Axial and Appendicular Skeleton
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
206
Adult skeleton consists of ___ named bones (most of which are paired)
Axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton
Bones of the skeleton can be grouped into 2 divisions
Axial skeleton
80 bones; Includes skull, auditory ossicles, vertebral column, hyoid, ribs, sternum, and thorax
Apendicular skeleton
126 bones; Includes upper and lower limbs and girdles (pectoral and pelvic)
Long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid
Most bones can be classified into 5 types based on their shapes
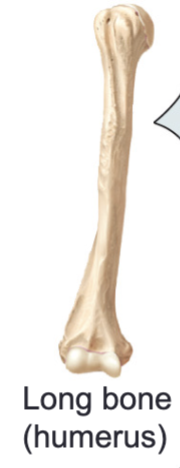
Long bones
Bones that are longer than they are wide, thick compact bone exterior
Ex/ Femur, humerus
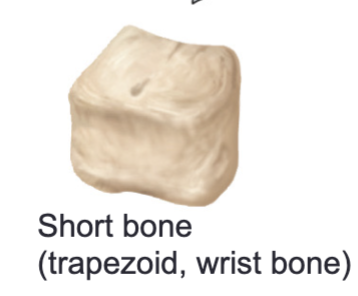
Short bones
Bones that are almost equal in width and length, thick spongy bone interior, thin compact bone exterior layer
Ex/ Carpals, tarsals

Flat bones
Bones that may be curved, thin spongy bone interior covered by a thin veneer of compact bone
Ex/ Cranial bones, sternum
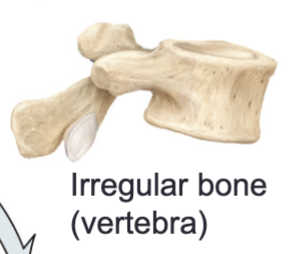
Irregular bones
Bones that do not easily fit into any of the other categories, the amount of compact and spongy bone varies
Ex/ Facial bones, vertebrae
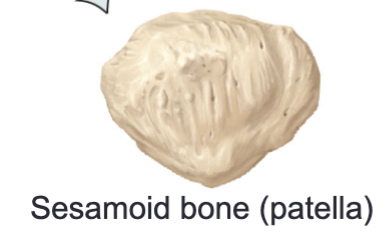
Sesamoid bones
Small bones that develop within certain tendons for protection against wear and tear, some can be found within the palms and soles
Ex/ Patella
Surface markings
