Anatomy and Physiology Honors
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 1 Test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
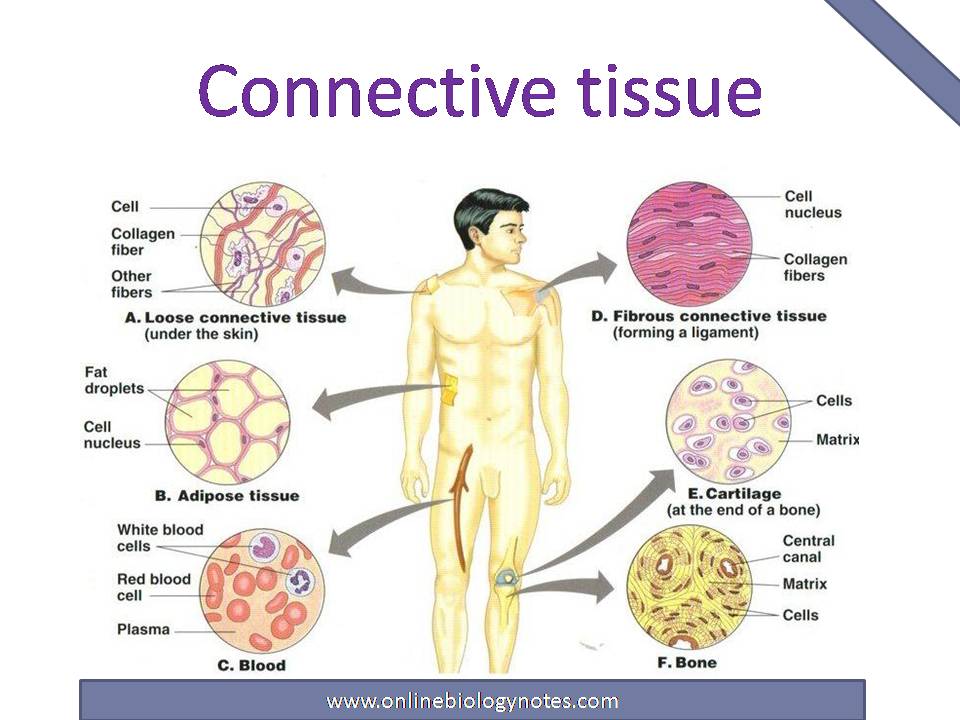
Connective Tissue
-The majority is bone (osseous) tissue
-Cartilage and dense connective tissue cover the bone’s external surface
Nervous Tissue
In its nerves
Epithelial Tissue
-In its blood vessels
-Provides nourishment
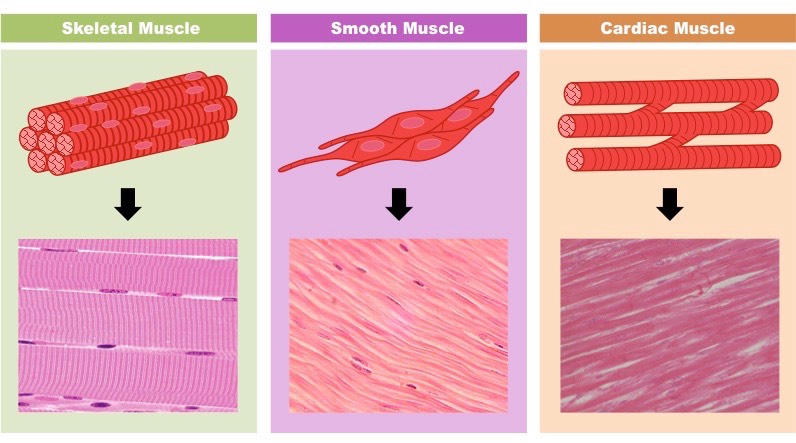
Muscle Tissue
-Skeletal muscle tissue
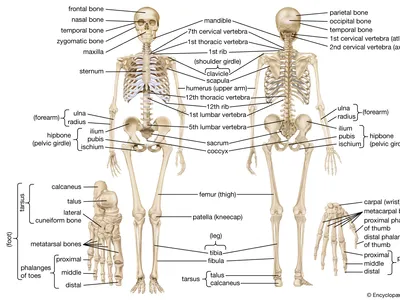
How many bones are in the human body?
