final
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
cypress family (cupressaceae)
mostly evergreen, scale-like or awe like. decussate arrangement, leaves fall off.
juniperus
berry-like cone, fleshy palate scales, scale-like or awe like leaves. decussate. sprays do not lie flat.
sequoia
linear needles, two-ranked, stomatal bloom below. only one tree in the genus. small woody cones with spirally arranged pelate scales.
giant sequoia
awe-like, spiral arrangement, glaucous
willow family (salicaceae)
riparian.
leaves: are deciduous, alternate, simple
flowers: mostly dioecious, catkins, appear before leaves.
fruit: capsule with numerous tiny, cottony seeds
genera: cottonwood, willow
populous(cottonwood, poplar,aspen) leaves
deltoid to round, truncate base, long petioles
birch family (betulaceae)
leaves: deciduous, alternate, simple
inflorescence: preformed catkins
fruit: tiny samaras in papery or woody catkin
western genera: birch alder
Lenticels
birch(betula) leaves
ovate to deltoid leaves, serrate margin, thin, floppy branches
alder(alnus) leaves
broad, ovate leaves, serrate to doublely serrate margin, straight veins
beech family (fagaceae)
leaves: alternate arrangement, simple deciduous OR evergreen
monoecious: usually, staminate catkins
fruit: nut enclosed in cup or bur
genera: oak, tanoak, chinkapin
oak (Quercus)
trees and shrubs, deciduous or evergreen, staminate catkins.
acorn: nut with scaly cap
white oak
deciduous or evergreen.
if deciduous, pinnately lobed with loaded lobes.
acorns mature in one season
black oak
deciduous or evergreen.
if deciduous, pinnately loved with spine tipped teeth
acorns mature in two seasons
live oaks
evergreen, may be in white or black subgroup
small leather unlocked leave
entire or spine toothed margin
tanoak (notholithocarpus)
evergreen
long oval leaves, usually serrate
fruit is an acorn with spiny cap
chinkapin (chrysolepis)
evergreen
narrow, lanceolate leaves with entire margins. golden underneath
nuts held in spiny bur
soapberry family (sapindaceae)
opposite leaf arrangement.
palmately lobed or palmately compound
western genera: maple, buckeye
acer (maple)
opposite leaves
palmately lobed and veined
fruit: double samara
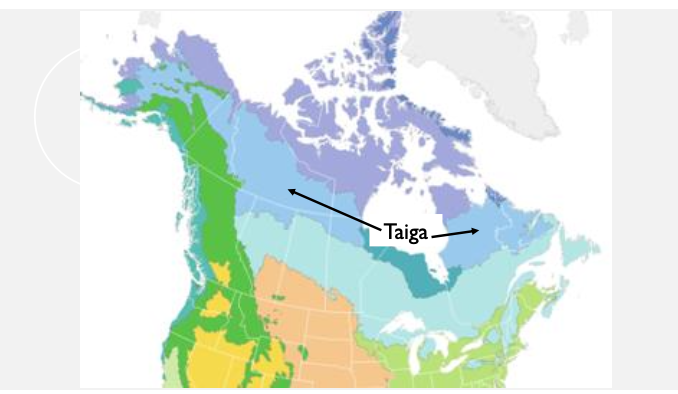
taiga biome
climate: long cold winters, short summers. moderate precipitation
dominant vegetation: spruce, fir, pine, larch
forest structure: closed canopy forest
two genera: pine, spruce
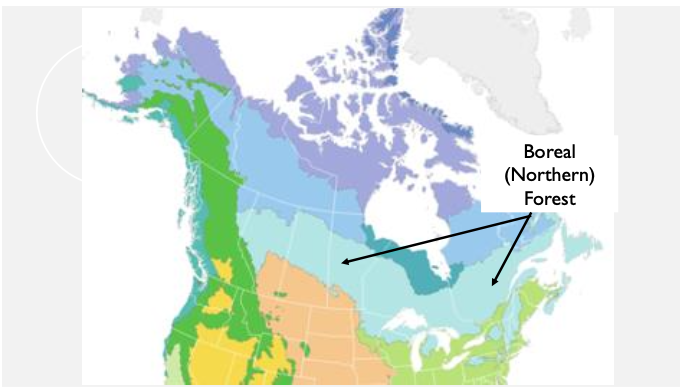
boreal(northern) forest
climate: long cold winters, short summers. 90 day growing seasons. snowy
dominant vegetation: needlelike, coniferous trees
forest structure: conical shaped evergreens
two genera: fir, spruce
eastern temperate forest
climate: four seasons, mid latitude, winters are cold with minimal precipitation
forest structure: closed canopy deciduous forests
two genera: oak, maple
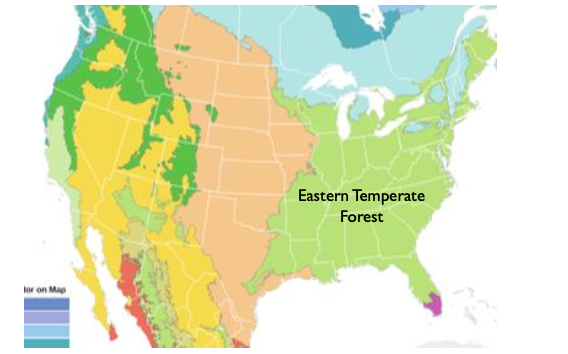
major eastern forest regions
northern, central, southern
fagus(beech)
deciduous, simple oval leaves with serrate margins, straight veins
long buds with imbricate scales
4-parted spiny “husk”
triangular nuts
chestnut(Castanea)
deciduous
long lanceolate leaves with serrate margins
spiny bur containing triangular nuts
walnut family (juglandaceae)
large trees
leaves: pinnately compound leaves with alternate arrangement
staminate catkins, notes are inside leathery husk (drupe)
eastern genera: walnut and hickory
hickory(carya)
pinnately compound leaves
3-branched staminate catkin
fruit is a nut with dehiscent husk
shell of nut is smooth
magnolia family (magnoliaceae)
leaves: simple leaves, alternate
flowers: large solitary flowers with leathery petal and numerous pistils
fruit: aggregate fruit
genera: magnolia, liriondeondron
liriodendron