Characteristic structural features adapted for specific function that bones possess
Depressions and openings & processes
2 major types of surface markings
Depressions and openings
Surface markings that allow for the passage of soft tissues, blood vessels, and nerves; Form joints
Processes
Surface markings that are projections or outgrowths that form joints and serve as attachment points for ligaments and tendons
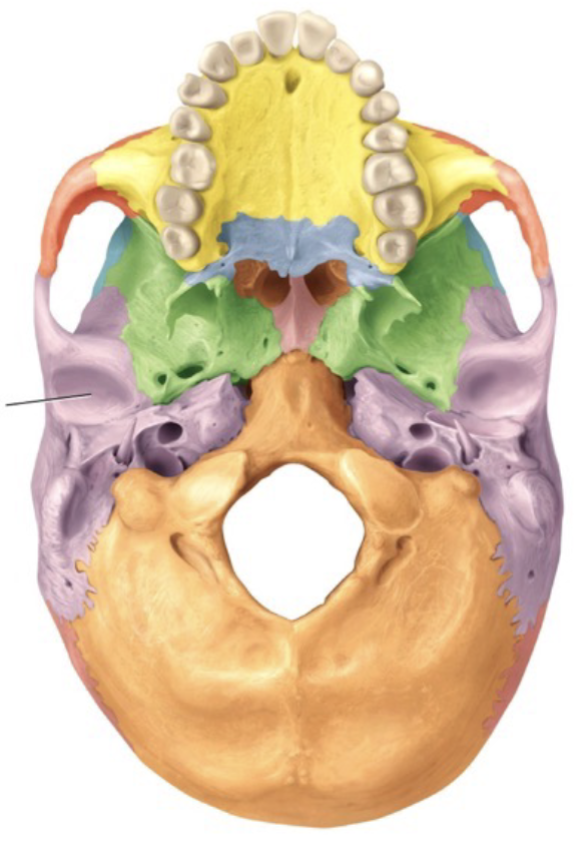
Fissure
Narrow slit between bones for passage of blood vessels or nerves
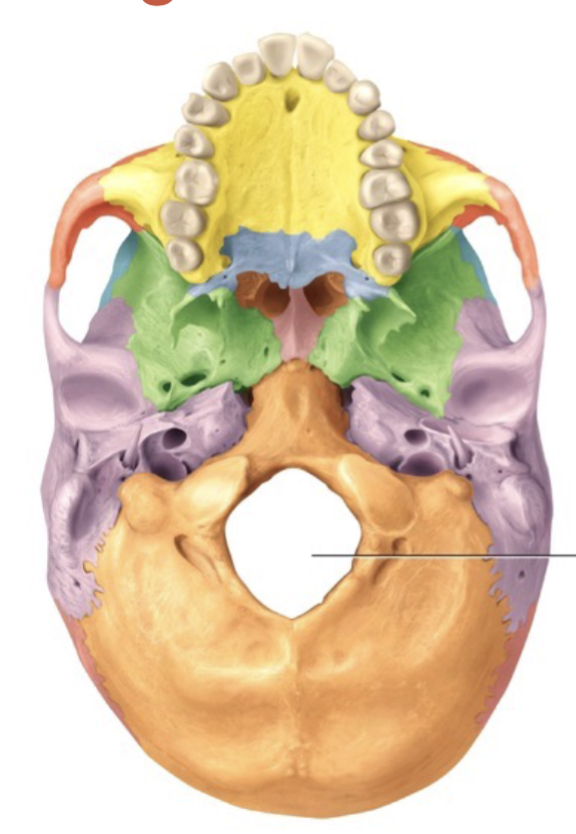
Foramen
Opening for passage of blood vessels, nerves, or ligaments
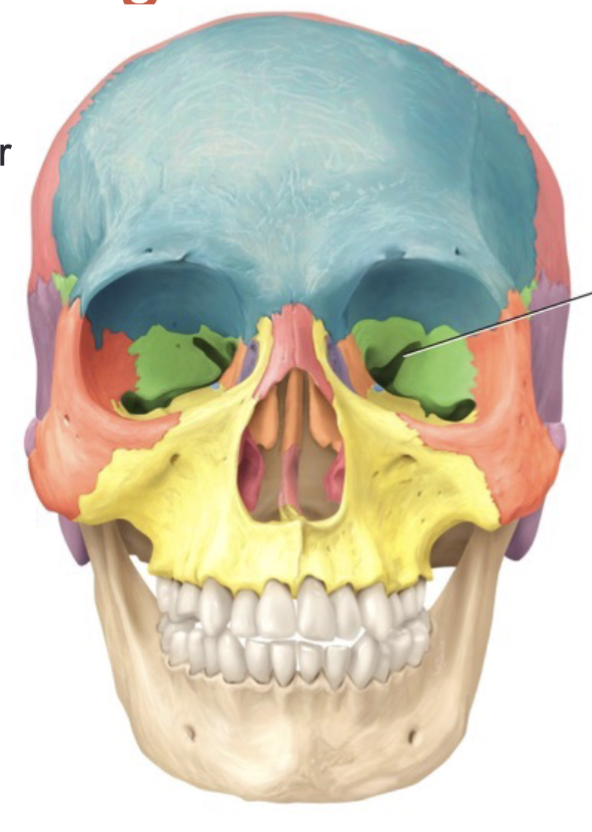
Fossa
Shallow depression
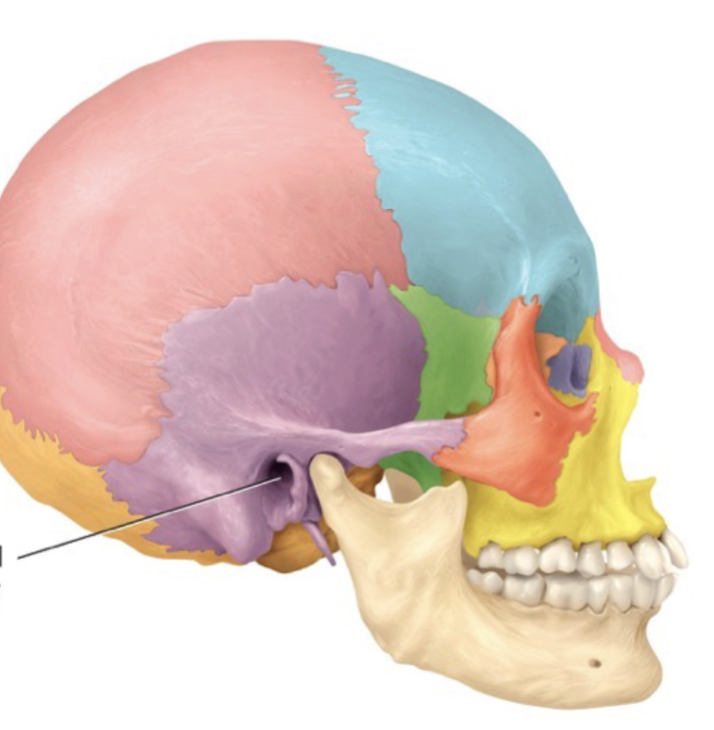
Meatus
A tube-like opening
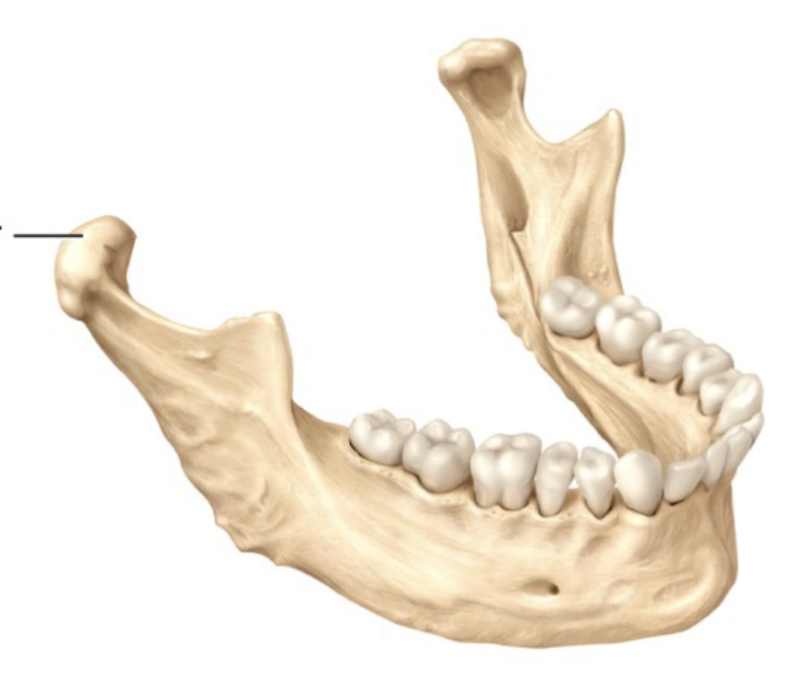
Condyle
Rounded projection with a smooth articular surface
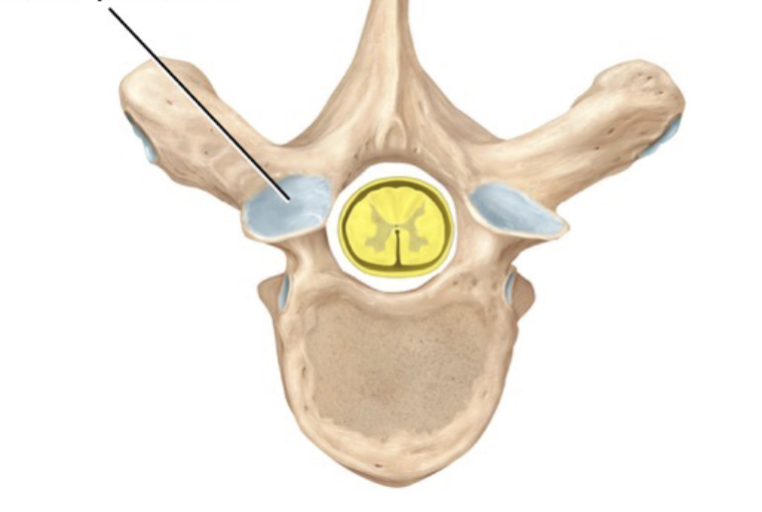
Facet
Smooth, flat, slightly concave articular surface
Head
Usually rounded articular process supported on a neck
Crest
Prominent ridge or elongated process
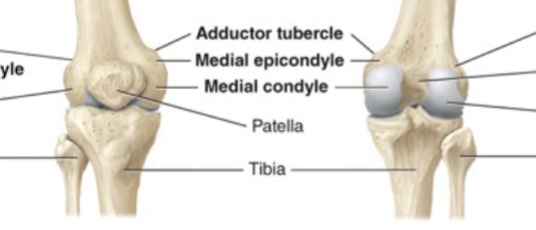
Epicondyle
Usually roughened projection on a condyle
Line
Long, narrow ridge or border (less prominent than a crest)

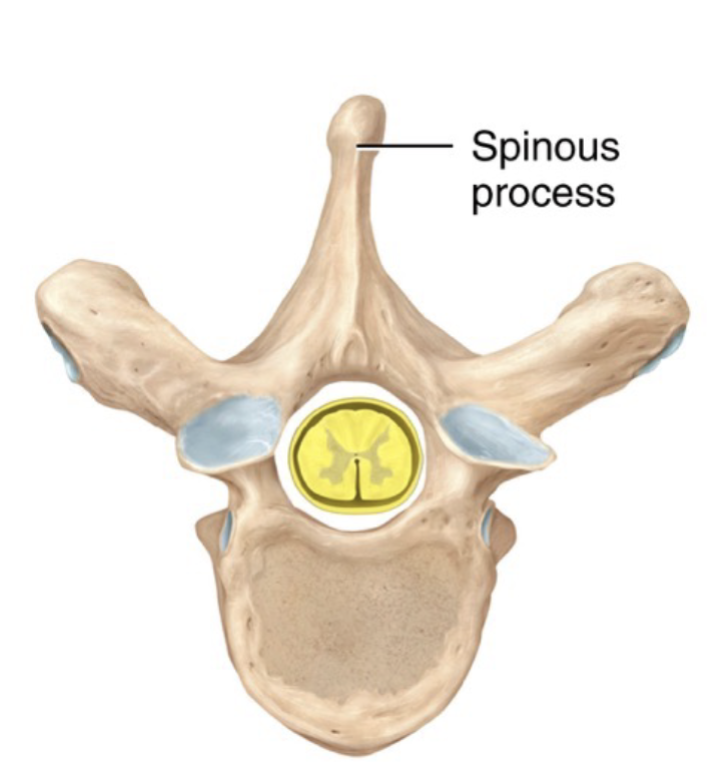
Spinous process
Sharp, slender projection
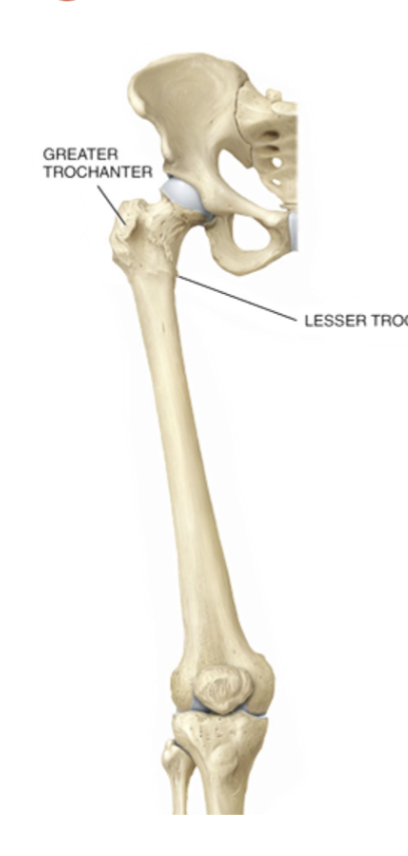
Trochanter
Very large projection
Tubercle
Variably sized rounded projection

Tuberosity
Variably sized rough projection with rough bumpy surface
Head