206
6 functions of the Skeletal System
-support
-protection
-movement
-Storage
-Blood cell formation
-Hormone production
Support in the skeletal system
Framework holding up the entire body
Protection in the skeletal system
-Guards the body’s most vital organs
ex:skull protecting the brain
Movement of the Skeletal System
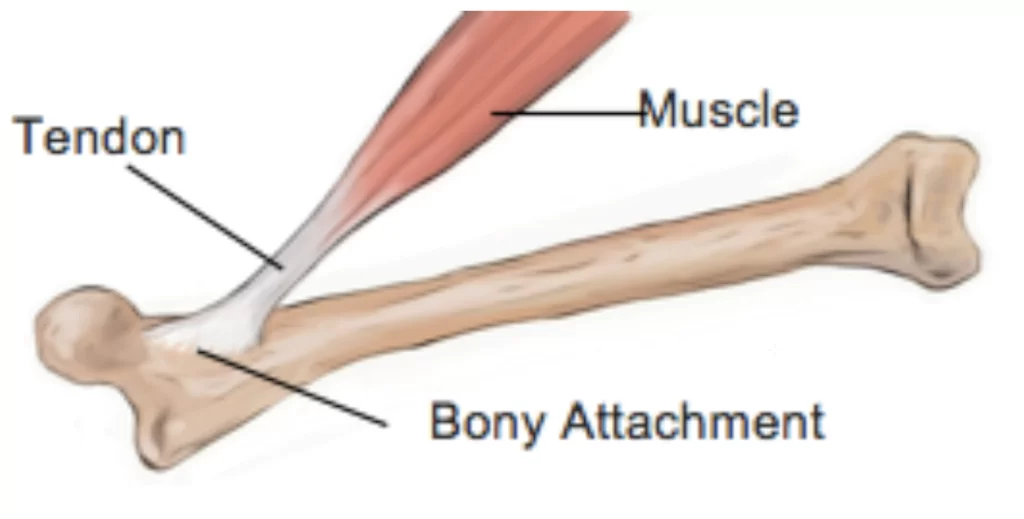
Skeletal muscles are connected to bones through tendons and use bones to produce movements
Storage in the skeletal system
-Stores minerals like calcium and phosphate
-Gets released into the blood
-Stores energy through fat in yellow bone marrow
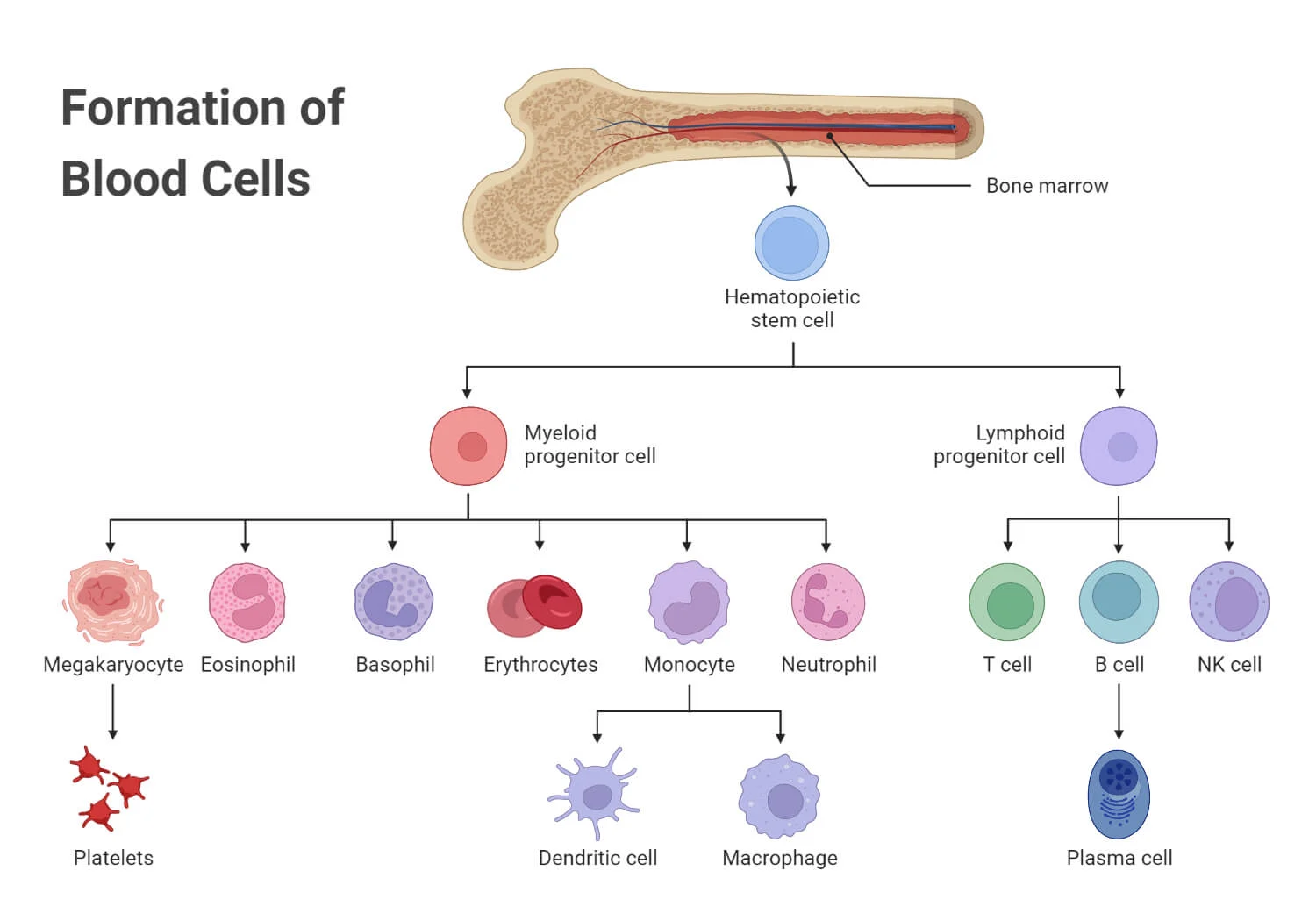
Blood cell formation in the skeletal system
-Hematopoiesis
-In red bone marrow of certain bones
Hormone Production in the skeletal system
-Critical for maintaining homeostasis
Ex: Regulating blood calcium levels
How are bones classified?
-Location in the axial vs appendicular skeletons
-Shape
4 main bone types
-Long bones
-Short bones
-Flat bones
-Irregular bones
Long Bones
-Longer than they are wide
-Longer shaft with a wider end
-Mostly located in the limbs
