciousness.
- A stroke is a bleed or blockage in the brain → results in brain cells dying due to lack of oxygen.
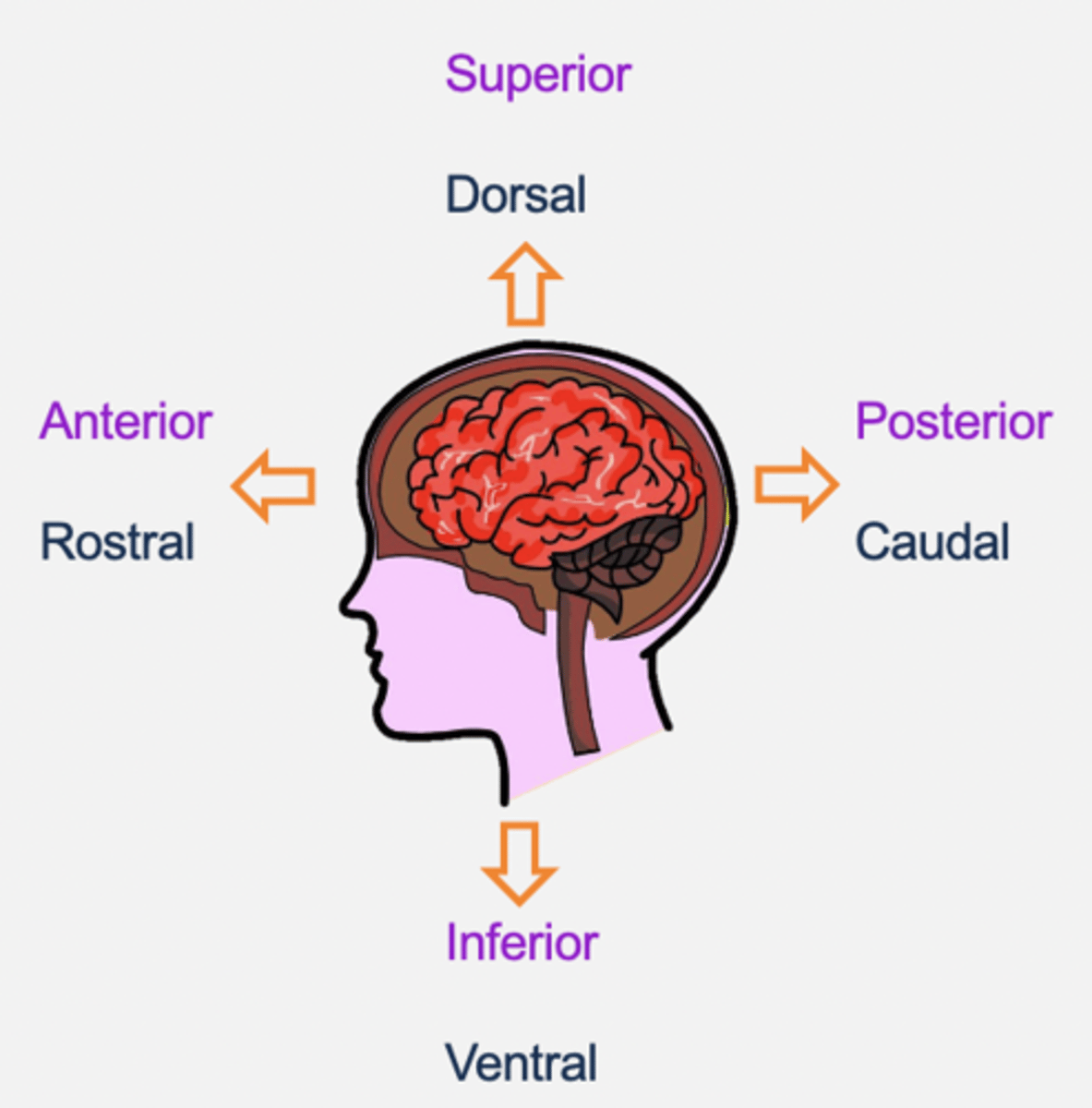
Anatomical directions
- Dorsal/superior (top of brain).
- Caudal/posterior (back of brain).
- Ventral/inferior (bottom of brain).
- Rostral/anterior (front of brain).
