T13: Exercise and Immunity
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
the function of the immune system
protects the body from infectious disease. It is involved in tissue repair and protection against harmful pathogens.
2 types of immune system responses
innate
adaptive
innate immune system
bodys first line of defense against pathogens entering the body
present from before any exposure to pathogens and is effective from the day you were born
innate mechanisms in response to damage:physical
skin, tears, epithelial linings, mucosal secretions
innate mechanisms in response to damage:physical, skin
physical barrier preventing entry
slightly acidic pH(oils+ sweat) discourages growth of organisms
presence of antimicrobial peptides which prevent growth of harmful bacteria
innate mechanisms in response to damage:physical, tears
mucus in trachea traps pathogens
tears contain lysosomes which kill bacteria
also wash away irritating substances and microbes
innate mechanisms in response to damage:physical, epithelial linings
cillia, remove pathogens on epithelial linings in intestines protect body from intestinal bacteria
act as a physical barrier
secrete mucous to trap+ remove pathogend
innate mechanisms in response to damage:physical, mucous linings
sticky mucus traps pathogens which is wafted away by cillia
epithelial linings
body tissue that forms the covering on all internal and external surfaces of your body,
innate mechanisms in response to damage:chemical
pH of bodily fluids, hormones + other soluble factors
innate mechanisms in response to damage:chemical, pH of bodily fluids
pH 2 stomach to kill bacteria
saliva+ vaginal fluids slightly acidic to protect against harmful bacteria
innate mechanisms in response to damage:chemical, hormones
cortisol: short term, supresses inflamation but elevated levels over time can weaken immune system
studies suggest oestrogen enhance immune function, testosterone suppressive effect
innate mechanisms in response to damage:chemical, other soluble factors
cytokines: messengers between immune cells which regulate and co-ordinate a response
innate mechanisms in response to damage: leucocytes
white blood cells that fight disease
adaptive immune system
develops after exposure to microbes, toxins and any other foriegn objects
slow to react first time however quicker the next due to memory cells
3 mechanisms in the adaptive immune system
inflammation
clotting
lymphocyte and antibody production
3 mechanisms in the adaptive immune system: inflammation
when body detects primary defenses have been damaged and pathogens have entered the body histamine is produced
dilates capillaries and increases permability in capillary walls
may cause redness, swelling, pain and heat
3 mechanisms in the adaptive immune system: blood clotting
clot forms to close the wound + prevent pathogens from entering.
body sends white blood cells to area to fight off any potential infection resulting in formation of pus
3 mechanisms in the adaptive immune system: lymphocyte and antibody production
foriegn antigens are detected
lymphocyte produces antibodies which are specific to the antigens
these attack the antigen
phagocytes engulf antigen
some antibodies stay in the body as memorycells provoking a more rapid response upon reinfection
effect of intense training on the immune system
tissue damage, microtears leads to inflammation, production of leucocytes
effects of high + prolonged training on the immune system
decrease in innate and adaptive immune function
drop in leucocytes compared to sedentary people
sustained adrenaline and cortisol which spress immune system
which highlights the reletionship between exercise intensity and susceptability to disease
J curve
URTI= upper respiratory Tract infection
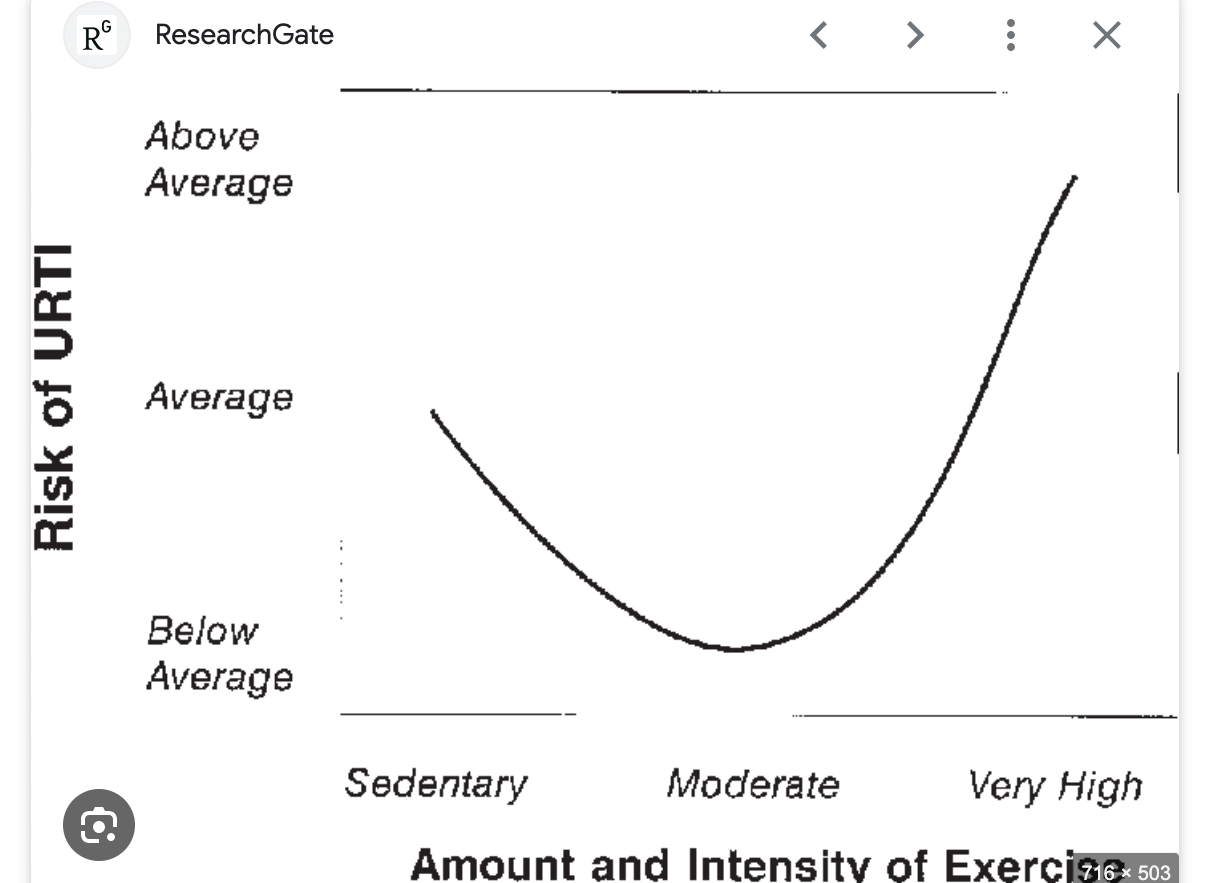
how do low levels of exercise affect immune function
low to medium immune function
poorer circulation preventing free movement of cells and substances of the immune system preventing them from fighting infection
how do moderate levels of exercise affect immune function
high immune function
better circulation, stronger hearts sllow free movement of cells and substances of the immune system increasing fight of infection
how do high levels of exercise affect immune function
very low
lower leucocytes caused by stress of exercise
inflammation of muscles due to exercise prevents blood flow and causes stress
deeper breathing in exercise= more bacteria/viruses to be inhaled
sustained increased levels of adrenaline and cortisol supress the immune system
how to minimise risk of infection among athletes
hygiene, rest, reletionships and diet
how to minimise risk of infection among athletes: hygine
reglar washing of hand/clothes/skin
limited hand/ mouth contact
oral hygiene
how to minimise risk of infection among athletes: rest
sufficient recovery+ sleep
incorporate sufficient recovery time into training programs
how to minimise risk of infection among athletes:diet
vitamins+ minerals
varied
pathogen free H2O