Ch 2: Thermochemistry
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
thermochemistry
allows us to study the relative energy of a molecule
strain
structural stress within a molecule that is not present in a reference compound
What makes a good reference molecule?
a completely different molecule without strain
same molecule with different orientation
internal energy
energy held within a molecule; potential energy
energy
ability to do work
reaction coordinate diagrams
allows us to study the relative energy of a molecule
Energy can be added to a system by...
mechanical means
thermal means
with light
Gibbs free energy
differences in the stability of two different combinations of an ensemble of molecules at standard state and pressure
Ideal gas law constant (R)
0.0821 L atm/mol K
8.314 J/(mol·K)
Exergonic
reactions that release energy, spontaneous in forward direction
Endergonic
reactions that absorb energy, spontaneous in reverse direction
Gibbs free energy equation
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
Enthalpy
change in heat between two different compositions of molecules at constant pressure if no work is done
Exothermic
Releases heat
endothermic
Absorbs heat
Entropy
a measure of the disorder of a system
degrees of freedom
number of molecular movements possible
Degrees of freedom in a molecule
translations, rotational, vibrational
What impacts entropy?
number of molecules, temperature, volume
bond dissociation energy
energy required to break a bond
homolytic cleavage
bond cleavage that forms two radicals
heat of formation
The heat change that takes place when one mole of a compound in its standard state is formed from its elements in their standard states
heat of combustion
the heat of reaction for the complete burning of one mole of a substance
stability
denotes a lower internal energy relative to a reference system, intrinsic property, thermodynamically related
persistence
long-lived, kinetic-related
Radicals and Carbocations are stabilized with...
resonance and hyperconjugation
conformational analysis
allows us to determine the relationship between structure and energetics
conformers
stereoisomers that interconvert by rotations around single bonds
constitutional isomers
two molecules with same formula, different connectivity
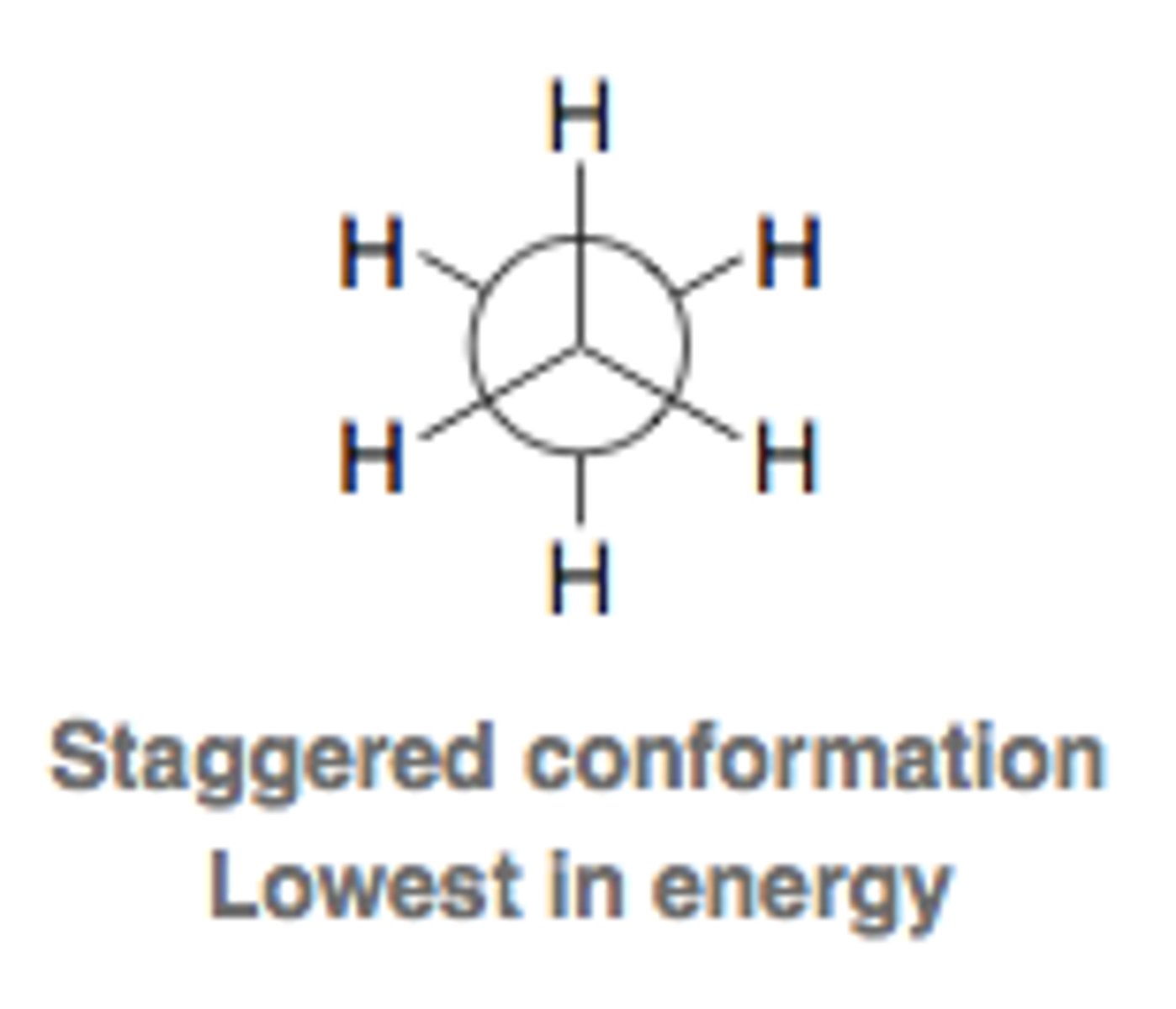
staggered conformation
no overlap of atoms along the line of sight
lowest energy
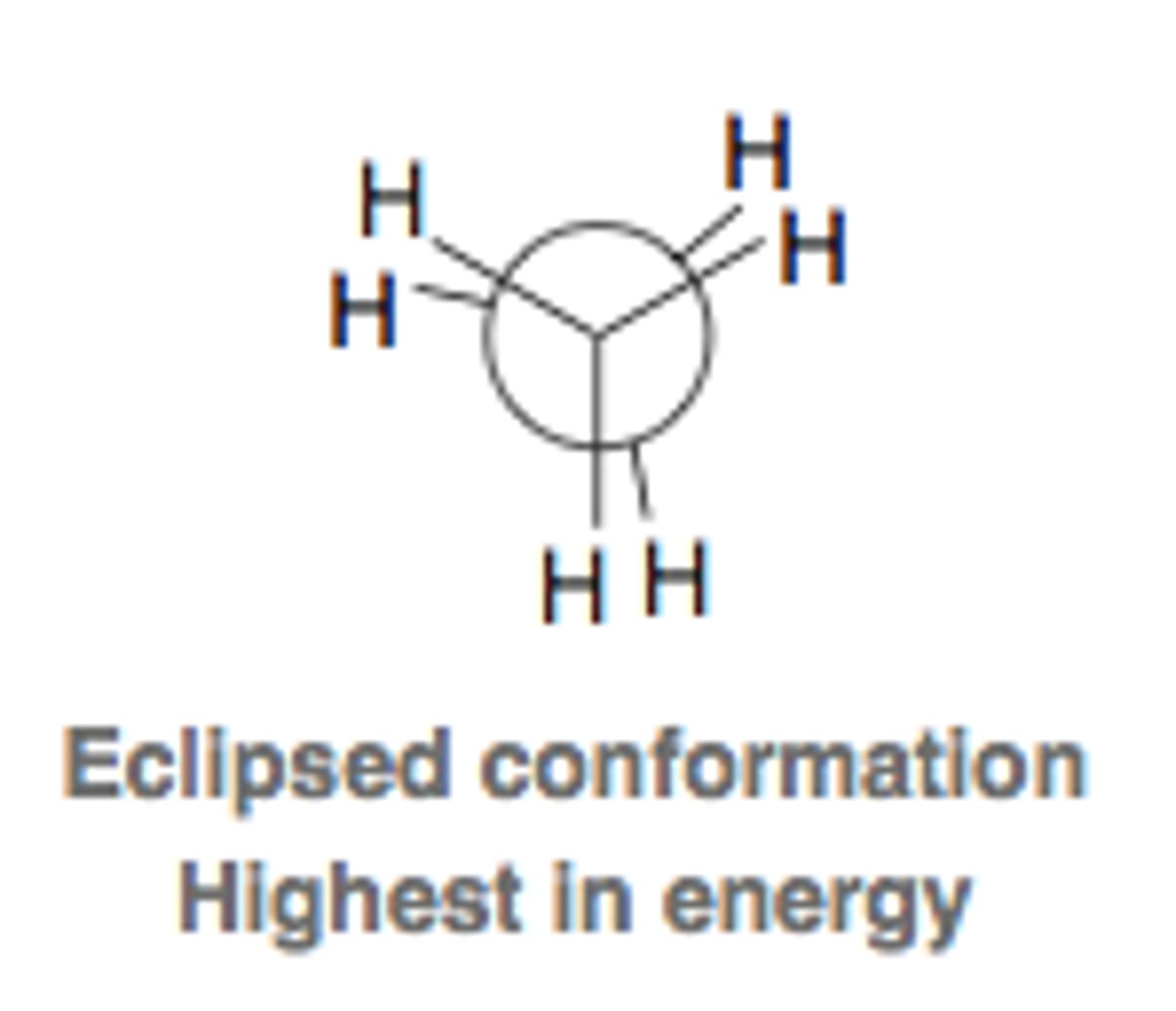
eclipsed conformation
highest energy
no separation or 120 separation.
