Azure VNets & Availability Zones
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is an Azure Virtual Network (VNet)?
A private network in Azure for secure communication.
Can connect Azure resources, on-premises networks, and the internet.
How are VNets assigned IP ranges?
Defined using CIDR blocks.
Must be non-overlapping with other VNets or on-premises networks.
Common private IP ranges:
10.0.0.0/8
172.16.0.0/12
192.168.0.0/16
What are the communication capabilities of Azure VNets?
Internet: Outbound communication is enabled by default; inbound via public IP or Load Balancer.
Azure resources: Use VNets, VNet peering, or service endpoints to communicate.
On-premises resources: Point-to-Site VPN, Site-to-Site VPN, or ExpressRoute for secure connection.
What are the three ways to connect on-premises networks to an Azure VNet?
Point-to-Site VPN (P2S): Secure remote user connections.
Site-to-Site VPN (S2S): Connects entire on-prem network to Azure.
ExpressRoute: Private, high-speed dedicated connection to Azure.
How does Azure route network traffic?
Default routing between subnets, VNets, on-prem, and the internet.
Custom routing via:
Route Tables (manual configurations).
BGP Routes (for ExpressRoute or VPN Gateways).
What are the methods to filter network traffic in an Azure VNet?
Network Security Groups (NSGs): Control inbound/outbound traffic.
Network Virtual Appliances (NVAs): Third-party firewalls or security
How many VNets can be created in Azure?
Multiple VNets per region per subscription.
What IP address ranges should be used in a VNet?
Use RFC 1918 private address ranges:
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255
Avoid reserved ranges:
Multicast: 224.0.0.0/4
Loopback: 127.0.0.0/8
Link-local: 169.254.0.0/16
What are the reserved IP addresses in an Azure subnet?
First four and last address in a subnet are reserved.
Example for
192.168.1.0/24:192.168.1.0: Network ID.192.168.1.1: Default gateway.192.168.1.2 – 192.168.1.3: Azure DNS mappings.192.168.1.255: Broadcast address.
What should you consider when designing an Azure VNet?
Non-overlapping IP ranges to avoid conflicts.
Subnetting strategy for organization and security.
Security isolation (NSGs, Firewalls).
Connectivity requirements (on-prem, peering).
Azure services that create their own VNets.
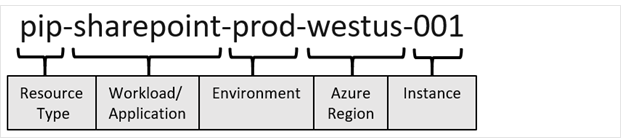
Why is a consistent naming convention important in Azure networking?
Helps identify resource purpose, type, and location.
Example:
vnet-prod-westus-001(Production VNet in West US).Scope levels:
Management Group (Top-level)
Subscription
Resource Group
Resource (e.g., VNets, subnets)
Can a VNet span multiple regions?
No, a VNet is region-bound.
VNet Peering allows inter-region connectivity.
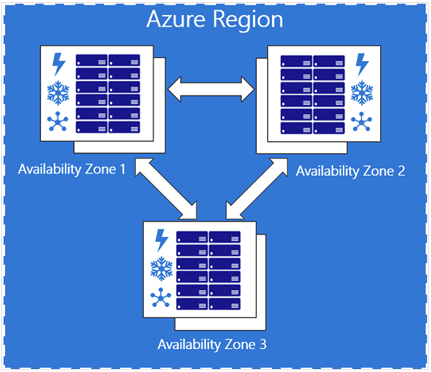
What are Azure Availability Zones?
Physically separate locations within a region.
Each zone has independent power, cooling, and networking.
Used for high availability and disaster recovery.
What are the three types of Azure services in Availability Zones?
Zonal Services: Resources are pinned to a specific zone (e.g., VMs, disks).
Zone-Redundant Services: Resources are replicated across zones (e.g., Storage, SQL DB).
Non-Regional Services: Available across multiple regions (e.g., Azure AD, Traffic Manager).
What are the key differences between Standard and Basic SKUs for public IP addresses?
Standard SKU: Secure by default, supports availability zones, routing preference, and global tier.
Basic SKU: Open by default, simpler, and does not support availability zones, routing preference, or global tier.
What is Custom IP Address Prefix (BYOIP) in Azure?
A feature that allows you to bring your own IP addresses to Azure and use them like Azure-owned public IPs.
What resources in Azure can you associate with a public IP address?
Virtual machine network interfaces
Virtual machine scale sets
Public Load Balancers
Virtual Network Gateways (VPN/ER)
NAT gateways
Application Gateways
Azure Firewall
Bastion Host
Route Server
What is the difference between zonal and zone-redundant public IP addresses?
Zonal: Associated with a specific availability zone.
Zone-redundant: Spread across multiple availability zones for high availability.
What are the benefits of using a custom IP address prefix (BYOIP) in Azure?
Allows you to bring your own IP addresses and use them like Azure-owned public IPs.
These IPs can interact with internal/private IPs and virtual networks and reach external destinations.
What are the key features of the Standard SKU for public IP addresses in Azure?
Secure by default: Closed to inbound traffic unless allowed by a Network Security Group (NSG).
Supports advanced features: Availability zones, routing preference, and global tier.
Idle timeout: Adjustable inbound (4-30 minutes, default 4), fixed outbound (4 minutes).
Use cases: Ideal for production workloads requiring high availability and security.
What are the key features of the Basic SKU for public IP addresses in Azure?
Open by default: No restrictions on inbound traffic (NSGs recommended but optional).
Limited features: No support for availability zones, routing preference, or global tier.
Idle timeout: Adjustable inbound (4-30 minutes, default 4), fixed outbound (4 minutes).
Use cases: Suitable for simpler, non-production workloads or testing.