The skull contains 22 bones (not including the bones of the inner ear) and makes up the bony framework of the
Nasal cavity, orbits, paranasal sinuses
Besides the cranial cavity, the skull also contains several smaller cavities including
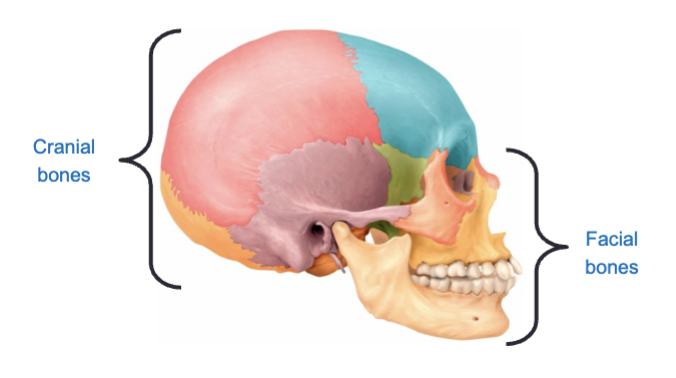
Cranial cavity bones and facial bones
Bones of the skull are grouped into 2 parts
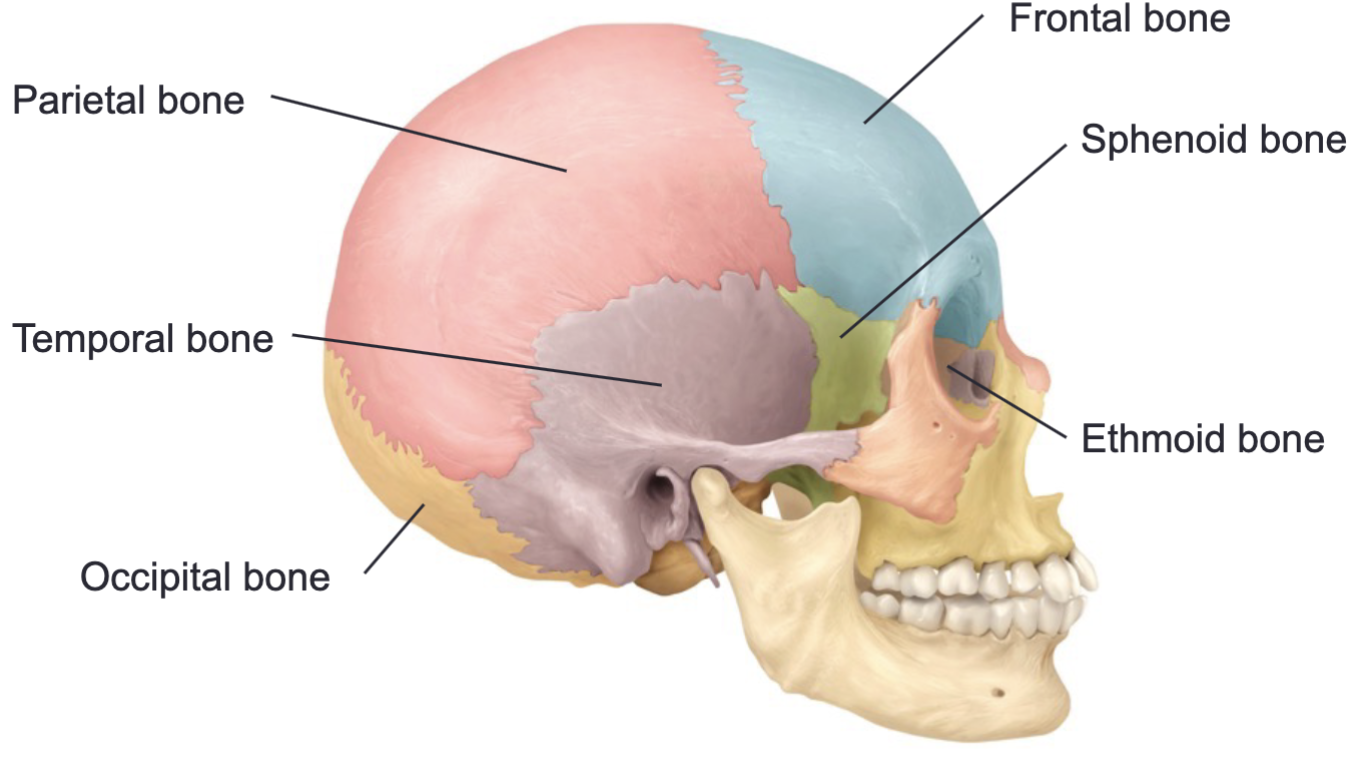
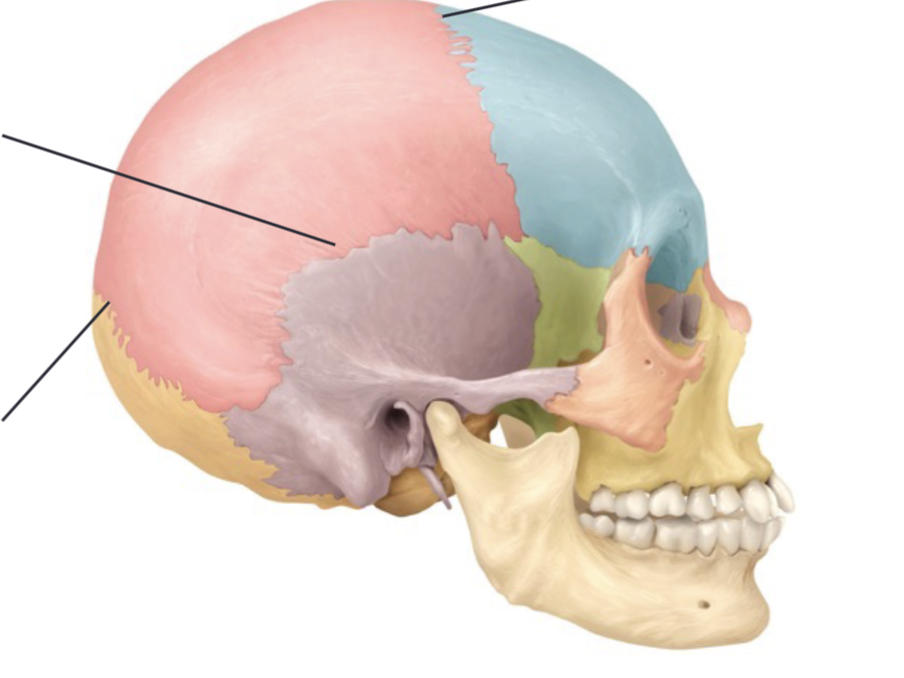
Frontal bone, parietal bone, temporal bone, occipital bone, sphenoid bone, ethmoid bone
8 cranial bones
Parietal bone and temporal bone
Of the cranial bones, there are 2 each of the
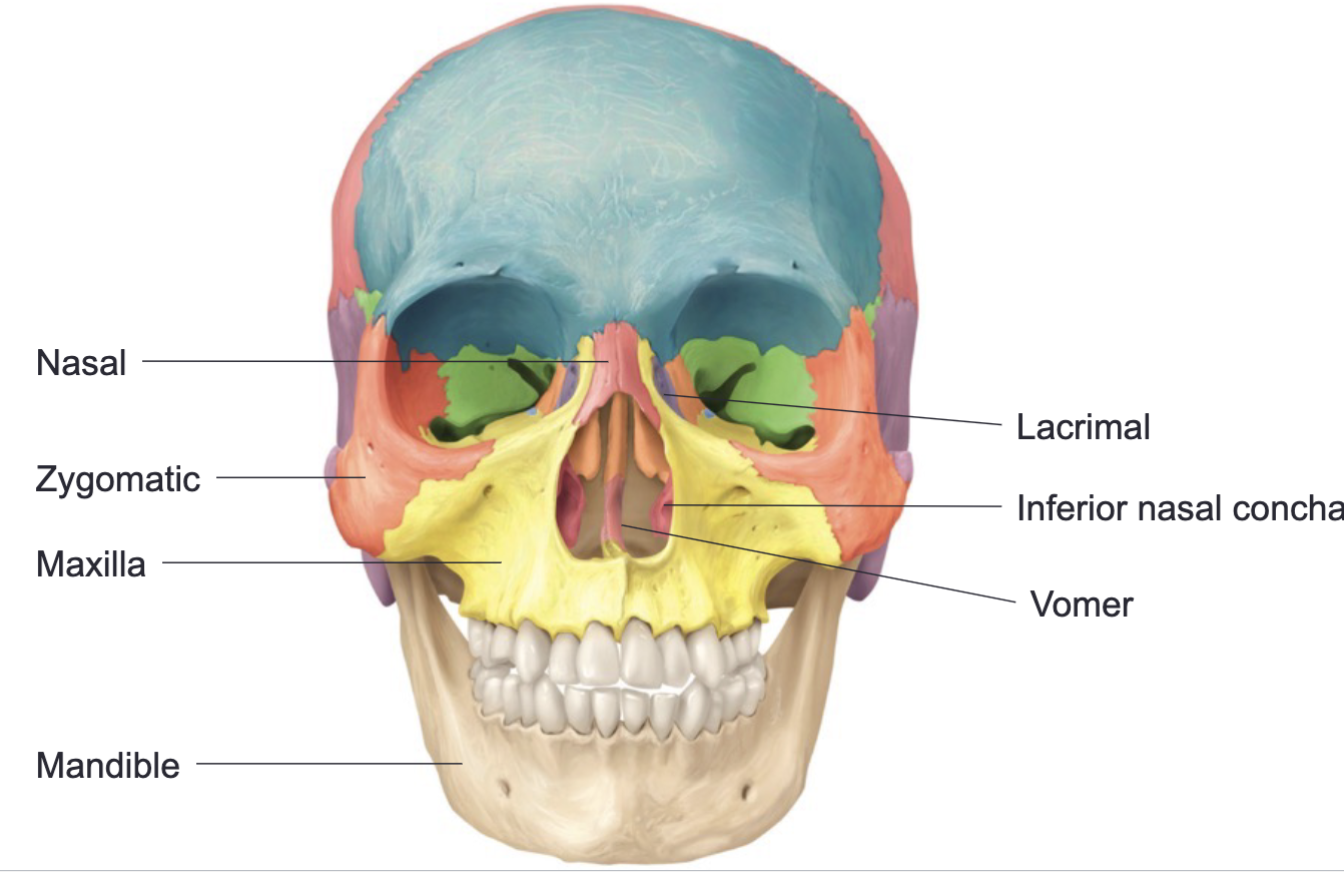
Mandible, maxilla, zygomatic bone, nasal bones, lacrimal bones, palatine bones, inferior nasal conchae, vomer
14 facial bones
Maxilla, zygomatic bone, nasal bones, lacrimal bones, palatine bones, and inferior nasal conchae
Of the facial bones, there are 2 each of the
Suture
A “seam”, an immovable joint between bones of the skull
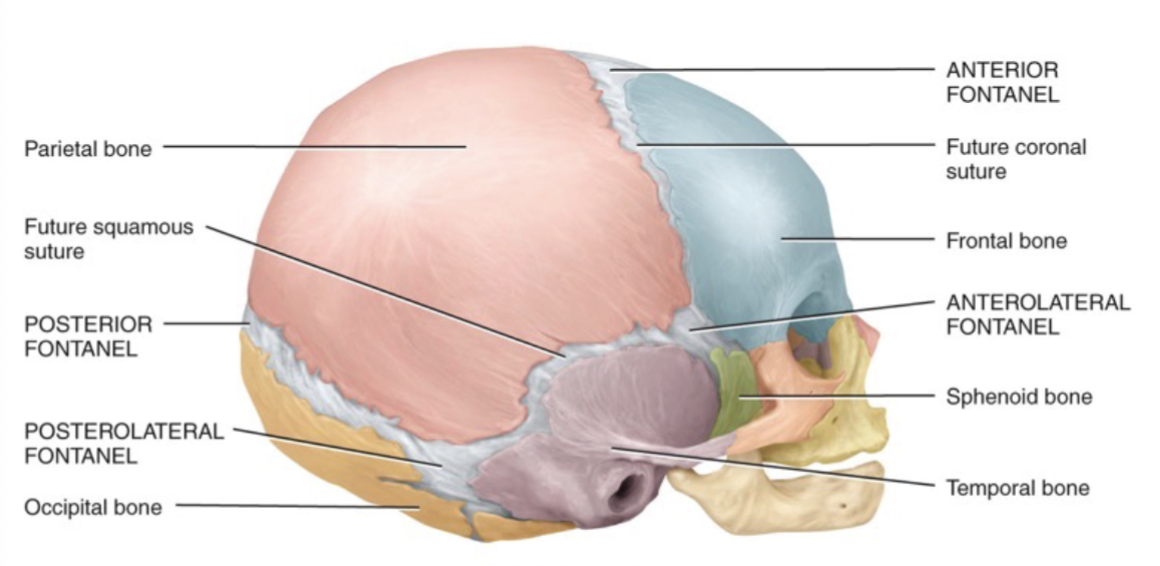
Fontanels
Soft, membrane-filled spaces between the cranial bones in babies; Will become suture joints in adults
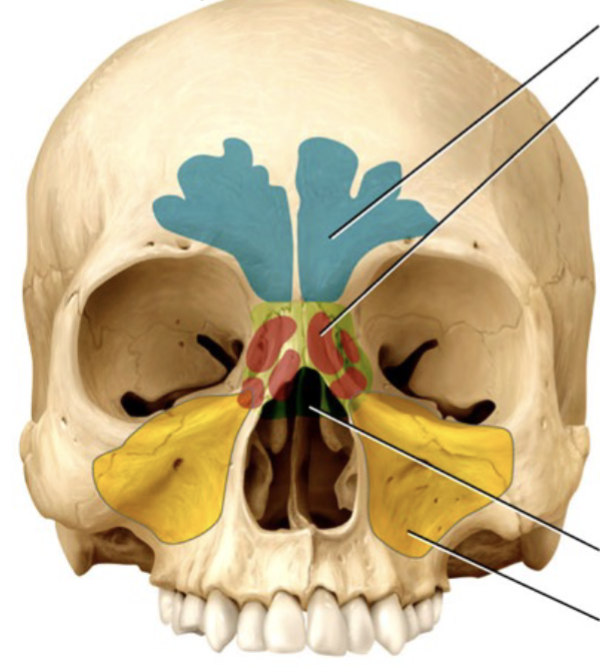
Paranasal sinus
A cavity within certain cranial and facial bones (maxillary, ethmoid, sphenoid, and frontal); Lined with mucus membranes (serve to humidify and warm air), reduces the weight of the skull, and helps to resonate the sound of our voice
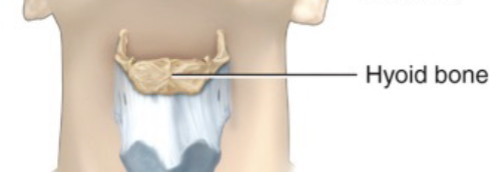
Hyoid bone
