Circuits (copy)
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
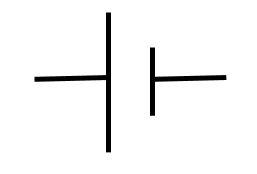
What does this symbolise?
Cell
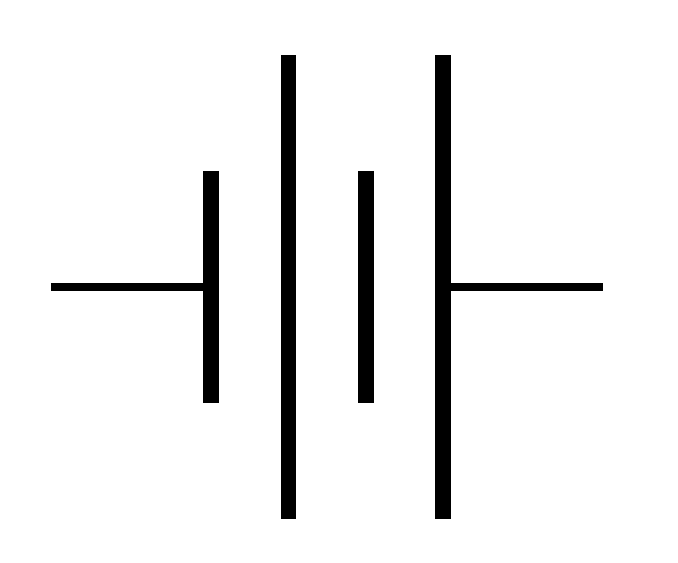
What does this symbolise?
Battery
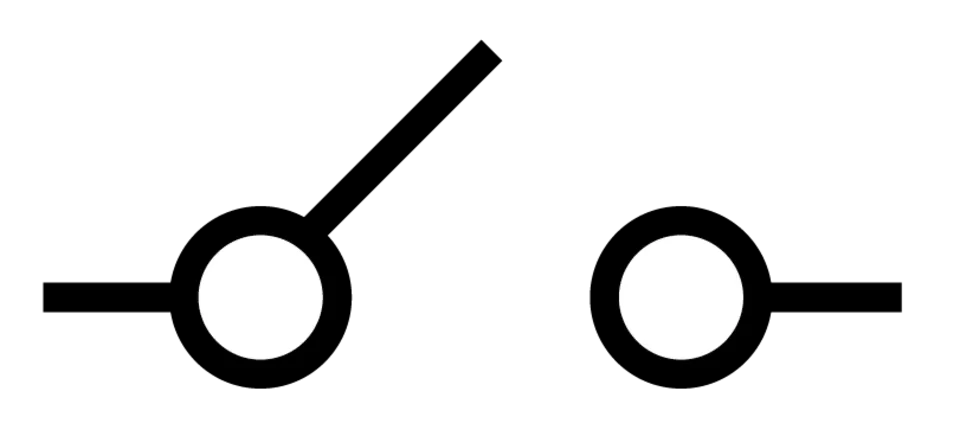
What does this symbolise?
Open switch
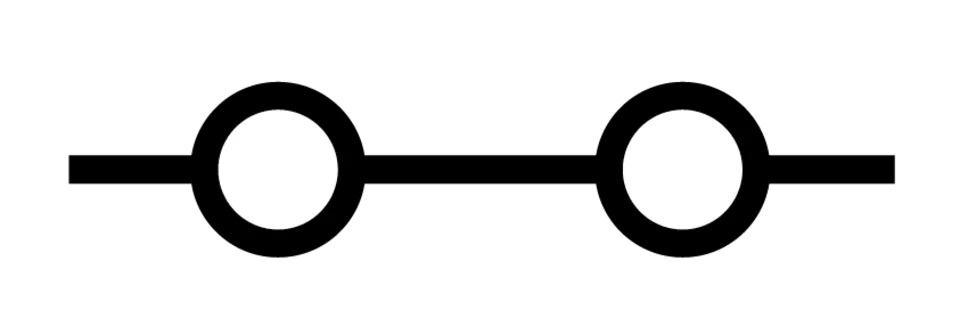
What does this symbolise?