- Medial: towards the middle
- Lateral: towards the side
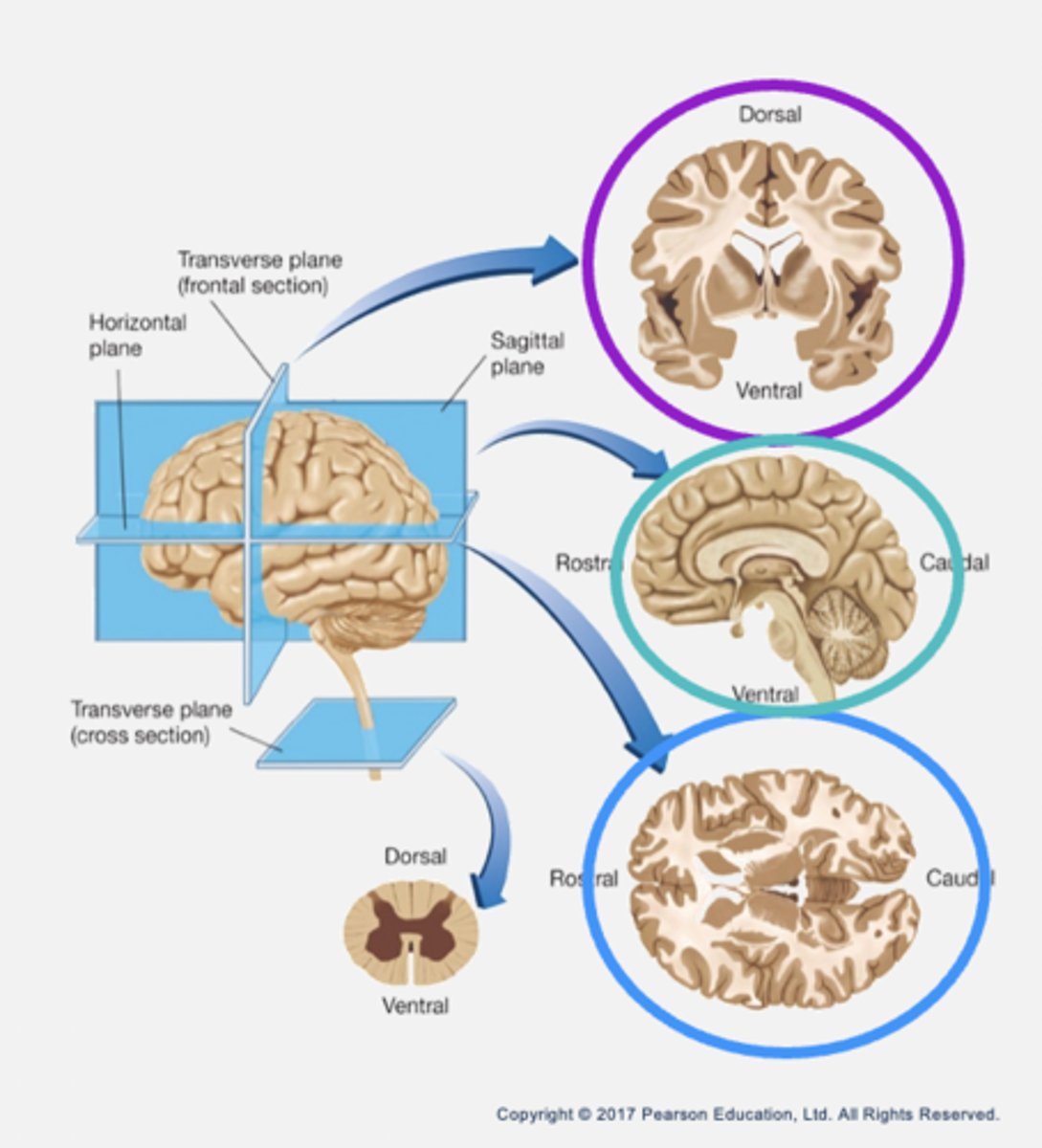
Slicing sections
- Frontal (coronal): parallel to forehead (cutting down).
- Sagittal: arrow (cutting sideways).
- Horizontal: parallel to the ground.
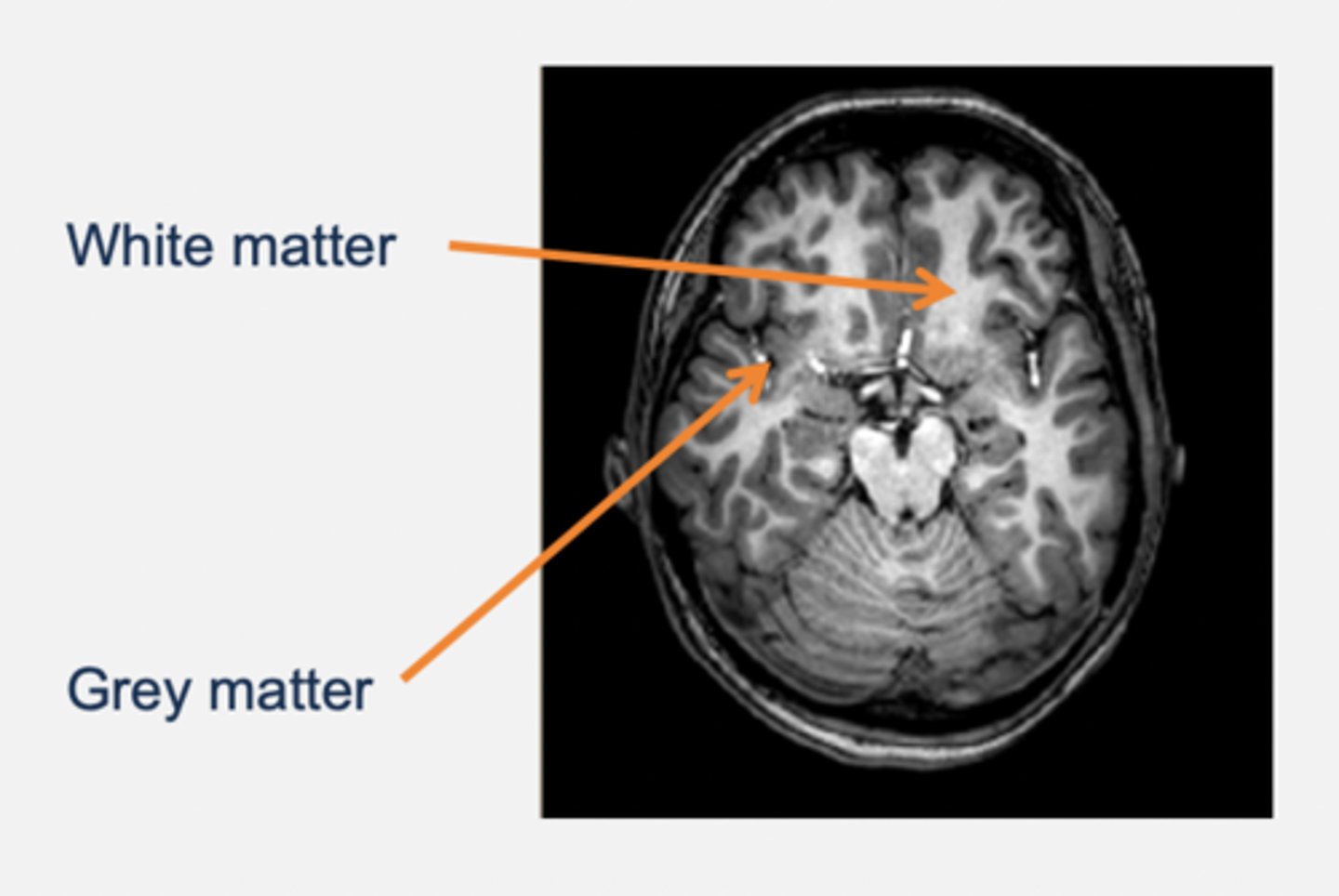