-Acts as a lever for mobility
Examples of Long Bones
-Arm bones
-Hand bones
-Leg bones
-Foot bones
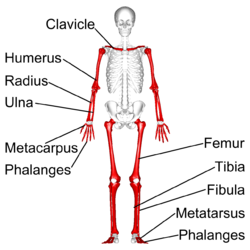
Short bones
-More cube shaped
-Tend to be equally wide and long
-Provide support and stability
Special type of short bones
-Sesamoid bones
-Means to be shaped like a sesame seed
- Are embedded within tendons
-Kneecap
Examples of short bones
-wrists
-ankles
Flat bones
-Thin and flat bones
-Has a large surface area for attaching to muscles
Examples of Flat bones
-Breastbone (sternum)
-Shoulder blades (scapula)
-Ribs
-Cranial bones
Irregular bones
-Everything else
-Have highly specialized shape and structure
Examples of irregular bones
-Hip bones
-vertebrae
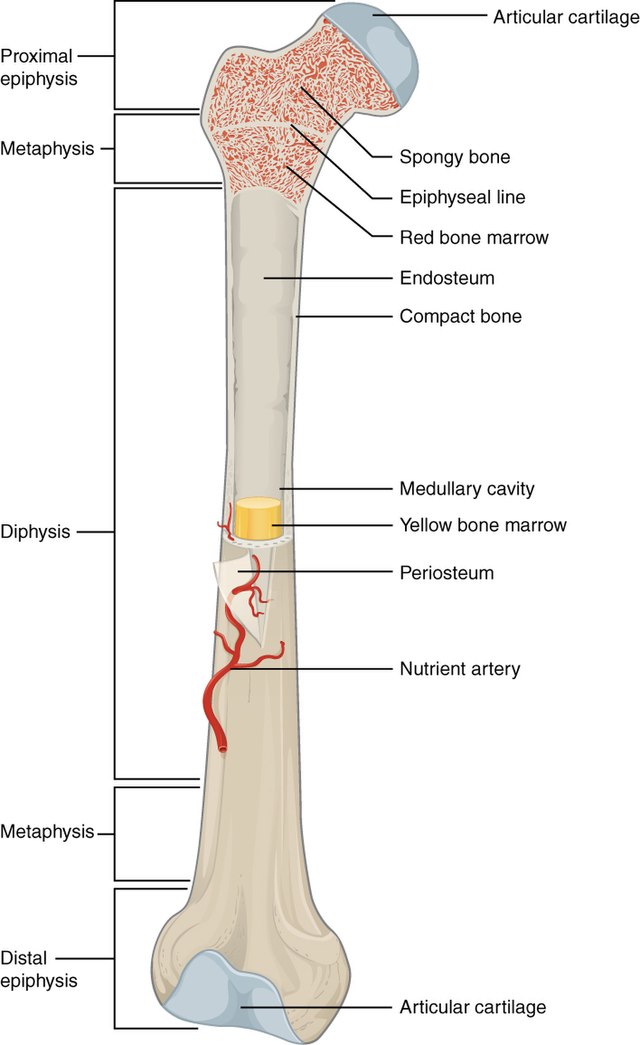
Bone Structure
Dense and smooth layer on the outside surrounding the more porous spongy bone tissue on the inside
Structure of Compact bone
-Made of osteons (circular parts in bone that provide strength and structure)
Lamella
-Group of hallow tubes in the bone
-Filled with salts and collagen fibers
What do salts and collagen fibers help with in lamella?