Closed switch
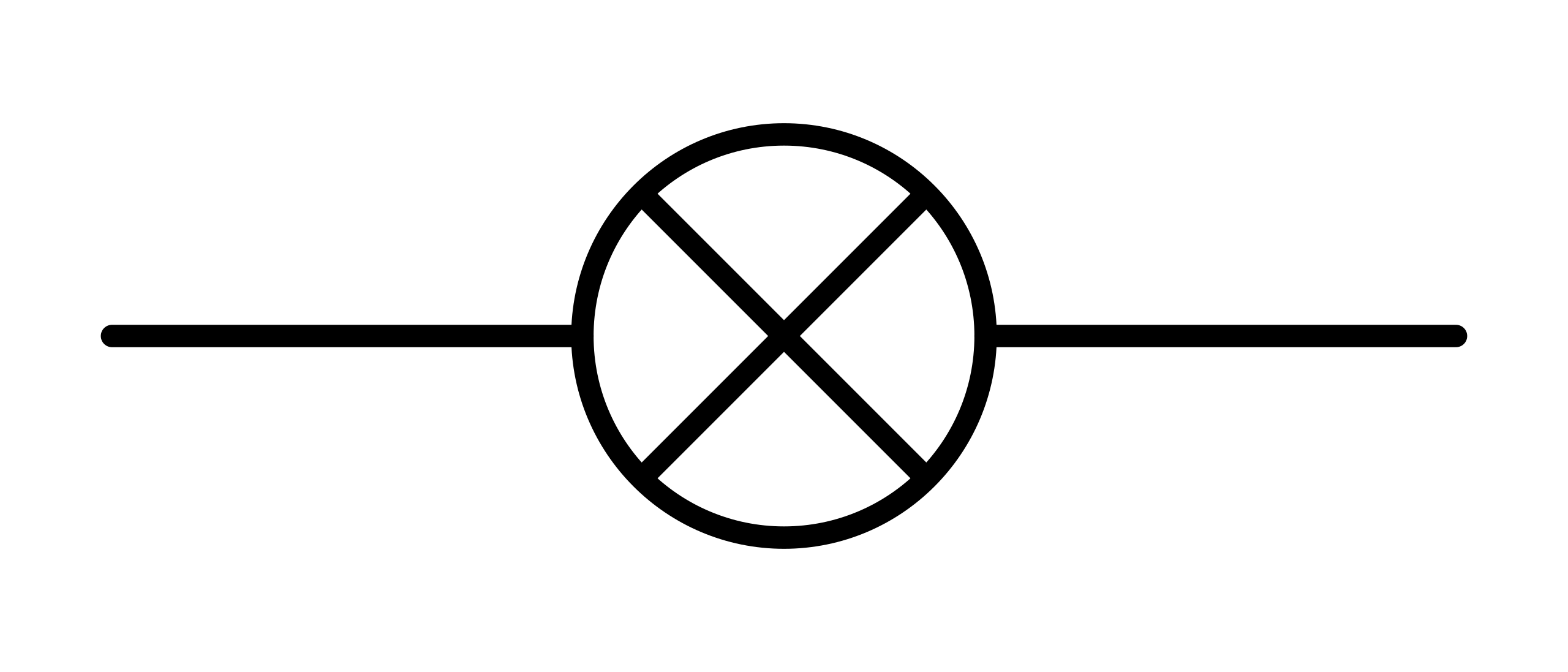
What does this symbolise?
Bulb/lamp
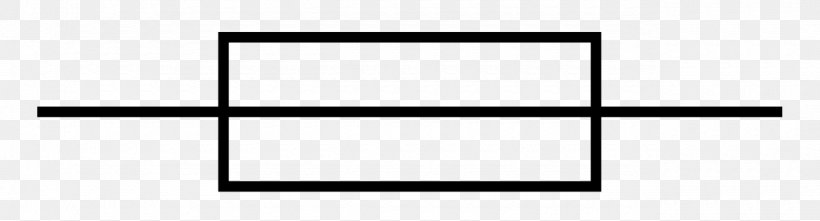
What does this symbolise?