Grey and white matter
Grey matter:
- Cell bodies and dendrites.
- E.g. cortex, basal ganglia, thalamus.
White matter:
- Myelinated axons.
- E.g. corpus callosum (a pathway that connects left and right side of hemisphere → commissure).
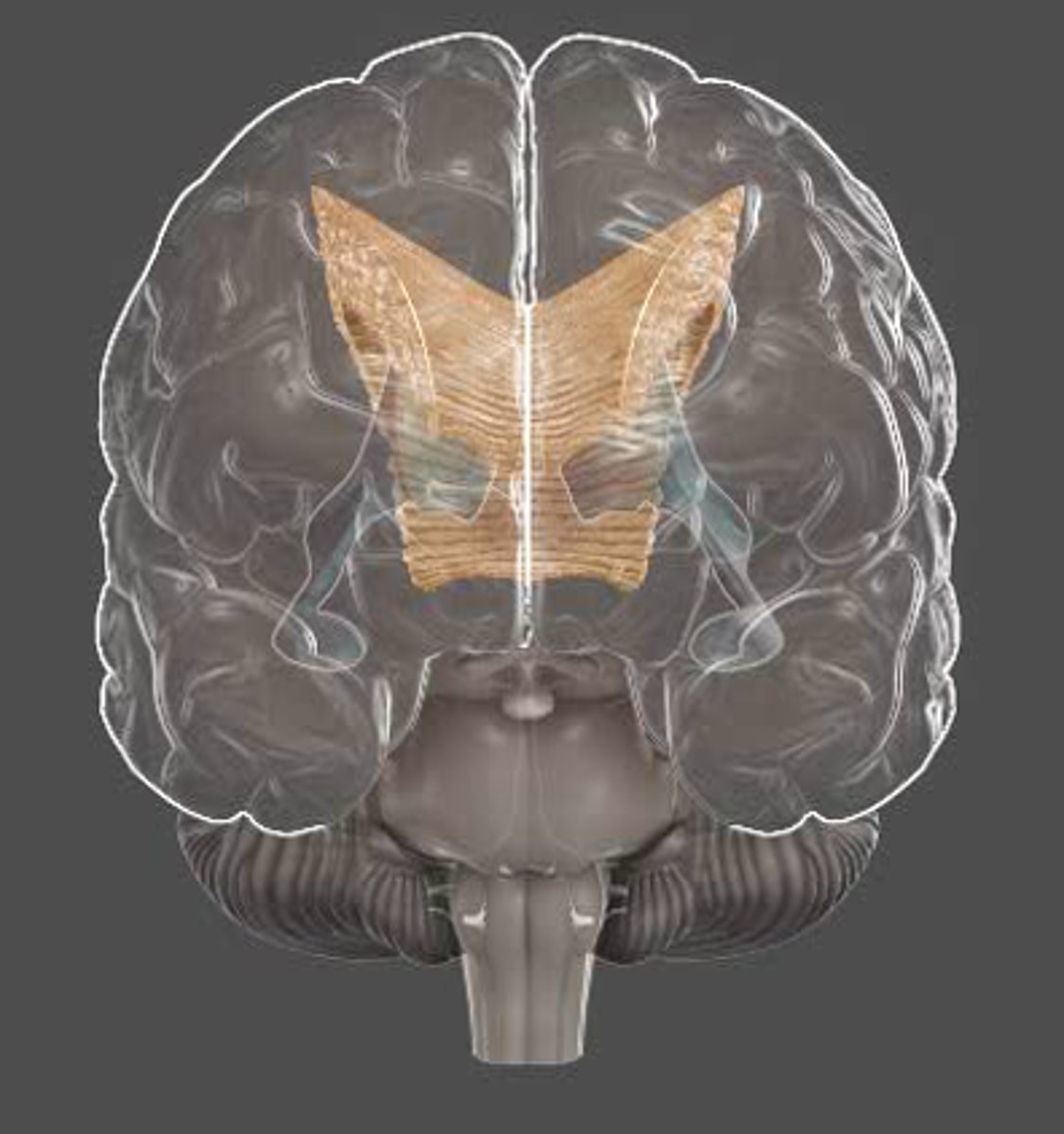
Corpus callosum
- "Hard body".
