UNIT 7: Isolationism & Neutrality to War
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Isolationism & Neutrality
- The transition in foreign policy from 1919-1941 and eventually war
1920s Isolationism
- The U.S. will be very involved in foreign affairs, but not committed to an entangling military alliance
- The U.S. will be involved to avoid conflict/ war, through:
(1.) Rejection of 1919 Treaty of Versailles
(2.) Refusal to join League of Nations
(3.) 1920-21 Washington Conference
(4.) 1924 Dawes Plan
(5.) 1927-28 Kellogg-Briand Pact
(6.) 1930 Young Plan "Dawes Pt.2"
(7.) 1930 London Conference
(1.) Rejection of 1919 Treaty of Versailles
- Even though Wilson signs the treaty, the U.S. Senate will reject it
- Rejected because -> Liberal opposition to the R&R, Moderate/ extreme conservative opposition to League as entangling alliance, and Wilson's stubbornness to compromise
(2.) Refusal to join League of Nations
- The U.S. will reject the Treaty of Versailles and refuse to join the League even though it was created by Pres. Wilson
- Rejected because -> Liberal opposition to the R&R, Moderate/ extreme conservative opposition to League as entangling alliance, and Wilson's stubbornness to compromise
(3.) 1920-21 Washington Conference
- U.S. hosts international naval disarmament (Wilson's 4th of 14 points) conference
- Reducing the size of navies decreases likelihood for war
- But, the big Western powers bring a 2nd objective -> Curb Japanese expansion in the Pacific
- Creates the 9-5-4 (# of countries signed) Powers Plan to stop Japan's expansion -> U.S. & Japan sign all
9 Powers Treaty
- 9 Powers (9 countries signed)
- Upholds open door policy in China -> Free trade, dissolves Spheres of Influence from Age of Imperialism
- The treaty intends to stop Japan from taking over China by putting pressure on Japan to agree to be bound by an international agreement not to invade China
5 Powers Treaty
- Naval disarmament -> Reduction of navies for each country
- Japan dislikes that they now have a smaller navy than the U.S. or UK
- Intended to disincentive war
4 Powers Treaty
- All countries must respect each other's territory holdings in the Pacific
- Intended to address concern about Japanese expansion in the Pacific
(4.) 1924 Dawes Plan
- Germany was unable to pay the demanded reparations imposed by the Treaty of Versailles for Germany's role in WWI
- Fear about a war over the unpaid reparations loomed, the Allies did not want a war so the U.S. will step in and prevent war through the Dawes Plan
U.S.'s Dawes Plan