pinnately lobed leaf, notched apex, deciduous, flower
pine family
evergreen trees
needle like leaves
spirally arranged cone scales
whorled branches
monoecious
pine (pinus)
acicular needles in fascicles
woody cones with spirally arranged scales
larix (tamarack, larch)
deciduous needles on spur shoots
small persistent cones with spirally arranged cone scales
spruce (picea)
sharp acicular needles on raised woody pegs
cylindrical cones with paper scales
ecological succession
autogenic (self-generated) change to the environment that is caused by the organism themselves. results in change to community and structure over time. initiated by disturbance.
disturbance
sets the stage for succession.
(type, intensity, severity, frequency, scale or extent)
disturbance regime
the pattern of disturbance in a particular location
tolerance
a trees ability to grow and and compete with other trees and disturbances
regeneration
the process of renewing tree cover, typically after a disturbance like a harvest or natural event.
attributes of pioneer species
fast-growing, shade-intolerant, and often reproduce rapidly via asexual or wind-dispersed means
attributes of mid-seral species
in-between pioneer and late successional. it depends on the climate they are in.
attributes of late successional species
slow growth, long lifespans, and shade tolerance.
post fire habitat
high light, tier and more temp extreme, low competition for space, OM is reduced, major soil changes in soil profile
fire resilient* (two traits of each)
bounces back after fire
high moisture content
physical protection
fire resistant* (two traits of each)
survives fire
thicker bark
higher water content in leaves and wood
types of tree defenses
bark, CODIT, resin
pathogen
microorganism, bacterium, or virus that can cause disease
disease
any condition that disrupts the normal functioning or development of the plant
pathways for infection
root contact, wounds, vascular system, and human related activities
wood-boring insects
species that eat and destroy wood
galls
abnormal growths on plants, often appearing as bumps, swellings, or distortions on leaves, stems, or roots
mycorrhizae
interaction between the roots and the plants where both benefit.
mast
the various nuts and fruits produced by woody plants
browse
the tender, edible portions of woody plants, such as leaves, twigs, and shoots, that are consumed by animal.
cavity
live trees with holes or other structures big enough to shelter animals
snag
a standing dead or dying tree, often missing a top or most of the smaller branches.
early seral habitat
the initial stages of forest development following a significant disturbance like fire, logging, or windthrow.
late successional habitat
a multi-layered tree canopy, including large-diameter trees, shade-tolerant tree species in the understory, and a high volume of dead wood, such as snags and logs
name one way that trees provide wildlife food
they produce nuts and seeds that wildlife consume
name one way that trees provide cover
the canopy of the tree provides shade for wildlife.
human uses for xylem
xylem is wood. we use it for everything. buildings, firewood, wood pulp for paper.
human uses for cellulose and lignin
used in paper, textiles, food additive
combustion
the process by which fuels in a forest, such as leaf litter, slash, and tree branches, burn and release heat and other products
pyrolysis
the heating of an organic material, such as biomass, in the absence of oxygen.
end grain
refers to the wood fibers running perpendicular to the length of a board.
long grain
refers to the wood fibers running parallel to the length of a board
uses of resin
coatings, adhesives, art, and various construction materials, as well as in traditional practices like incense and perfumes.