- Largest fibre bundle that connects the two hemispheres.
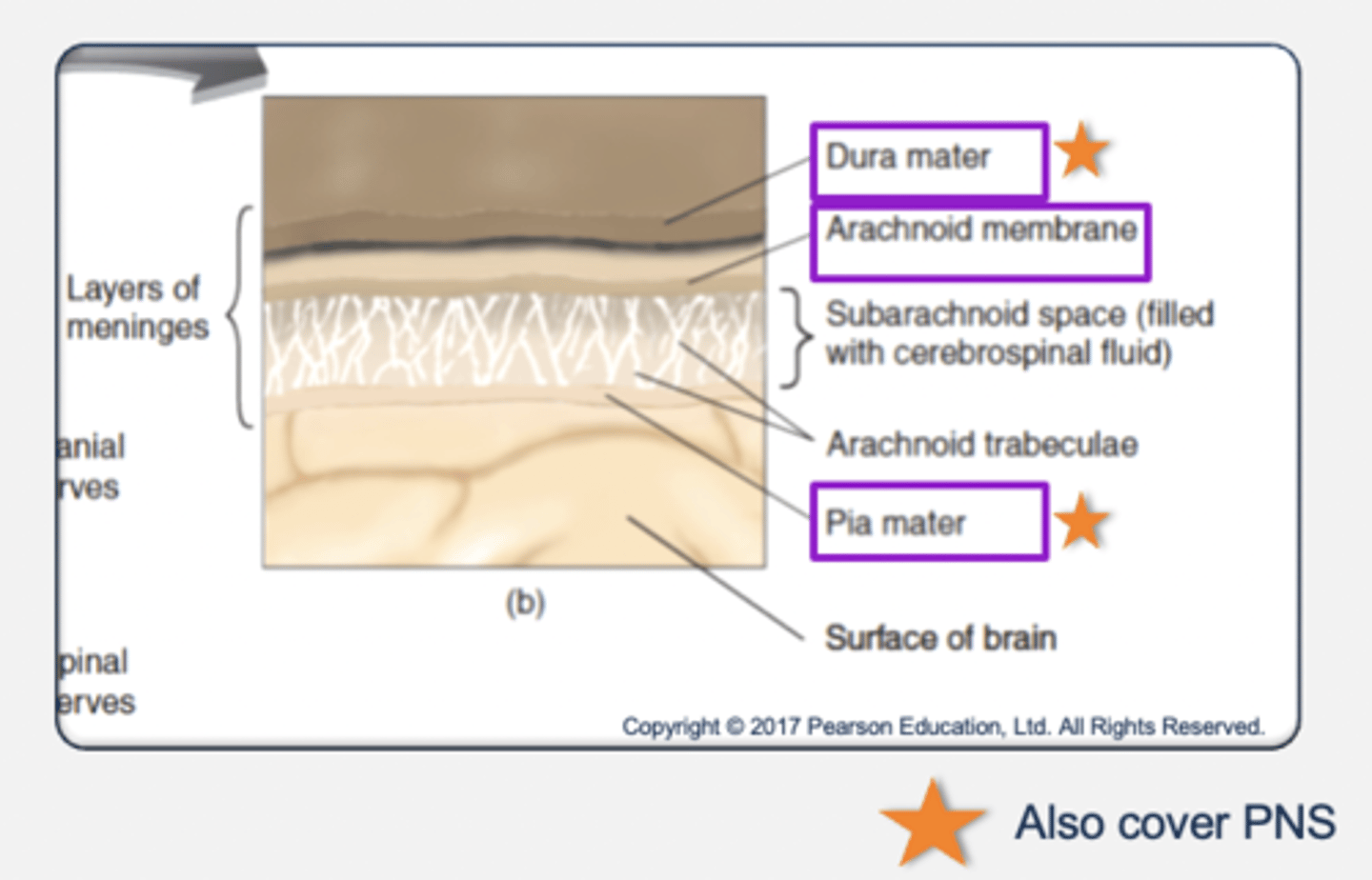
Protection of the nervous system
Meninges: 3 layers of tissues that protect the CNS.
- Outer layer: dura mater (hard mother) → thick and rough.
- Middle layer: arachnoid membrane (spider-like).
- Inner layer: pia mater (tender mother) → covers the brain.
- Meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges resulting from viral or bacterial infection.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF):
- A clear liquid that fills the subarachnoid space.
- Functions as a shock absorber.