- Reduces reparations Germany must pay to a reasonable amount -> But Germany still has no money so the U.S. lends Germany money
- Creates circular flow -> The U.S. will lend Germany money -> Germany pays reparation to UK & France -> UK & France pay the U.S. for war debts
- Successful -> No war, reduced tensions
(5.) 1927-28 Kellogg-Briand Pact
- Bans war as a means to settle international conflict
- Nations are coerced into joining or else they'll look like the bad guy
- Pact is very idealistic & naive -> What if there's a Hitler or Stalin?
(6.) 1930 Young Plan "Dawes Pt.2"
- Germany again cannot pay the reparations, even after lowered by the Dawes Plan
- The fear of war looms again, but no one wants that so the Young Plan is created
- Lowers German reparations & revives the circular flow of the Dawes Plan
(7.) 1930 London Conference
- Naval disarmament agreement sponsored by the British
- U.S. signs the agreement and reduces their excess ships by sinking them in the ocean
1930s Neutrality
- U.S. response to fascist aggression from emerging fascist powers (Italy, Germany, Japan)
Fascism
- System of Government that emerges after WWI
- Military dictatorship political system mutually supported by a capitalist economic system
- Fascism will rise in Italy, Germany, and Japan because of the economic disorder and Great Depression post WWI
- "Fasces" -> Axe surrounded by bundle of sticks symbolizing the power & authority of the Roman empire or Senate
Emerging Fascist Powers
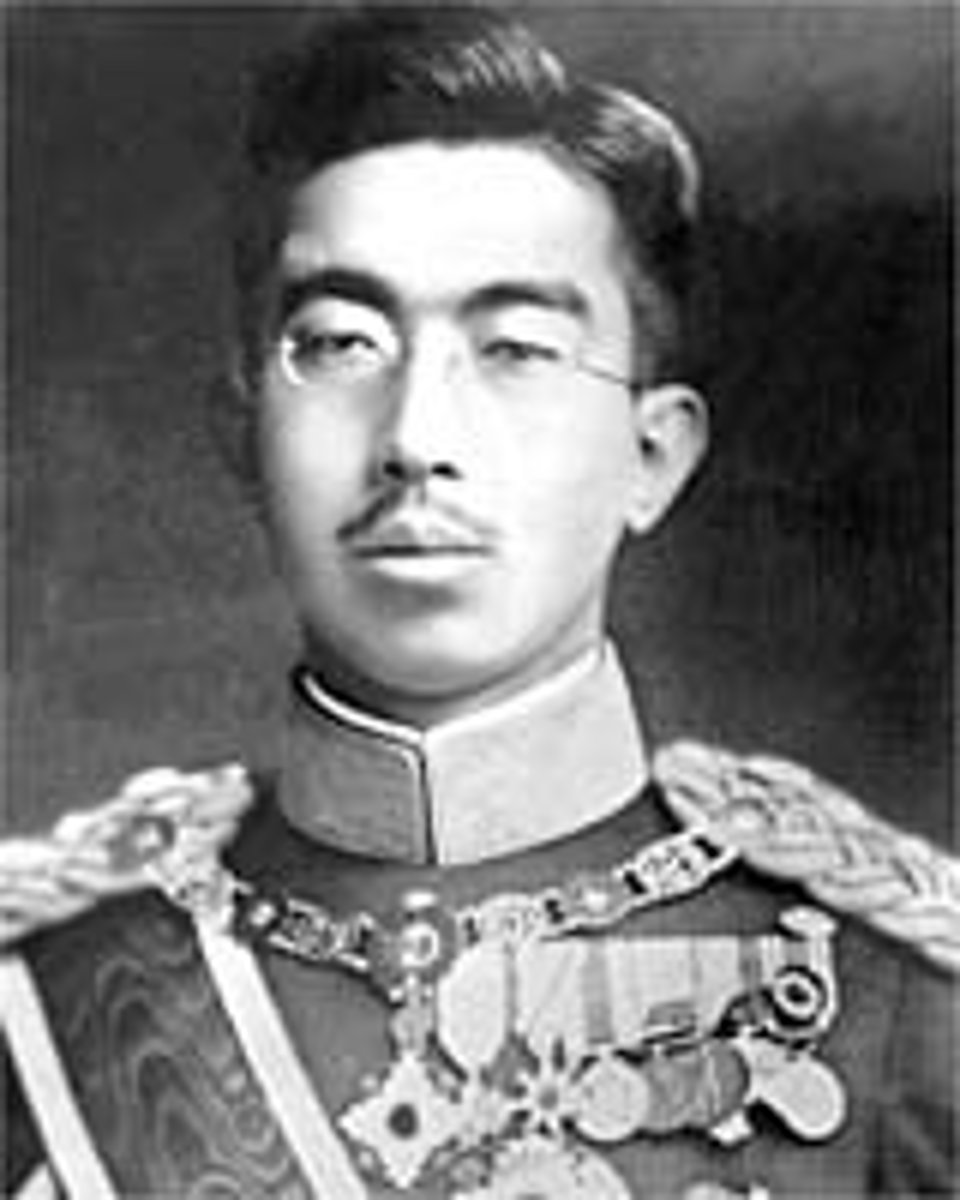
(1.) Japan -> Japan will develop it's own version of Fascism, a dictatorship & capitalist system, under Emporer Hirohito, but the Emperor is just a puppet of the military under Tojo
(2.) Italy -> Fascism rises in 1920 under Mussolini, who will take power and establish a dictatorship supported by capitalism
(3.) Germany -> Fascism rises in 1930s under Hitler & the Nazi Party that will establish a dictatorship supported by capitalism
Fascist Expansion
- By 1930 Italy, Germany, and Japan are looking to expand for political, economic and social reasons
- The Allies believe fascism's expansion threatens world peace, but the League of Nations will fail to stop the 3 imperialist expanding Fascist powers
(1.) Fascist Japan
- Japan will develop it's own version of Fascism, a dictatorship & capitalist system, under Emporer Hirohito, but the Emperor is just a puppet of the military under Tojo
- Japan will invade Manchuria, China to grow it's fascist empire

1931 - Manchuria Invasion
