therapeutic exercise considerations
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
center of gravity
the point mass of a body or segment
true
the COG changes w motion and with weight
t ro f
false
the COP changes w motion and with weight
t ro f
true
the lower the COG is the more stable an object is
t or f
false
the higher the COG is the more stable an object is
t or f
base of support
the 2D area between and including the object’s point of contact in the supporting surface
wider
a ____ BOS means increased stability
narrow
a ___ BOS indicates a decreased stability
stability
occurs when the lone of gravity falling within the base of support
lateral
with a wide BOS means a ____ perturbation has a dec chance of falls
anterior/posterior
with a narrow BOS means a ____ perturbation has a dec chance of falls
lever
a simple machine that contains a rigid bar and a fulcrum
first class
a ____ lever has the fulcrum between the resistance and force arms
second class
the ____ lever has the resistance point between the fulcrum and the force arm
third class
the _____ lever has the force point between the fulcrum and the resistance arm
true
this is an example of a first class lever
t or f
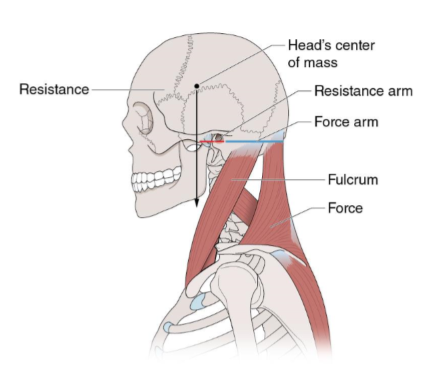
false
this is an example of a second class lever
t or f
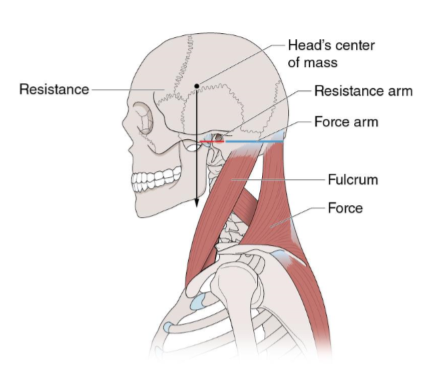
true
this is an example of a second class lever
t or f
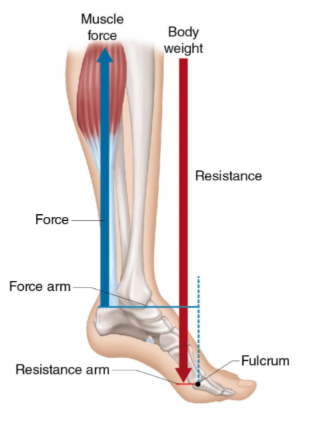
false
this is an example of a third class lever
t or f
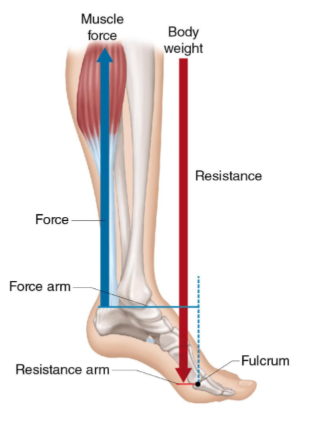
true
this is an example of a third class lever
t or f
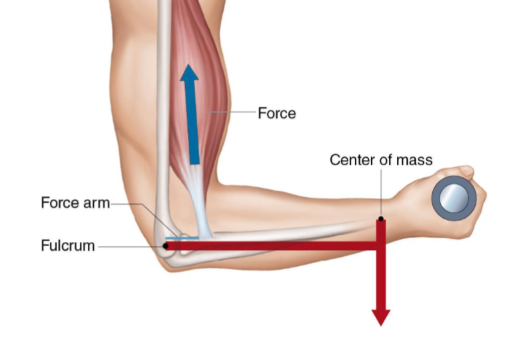
false
this is an example of a second class lever
t or f
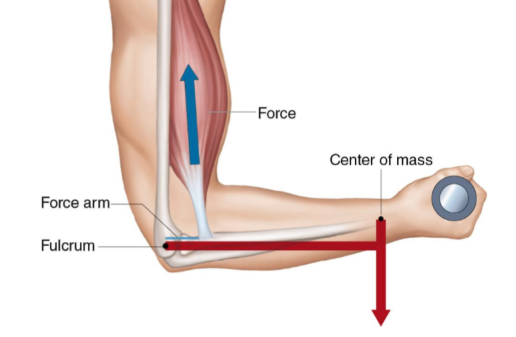
true
in a lever when speed of motion increases then the ROM and forces decreases
t or f
false
in a lever when speed of motion increases then the ROM and forces increases
t or f
linear motion
occurs with a straight line movement from a force
angular motion
occurs with a rotational movement from a force
torque
a product of force and the force arm length during angular motion
moment arm
the lever arm or force arm is the ______ or the distance from the fulcrum to the force vector
line of pull
the long axis of the muscle or the direction along which a muscle exerts a force going along origin to insertion
angle of pull
the angle between the muscle line of pull and long axis bone
true
the angle of pull and moment arm change w joint motion
t or f
false
the line of pull and moment arm change w joint motion
t or f
true
maximum rotation force occurs at 90 deg
t or f
false
maximum rotation force occurs at 45 deg
t or f
true
when muscle lengths decrease the max tension of the muscle decreases
t or f
false
when muscle lengths decrease the max tension of the muscle increases
t or f
summation of forces
a sequence of movements timed so each contributes to the next movement to make a desired outcome
strength
ability to resist or make a force
work
the force x time over it is applied
power
work produced divided by time
energy
the capcity to do work
velocity
the rate of change in an object’s position
acceleration
the rate of change of which velocity increases
elasticity
the object’s ability to return to normal size/shape after a deforming force is applied
elastic limit
the point of the object’s ability to return to normal shape and size before having plastic changes
yield point
the tissue’s point where deformation starts to occur and leads to tissue damage
stiffness
the ability to resist deformation when stress is applied
strain
the change in an object when a stress is applied
stress
the force that is applied to a tissue over time
creep
the permanent tissue elongation in response to a low level stress applied over time
structural fatigue
continuously applying a force causing fatigue overtime leading to eventual breaking or failure from continous weakening
friction
the resistance to a movement from 2 different surfaces