Anatomy and Physiology: Membranes and Integumentary System
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What are the 4 types of membranes?
mucous (mucosa)
serous
cutaneous
synovial
Where are mucosa membranes found?
mucosa membranes line compartments that are open to the external environment
In what organ systems are mucosa membranes found?
digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts
What are the functions of mucous membranes?
absorption
protects
secretory functions
Where are serous membranes found?
they line body cavities that aren’t open to the external environment
What type of cells make up serous membranes
simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium)
What do serous membranes do?
they reduce friction between opposing surfaces
What are the parts of the serious membrane
parietal (outer layer)
visceral (inner layer; lines the outside of the organ)
serous cavity (area in between parietal and visceral layers)
serous fluid (fluid in the serous cavity)
Where are cutaneous membranes found?
the SKIN (cutaneous membranes are just skin)
the external surface of the body
What type of cells are cutaneous membranes made of?
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
What is the function of cutaneous membranes?
protecting internal organs
preventing water loss
Where are synovial membranes found?
they line some joints of the body
What cells make up synovial membranes?
areolar CT (loose CT; squamous epithelial cells without basement membranes)
What is the function of synovial membranes?
reduces friction between moving bone parts (synovial fluid)
distributes nutrients to cartilage
What is integument?
SKIN
Where is the integumentary system?
covers the whole body
What organs and tissues make up the integumentary system?
skin
accessary tissues (nails, hair, sweat glands, sebaceous glands)
What are the functions of integument?
protection
preventing water loss
temperature regulation
sensory perception
excretory organ
formation of vitamin D
What are the layers of integument?
Epidermis and dermis (NOT SUBCUTANEOUS layer)
What are the layers of the epidermis in order from most superficial to deepest? (CLGSB)
Stratum corneum
Stratum lucidum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum basale
Which layers of the epidermis are living (not dead cells/keratinized)
Stratum granulosum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum basale
*Deepest 3 layers
Distinctive features of the stratum basale?
one layer of cells
melanocytes (pigment cells that absorb UV radiation)
stem cells (create new epidermal cells)
Distinctive features of the stratum corneum?
layers and layers of dead/keratinized cells
What is the difference between thick skin and thin skin?
Thin skin doesn’t have stratum lucidum (3rd layer of epidermis)
thin skin is more sensitive than thick skin
Where is thin skin found?
crook of the elbow
back of the knee
face (eyelids, checks, lips)
genitals
armpits
Where is the dermis found?
UNDER the epidermis
What type of cells make up the dermis?
dense (IRREGULAR) CT
What structures are found in the dermis?
blood vessels
sweat glands
sebaceous gland
hair follicles
sensory nerve endings
arrector pili muscles
What are the two subdivisions of the dermis?
papillary layer (makes fingerprints!)
reticular layer (has the “important structures mentioned)
What are the types of sensory nerves?
free nerve endings
Meissner’s corpuscles
Pacinian Corpuscles
What is the function of Meissner’s corpuscles (sensory nerves)?
to sense LIGHT touch, temp, texture, slow vibrations
Where are Meissner’s corpuscles (sensory nerves) found?
in papillary layer of dermis(near basal layer of epidermis)
What is the function of Pacinian Corpuscles (sensory nerves)?
to sense deep pressure and fast vibrations
Where are Pacinian corpuscles (sensory nerves) found?
in reticular layer of dermis
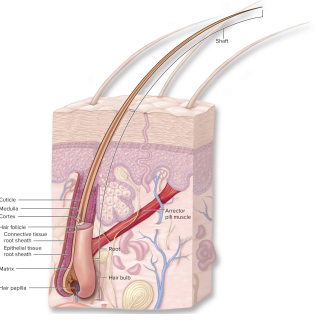
What are the parts of a hair?
hair bulb (base of the hair, largest part)
root (length of hair from the bulb to the skin’s surface)
shaft (length of hair exposed to the outside environment)
arrector pili muscle
What is an arrector pili muscle?
a smooth muscle attached to the hair follicle that, when contracted, causes goosebumps
What steps make up the hair growth and replacement cycle?