- Japan will invade and conquer Manchuria, a NE province of China, for its natural resources for Japan's military industrial complex that the island of Japan lacks
- Japan will violate treaties with the U.S. and the sovereignty of China
- Marks the beginning of Fascist aggression leading to WWII
- China calls on the League of Nations, as a member, for help while being invaded
Manchuria Invasion - League of Nation Response
- Condemns Japan for the invasion, but won't intervene, leaving China to fend for itself
- League won't get involved because of the economic crisis (GD) & racism/ prejudice -> White Westerners don't care about the Asians
Manchuria Invasion - U.S. Response
- U.S. is Not a member of the League of Nations
- Issues Stimson Doctrine -> U.S. version of the League's condemnation -> Tells Japan they're violating treaties, but the U.S. will not intervene
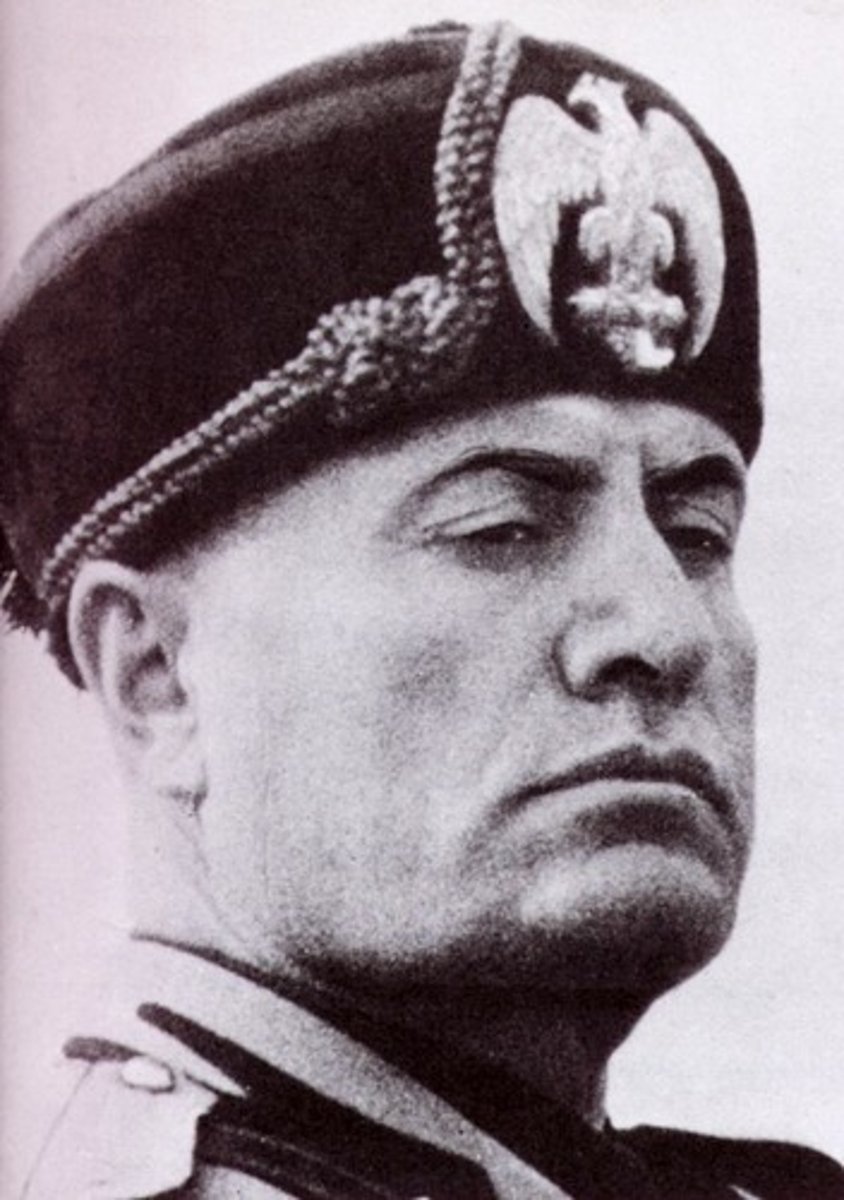
(2.) Fascist Italy
- Fascism rose in 1920 under Mussolini, who took power and established a dictatorship supported by capitalism
- Italy will try again to invade Ethiopia (Abyssinia)

1935 - Ethiopia (Abyssinia) Invasion
- During the Age of Imperialism Italy tried to invade & conquer Abyssinia, but are driven out by the inhabitants
- Italy, a world power, is embarrassed to have been beaten by a bunch of "spear-chucking monkies" and Mussolini is returning now with tanks & aircraft to restore Italy's honor to the height of the Roman Empire
- Italy will successfully invade Abyssinia
- King of Ethiopia, Haile Selassie, asks for the League of Nation's help while being invaded by Italy
Ethiopia (Abyssinia) Invasion - League of Nation Response
- King of Ethiopia, Haile Selassie, asks for the League of Nation's help while being invaded by Italy
- League issues condemnation to Italy, but doesn't intervene because of the economic crisis (GD), and racism -> White Westerners don't think they're worth going to war for
- Halie Salassie warns the Europeans in the League that if they don't stop the fascists now, they'll be the next targets and he will be right
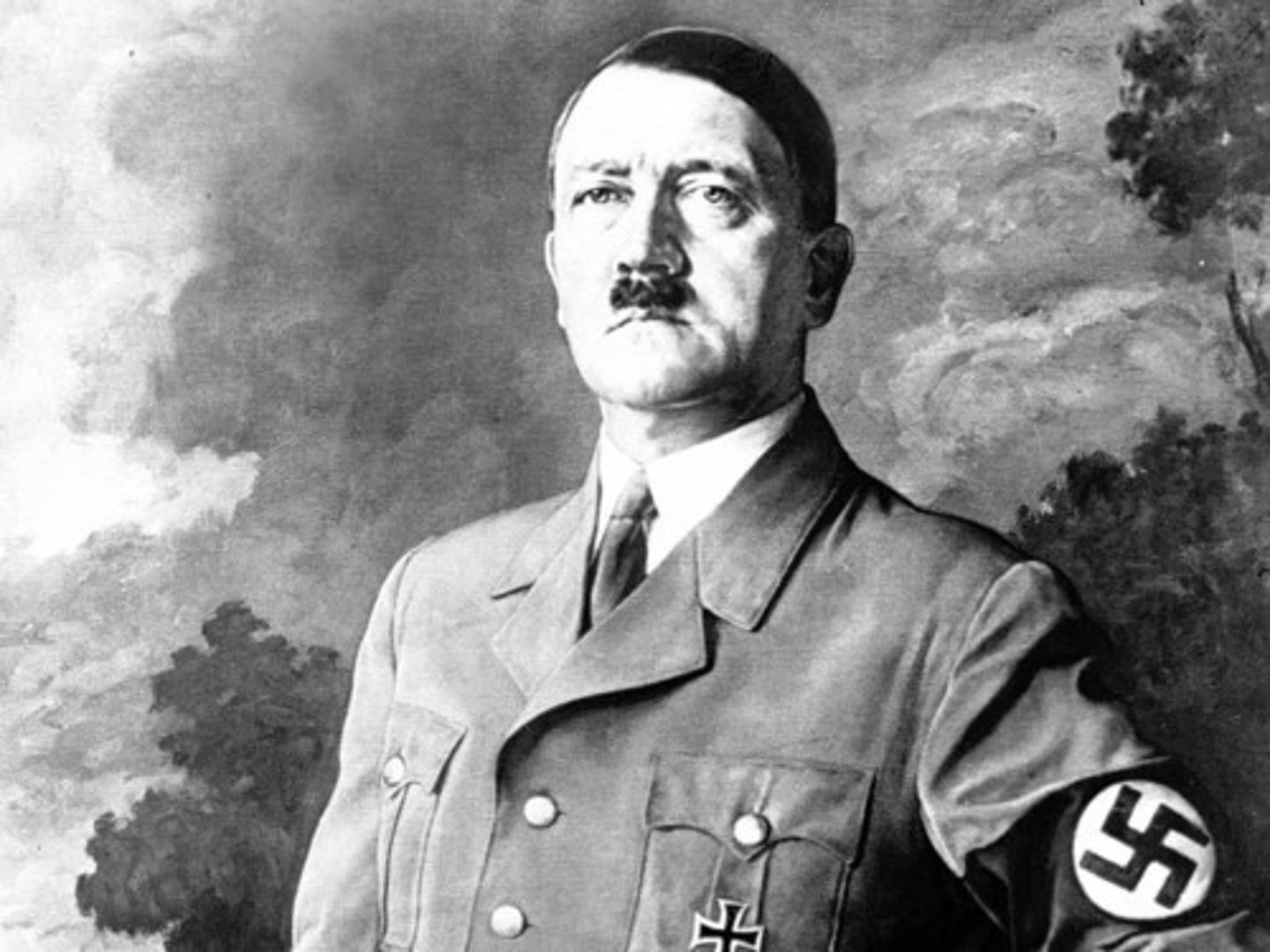
(3.) Fascist Germany
- In 1935 Germany is ruled by Hitler, who is violating the Treaty of Versailles by starting to re-arm Germany
- Germany will impose a draft, build tanks, submarines, and aircraft
- Hitler 'rejuvenates' Germany -> The increase in production and employment creates an upward spiral, pulling Germany out of the Great Depression sooner than other Europeans
- Hitler uses slave labor, using anyone who contradicts or opposes him, which evolves into the Holocaust