A U-shaped bone situated at the top of the larynx that supports the tongue and provides attachment for some of the muscles in the neck and pharynx
Hyoid bone
Only bone in the body that does not articulate with any other bones
Vertebral column
Other names for this include: spinal column, backbone, and spine
Vertebral column
Encloses and protects the spinal cord, supports the head, serves as a point of attachment for the ribs and pelvic girdle, and provides attachment for muscles of the back and upper limbs

Vertebral column
Composed of 26 vertebrae divided into 5 regions, each of which have unique characteristics to help identify which type they are
Spinal curvatures
4 slight bends in the normal adult vertebral column seen when viewed from the side that function to increase the strength of the vertebral column, help maintain balance and upright position, absorb shocks during walking, and help protect the vertebrae from fracture
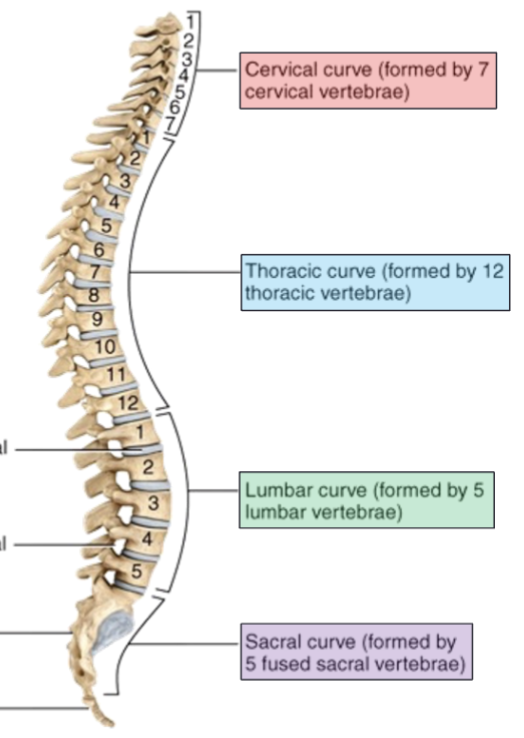
Thoracic and sacral
Primary curves that are concave
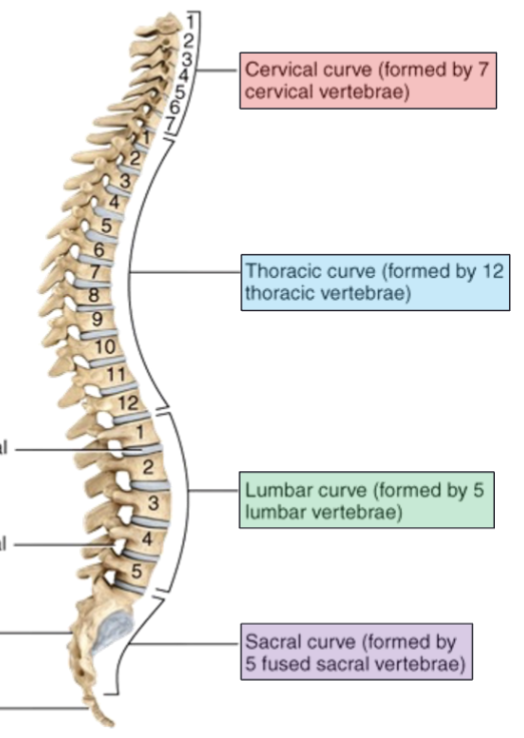
Cervical and lumbar
Secondary curves that are convex
Abnormal spinal curvatures
Various conditions may exaggerate the normal spinal curves, sometimes causing severe disability
Ex/ Scoliosis, kyphosis, lordosis
Intervertebral discs
Found between the bodies of adjacent vertebrae and functions to absorb vertical shock and form joints which are strong yet still permit movement of the spine
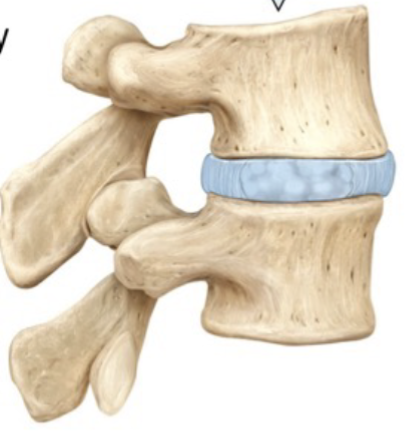
Annulus fibrosus