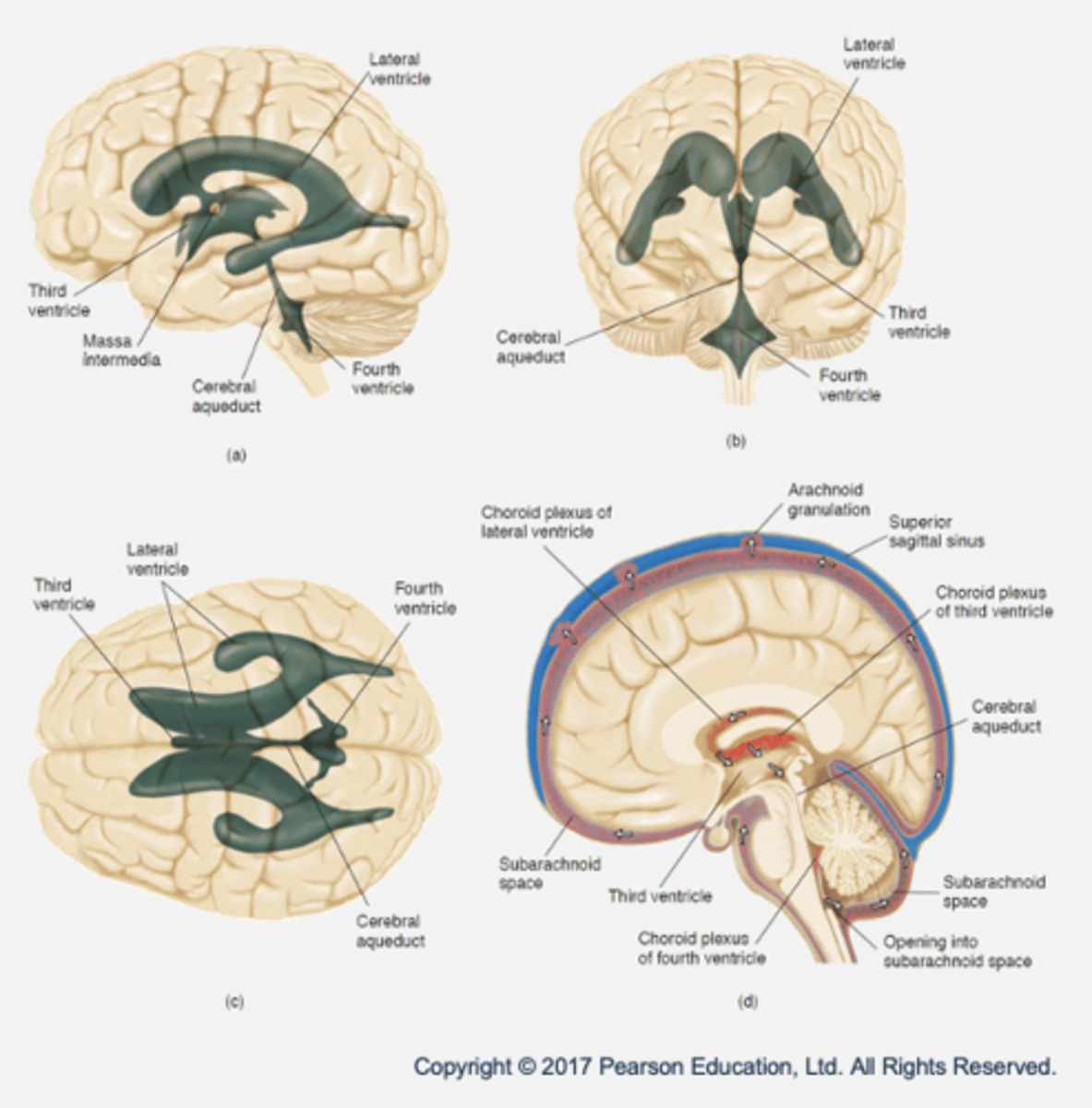
The ventricular system
- Ventricles: hollow cavities filled with CSF.
- Lateral ventricles (x2): membrane called choroid plexus produces CSF by filtering blood.
- Third ventricle
- Cerebral aqueduct
- Fourth ventricle
- Function of CSF and ventricles: exchange of materials between blood vessels and brain tissue → nutrients supplied and waste removed.
Blood-brain barrier
A semipermeable barrier between the blood and the brain produced by the cells in the walls of the brain's capillaries.
- Small molecules (oxygen, carbon dixoide) and lipid-soluble substances can pass through.
- Large molecules (e.g. glucose) must be actively transported through walls.
- Purpose is to provide protection from damaging chemicals and maintain a stable environment.
- Can make it difficult for certain medicines to get in the brain (e.g. chemotherapy drugs).
Cerebral cortex
- Outer surface of the cerebrum.
- 3mm thick
- Folded to allow for bigger surface area (more neurons).
- Sulci: clefts/cracks/groves.
- Fissures: major grooves.
- Gyri: folds/bulges.