1935 Germany - League of Nation Response
- Issues condemnation for Hitler's violation of the Treaty of Versailles (re-arming Germany), But doesn't intervene
- Turning point for the fascists -> They realize no one is going to stop their expansion
1935 Germany - U.S. Response
- U.S. sees trouble on the horizon with the rise of Italy, Germany and Japan as expanding fascist powers
- The U.S. Senate passes the 1935 & 1936 Neutrality Acts as an effort to avoid being pulled into war at all costs
1935 Neutrality Act
- Prohibits arms sales to belligerent nations (military imperialist and war driven nations -> Italy, Germany & Japan)
- U.S. factories are barred from selling military equipment to the belligerents
- Prohibits U.S. citizens from sailing on belligerent nation vessels -> Avoid another Lusitania incident
1936 Neutrality Act
- Prohibits American loans to belligerent nations -> U.S. doesn't want to be pulled economically into a foreign conflict
1936-1939 Spanish Civil War
- A far left radical coalition wins the election in Spain and tries to establish a Communist Government, and begins to terminate opposition, by executing religious leaders
- The Spanish citizens are aghast by the party's actions and a Fascist, Fransico Frano leads the rebellion against the radical Government
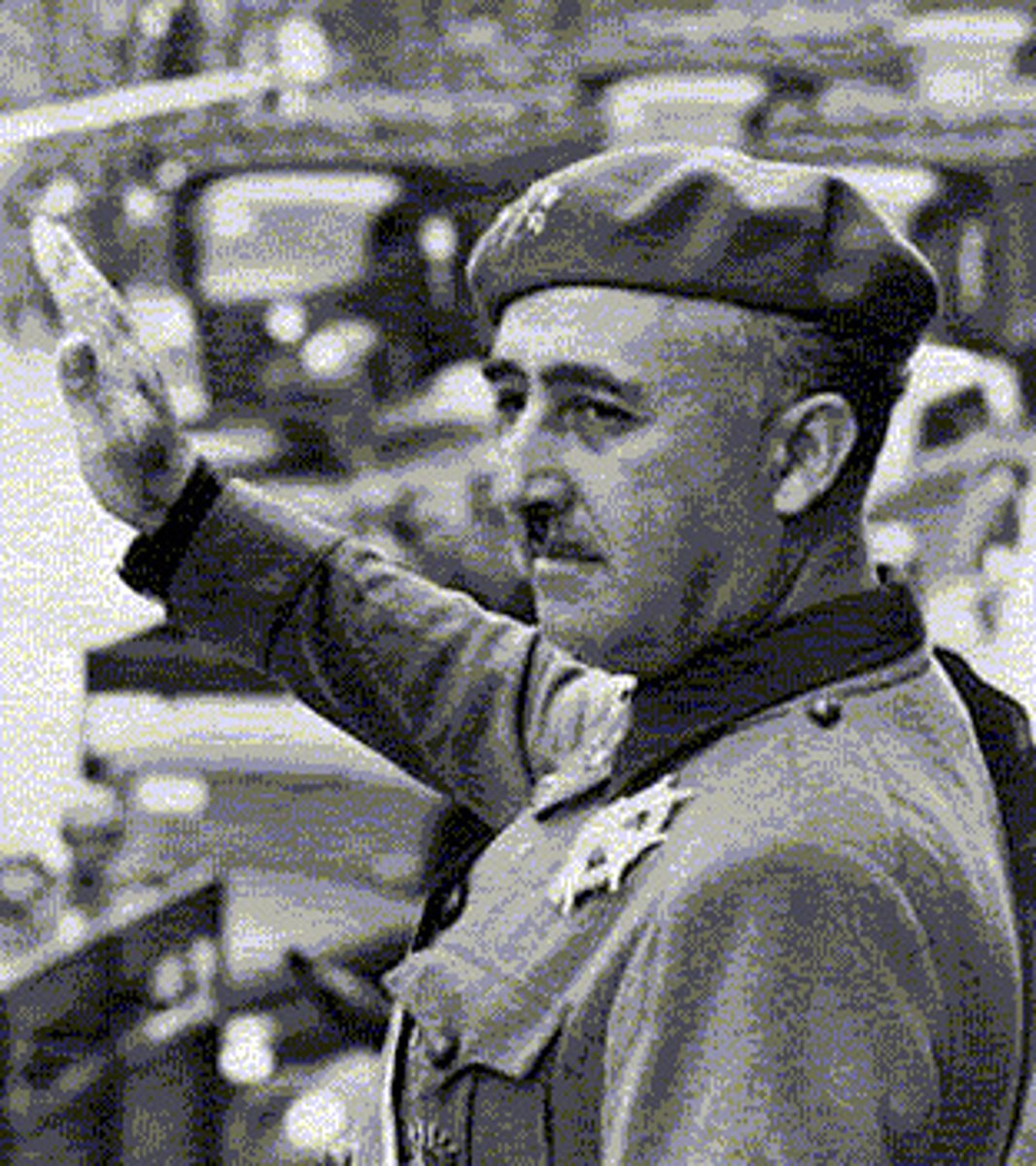

Francisco Franco Rebellion
- Leads the Spanish military against the radical Government
- Franco exercises fascism to bring order and traditional Spanish values back to the country, and drive out the Communists
- Franco is supported and supplied by Germany & Japan, Germany uses the Civil war to test war weapons & tactics
- Franco is also supported and supplied by the Soviet Union under Stalin
Results of 1936-1939 Spanish Civil War
- It was a Civil War so the League & U.S. were not involved
- U.S. issues the 1937 Neutrality Act
1937 Neutrality Act
- U.S. issues in response to the Spanish Civil War
- Prohibits military equipment sales to belligerents in the Spanish Civil War
March 1937 - Japan Invades China Proper
- Japan will invade the coast of China, conquering many of the major port cities
- Japan will conquer North to South
- Japan is met with strong Chinese resistance (stronger than in their invasion of Manchuria) -> The Japanese invaders resort to total warfare, by bringing the war to the civilian population and destroying China's ability to fight
- Japan will rape, pillage and plunder China -> Rape is used as a means of conveying control
- Japan develops its own master race theory to justify its invasion of China