Tough, outer ring of fibrocartilage of each intervertebral disc
Nucleus pulposis
Soft, pulpy nucleus that is surrounded by the annulus fibrosus in each intervertebral disc
Decompression and rehydration
During the course of a day the intervertebral discs compress and lose water from their cartilage, therefore we are a bit shorter at night and during sleep 2 things occur
Herniated intervertebral disc
Clinical issue of intervertebral discs that can be caused by trauma or can be associated with aging
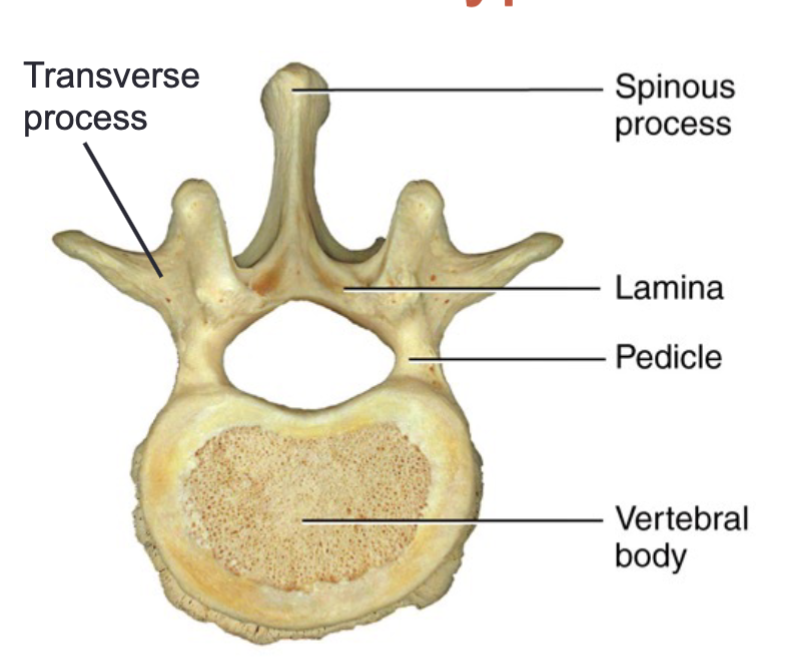
Body, transverse processes, spinous process, pedicle, and lamina
Typical vertebrae consists of
Pedicle
Connects body to the transverse process
Lamina
Connects transverse process to spinous process
Intervertebral foramina
Formed by notches on the superior and inferior aspects that come together to allow spinal nerves to pass through
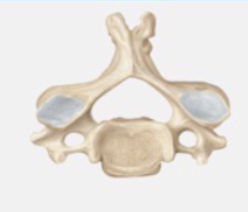
Cervical vertebrae
7 bones that comprise the neck and support the head; Smallest of the vertebrae
Transverse foramina
The cervical vertebrae have distinct _____
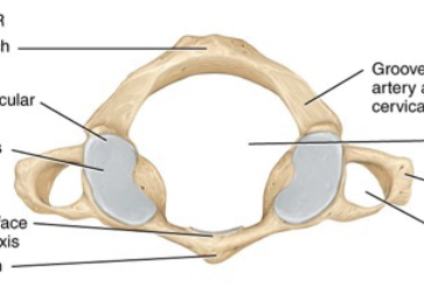
Atlas
CV1 is the first of the cervical vertebrae and supports the head
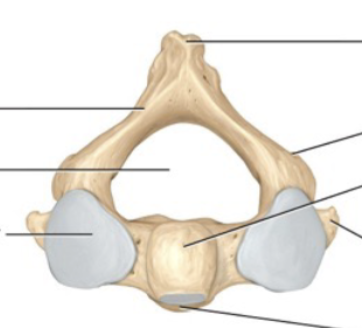
Axis
CV2 is the second of the cervical vertebrae and provides a pivot for the atlas
Bifid
The cervical vertebrae has a _____ spinous process (CV2-CV5)
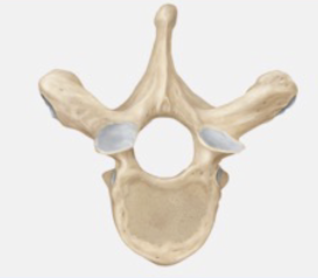
Thoracic vertebrae
12 larger vertebrae in the upper back; Spinous process is long and points down and back; Articulates with the ribs
