Carbohydrates
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Functions of carbohydrates
Energy source
Energy storage
Structural uses
Types of carbohydrates
Monosaccharide
Disaccharides
Polysaccharide
Monosaccharide and give an example
Simplest carbohydrate, can’t be broken down further. Can be joined together to form larger carbohydrates. Examples are glucose, fructose, ribose and galactose
Disaccharides and give an example
Carbohydrates which are made by joining up two monosaccharide units. For example sucrose, maltose, and lactose
What two monosaccharides make up sucrose
Glucose + Fructose
What two monosaccharides make up maltose
Glucose + Glucose
What two monosaccharides make up lactose
Galactose + Glucose
Polysaccharides and give an example
Carbohydrates made from a large number of monosaccharide units. For example starch, cellulose, glycogen
How many naturally occurring monosaccharides, containing between 3-7 carbon atoms.
20
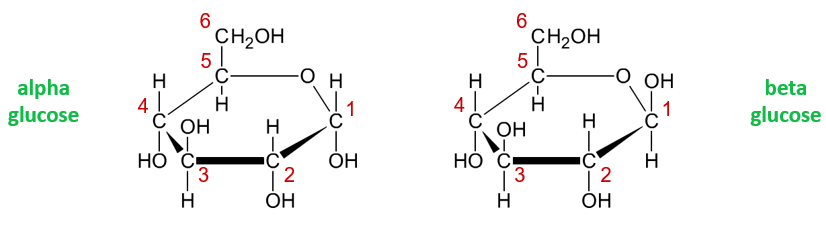
What is the difference between alpha and beta glucose
In alpha glucose the hydrogen is above the first carbon and in beta the hydrogen is below the first carbon
What happens when joining two monosaccharides
There is a condensation reaction forming a 1-4 carbon glycosidic bond
What reaction breaks the glycosidic bond
A hydrolysis reaction, where water us added breaking the glycosidic bond.
When two beta glucose are joined together what occurs
One of the glucose flips 180o to allow the 1-4 carbon glycosidic bond to form.