Japan's Invasion of China - U.S. Response
- FDR remains neutral but, issues his "Quarantine Speech" condemning the invasion and warning the world of fascist aggression
FDR's Quarantine Speech
- FDR gives speech in response to Japan's invasion of China & Italy & German fascist aggression
- FDR warns of military imperialism & aggression spreading across the world like a disease, and if we don't cut it off (quarantine it) it will spread further, threatening democracy
- FDR doesn't say the U.S. should be involved, but the speech represents the U.S. moving farther from isolation & neutrality and to intervention to save democracy
March 1938 - Germany Annexes Austria
- Not an invasion
- Hitler wants to unite the "fatherland" and orders troops to take over Austria, if they meet any resistance to immediately retreat back, but the troops are welcomed and Germany will freely annex Austria
- Over the last few decades Nazis had been infiltrating & indoctrinating Austrians into Nazi ideology
- The annexation violates the Treaty of Versailles -> the annexation is an "Anschluss" (union) between the countries
Germany Annexes Austria - League of Nations Response
- Condemns annexation for violating the Anschluss (No uniting Austria & Germany) in the Treaty of Versailles which Hitler had agreed to
- No intervention by the League
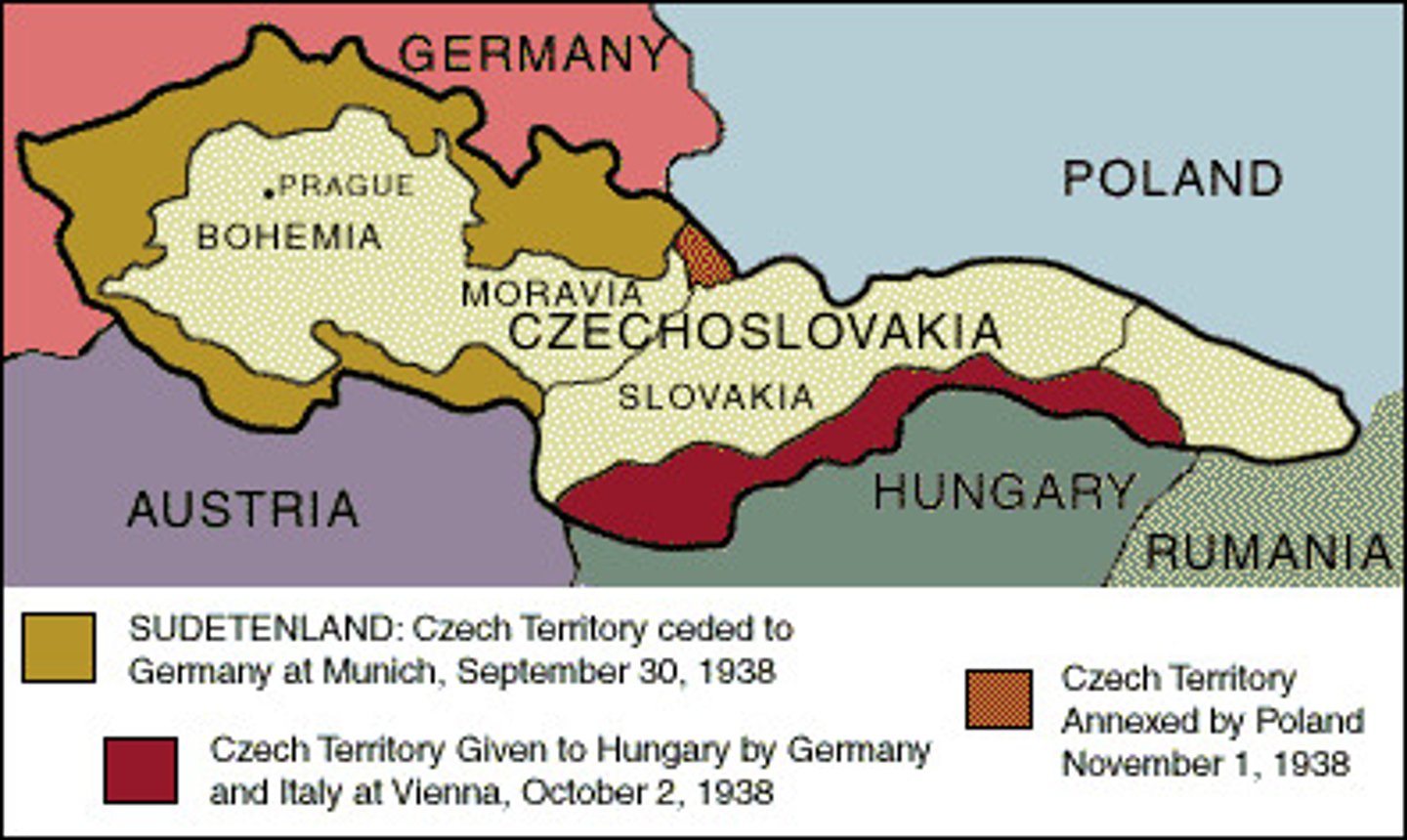
1938 - Sudetenland Crisis
- Hitler wants to unite the "fatherland," and demands Czechoslovakia (Made by the division of Treaty of Versailles), give Sudetenland back to Germany, Sudetenland is ethnically populated by Germans
- Czechoslovakia asks the League of Nations for help, but the League will not intervene, so the British and French will
- Britain & France threaten Hitler, if he continues they will go to war to protect their ally
- Hitler is not ready for war, so they meet for the Munich Conference
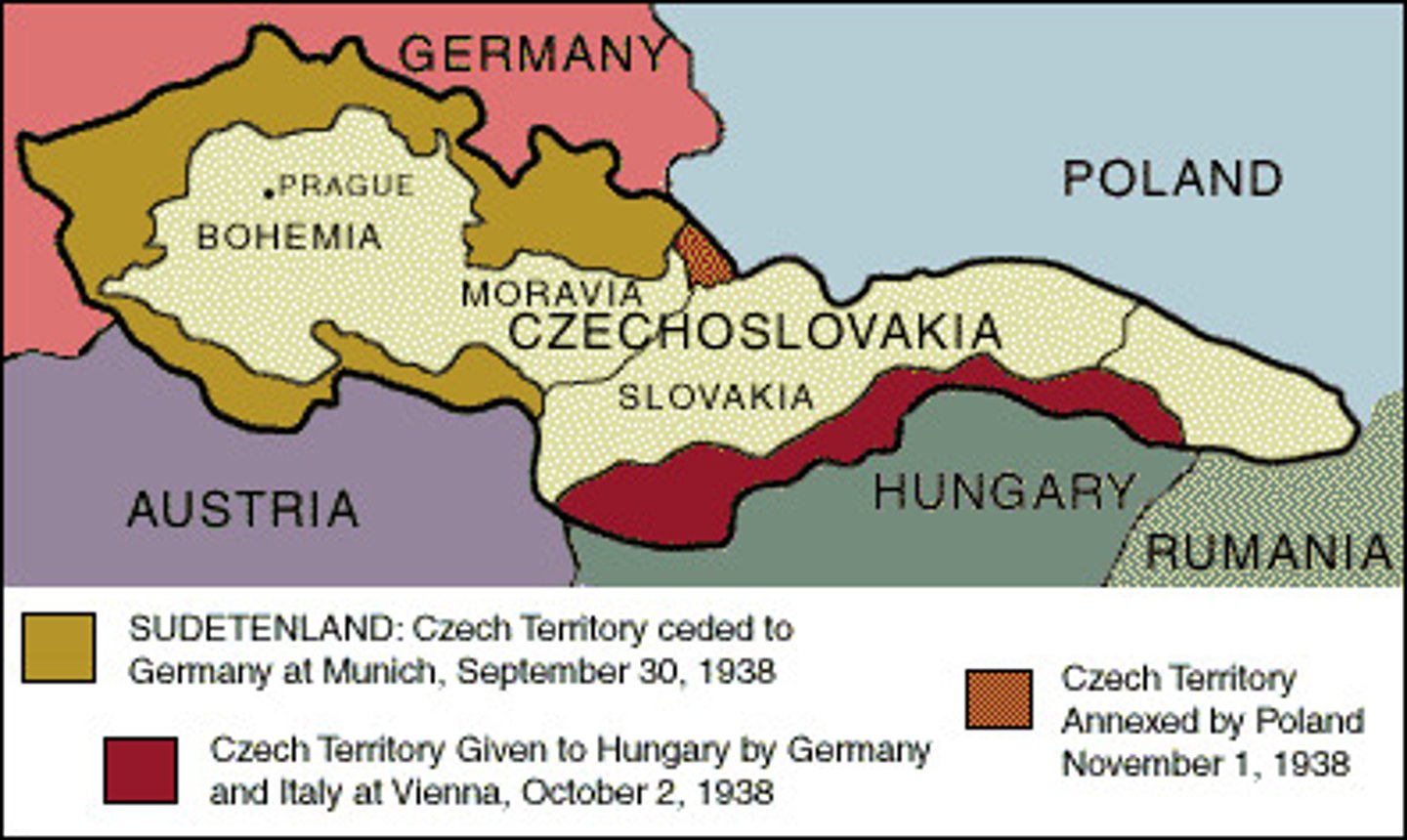
Countries Attending Munich Conference
- Czechoslovakia is left out of the conference about its own country -> Britain & France assure Czech. that they will protect them & represent their best interests (Not really)
- Germany -> Hitler
- Italy -> Mussolini
- UK -> PM. Chamberlain
- FR -> PM. Daladier
Munich Conference
- Goal -> Make a peaceful resolution to the Sudetenland Crisis
- Britain & France create the Munich Pact -> offer Germany control of Sudetenland if Hitler promises for no more expansion, Hitler accepts the Pact
- Czech. is outraged by Britain & France giving away Sudetenland, but they assure Czech it was a sacrifice for world peace