-Resistance t
Haversian Canal
-Runs through the middle of each osteon
-Contains small blood vessels for nourishment
-Nerve fibers for signaling
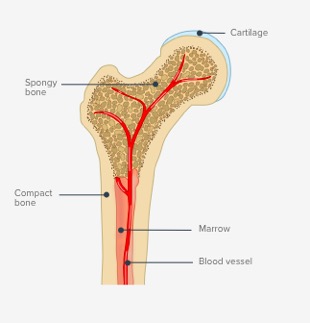
Spongy bone
-Less organized than compact bome
-No osteons
-Have trabecula

What is a trabecula?
-Tiny bone struts
-Helps bone resist stress
-Where bone marrow is
3 bone structure markings
-Projections
-Surfaces
-Depressions and Openings
Projections
Where muscles and ligaments attach
Surfaces
Form on joints
Depressions and Openings
Where blood vessels and nerves run through
Osteocytes
-Maintain healthy bone structure
-in lacunae
-Leaders in the construction site
Lacunae
Gapes between the lamellae
Osteoblasts
Build and construct bones by calcifying bone as it forms
-not breaking down, but building up
Osteoclasts
-Critical in the regeneration of bones through remodeling
Ossification
The process of bone tissue reformation
Importance of Osstification
-Forms skeleton
-essential for bone growth
-Used for bone remodeling and repair
Types of ossification
-Intramembraneous ossification
-Endochondral ossification
Intramembraneous ossification
-Bone develops from fibrous membrane
-clavicle and skull bones
Endochondral ossification
-Bone develops by replacing cartilage
-All other bones
Bone remodeling
-Osteocyctes
-osteoclasts
-macrophages
-osteoblasts
osteocytes
Release chemical signals to tell osetoclasts to go to the damage
Osteoclasts