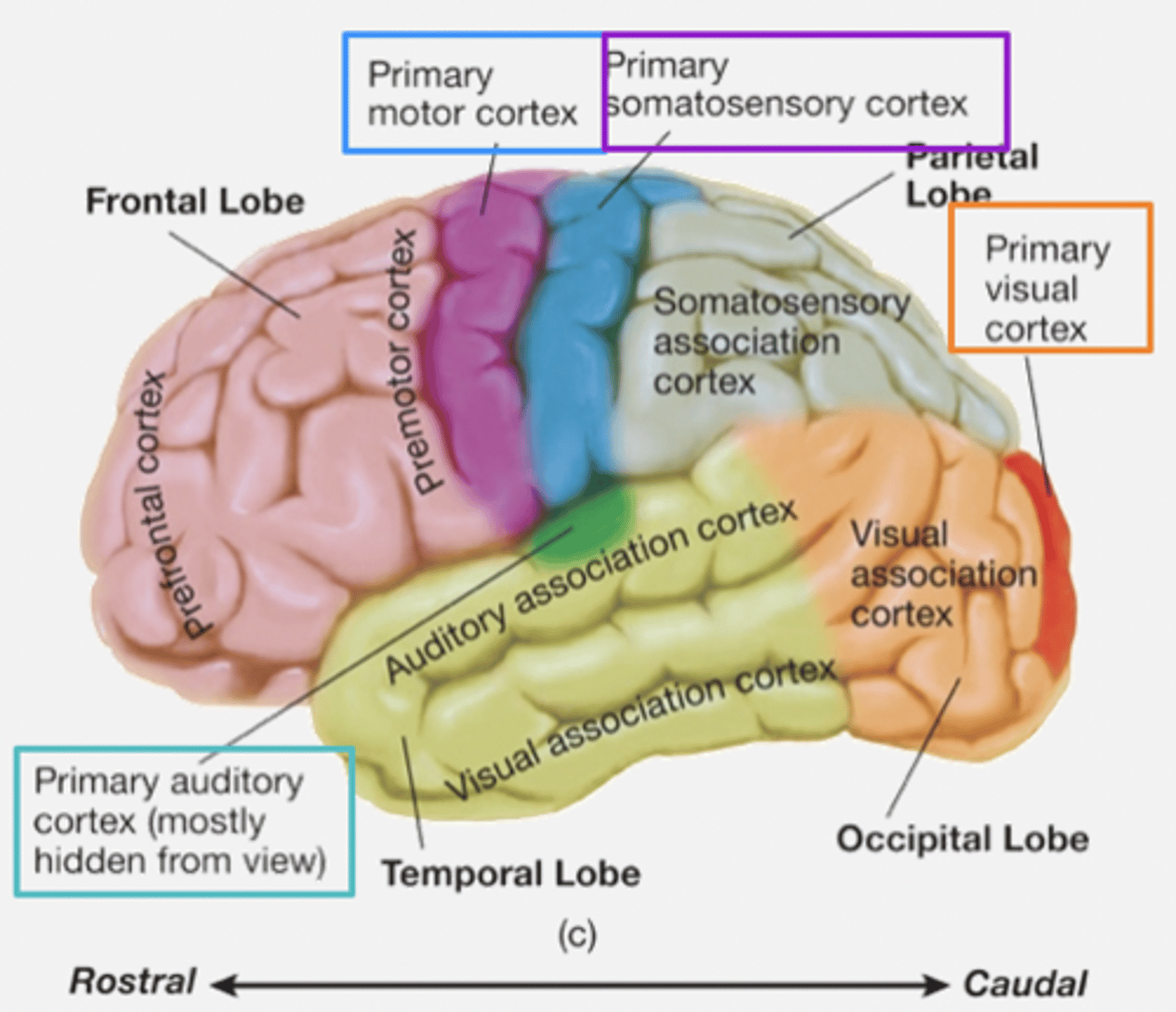
Cerebral cortex: lobes
Frontal
Parietal
Occipital
Temporal
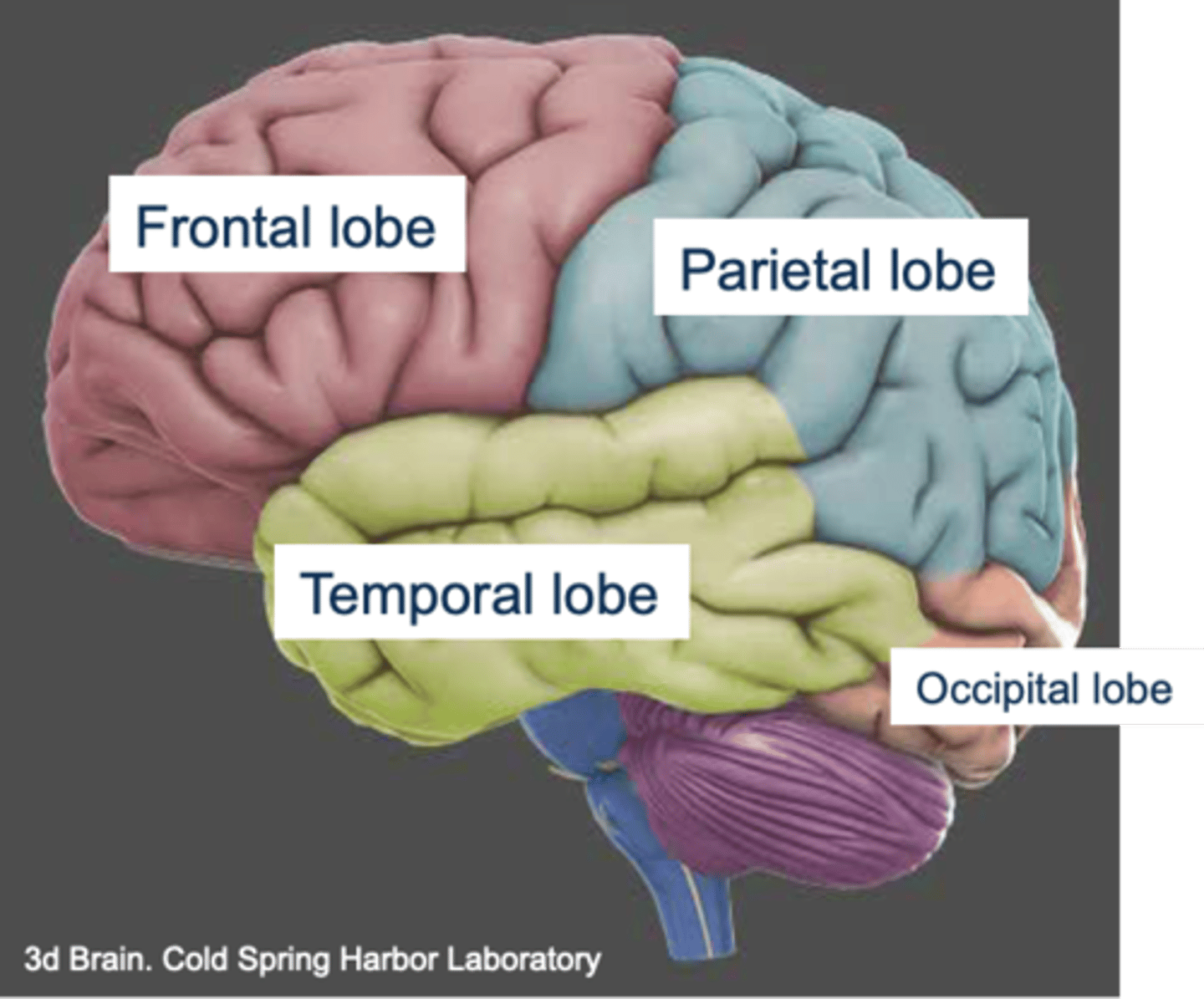
Major sulci and gyri
- Central sulcus: divides frontal and parietal lobes.