- But in reality Hitler was really appeasing Britain & France and invades the rest of Czech. soon after
March 1939 - Germany Invades Czechoslovakia
- 6 months after the Munich Conference, Hitler will violate the Munich Pact by taking over the rest of Czechoslovakia
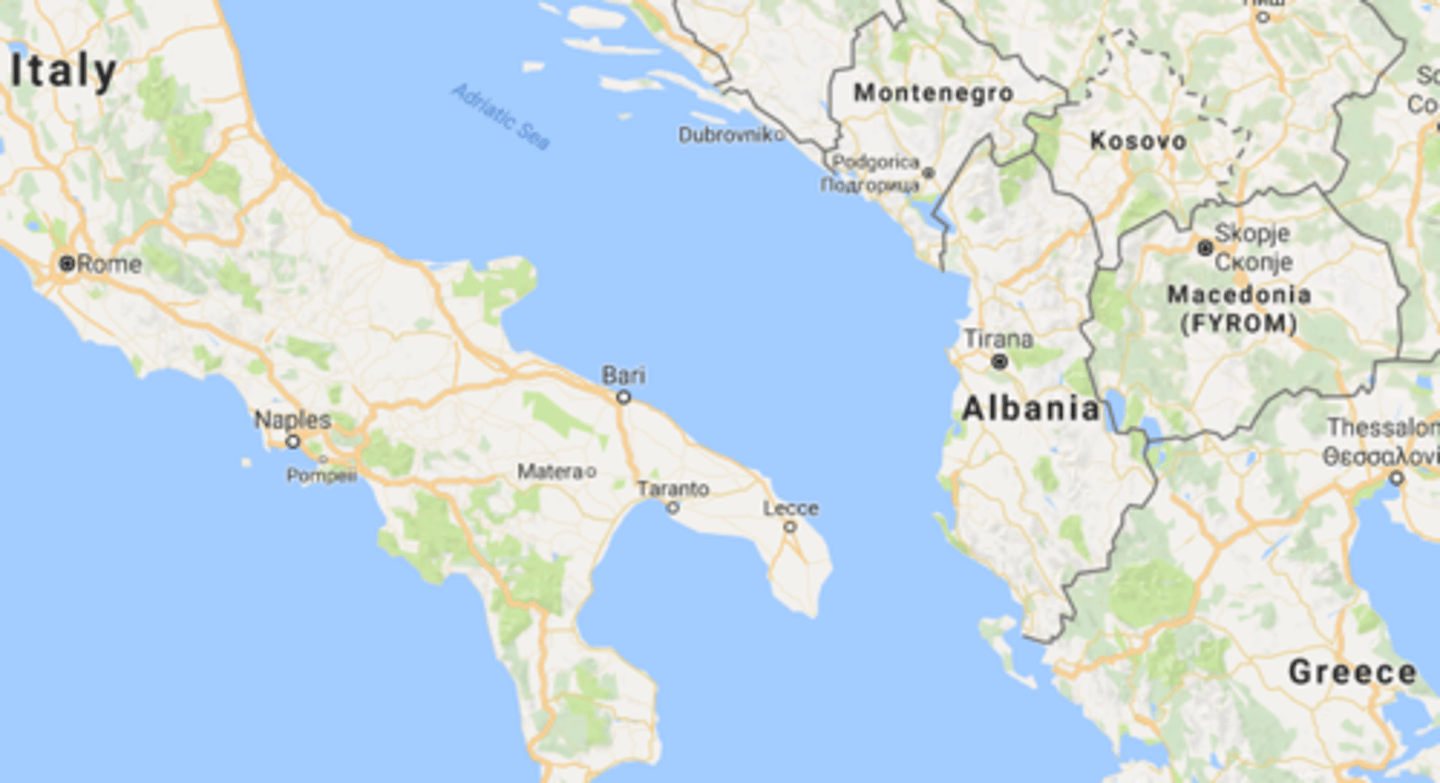
April 1939 - Italy Invades Albania
- Mussolini will invade Albania in a strategic move to be able to have control of movement in/out of the Adriatic Sea, allowing Italy to defend it's East Coast
- The League of Nations will not intervene
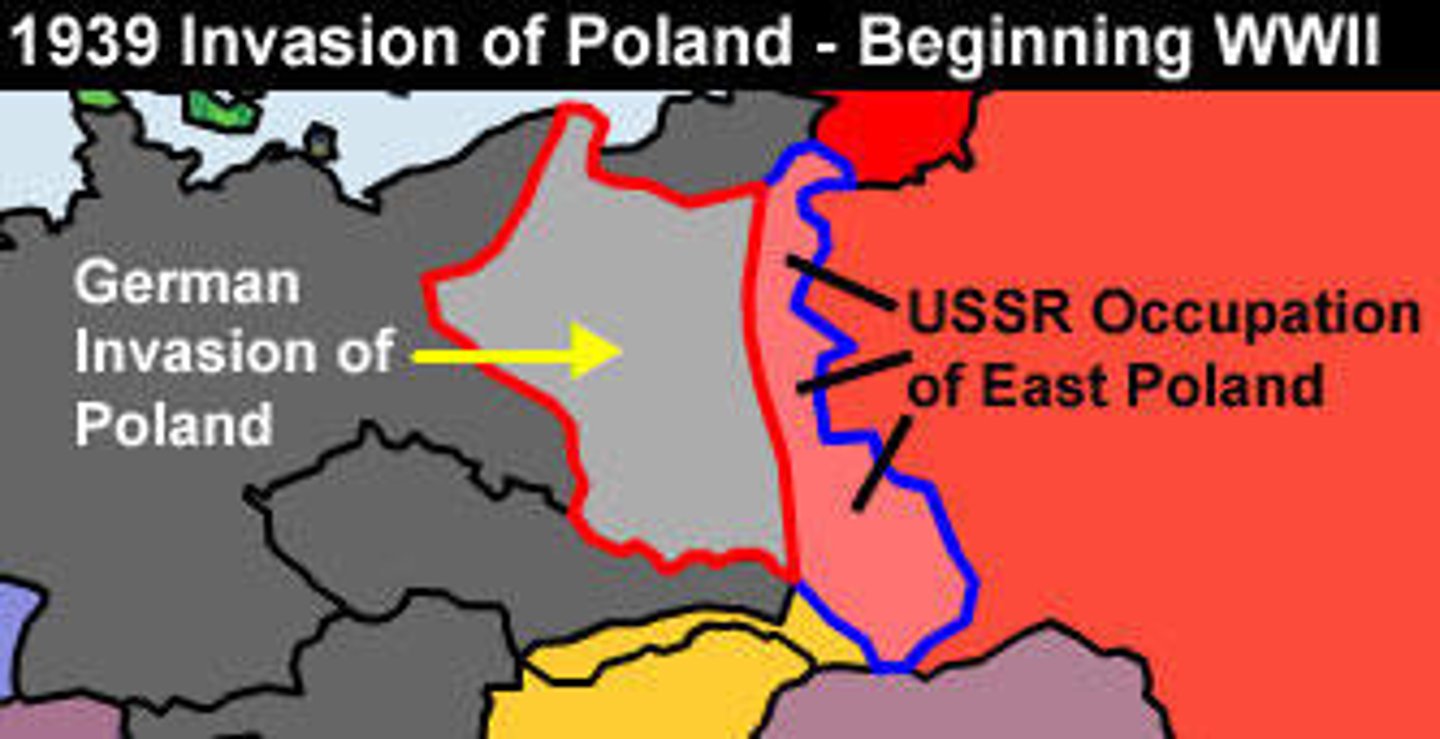
Summer 1939 - Germany Pressures Poland
- Hitler demands Poland surrender the land taken from Germany in the Treaty of Versailles, the "Polish Corridor," a strip of land giving Poland access to the sea
- Hitler also demands that Germany regain control of the Independent City State of Danzig (taken from Germany in the Treaty of Versailles)
- Hitler is planning to invade Poland and needed to let a paranoid Stalin and the Soviet Union know so they won't fear a German invasion into their country
Hitler & Stalin Secret Meetings
- Hitler (Germany) & Stalin (U.S.S.R) meet in secret and Hitler assures Stalin that Germany will invade Poland, and not be going for the Soviet Union (yet)
- Both sides agree to a Non-Aggression Pact -> Hitler wants the Soviet Union to join in the invasion of Poland with Germany by pretending to be coming to Poland's aid
- The Pact also would to divide Poland keeping the East for Germany, and West for the Soviet Union
- The Pact help divert attention away from Poland while pressures coming from Germany increased
- When the Pact leaked the public is surprised -> Fascists and Communists had always hated each other
Non-Aggression Pact - British & French Response
- Britain and France come to Poland's defense, threatening retaliation if Germany attacks their ally, Poland, but Hitler blows it off

Sept. 1st 1939 - Germany Invades Poland - START OF WWII
- Germany kicks off WWII by invading Poland
- On the next day, Sept. 2nd 1939, Britain & France declare war
Allied Powers vs. Axis Powers
Allied -> Britain & France
Axis -> Germany, Italy, Japan
FDR's Proclamation of Neutrality
- In response to the invasion of Poland and start of WWII, FDR will issue a proclamation of neutrality -> The U.S. will be staying out of this European affair
- U.S. sympathizes with the Allies for fighting for Democracy over Dictatorship
- Although the U.S. claims neutrality, it will immediately begin taking gradual steps away from neutrality and towards supporting the Allies -> 1st Step: Cash & Carry