Release enzymes at the damaged area and digest calcium phosphate
Resorption
Put calcium and phosphate back into the blood
Microphages
Promote bone tissue remodeling
Osteoblasts
Come in and build new bone before they go through aptosis
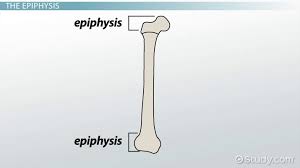
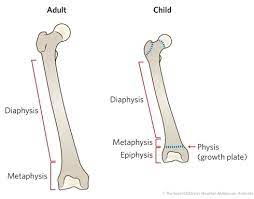
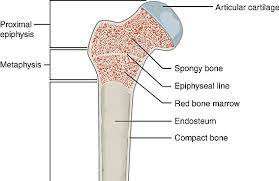
Epiphysis
The end of long bone on any part of the bone
-proximal and distal
Diaphysis
The shaft of the strong central bone
Articular Cartilage
Evidence of adult bone cartilaginous past
-smooth, slippery, malleable, and bloodless
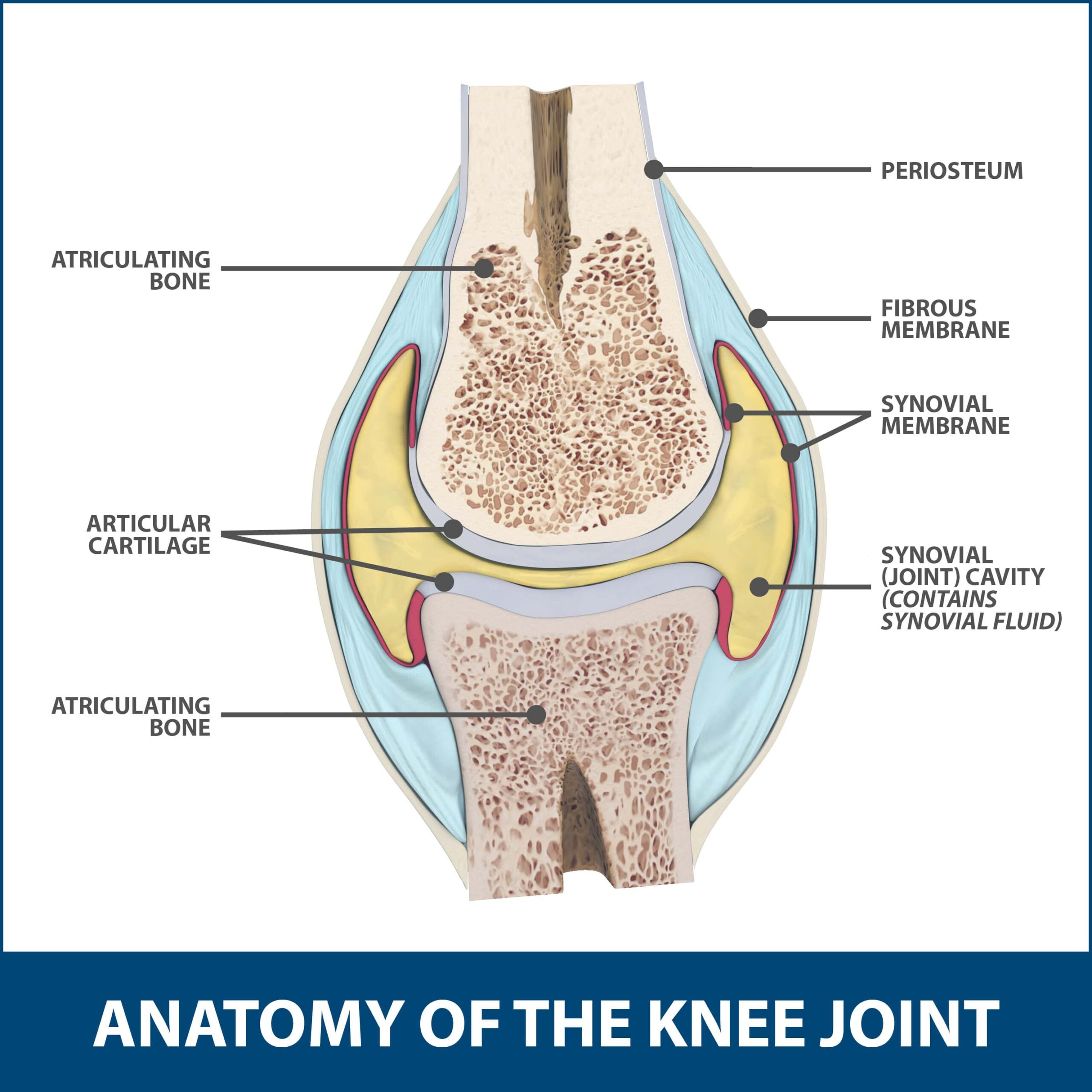
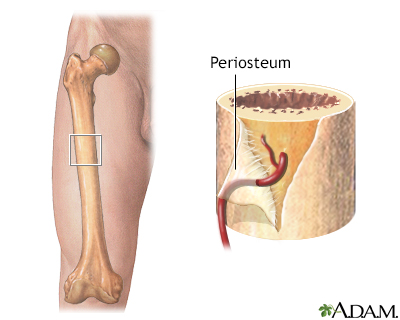
Periosteum