- Precentral gyrus:
- Postcentral gyrus:
- Sylvian/lateral fissure: divides temporal lobe from frontal and parietal lobes.
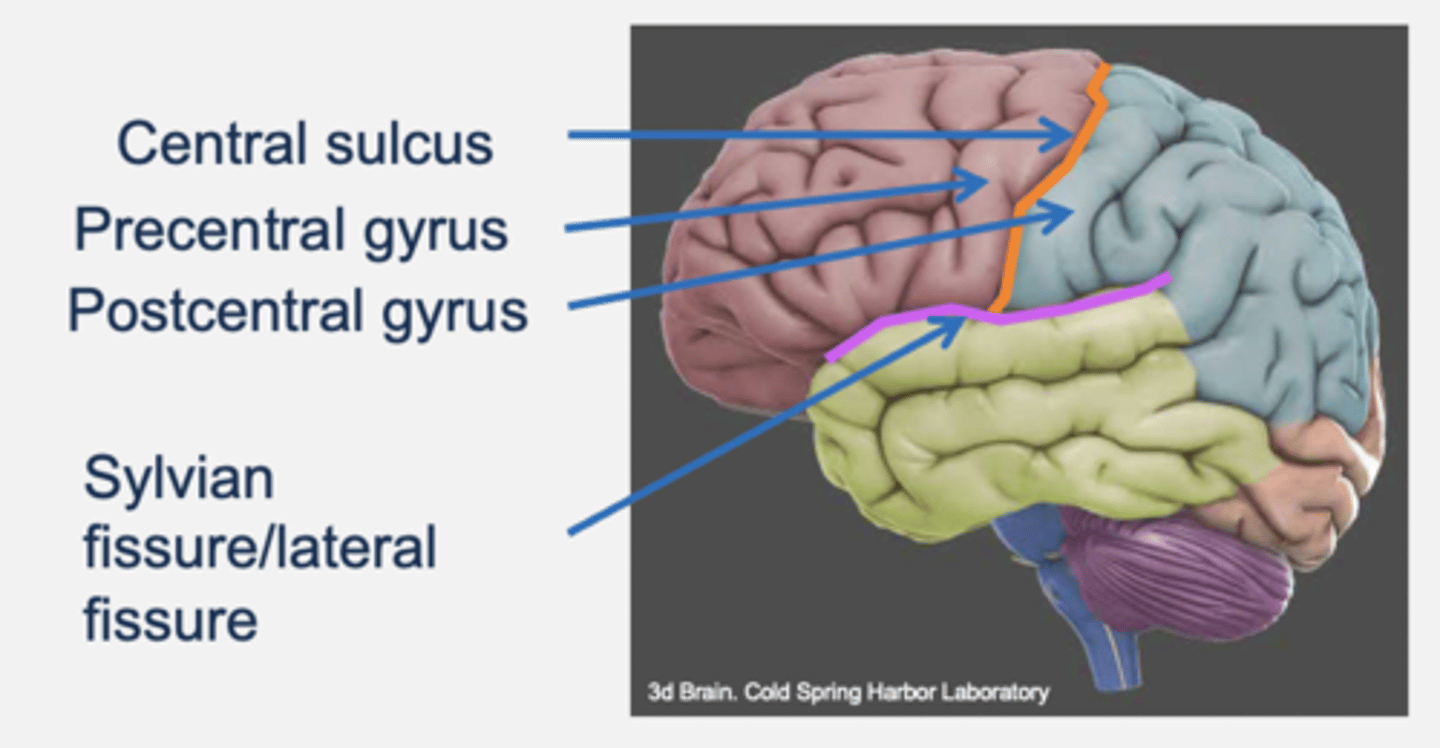
Frontal lobe
- Anterior area of cortex.