Fuse
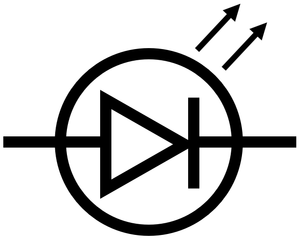
What does this symbolise?
LED
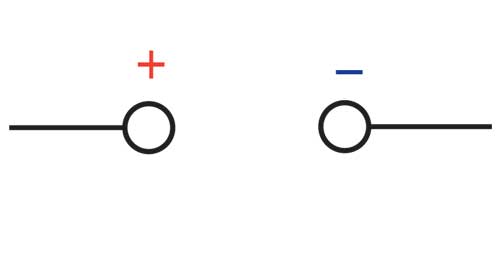
What does this symbolise?
DC power supply

What does this symbolise?
AC power supply
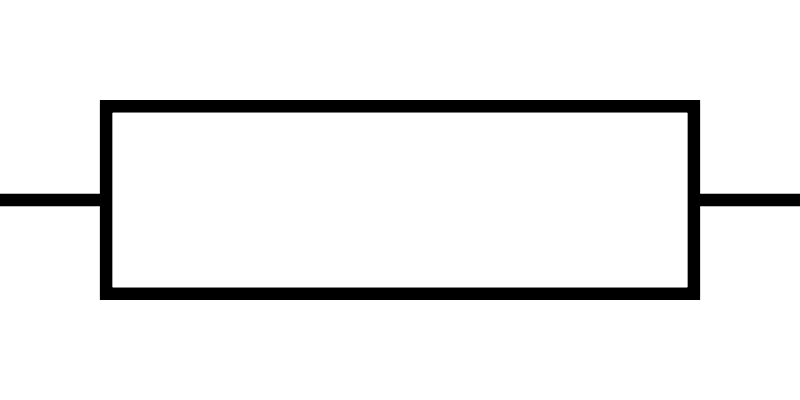
What does this symbolise?
Resistor
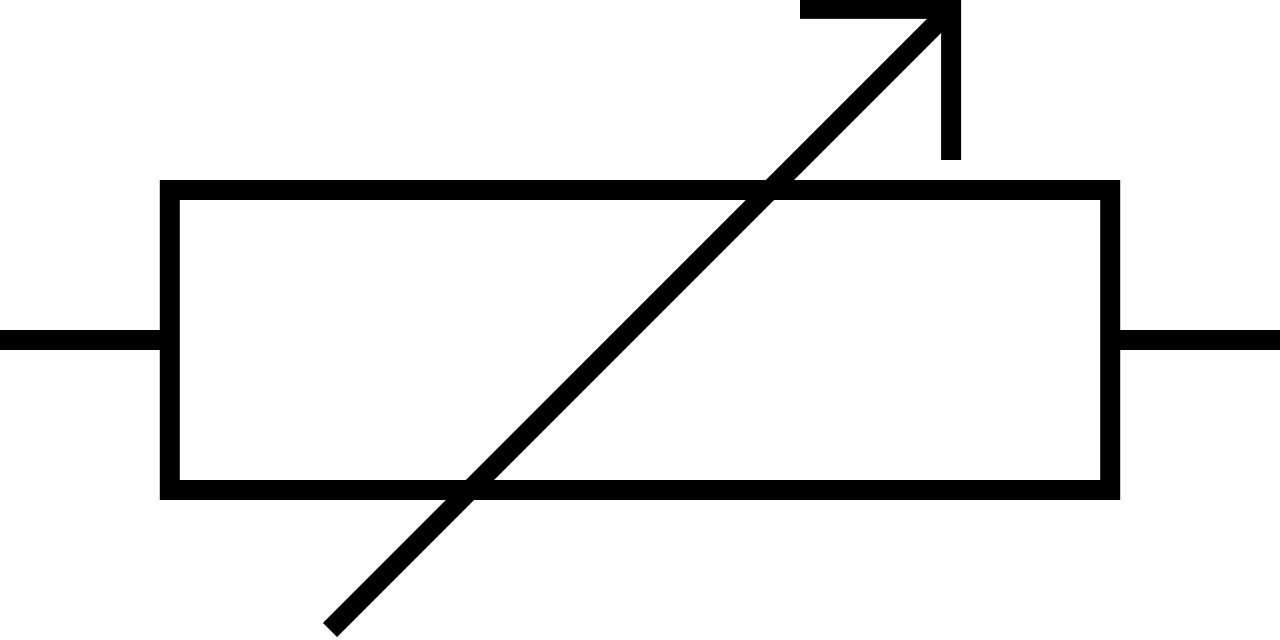
What does this symbolise?