Cash & Carry
- Repeals the neutrality acts of the 1930s that had banned U.S. arms sales to belligerent nations
- U.S. now allows arms sales to belligerents, so long as they pay in cash
- To remain neutral the U.S. offers to both the Allies and Axis sides, and both must carry arms away on their ships -> But only the Allies take advantage of the arms sales because the Axis have been manufacturing their own weapons
- 1st step away from neutrality and towards war
Fall 1940 - Selective Service Act
- The U.S. is still neutral in WWII, but FDR sees U.S. involvement in the future and takes steps to prepare the U.S.
- The Selective Service Act is a draft, that helps lower the staggering unemployment rate during the Great Depression
Sept. 1940 - Destroyer for Bases Deal
- FDR makes an executive agreement with PM. of UK, Churchill
- The British had been using U.S. Cash & Carry services, but the majority of equipment was never reaching the UK because of German blockades
- FDR's agreement gives the UK 50 destroyer ships to hunt down and destroy submarines, in exchange the UK gives the U.S. islands in the South Atlantic for naval bases in case the Axis go farther West
January 1941 - FDR's 4 Freedoms Speech
- FDR's speech that seems like is laying out war goals and objectives while the U.S. is still neutral
- FDR knows war is coming to the U.S. and tries to start getting the public prepared by reminding the U.S. that we will defend Democracy (City Upon a Hill)
- FDR wants to base a post-war world on 4 essential freedoms:
(1.) -> Freedom of speech & expression everywhere in the world
(2.) -> Freedom of religion everywhere in the world
(3.) -> Freedom from want (no poverty/hunger) everywhere in the world
(4.) -> Freedom from fear (world peace) everywhere in the world
March 1941 Lend-Lease Act
- Replaces Cash & Carry
- The Allies are broke -> They can't pay for Cash & Carry services & have few ships to carry equipment back home on
- U.S. allows the Allies to buy arms on credit which can be taken care of after the war (but, the U.S. never asks for reimbursement)
- U.S. offers to transport arms on their ships which now become targets of the Germans -> Americans will be killed and injured in another undeclared naval war with Germany
U.S. Response to U.S. Merchant Ships Being Attacked
- FDR issues an executive order to arm the merchant ships and educate the crews on how to operate them
- The merchant ships can only fire when fire upon, but this goes quite poorly and FDR issues another executive order -> "Shoot on Sight"