-Fibrous cellular, vascular, and highly sensitive. On the outer portion of the bone
-Source for osteoprogenitor
Spongy Bone
-Consists of interwoven beams
-filled with red or yellow marrow and blood vessels
Compact bone
-Dense bone characterized by long cylinders
Medullary Cavity
-Cavity of the diaphysis
-contains marrow that turns yellow as bone gets older
-hallow portion
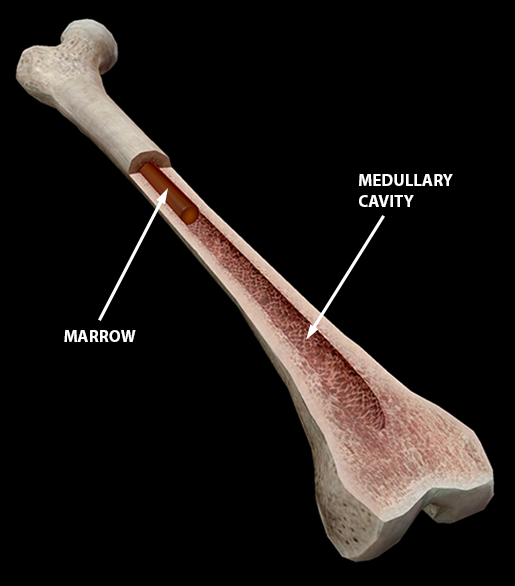
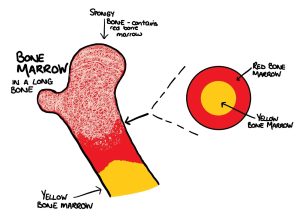
Red marrow
-Gelatinous substance composed of red and white blood cells
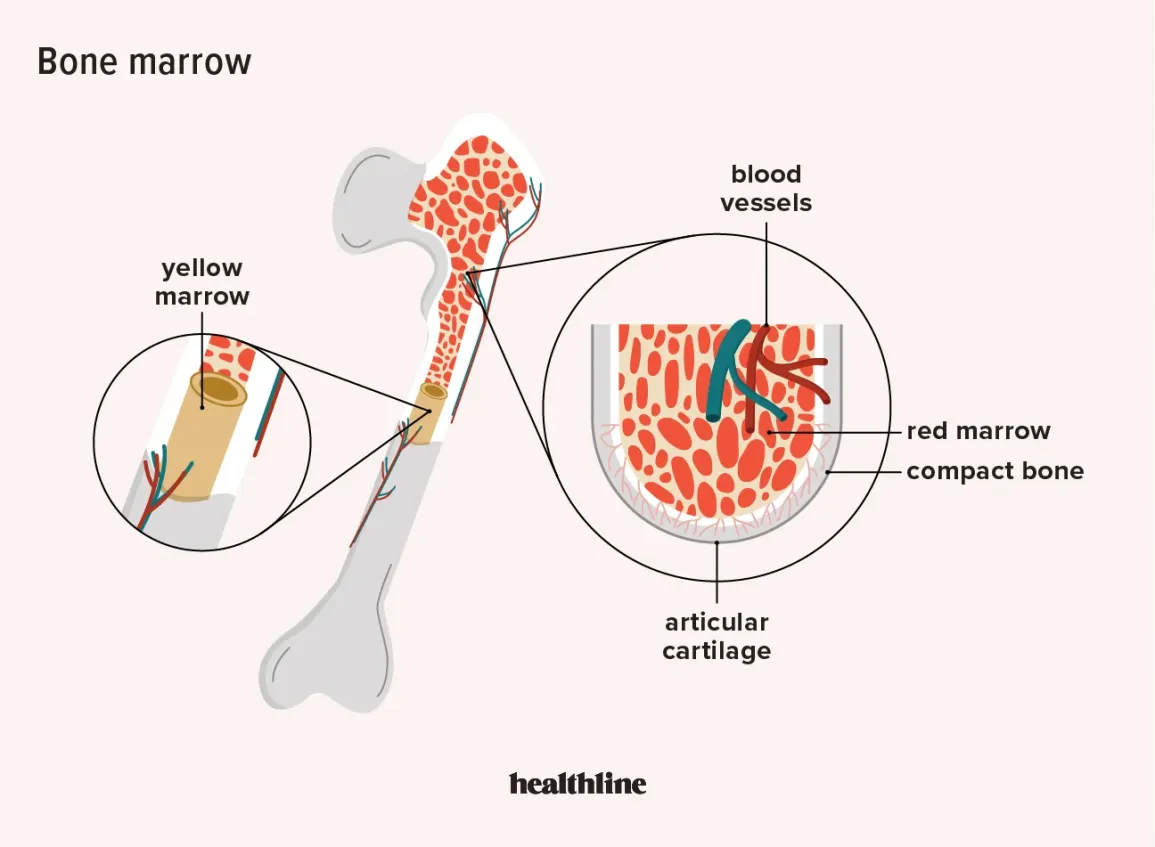
Yellow Marrow
-Fatty connective tissue
-no production of blood cells
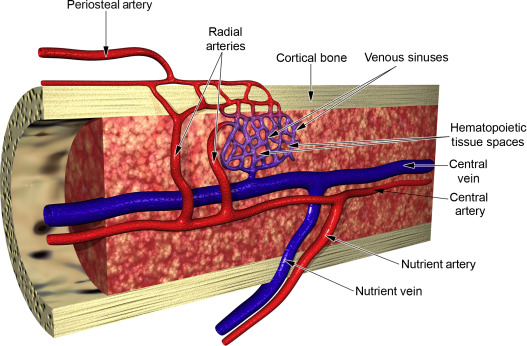
Nutrient artery
Major supplier of oxygen and nutrients