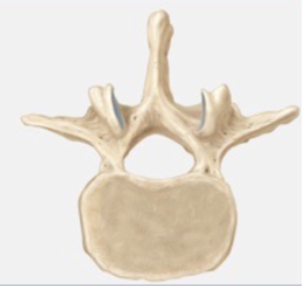
Lumbar vertebrae
5 vertebrae in the lower back; Largest of the typical vertebrae and supports the weight of the body; Spinous process is short and protrudes horizontally and its vertebral body is kidney shaped
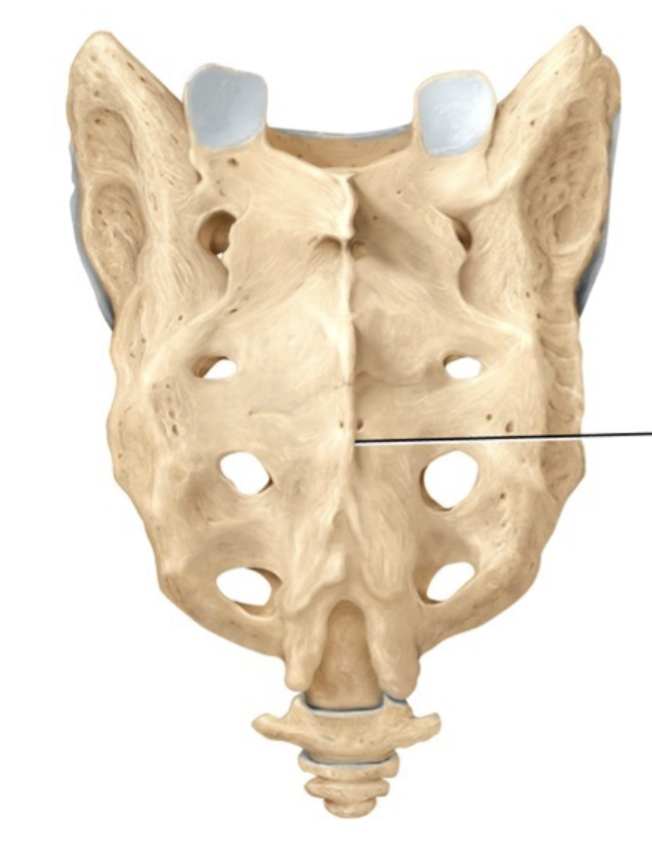
Sacrum
A triangular shaped structure at the base of the vertebral column that is composed of 5 vertebrae that are fused together into one bone and attaches to the bones of the hip to form the bony pelvis; Openings on the anterior and posterior surface allow passage of spinal nerves
Coccyx
The lowest bart of the vertebral column that is composed of 4 fused vertebrae
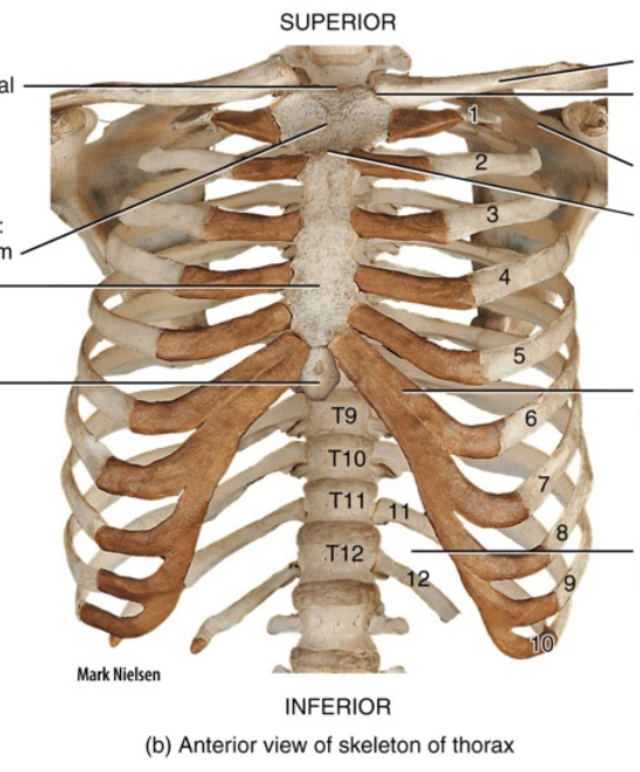
Thorax
Refers to the entire chest region and is formed from the sternum and the ribs and costal cartilages; Functions to enclose and protect the organs in the thoracic and abdominal cavities, providing support for the bones of the upper limbs and playing a role in breathing
Thoracic cage
Final part of the axial skeleton
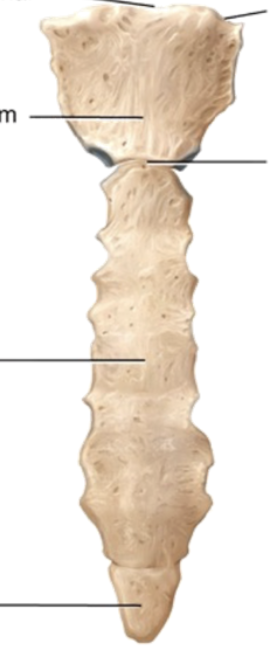
Sternum
Located anteriorly in the center of the thoracic wall and consists of 3 segments: the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process; The “breastbone”
12 pairs of ribs
Gives structural support to the sides of the thoracic cavity
Costal cartilages
Bars of hyaline cartilage connecting the sternum to the ribs; Contributes to the elasticity of the thoracic cage
12