FDR's - "Shoot on Sight" Executive Order
- Authorizes merchants ships to now fire once they see the enemy instead of in self-defense (Shoot on sight)
- But still, the merchant ships stand little chance against Germany's battleships
August 1941 - Atlantic Charter
- FDR (U.S.) & Churchill (UK) meet in the North Atlantic Ocean and draw up the Atlantic Charter
- Even though the U.S. is not at war, the Charter lays out common war goals and strategy
- U.S. acts like Britain's Ally

1940-41 - Embargo on Japan
- Congress places a series of embargos on Japan -> Cuts off trade with Japan -> Especially no war materials or natural resources for their war effort
- Congress places the embargo because of fascist Japanese aggression, in an attempt to limit them
- The series of embargos is the final straw for Japan -> The U.S. had tried limiting Japan's expansion since Pres. Roosevelt
- Leads to Pearl Harbor
December 7th, 1941 - Pearl Harbor Attack
- Japan will attack Pearl Harbor after a decade of spying and practicing -> Spies knew U.S. battleships were brought into harbor when the weather was poor and so Japan waited until the conditions were right, and the ships all lined up to attack
- Japan did not want invade the U.S. -> Just to destroy the U.S. Pacific fleet & negotiate an end to war from a position of power
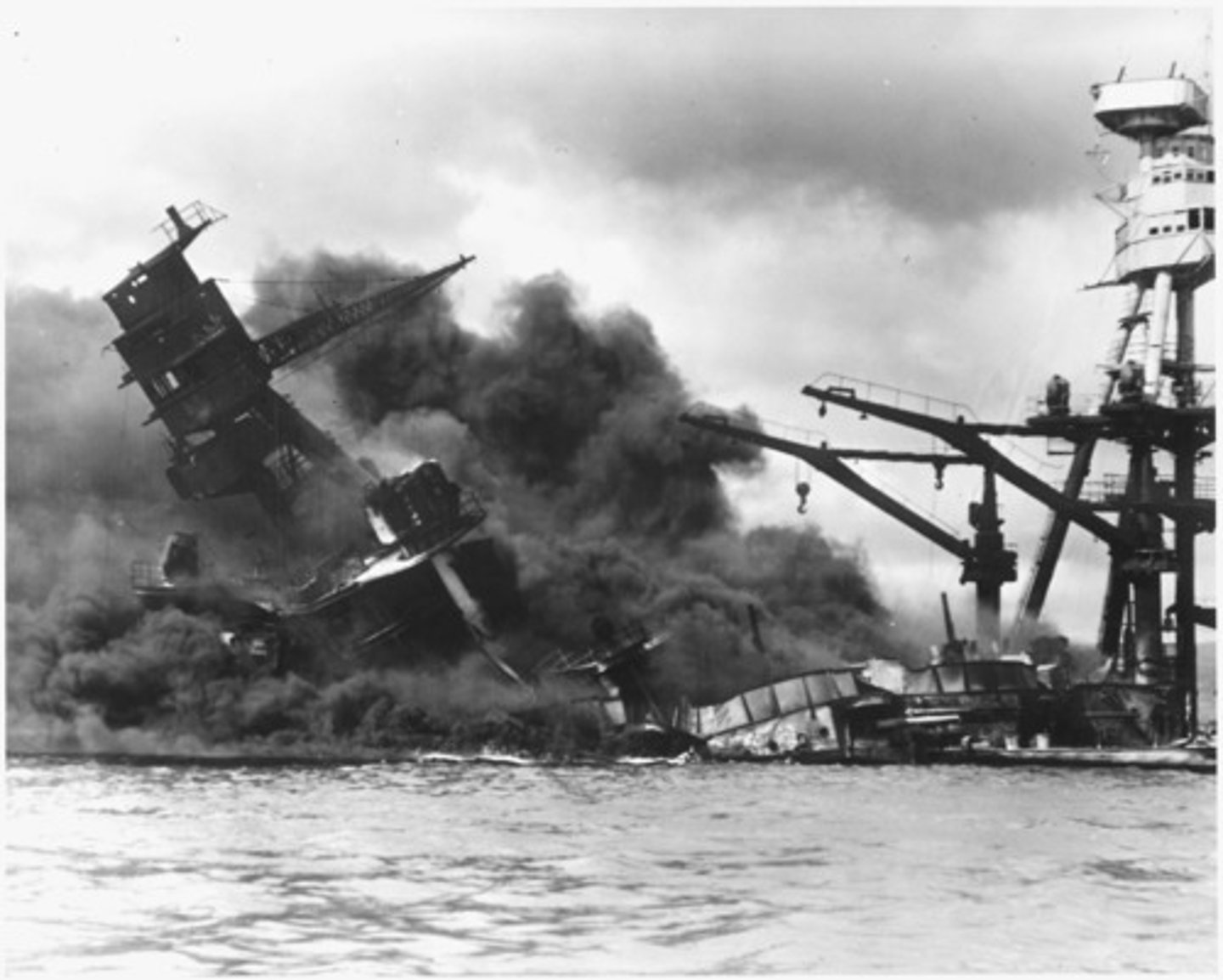

Aftermath - Pearl Harbor Attack
- The attack is very successful -> Japan destroys all U.S. ships that were in harbor and destroys airports on the island
- But, as Yamamoto warns, they have "awoken a sleeping dragon"

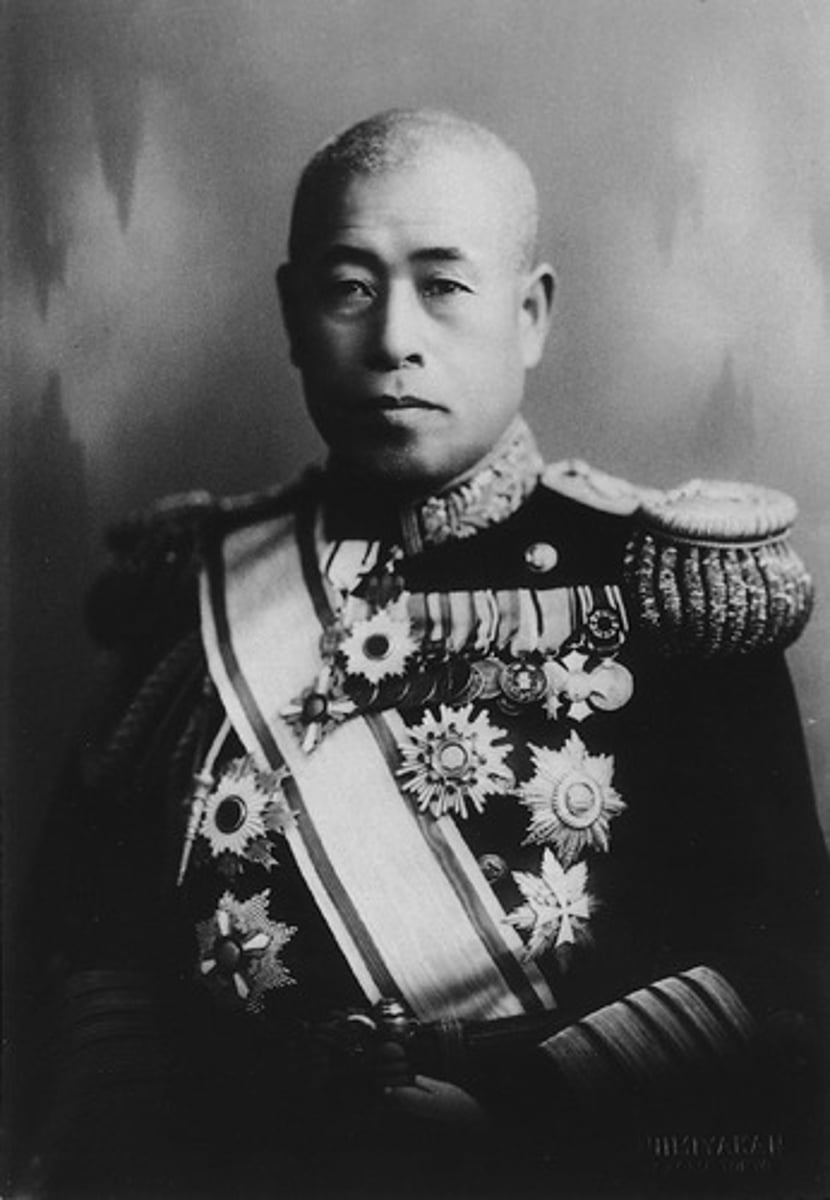
Yamamoto
- Japanese Naval Officer who knows Japan will be able to destroy the U.S. fleet at Pearl Harbor -> But, unlike the rest of the Japanese command he knows America won't just roll over and give in after their strike
- Yamamoto warns Japan will "awaken a sleeping dragon"
- Begs Japan Command to not attack Pearl Harbor, knowing Japan can't match a U.S. retaliation, but the rest of the commanders don't listen to him

Japan & U.S. Declaration of War
- In Japan's original plan Japanese diplomats would deliver a declaration of war to the U.S. State Department before their attack on Pearl Harbor, but the message they received took too long to decode and the U.S. declares war before the Japanese declaration is decoded and delivered
- FDR had requested Congress declare war, and because Japan took too long to produce their declaration of war, the U.S. can propagandize the attack as a surprise & cowardly