- Rostral to parietal.
- Dorsal to temporal.
- Divided from parietal by central sulcus.
- Functions: motor and cognition.
Parietal lobe
- Caudal to frontal.
- Dorsal to temporal.
- Function: somatosensory → directing movement (e.g. when interacting with objects in the environment).
Occipital lobe
- Caudal to parietal and temporal.
- Function: visual processing.
Temporal lobe
- Rostral to occipital.
- Ventral to parietal and frontal.
- function: hearing, vision, cognition and emotion.
Primary areas
Areas of the cortex involved in sensory functions and in the direct control of motor movements.
- Primary somatosensory cortex: recieves input from somatosensory system (e.g. touch and body position).
- Primary visual cortex: receives input from visual system
- Primary auditory cortex: receives input from auditory system
- Primary motor cortex: controls muscles
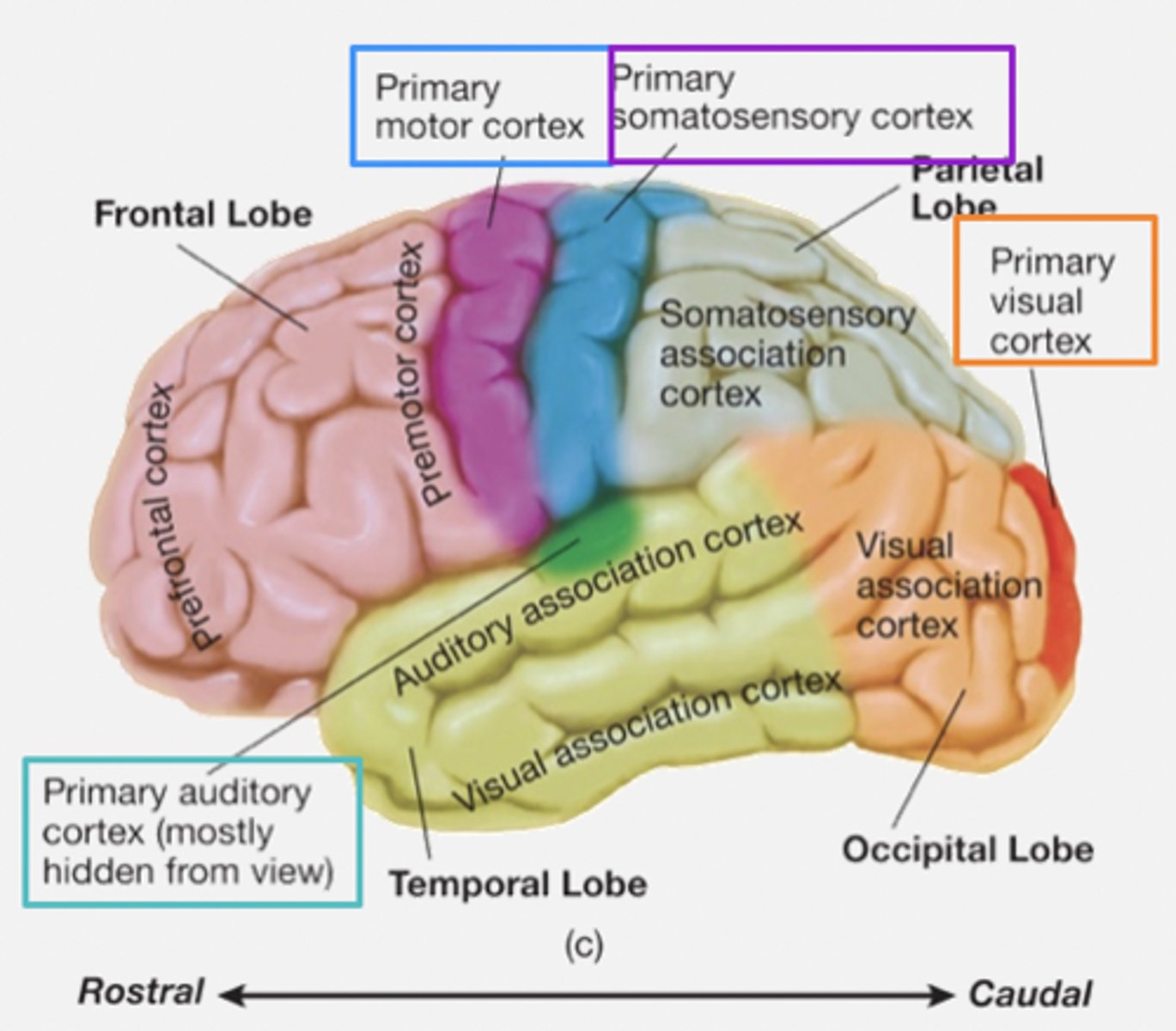
Primary association areas
Sensory association areas:
- Receive and analyse info from primary regions.