Variable resistor
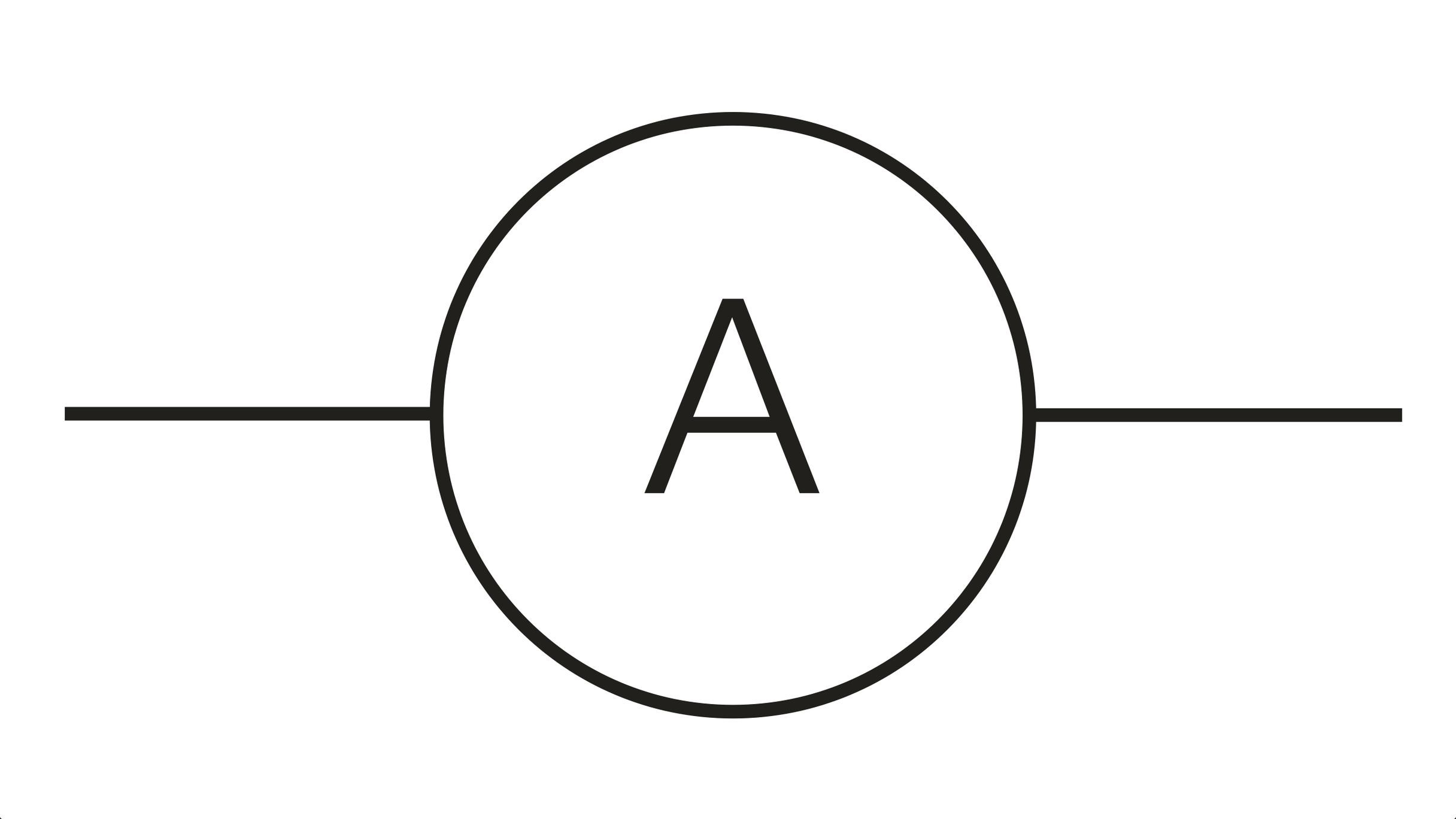
What does this symbolise?