Humans have__ pairs of ribs that attach to the thoracic vertebrae
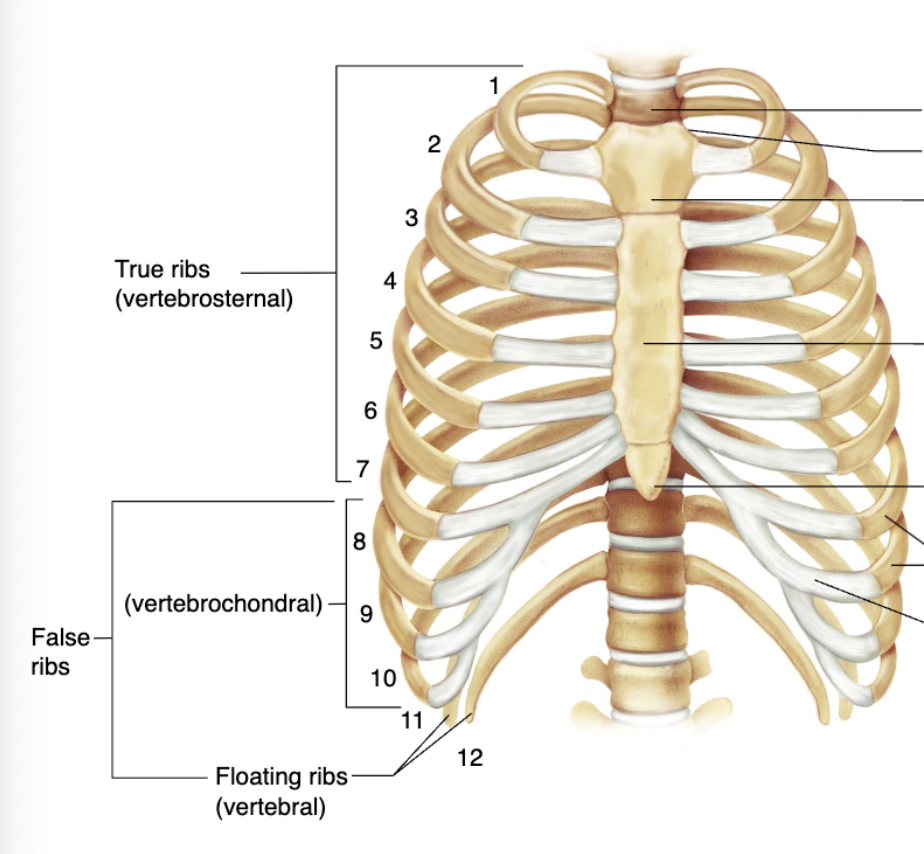
True ribs
The first 7 pairs of ribs that join the sternum directly by their costal cartilages; Vertebrosternal
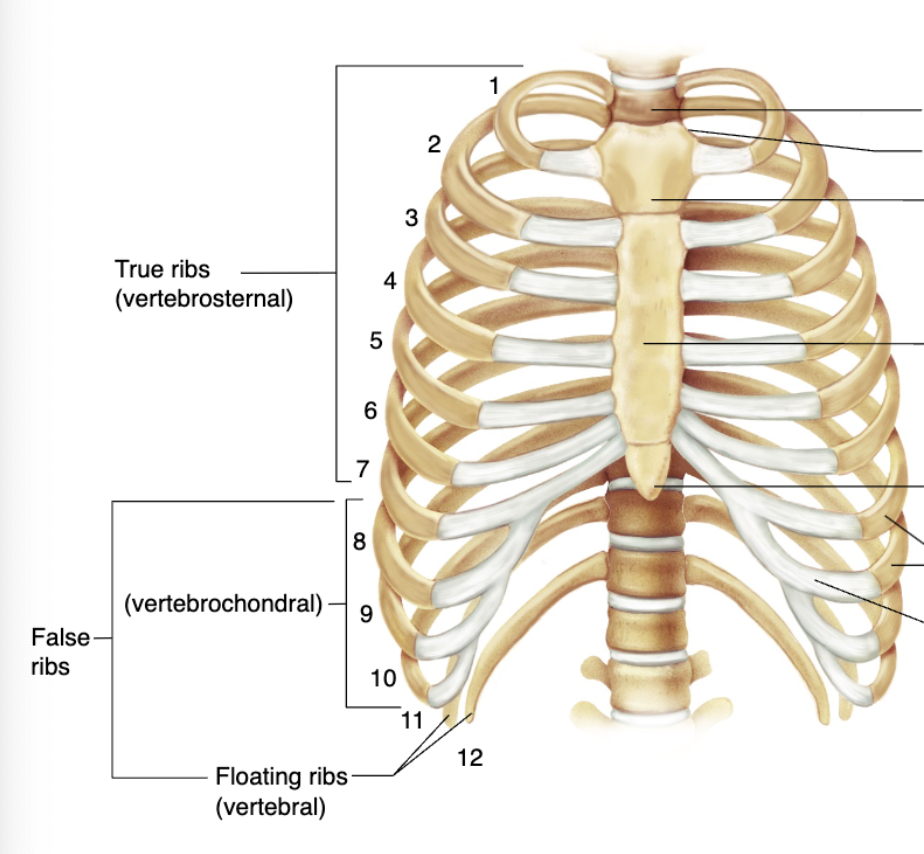
False ribs
Remaining 5 pairs of ribs that do not reach the sternum directly

7
Ribs 8-10 join the cartilages of the __th rib; Vertebrochondral
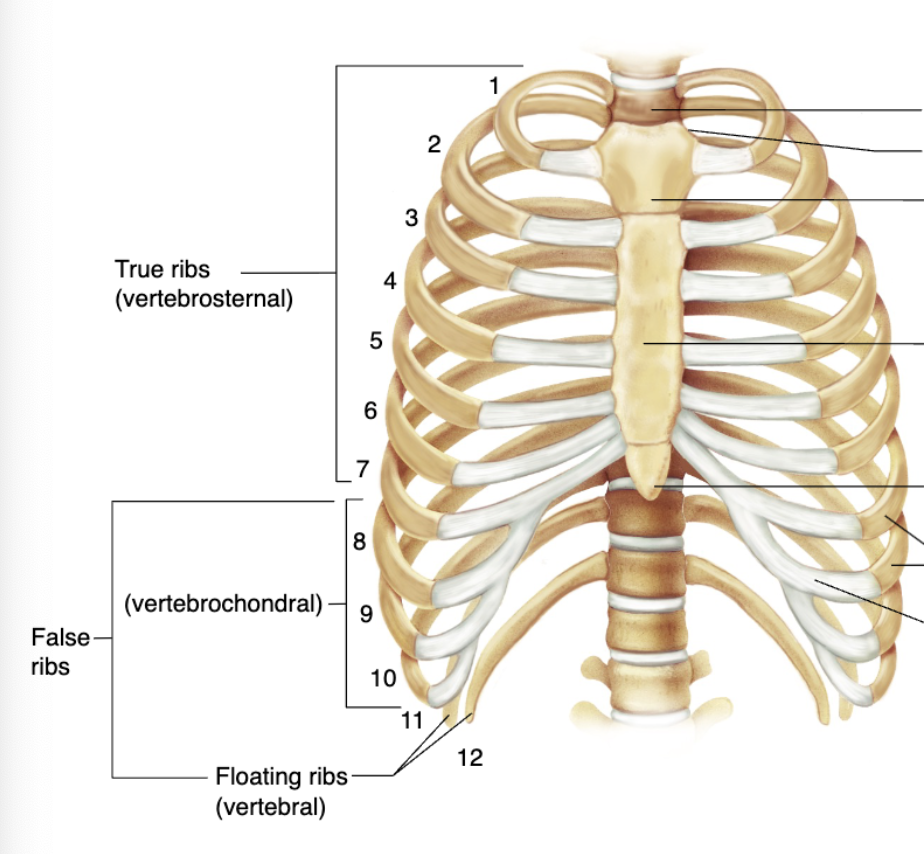
Floating ribs
Last 2 ribs that have no cartilage; Vertebral; Also considered false ribs
126
There are ___ bones in the appendicular skeleton
Appendicular skeleton bones
Primarily concerned with movement and make up the “appendages” (upper and lower limbs) and includes the girdles that attach them: pectoral and pelvic girdle
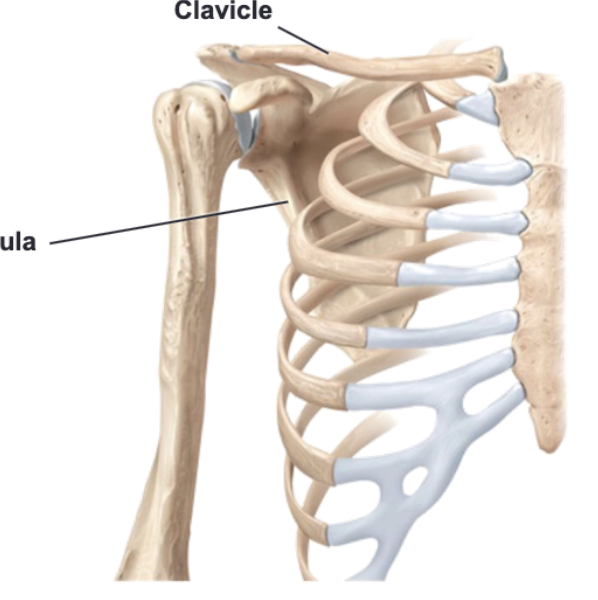
Pectoral girdle
Bones of the _______ include the scapula and clavicle
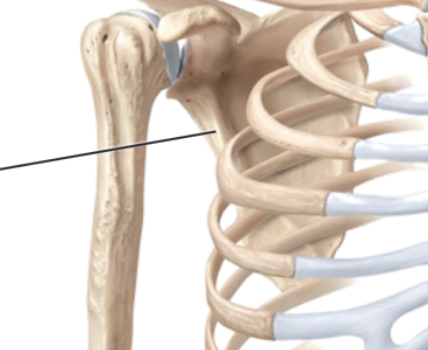
Scapula
Triangular shaped bone that has distinct features that provide attachment for muscles and allow it to articulate with other bones; Shoulder blade
Glenoid fossa
Lateral part of the scapula that is a shallow, cup-like depression that articulates with the rounded head of the humerus to form the glenohumeral joint
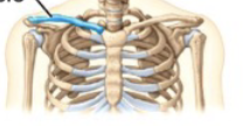
Clavicle
S-shaped bone; “Collar bone”
Sternoclavicular joint
Medial end of the clavicle articulates with the manubrium of the sternum forming
Acromioclavicular joint
Lateral end of the clavicle articulates with the acromion of the scapula forming
