Immunity thrid line of defence w vacciness
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
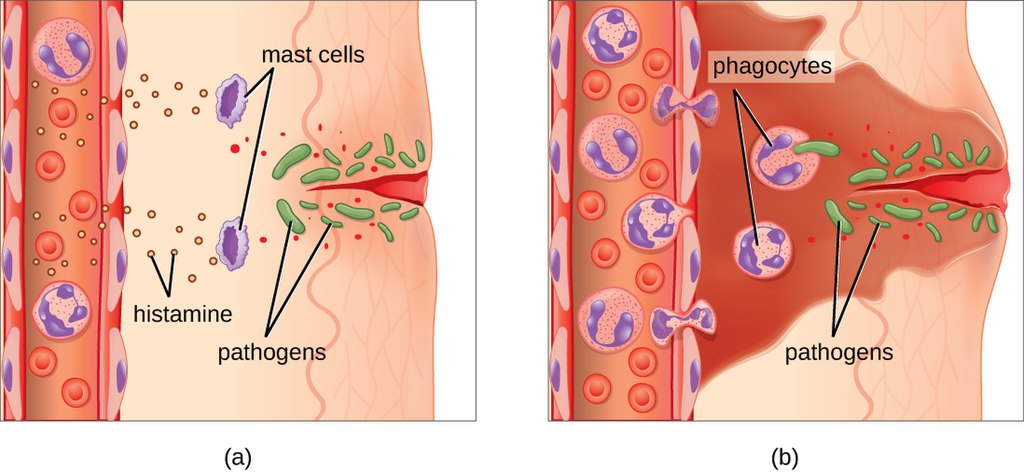
Any pathogens that are able to survive after the non-specific immune response/ second line of defence are targeted according to their type

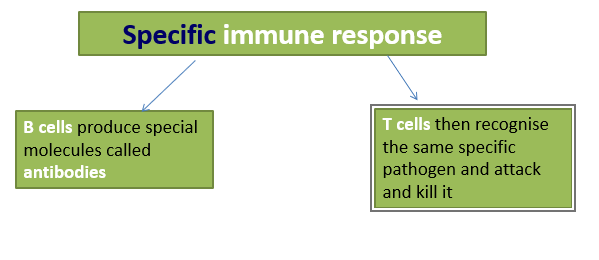
Specific immunity response
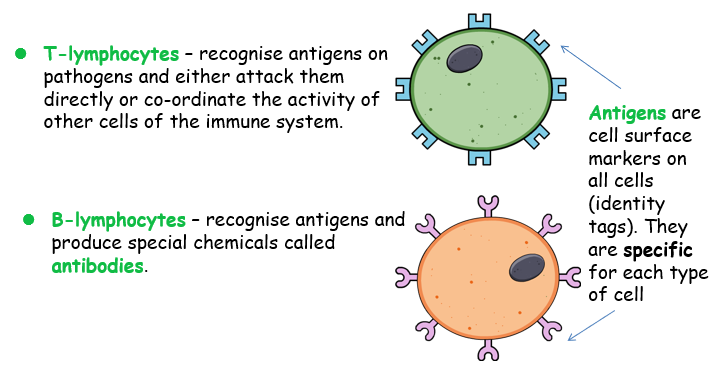
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell found in the blood or lymph nodes and made by bone marrow. There are several types of lymphocyte, including:

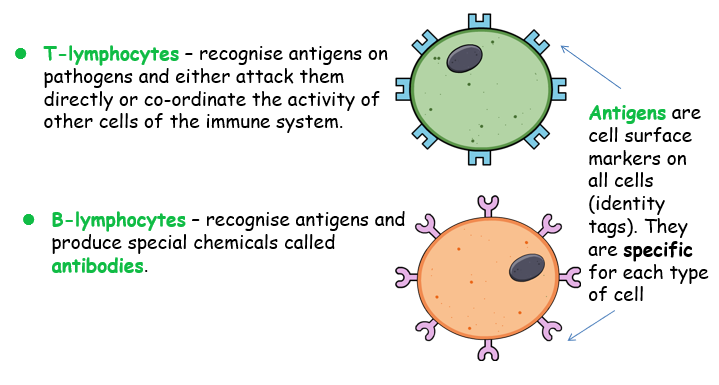
Antigens - type 2
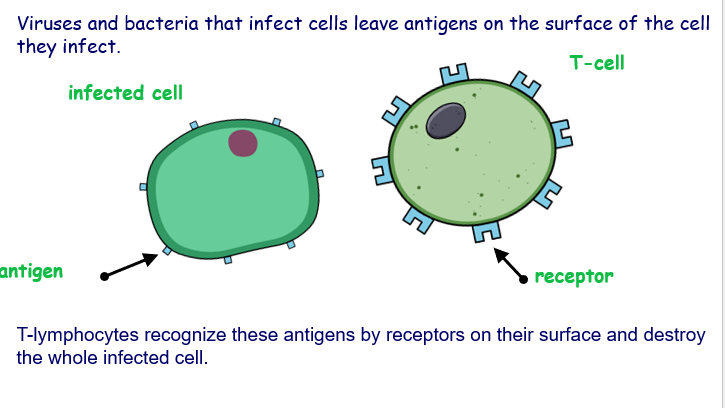
Antigens are cell surface markers on all cells (identity tags). They are specific for each type of cell

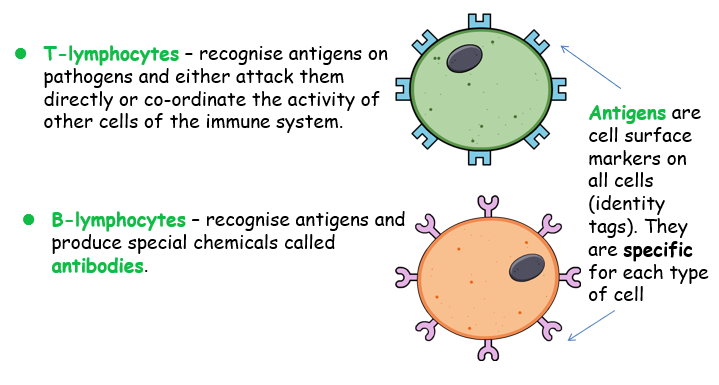
B lymphocytes
lB-lymphocytes – recognise antigens and produce special chemicals called antibodies.

ANtibodies
Antibodies are special
Y-shaped proteins produced by B-lymphocytes in response to antigens.
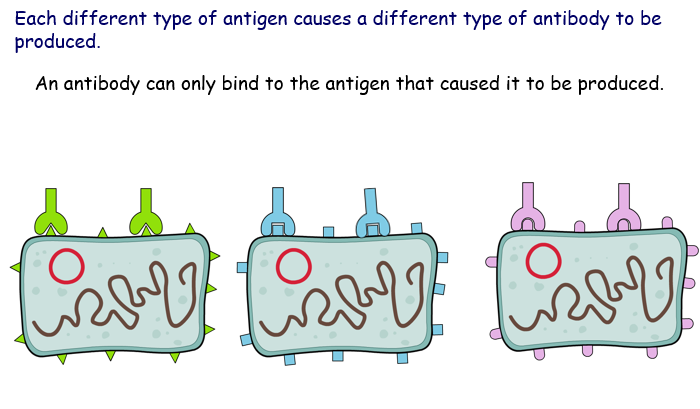
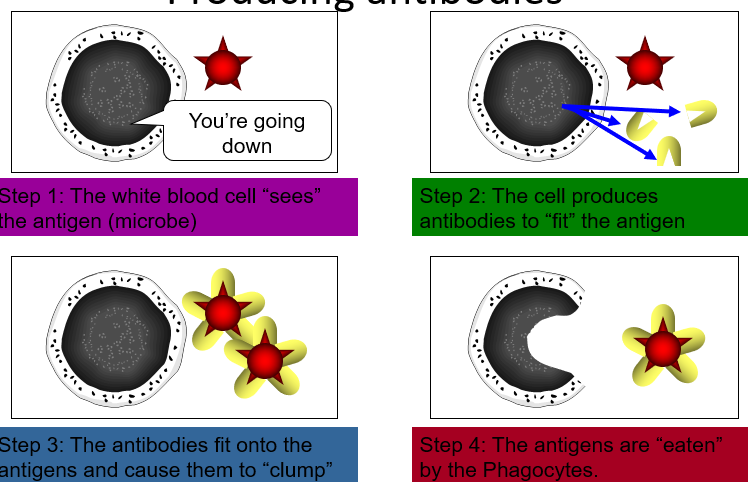
Antibodies work by binding to antigens on pathogens, ‘labelling’ them and causing them to clump together. The pathogen can then be destroyed by:
Phagocytosis by macrophages , T lymphocytes , the antibodies
Each antibody will fit into one sectipn of the pathogen . This will cause the pathogen to become locked together and stops them from invading
T lymphocyte - Type 1 lympo
T lymphocytes then recognise antigens on pathogens and either attack or coordinate the activity of other immune system cells.
Memory cells
Both B and T cells keep some memory cells alive, in case the pathogen tries to invade again.
This means the pathogen will be attacked and killed before it can cause damage a second time. Your body will be protected from reinfection in the future. You are now immune.
antibodies
Producing antibodies
Delayed response
The B-lymphocyte that produces the correct antibody for the antigen begins dividing to produce many more antibody-producing cells.