1.) anagen phase
2.) catagen phase
3.) telogen phase
What happens during the anagen phase (hair growth cycle)
first step of cycle
active phase where cells grow and divide
longest part of the cycle
What happens during the catagen phase (hair growth cycle)?
brief regression/ cell division stops
What happens during the telogen phase (hair growth cycle)?
resting phase
hair is shed
cells of bulb start to regrow after 3-4 months (cycle repeats)
What are the types of glands?
exocrine glands
endocrine glands
What are exocrine glands?
CT lined with epithelial cells that secrete stuff (sweat, milk, saliva, etc)
What are endocrine glands?
specialized organs that secrete (specifically) hormones into the blood
What are examples of endocrine glands?
thyroid
pituitary
testicles
ovaries
What are the types of sweat glands?
Merocrine
Apocrine
What do merocrine glands do?
secrete sweat (99% water)
What do apocrine glands do and where are they located?
location: axillary, pubic, and anal region
function: secrete proteins and lipids (reactions with bacteria which leads to sweat)
What are sebaceous glands and what do they do?
Exocrine glands in integument
produce oily sebum (lubricant for skin and hair from hair follicles)
sebum contributes to acne
What are the two ways tissue can be repaired?
regeneration
fibrosis
What is regeneration?
using cell division to replace dead/damaged cells to restore tissue function
What is fibrosis?
extensive damage requires scar tissue throughout CT during healing
What are the steps of wound healing?
1.) blood comes from wound (clotting proteins, WBC, antibodies gather at wound)
2.) blood clot forms (prevents infection; WBC clean wound)
3.) Damaged blood vessels regrow (fibroblasts produce new collagen fibers, macrophaes remove clot)
4.) epithelium regenerates from cell division (more CT replaced by fibrosis, scab forms)
What is fibrosis?
process that puts a thicker layer of CT back in the place of a wound. Can impair function if a lot of CT is needed to repair wound.
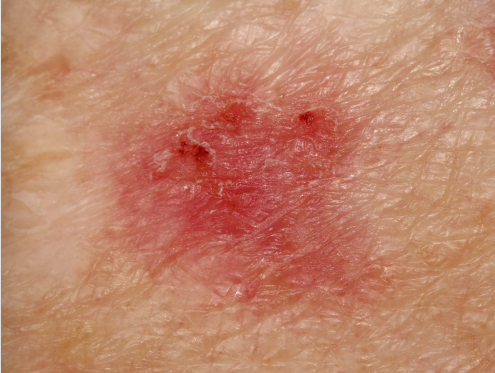
What is basal cell carcinoma?
most frequent type of skin cancer
in stratum basale (deepest layer of epidermis)
slow growing; metastasis rare
usually from sun exposure
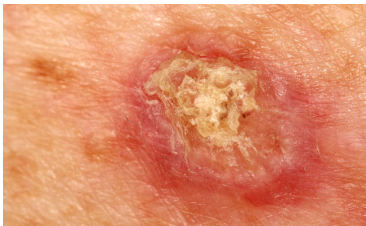
What is a squamous cell carcinoma?
originates from stratum spinosum
rough malignant nodule
can metastasize (surgical removal, chemo sometimes)
from sun damage or burns
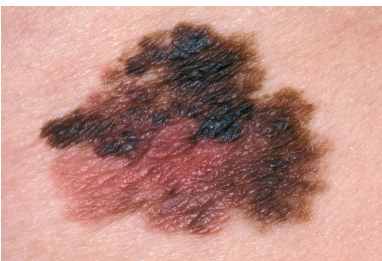
What is a malignant melanoma?
most deadly
from melanocytes, preexisting mole
high risk of metastasis
sun exposure
ABCDE rule of melanoma vs. mole
A - asymmetry (moles are symmetrical)
B - boarder (moles have even boarders)
C - color (moles are one color)
D - diameter (moles are less than .25” diameter)
E - evolution (moles don’t change in size or shape quickly)