Upper limb
Each has 30 bones in 3 locations: arm, forearm, and hand
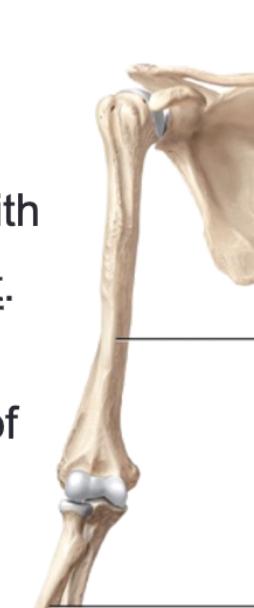
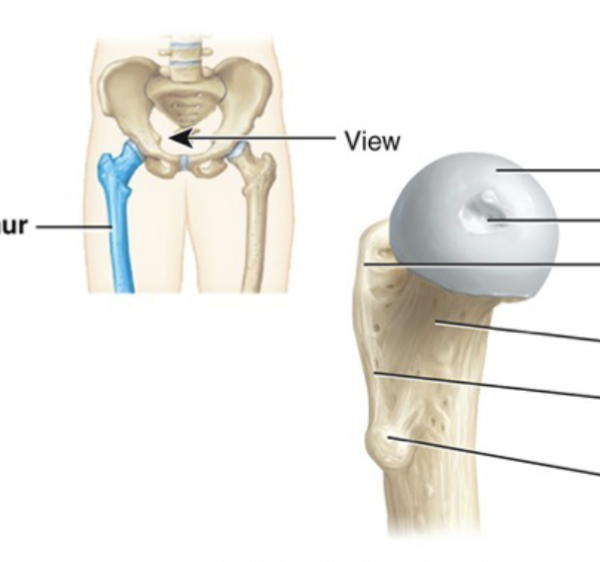
Humerus
Only bone in the arm
Glenohumeral joint
Proximal end (head) of the humerus articulates with scapula to form
Elbow joint
Distal end of the humerus articulates with bones of the forearm to form
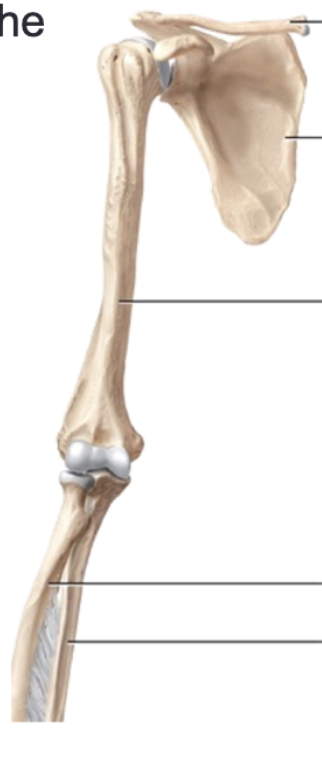
Forearm
Composed of the radius and the ulna
Radius
Lateral bone that is narrow at the proximal end and rotates over the ulna in pronation
Ulna
Medial bone that is narrow. at the distal end and has the olecranon process
Interosseus membrane
Diaphysis of the radius and the ulna are connected by _____
Proximal and distal
Two types of radioulnar joints in the forearm
Hand
Composed of the wrist, palm, and fingers
Wrist
Made up of 8 carpal bones arranged in 2 rows
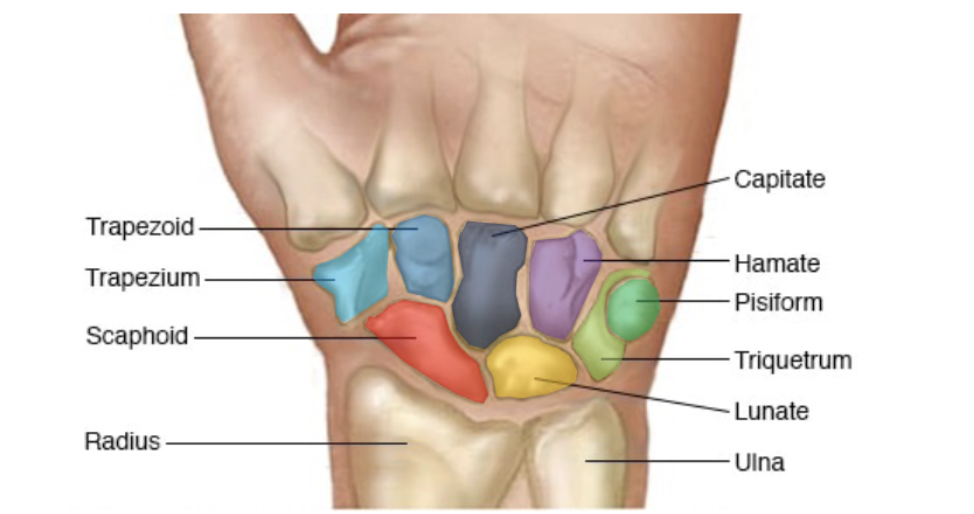
Scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform
Carpals proximal row (lateral to medial) listed
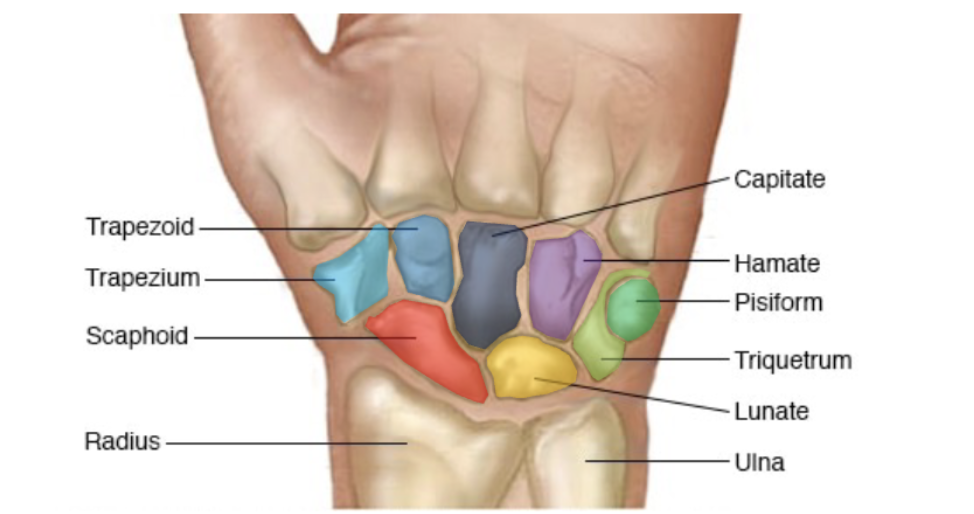
Trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
Carpals distal row (lateral to medial) listed
Palm
Composed of 5 metacarpal bones
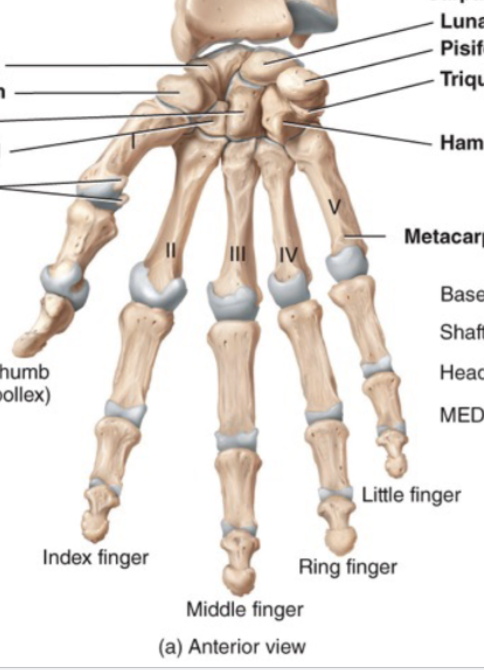
Fingers
Each are composed of 3 phalanges: the proximal phalanx, middle phalanx, and distal phalanx, (except the 1st digit which has 2)
Thumb (pollex)
Metacarpals and phalanges are numbered 1-5 starting with the ______
Pelvic girdle
Composed of 2 os coxae (hip bones)