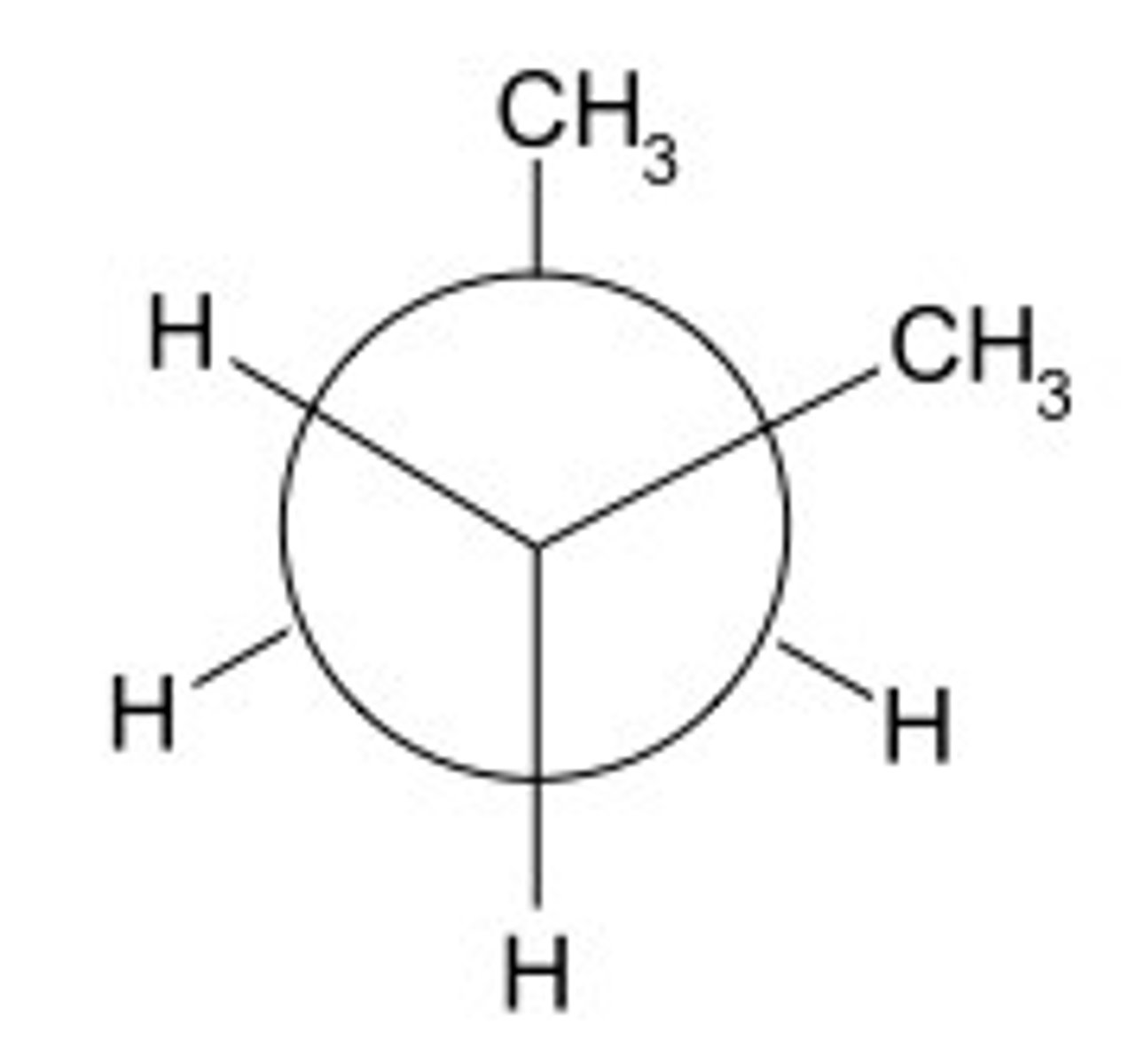
gauche conformation
a conformation with a 60 degree dihedral angle between the largest groups
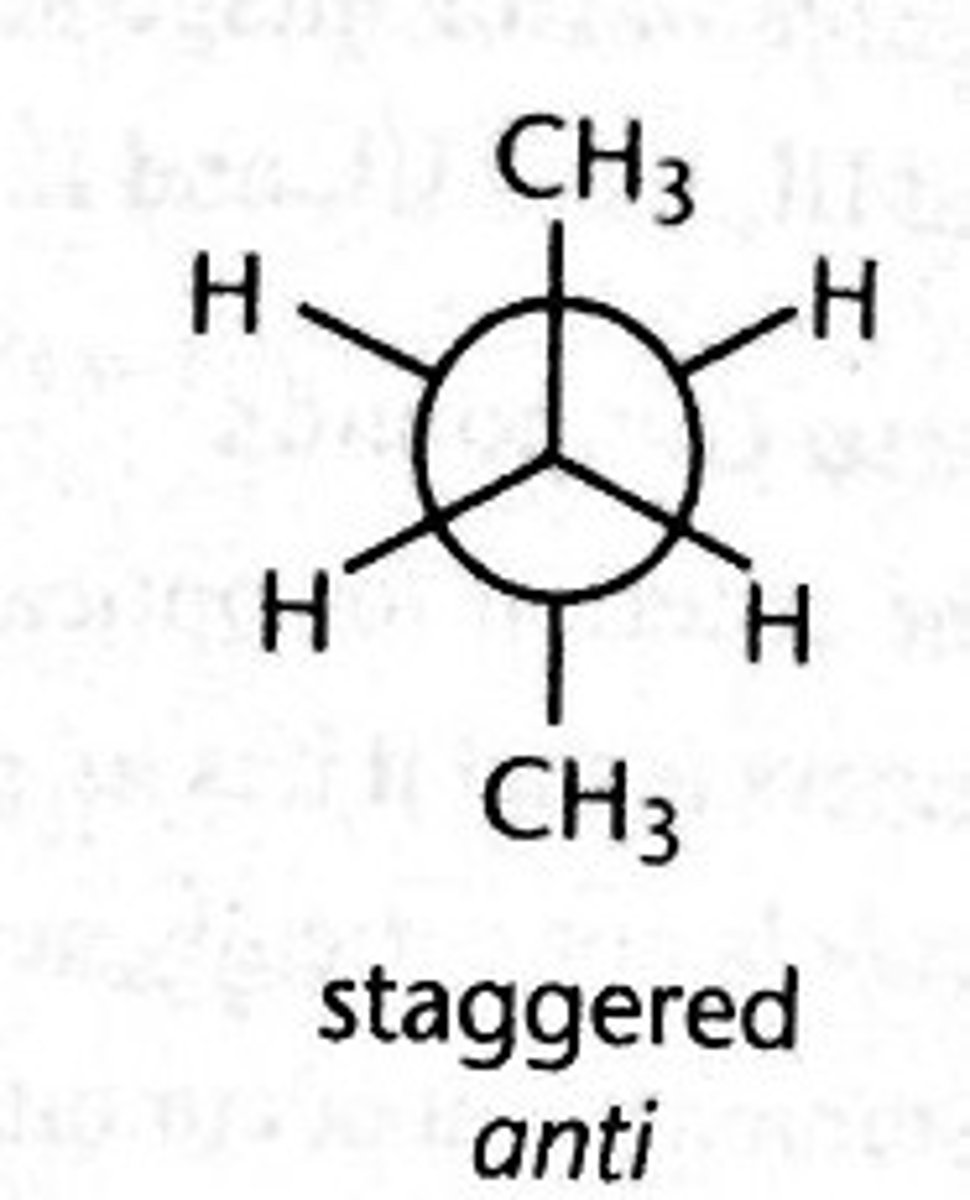
anti conformation
A type of staggered conformation in which the two largest groups are antiperiplanar to each other
the most energetically favorable conformation
1,3-diaxial interaction
the strong steric strain between two axial groups on cyclohexane carbons with one carbon between them
chair conformation
The chair-shaped conformation of cyclohexane that has no angle strain and has no torsional strain because it is perfectly staggered about all the C-C bonds. It is strain free.
boat conformation
a nonplanar conformation of a cyclohexane ring in which carbons 1 and 4 of the ring are bent toward each other
conjugation
direct attachment of alkenes without intervening atoms
trans conformation is preferred
pi electrons prefer to be in a _____ orientation
planar
Huckle Rule
any hydrocarbon or heterocycle with 4n+2 pi electrons in a fully conjugated cyclic pi-system is aromatic
Homoaromaticity
molecule whose geometry allows for orbital overlap, but has a saturated center
Anti-aromatic
planar pi-systems with 4n electrons
generally unstable
orbital effects
orbitals will orient to lower internal energy
anomeric effect
lone pairs of glycosytic bond donates into anti-bonding orbital of adjacent functional group