Ammeter
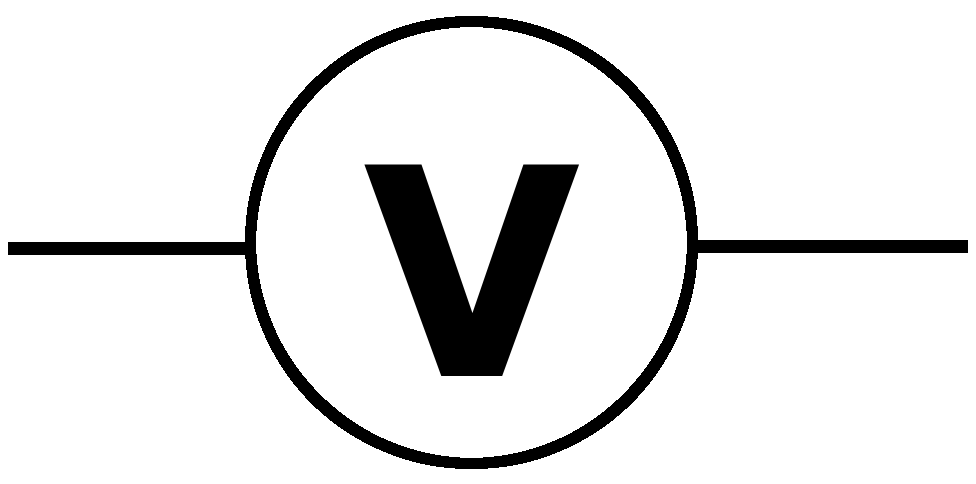
What does this symbolise?
Voltmeter
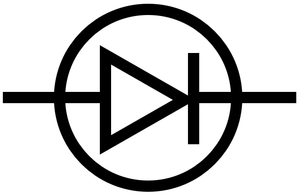
What does this symbolise?
Diode
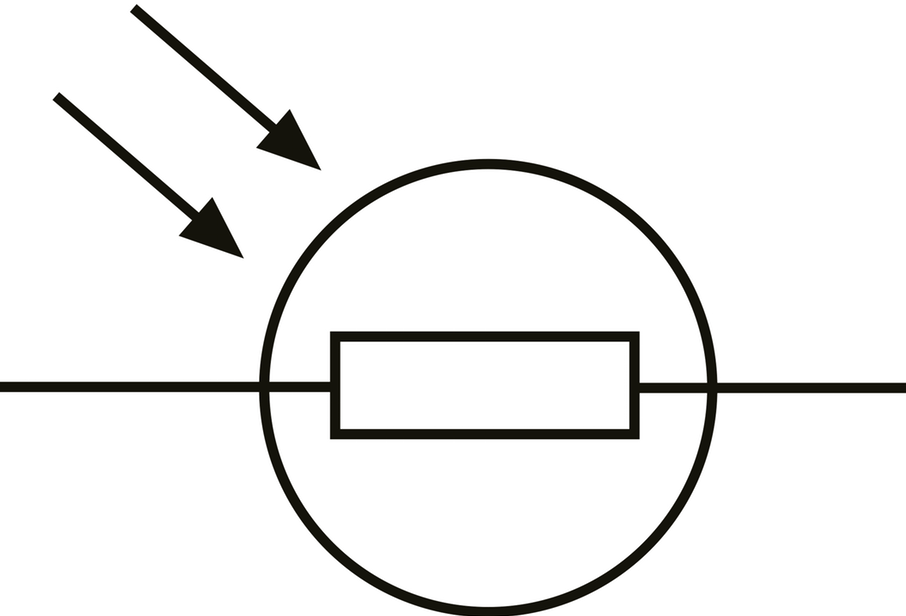
What does this symbolise?
LDR
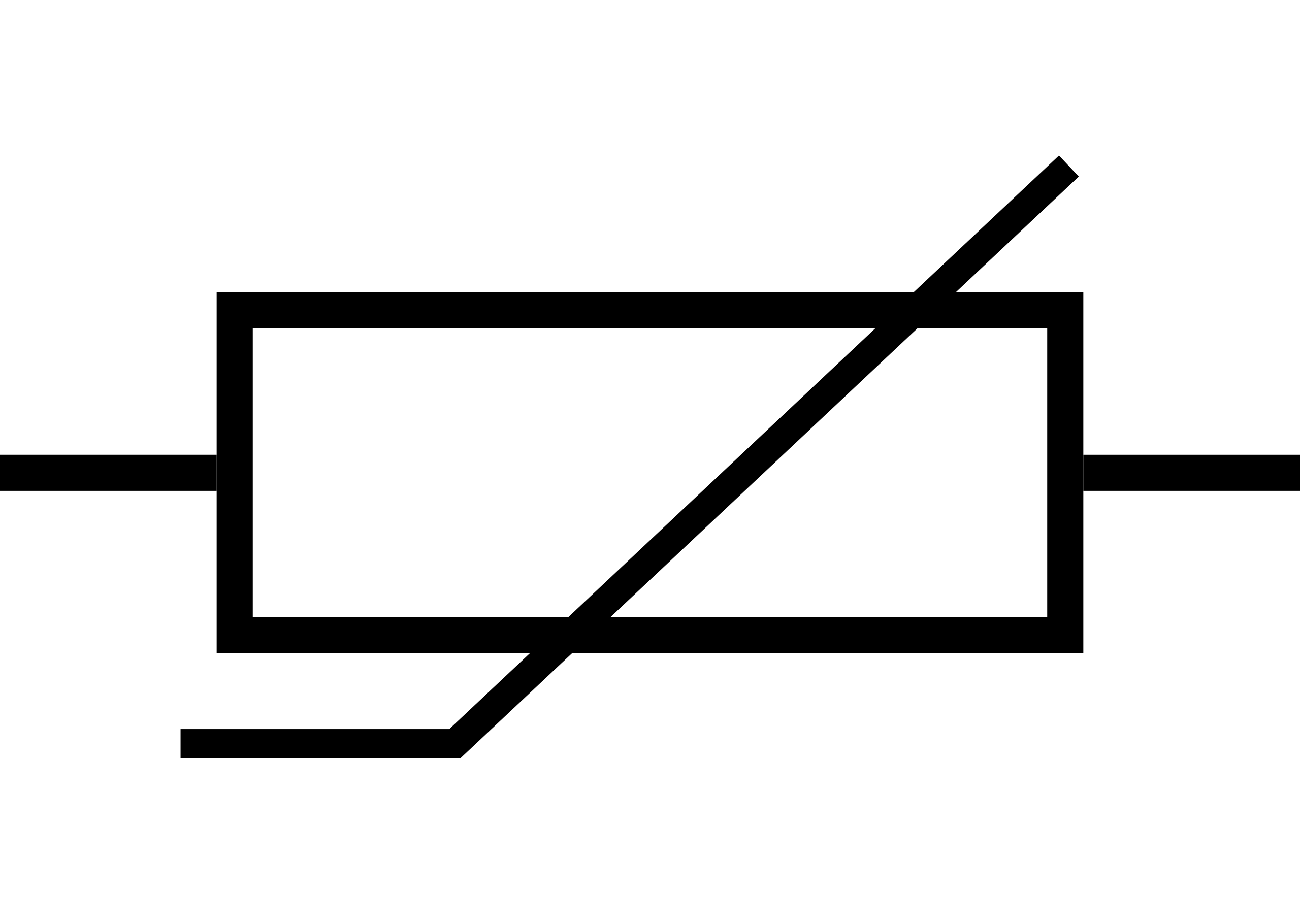
What does this symbolise?
Thermistor
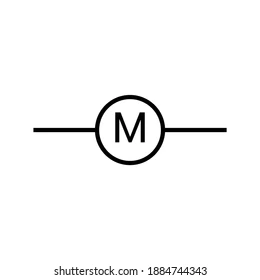
What does this symbolise?
Motor
What is current?
Flow of electrical charge
What is current measured in?
Amperes
What is potential difference?
Driving force that pushes the charge
What unit is potential difference measured in?
Voltage
What is resistance?
Anything that slows the current down
What is resistance measured in?
Ohms
In metals, what is current caused by?
Flow of electrons
What is charge measured in?
Coulombs
What is the symbol for amperes?
I
What is energy measured in?
Joules
What is the symbol for voltage?
V
What happens to resistance (usually) when temperature increases?
Increases
When resistance increases, what happens to current?
Decreases
How does resistance work?
Current has to do work against it and therefore slows down
What does the work done against resistance cause?
Transfer of energy of which some is useful and some is dissapated
When a current flows through a resistor, what happens to its temperature?
Heats up
Why does the resistor heat up when current flows through it?
Electrons collide with the ions and then the ions gain energy, vibrate, heat up, and makes it harder for the electrons to get through the resistor
What happens to the resistance of a thermistor as temperature increases?
Decreases
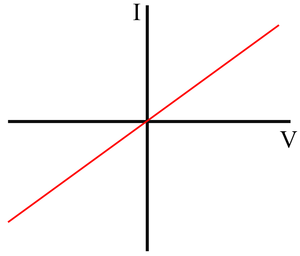
What kind of graph is this?
Resistor
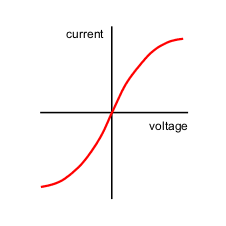
What kind of graph is this?
Filament lamp
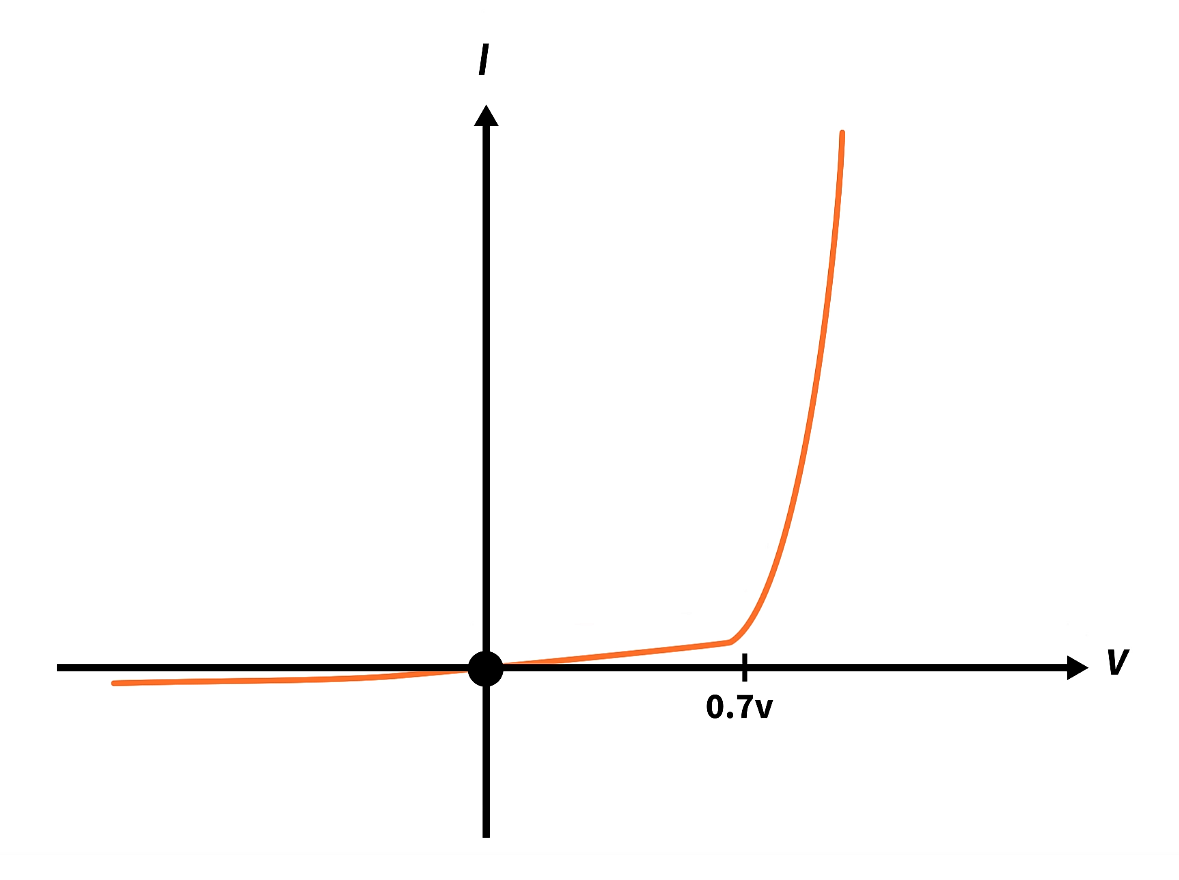
What kind of graph is this?
Diode
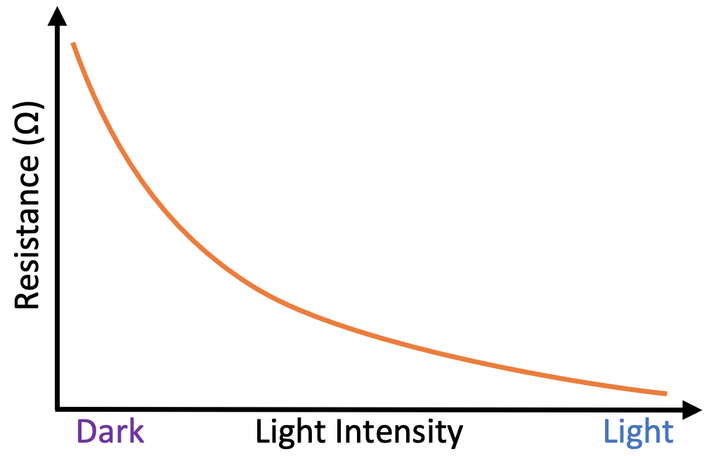