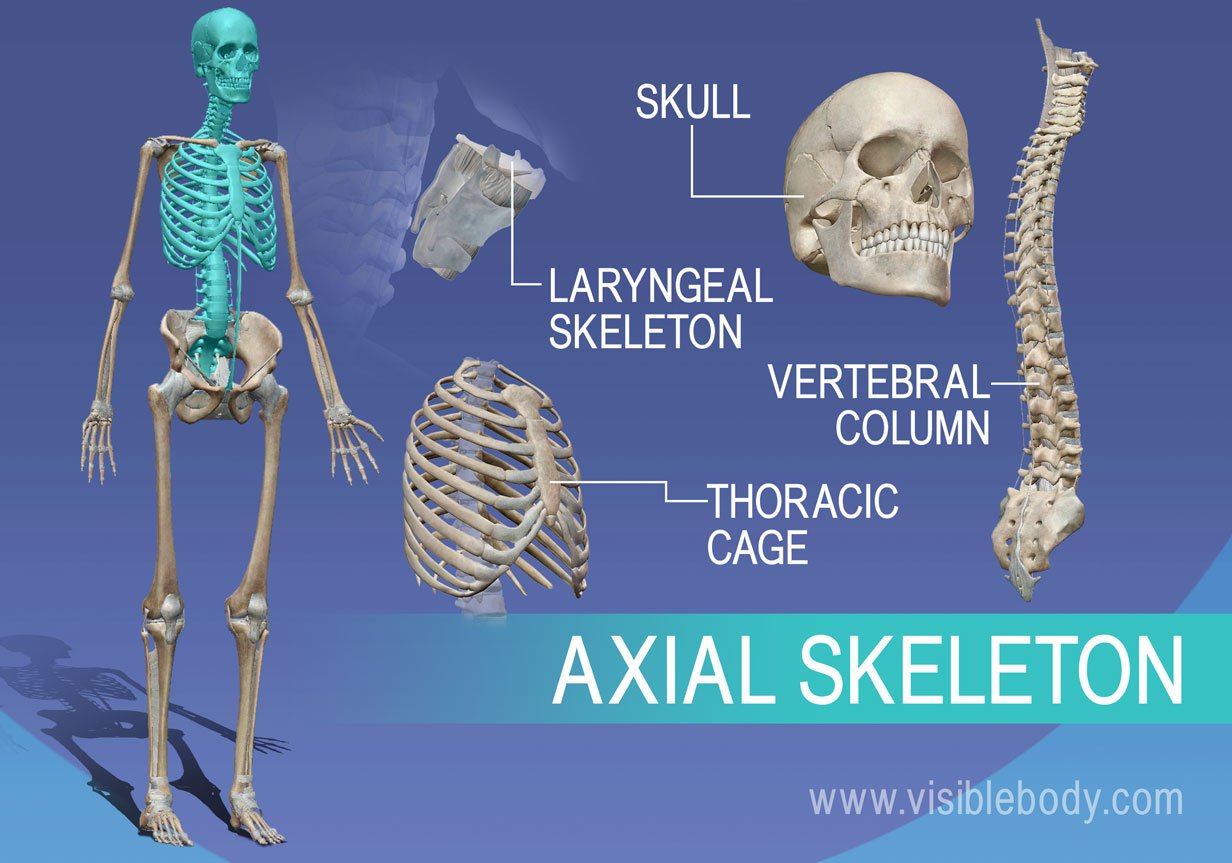
Axial Skeleton
-Principle of supportive structure of the body
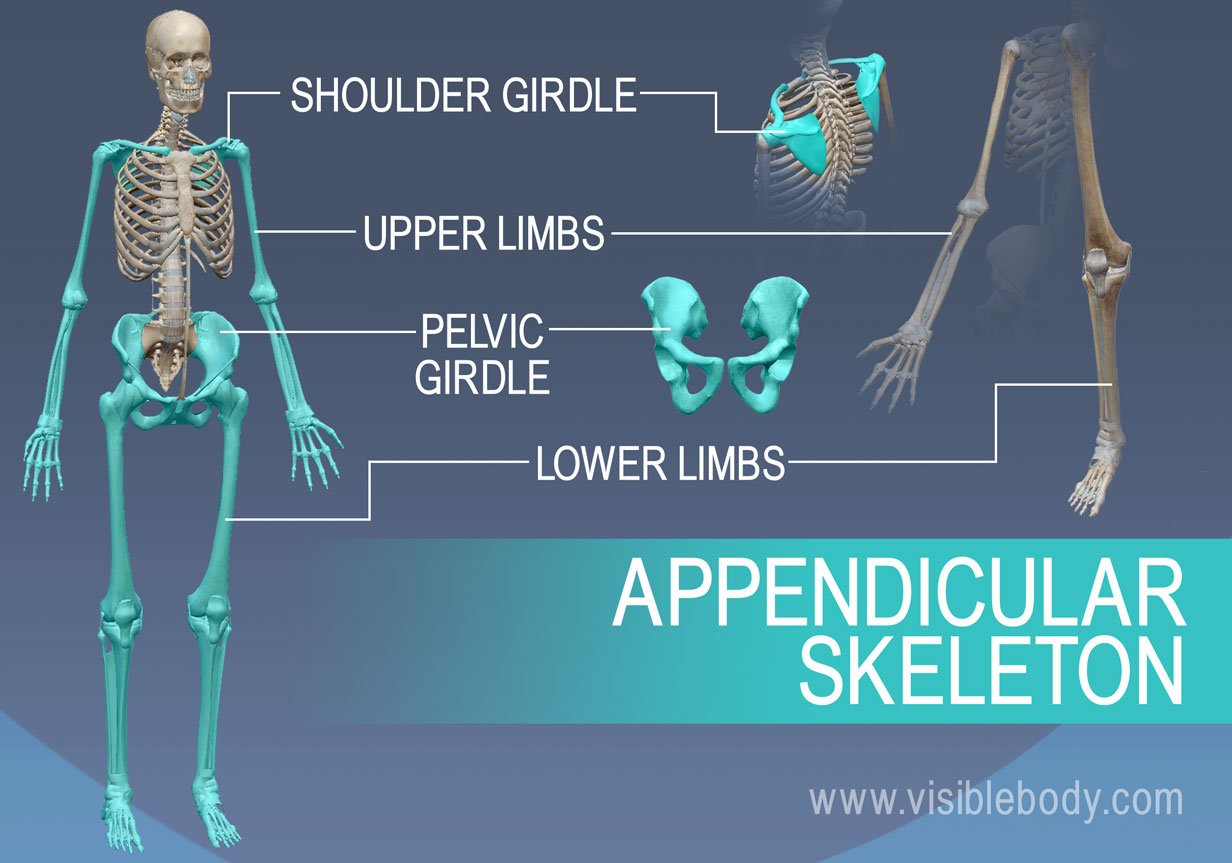
Appendicular skeleton
Make possible a considerable degree of freedom for the upper and lower limbs
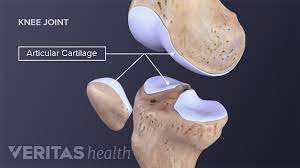
What is cartilage
a flexible connective tissue found in the articular ends of bones.
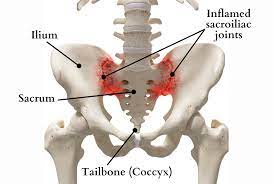
what is the sacrum
a solid base of the vertebral column that connects to the ilium.
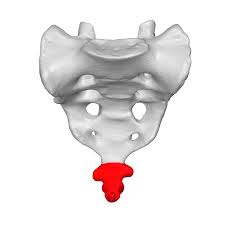
What is the coccyx
is the last four fused vertebrae in the spinal column.
Tendon
a connective tissue that connects muscles to bones.
What is a ligament?
connective tissue that connects bones to bones.