Anatomy exam
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What hormone is the single most important regulator of calcium levels in the blood?
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
How do glucocorticoids enable the body to deal appropriately with stress
Increase blood glucose, fatty acid, and amino acid levels, and increases blood pressure
What regulates the secretion of ACTH?
Hypothalamus
Is the release of oxytocin an example of positive or negative feedback?
Positive, as it enhances uterine contractions during labor
When is insulin released?
Insulin is released when blood glucose levels rise, typically after eating, to help lower blood sugar
What does GH target for growth?
Bone and Skeletal Muscle
What is up-regulation? Down-regulation?
Up - targets cells form more receptors in response to rising blood levels
Down - it desensitize the target cells, so that they respond less vigorously
What is the most important regulator of electrolyte concentration?
Aldosterone
Why is the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland not considered a true endocrine gland?
Stores hormones from the Hypothalamus and does not make hormones
What secretes aldosterone?
adrenal cortex
What is the ability of a specific tissue or organ to respond to the presence of a hormone dependent on?
the presence of specific receptors for that hormone on the target cells/organ
Label the glands in the body
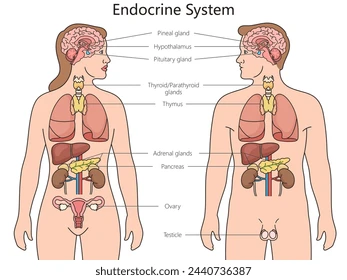
What organ or gland produces corticoids?
The adrenal gland/cortex
What glands may influence our night/day cycle
The pineal gland, which secretes melatonin and regulates sleep-wake cycles
The adenohypophysis will release what hormone in response to stress?
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
What is the difference between autocrine and paracrine?
autocrine - chemicals that exert their effects on the same cells that secrete them
paracrine - will activate the cells around the cell that is secreting
What hormone does the alpha islet cells produce in the pancreas?
Glucagon, which raises blood glucose levels by promoting gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis
What are some symptoms of diabetes mellitus?
Blood levels of fatty acids will increase - cause PH to drop - lead to rapid breathing and increase blood PH
What could cause Addison’s disease?
what are the symptoms
on the adrenal gland
hypoglycemia (low glucose levels in the blood)
bronzing of the skin
low body weight
low sodium levels
Low blood pressure
dehydration
In the development of basophil, what is the precursor of the basophil?
Myoblast
What triggers erythropoiesis?
Erythropoiesis is red blood cells, so it's triggered by the Need for oxygen
What are the characteristics of polycythemia?
There are too many red blood cells
Blood is thicker, so it caused high blood pressure
Increased blood volume
Has a high hematocrit
What happens to blood cells as they age?
Cell membranes wear out, and cells become damaged
What is the developmental sequence leading up to a late erythrocyte?
Proerythroblast, late erythroblast, normoblast, reticulocyte
What conditions can impair coagulation?
Hypocalcemia
Vitamin K deficiency
Liver diseases
What organ regulates erythrocyte production?
kidneys
What are the general characteristics of platelets (age, nuclei, etc)?
Does not have a nucleus
Only lives for a few days
Sticks to damaged areas (its function)
What are the general characteristics of plasma?
It's 90% water
Hundreds of dissolved material
Diagrams of granulocytes and agranulocytes.
2 phils and 2 agranulo cytes (review what they look like)
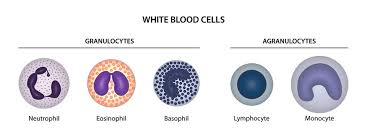
Why is blood a connective tissue?
Because it has a matrix
Which leukocyte phagocytizes bacteria?
Neutrophil
What is the buffy coat found in centrifuged whole blood?
Leukocytes (while blood cells)
What happens during the normoblast phase in the development of an erythrocyte?
The nucleus is ejected
What is the most common white blood cell found in whole blood?
neutrophil
What is hemoglobin made of? How many molecules of oxygen can it transport?
Pigment - heme
Globin - protein
4 oxygens
What WBC kills parasitic worms? Phagocytizes bacteria?
are killed by eosinophil
Where is the RBC graveyard?
spleen
Why would there be a cause for concern if a young pregnant mother is Rh negative, her husband is Rh positive, and this is their 2nd child?
Erythroblastosis Fetalis
Hemolytic disease of the newborn
Mom will have antibiotics for the Rh factor for the first baby, so if the second is Rh positive, it could cross the placenta wall and kill its red blood cells. Solve by giving mom a shot to kill her immune system.
How are cardiac muscle cells like skeletal muscle cells?
They are straightened A and I bands
What vessels does blood enter during ventricular systole?
Into the aorta and pulmonary arteries
What valves are supported by chordae tendinae and what is its purpose?
AV values, prevents the valve from going back up into the atrium
When is the tricuspid valve closed?
during ventricular systole (when the right ventricle contracts)
How can you determine the left and right side of the heart?
The thickness of the ventricular wall (left is thicker)
Why is the left ventricular wall of the heart much thicker than the right wall?
Because it pumps the most blood (the entire body)
What is ischemia? pericarditis? angina pectoris? myocardial infarct?
Not on the test. Due to no blood supply to the heart
Heart sounds are made by what?
Valves closing
What is the foramen ovale?
Connects the two atria of the heart during fetal development, allowing blood to bypass the lungs
Blood within the pulmonary veins returns to what chamber?
Left atria
Where will pressure increase if stenosis of the mitral valve occurs?
Pulmonary circulation due to restricted blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle.
What are some age related changes that affect the heart?
atherosclerosis (build up of plack)
Valves thicken
Heart becomes for fibrosis
Cardiac reserve declines (doesn't have as much oxygen)
What is systole and diastole? What sides of the heart are associated with each?
Systole - contractions; when ventricles pump blood out of the heart.
Diastole - relaxation; when the ventricles fill up with blood
(can survive without atrial contracting)
Blood flows within the heart.
study with the photo
What are Purkinje fibers?
Neural branches that surround the ventricles
for ventricular contractions
Why is oxygen so critical to the heart?
No atp no energy, and muscles need oxygen
What valves contain chordae tendineae? Which valves do not?
(AV Valves) bi and tri valves have, semilunar valves do not (aortic and pulmonary)
What membrane covers the heart?
Pericardium, there is serous fluid between membranes
What is bradycardia? Tachycardia?
B - below 60
T- is over 100
When would an artificial pacemaker be surgically implanted?
Pass out, fainting, shortness of breath, sa or av nodes not functioning properly
Location and function of ductus arteriosus.
its a shunt, after birth it will close, connects the aorta and pulmonary artery
allows the fetus blood to bypass the lungs
Label the heart
picture
Edema is caused by the failure of what side of the heart? Breathing problems due to the failure of what side?
Edema - is right, blood pools and causes swelling
Breathing - left