What kind of graph is this?
LDR
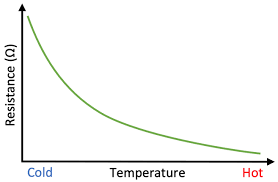
What kind of graph is this?
Thermistor
What does LDR depend on?
Light
What happens to LDR resistance in bright light?
Low
What happens to LDR resistance in darkness?
High
What are LDR’s used for?
Automatic night lights
Outdoor lighting
Burglar detectors
What is thermistor dependent on?
Temperature
What happens to thermistor resistance if the temperature is cool?
High
What happens to thermistor resistance if the temperature is hot?
Low
What are thermistors used for?
Thermostats
Car engine temperature sensors
What is a series ciruit?
Current flows through one pathway
What is a parallel circuit?
Current flows through more than one pathway
What happens to a series circuit if you remove one component?
It will stop working
What happens to a parallel circuit if you remove one component?
Won’t affect the others at all
How are voltmeters always connect to a circuit - no matter what?
Parallel
What happens to current in a parallel circuit?
It is distributed across components
What happens in a junction of a parallel circuit?
Current splits or rejoins
Does the total current entering a junction equal total current leaving?
Yes
What happens in a series circuit when a resistor is added?
Total resistance increases
What happens in a parallel circuit when a resistor is added?
Total resistance decreases
The larger the current the ____ energy transferred:
a. More
b. Less
More
What happens to efficiency usually when a component is heated?
Reduced
Can components in a circuit melt?
Yes