Delayed response
It takes a few days to produce enough antibodies to destroy the pathogen. This means there is delay between infection and the person beginning to feel better.
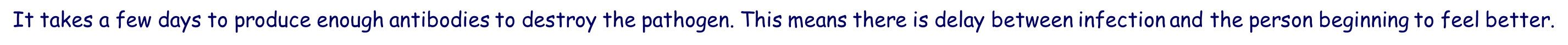
Delayed response
Once a pathogen has been destroyed, a few memory cells remain. These recognize the pathogen if it re-infects, and make the immune response much quicker and more effective. This is called active immunity.

Hidden pathogens - how does the body eal with pathogens
Memory cell
an immune system cell that recognizezes and kills pathogen
•Once you have had a vaccination and your body has responded to the antigens, memory cells will be produced.
•these remember the antigen in the pathogen. If they come into contact with it again they will reproduce fast killing the pathogen giving you immunity.
Immune
Abte to fight an infection as a result of propr exposure
Vaccination and types if vaccination .
ANother way to aquire immunity is ingestion or An injection of an inactive or artificial pathogen that results in the individuals becoming immmune to a particulat disease ,
b Vaccination or inocilation is made up of
The dead pathogen
A living but non virulrnt form of pathogen
Gneetic material from viral pathogen
-Weakened form of the pathogen
-Parts of the pathogen
describe how vaccinations work by helping the body produce memory cells
through vacination , a person makes antibodies and memort cells which will recognise the pathogen in the future , leading to immunity to specific pathogens without causing the disease.
vacination
Eg. the Flu vaccine, which provides immunity against the influenza virus.
prevent covid 19
the modified genetic material from sars corona virus can be use for vaccinations . meaining that the person wulll have antibodies and t cells already activated in their body to prevent the virus .
Active immmunity
immunity given by a vaccine to make the body produce antibodies.
boster infection
\

Explain how the use of vaccines can help prevent the spread of covid-19 . In your response , refer to temrs vaccinations , virus , thirld line of defence antigen etc .
Vaccinations introduce a weakend or inactive form of virus or its antigen into the body .
This triggers the third line of defence where b cells are produce specific antibodies to fight the virus , and t cells help destroy the infected cells
after , memory cells remain , allowing the body to respond faster if exposed again ,reducing the spread of covid 19
why is the third line specific
considered specific because it targets and eliminates specific pathogens that have been encountered by the immune system before
diseases were vacinated too
-measles,
-mumps,
rubella,
whooping cough,
polio,
tetanus
Why is there delay between person infection and feeling better
due to the time it takes for the body's immune system to respond to the invading pathogens
and for the pathogens to reproduce to a significant enough level to cause noticeable symptoms.
Antigen
a toxin or other foreign substance which induces an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies.