Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
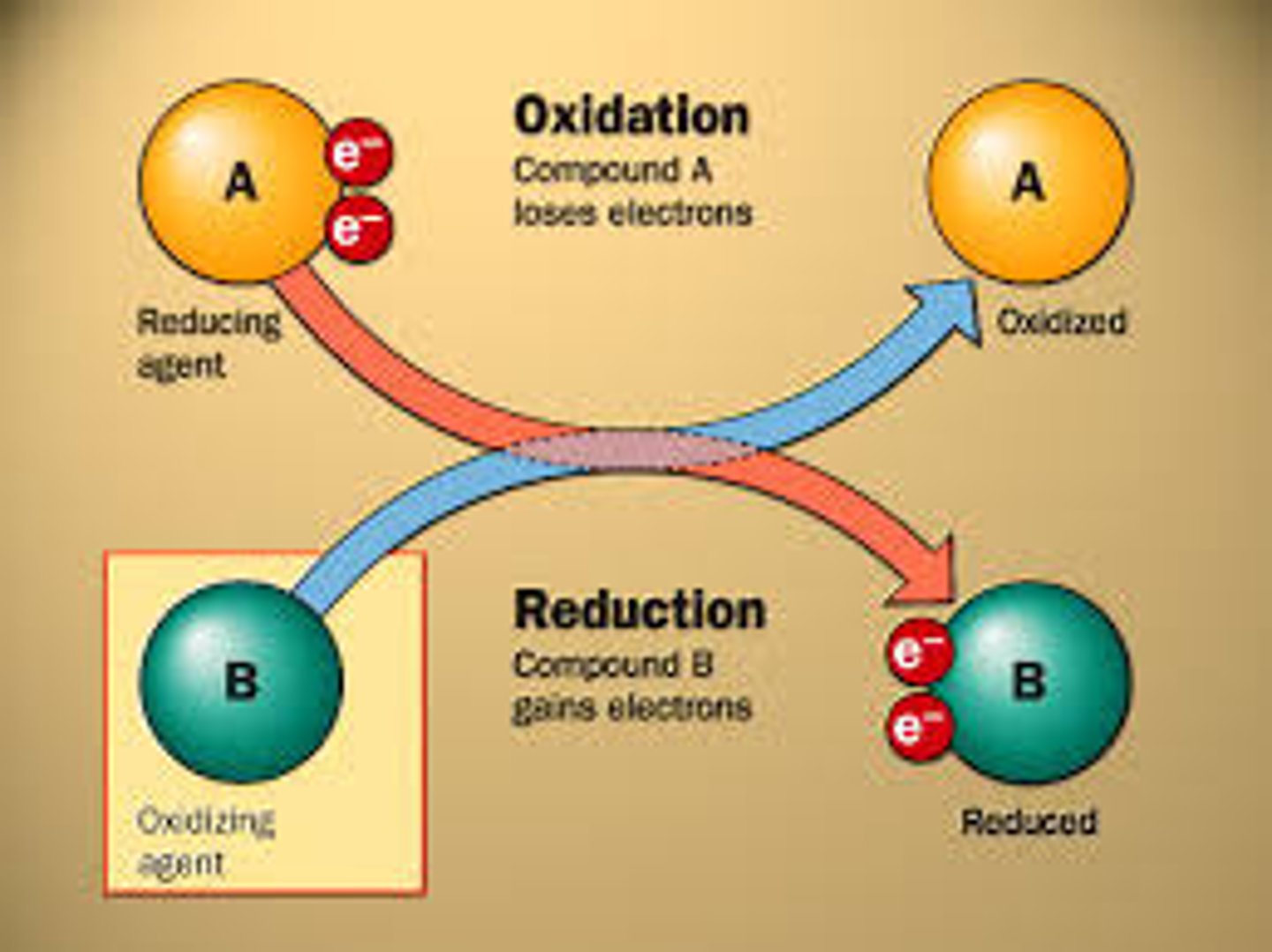
reduction
Gain of electrons by a chemical reactant; any reduction is accompanied by an oxidation.
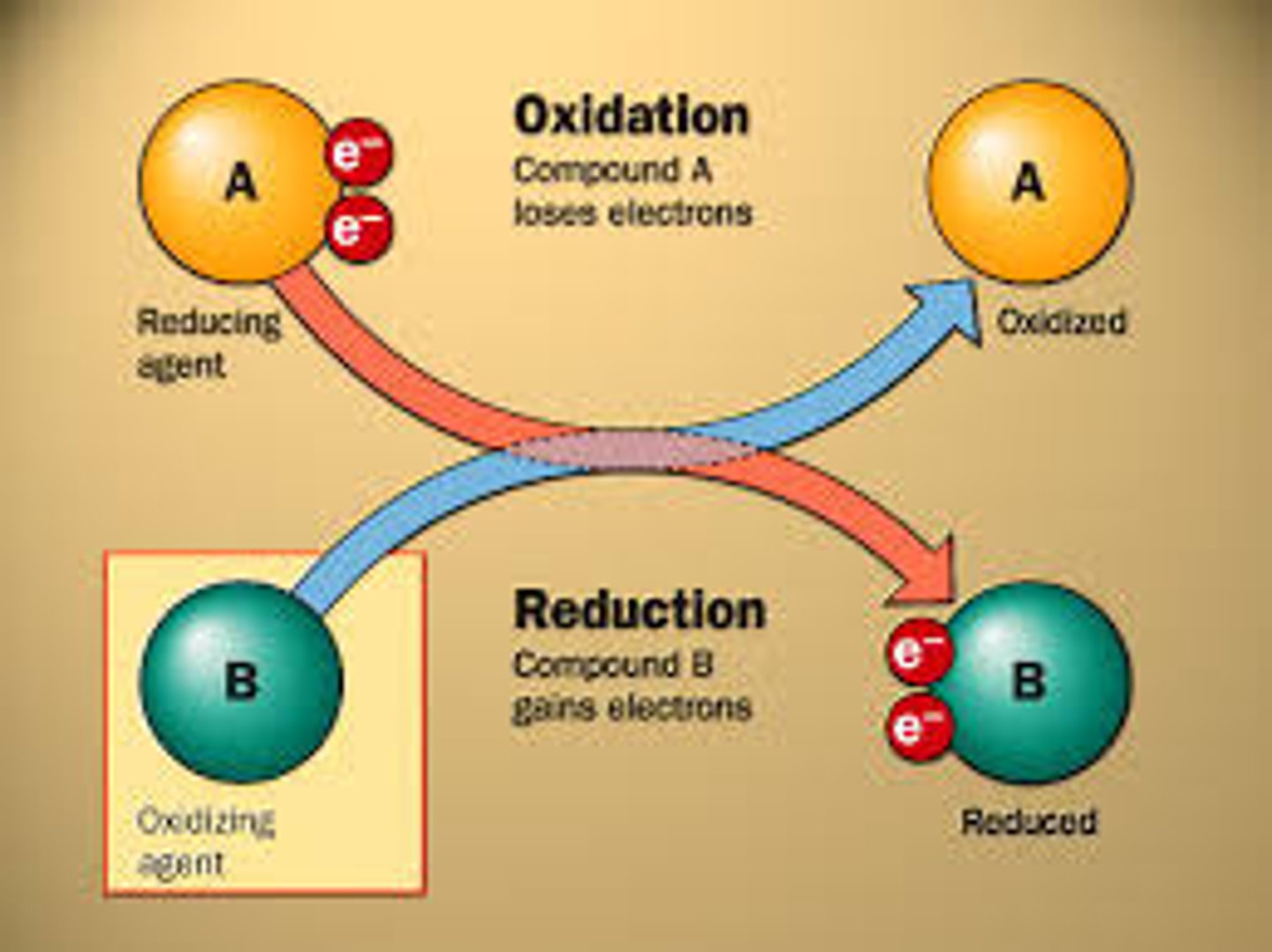
oxidation
Relative loss of electrons in a chemical reaction; either outright removal to form an ion, or the sharing of electrons with substances having a greater affinity for them, such as oxygen. Most oxidations, including biological ones, are associated with the liberation of energy.
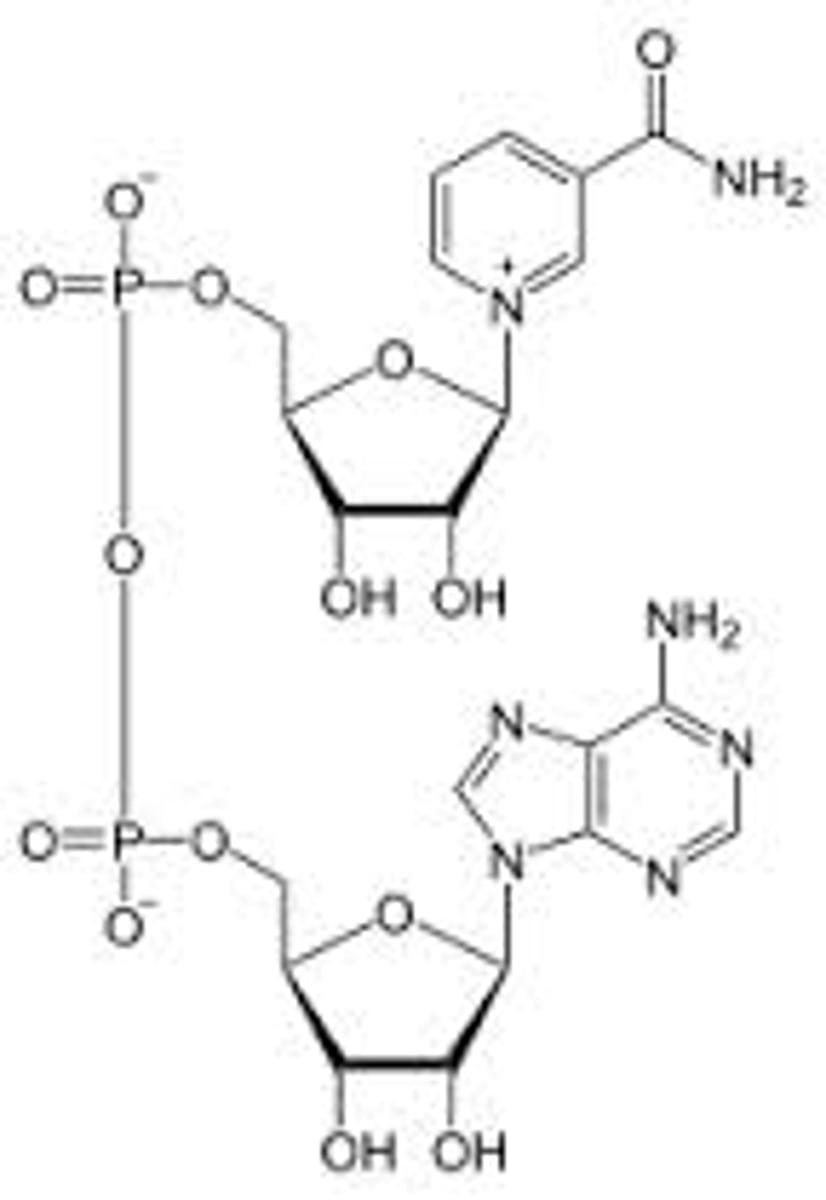
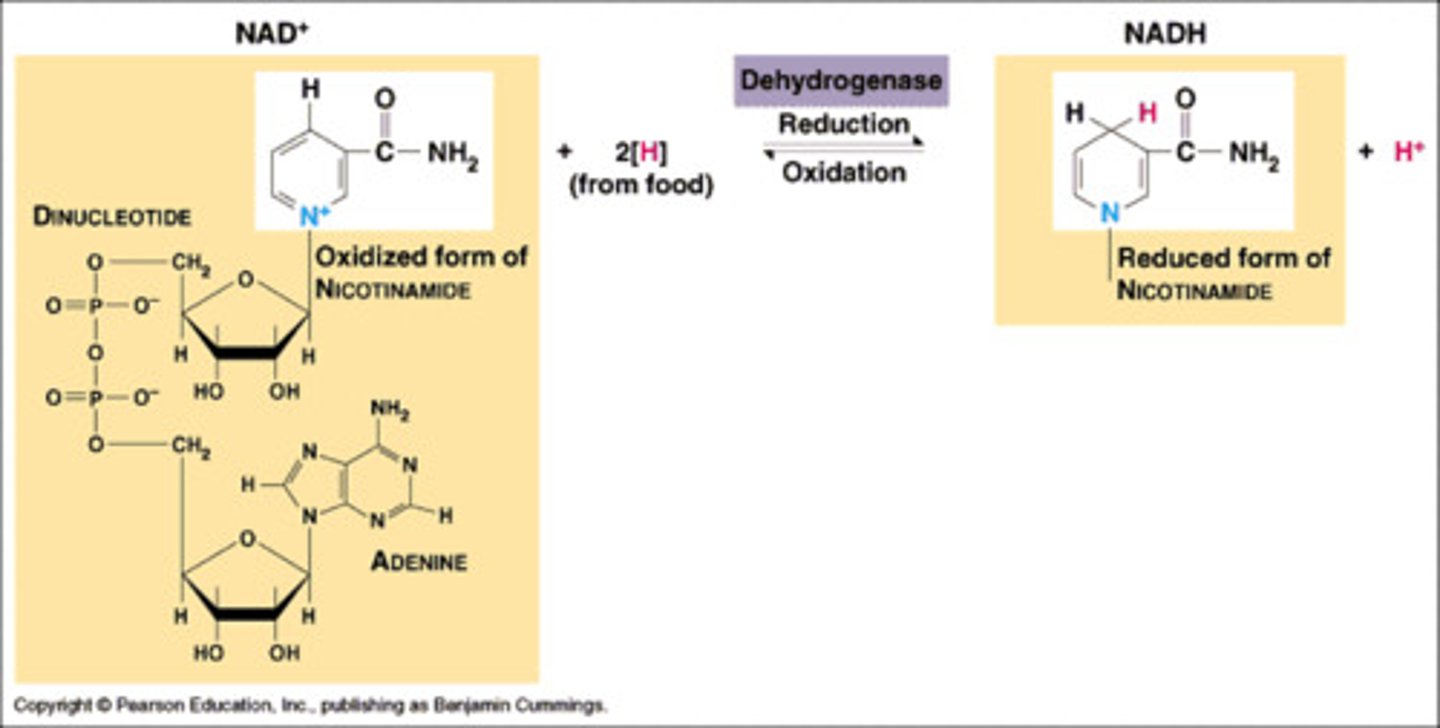
NAD+
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide - a coenzyme that is an electron carrier; NAD+ is oxidized, NADH is reduced
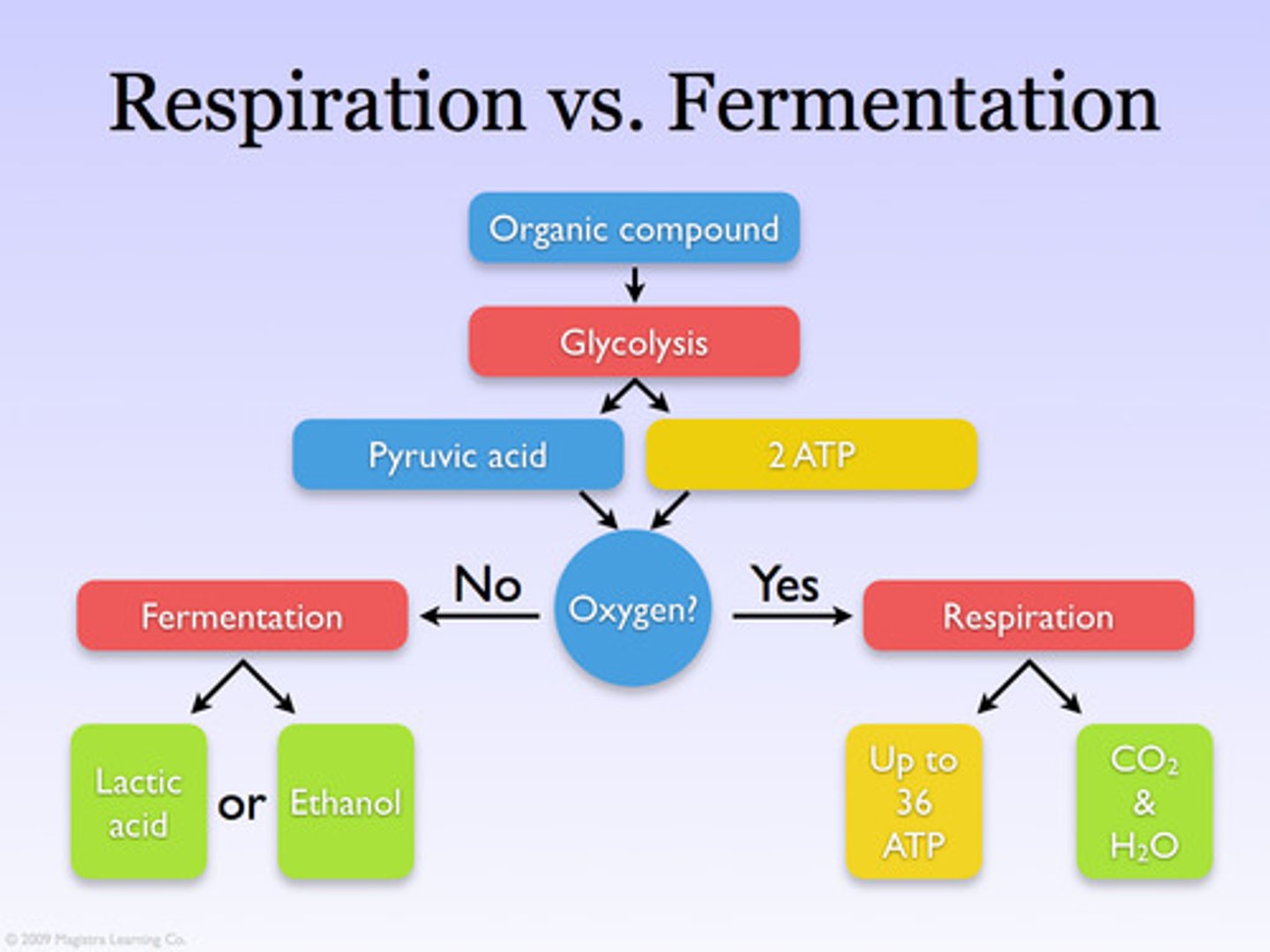
cellular respiration
The catabolic pathways by which electrons are removed from various molecules and passed through intermediate electron carriers to O2, generating H2O and releasing energy.

aerobic
Requiring molecular oxygen, O2
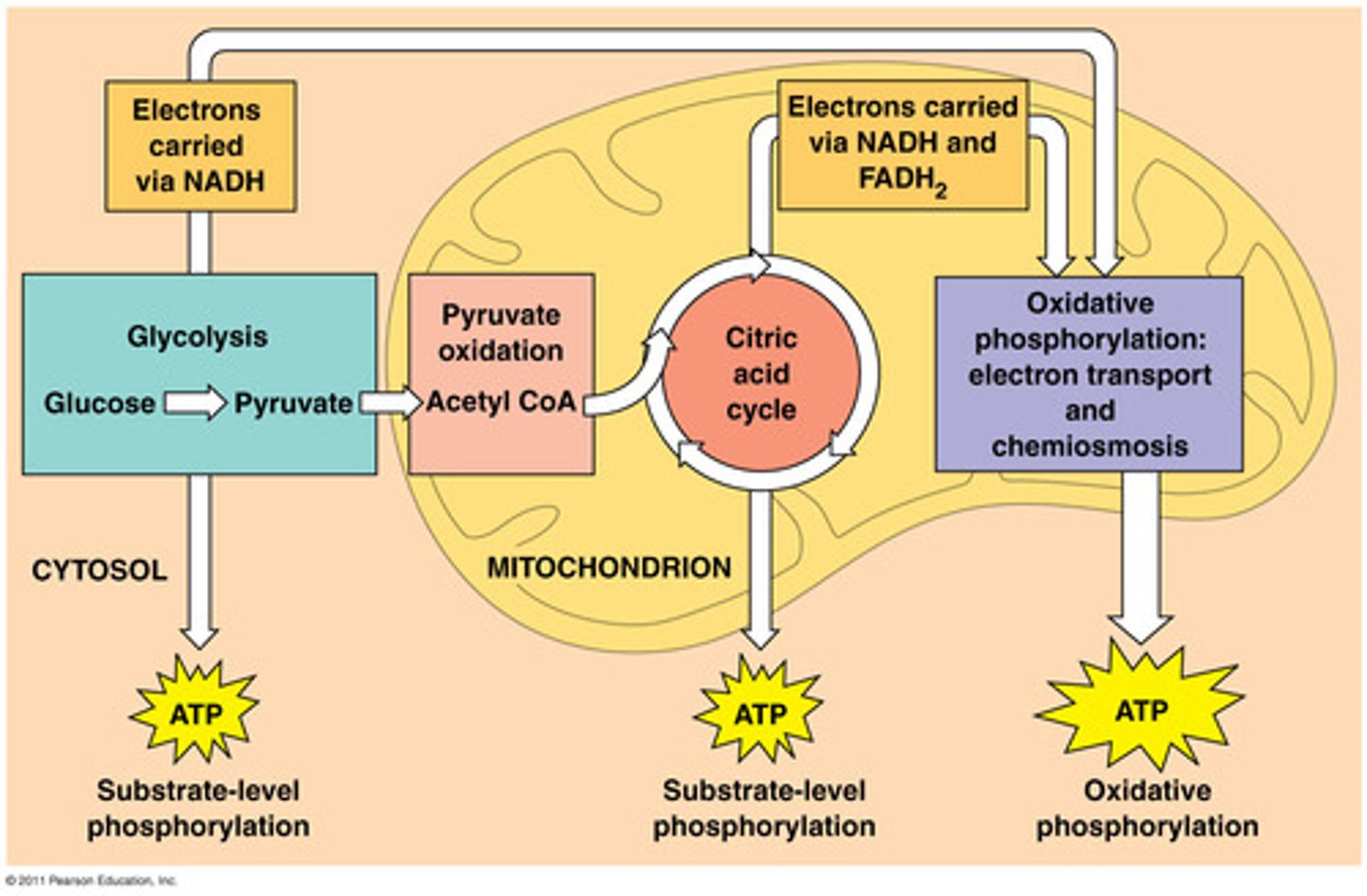
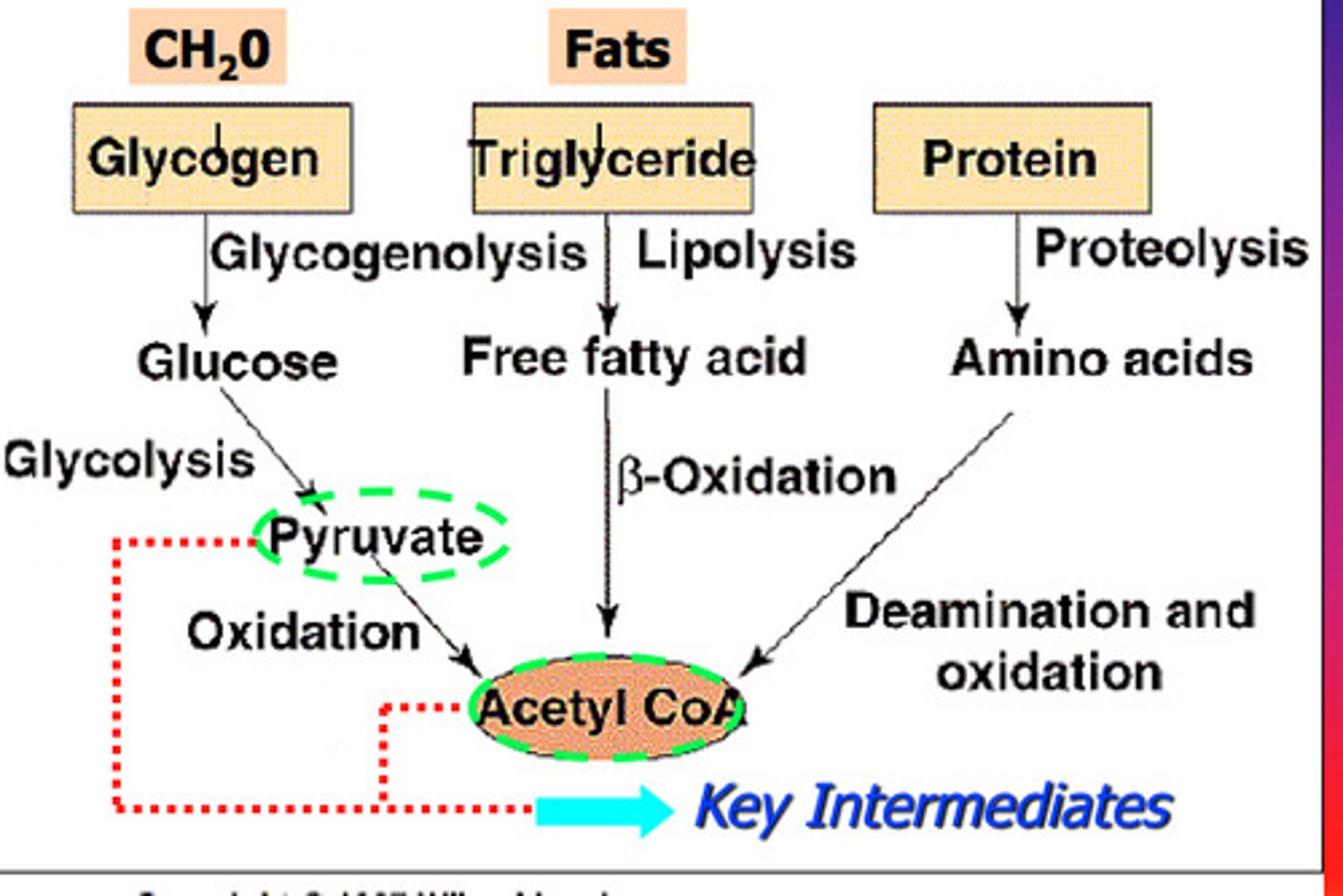
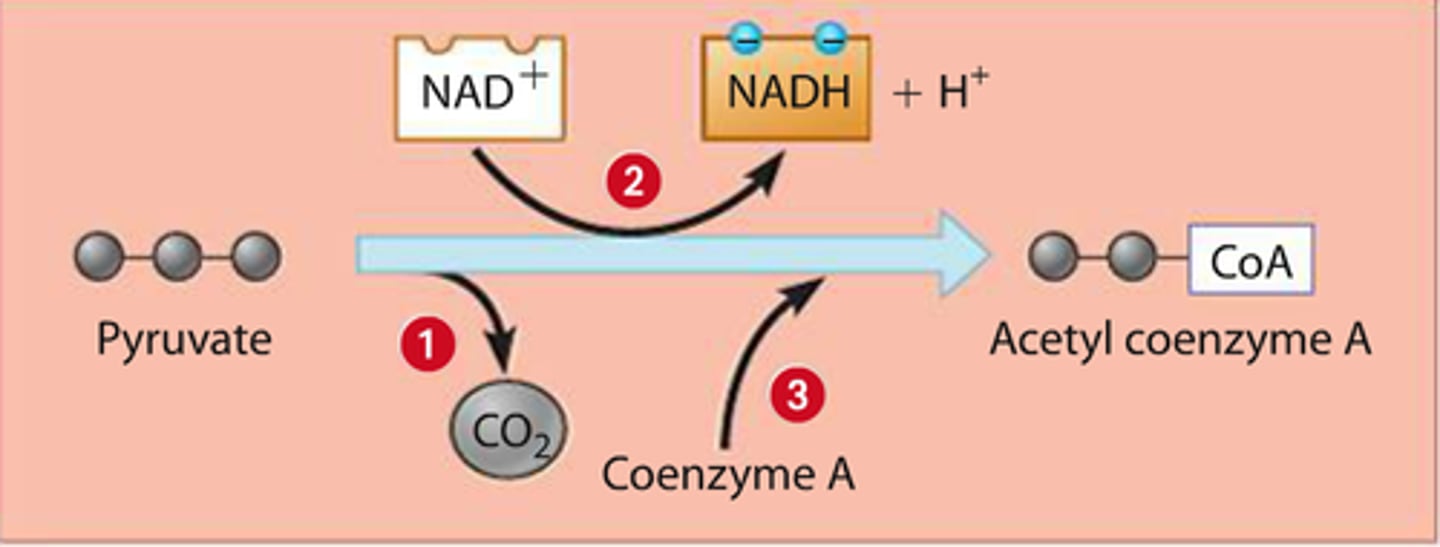
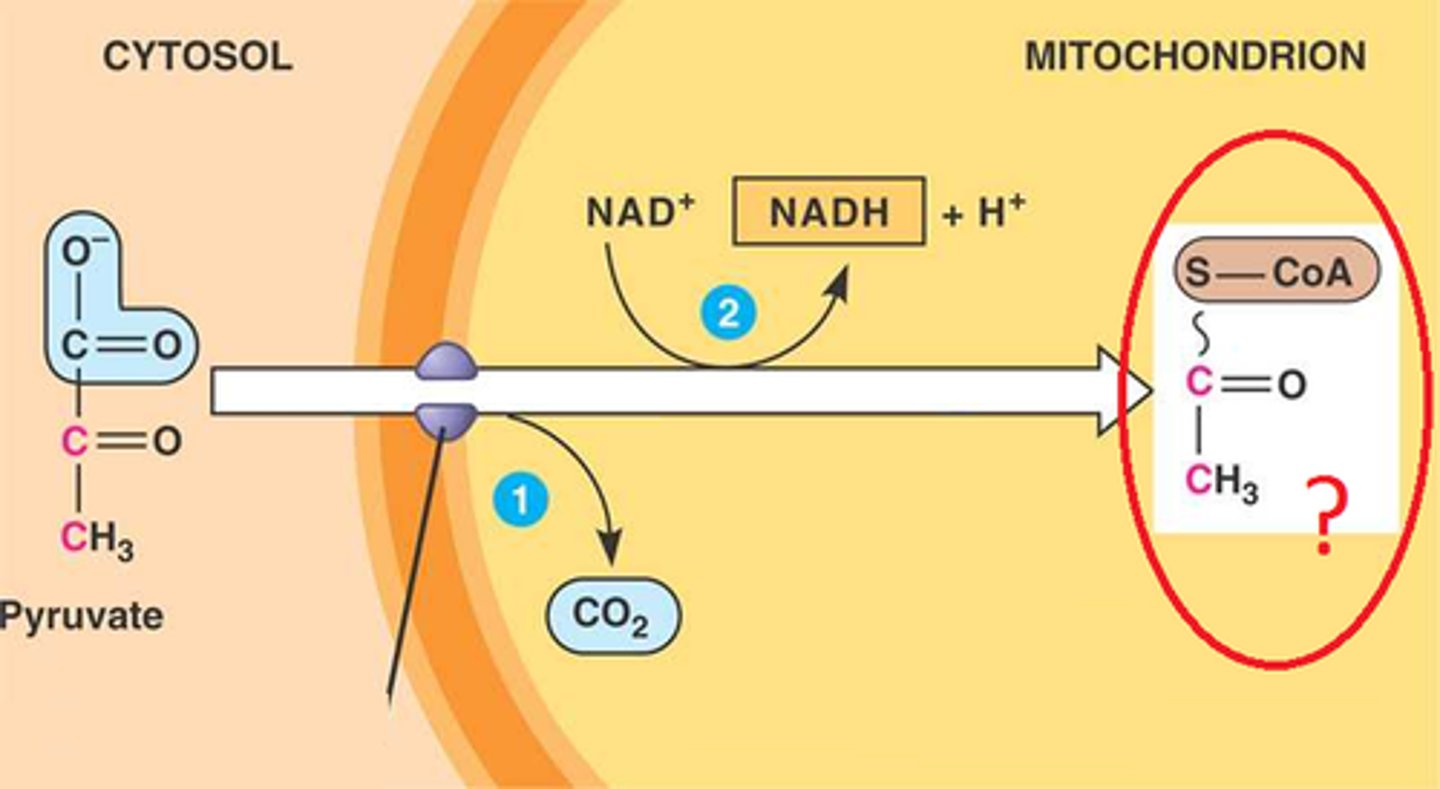
pyruvate oxidation
pyruvate molecules are oxidized and produces acetyl-CoA, CO2, and NADH
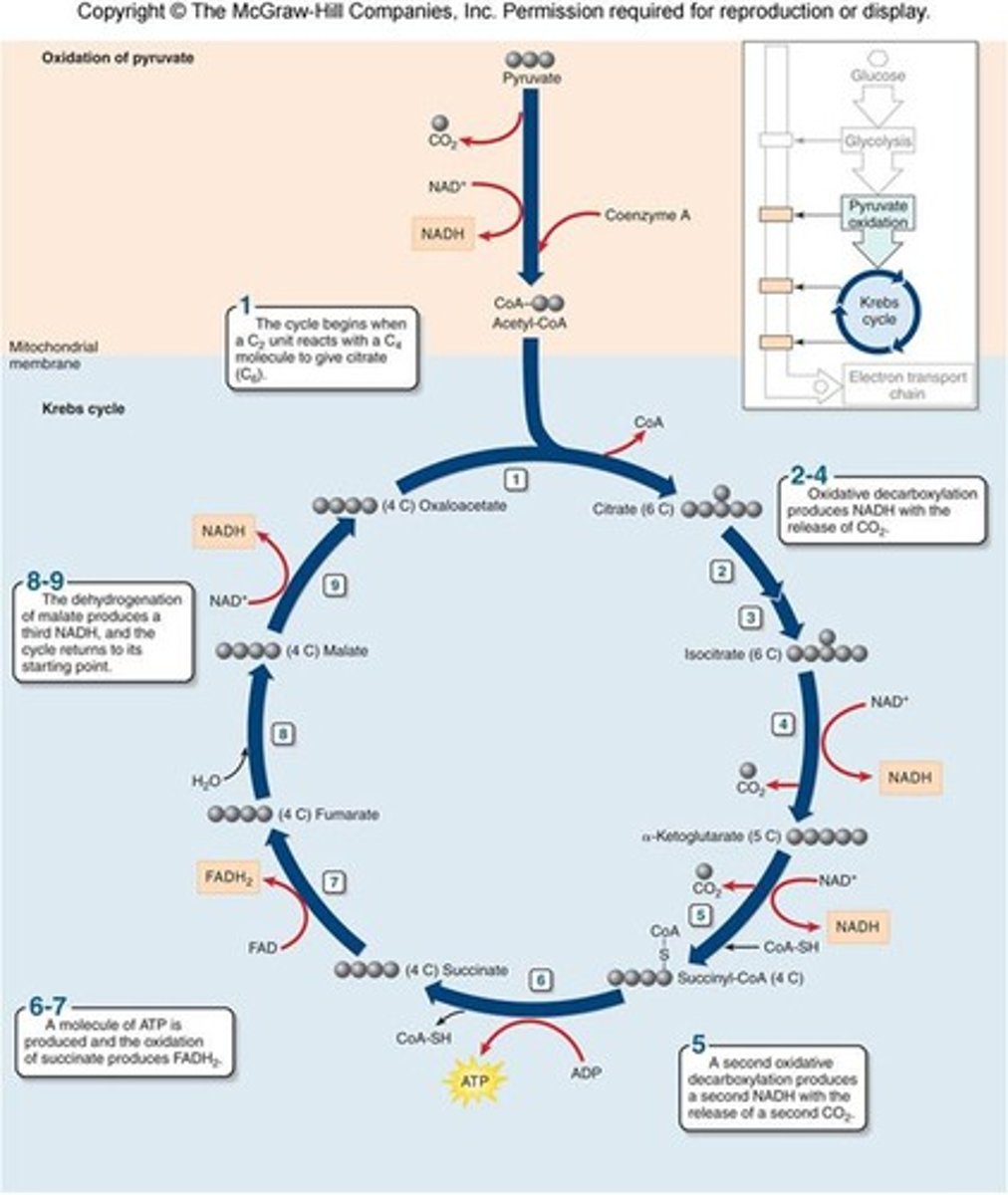
citric acid cycle
In cellular respiration, a set of chemical reactions whereby acetyl CoA is oxidized to carbon dioxide and hydrogen atoms are stored as NADH and FADH2. Also called the Krebs cycle.
pyruvate
Three-carbon compound that forms as an end product of glycolysis.
NADH
reduced electron carrier molecule formed in glycolysis
Krebs cycle
another name for the citric acid cycle
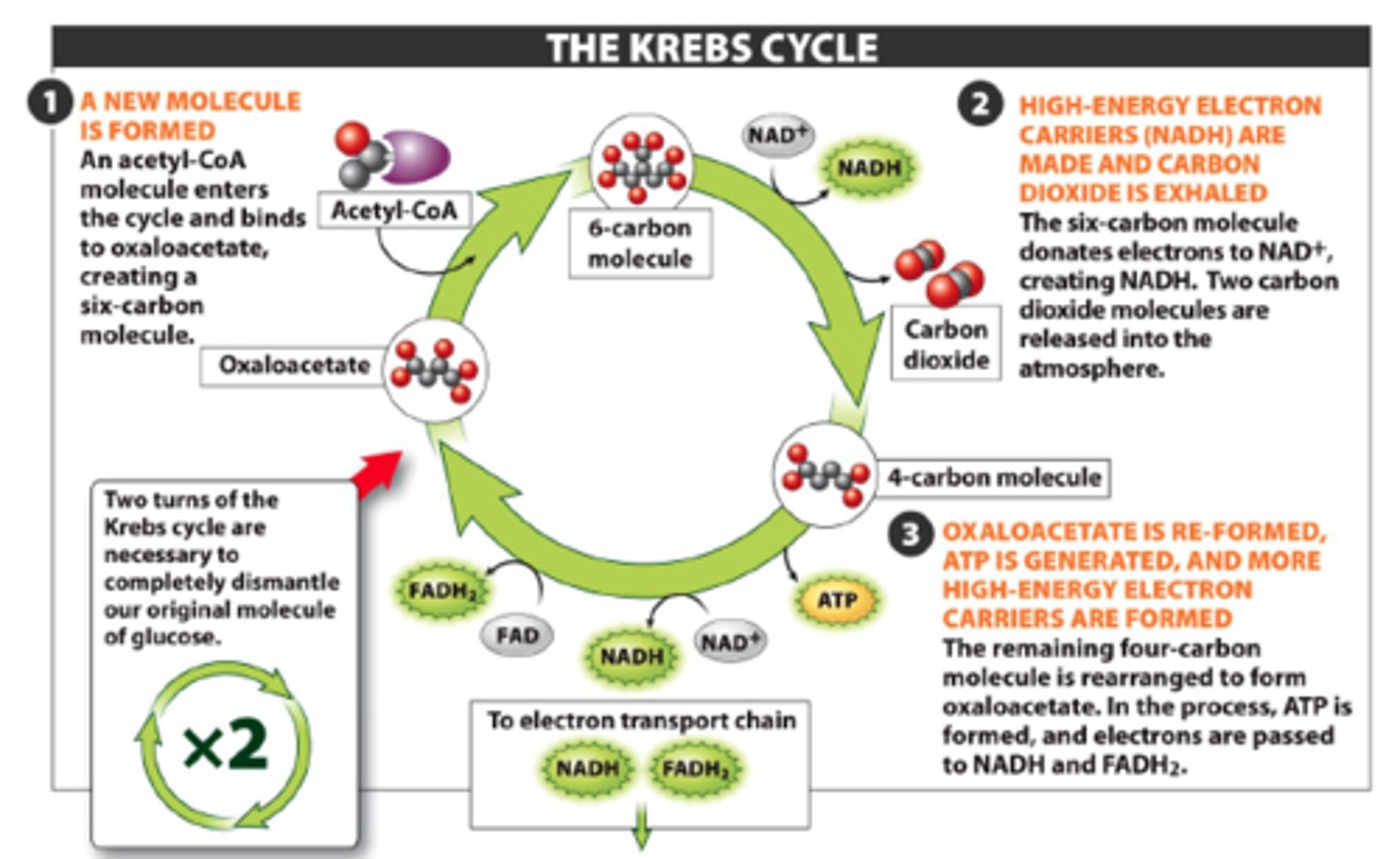
acetyl CoA
molecule formed from the oxidation of pyruvate
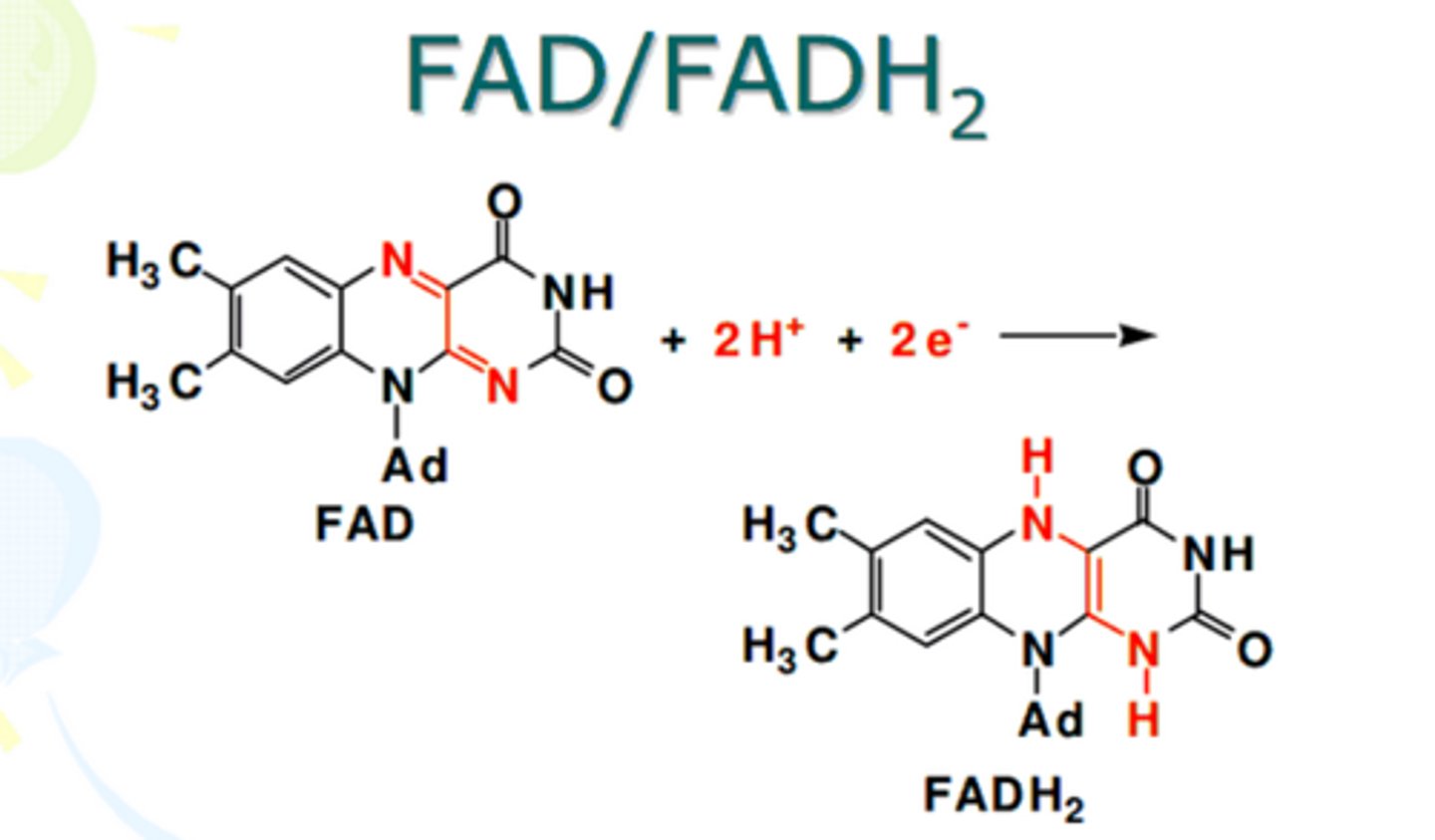
FADH2
a reduced coenzyme similar to NADH, an electron carrier
anaerobic
Occurring without the use of molecular oxygen, O2.
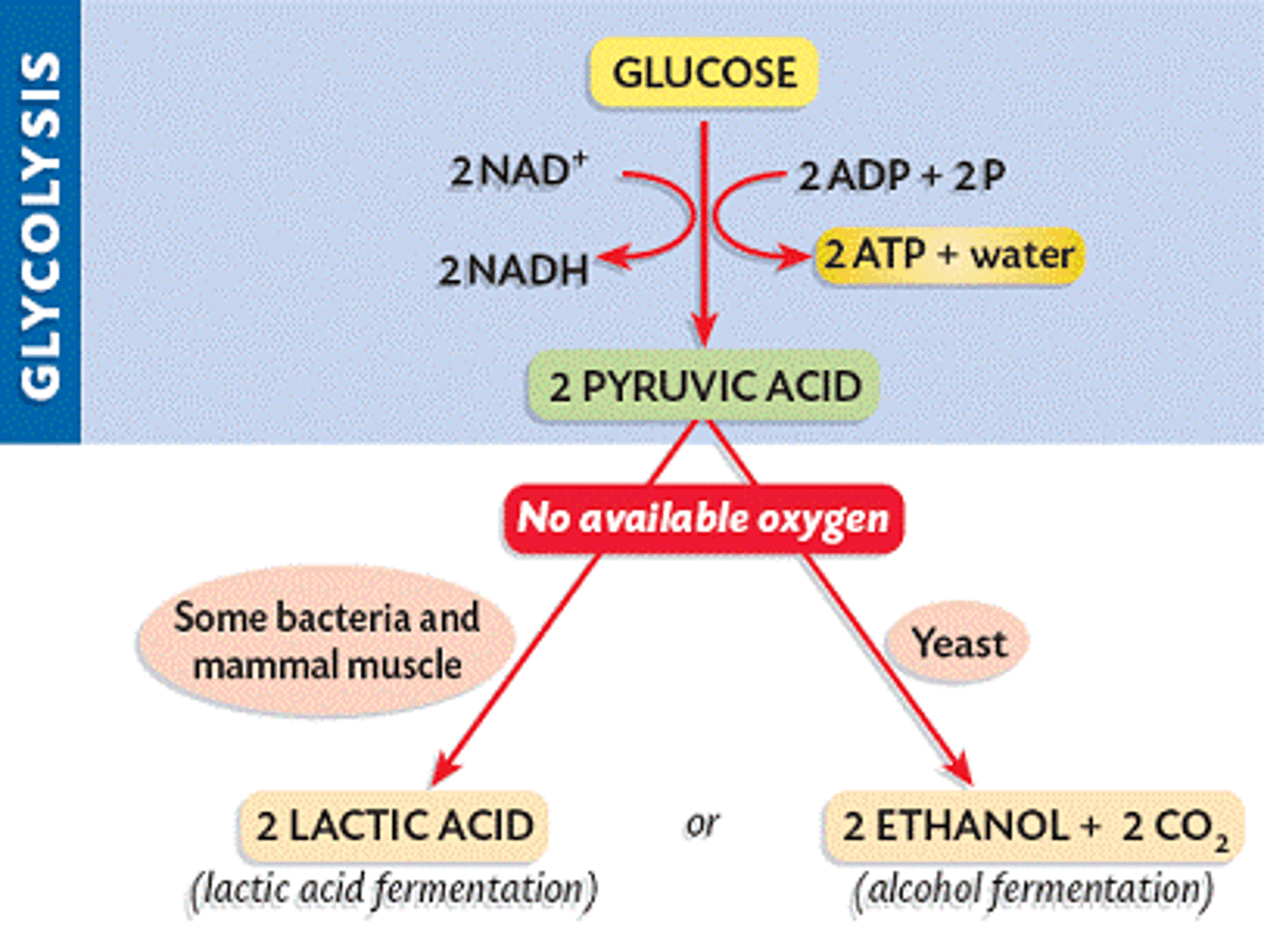
fermentation
Speaking specifically about energy metabolism, the anaerobic degradation of a substance such as glucose to smaller molecules such as lactic acid or alcohol with the extraction of energy. (2) Speaking generally, metabolic processes that occur in the absence of O2.
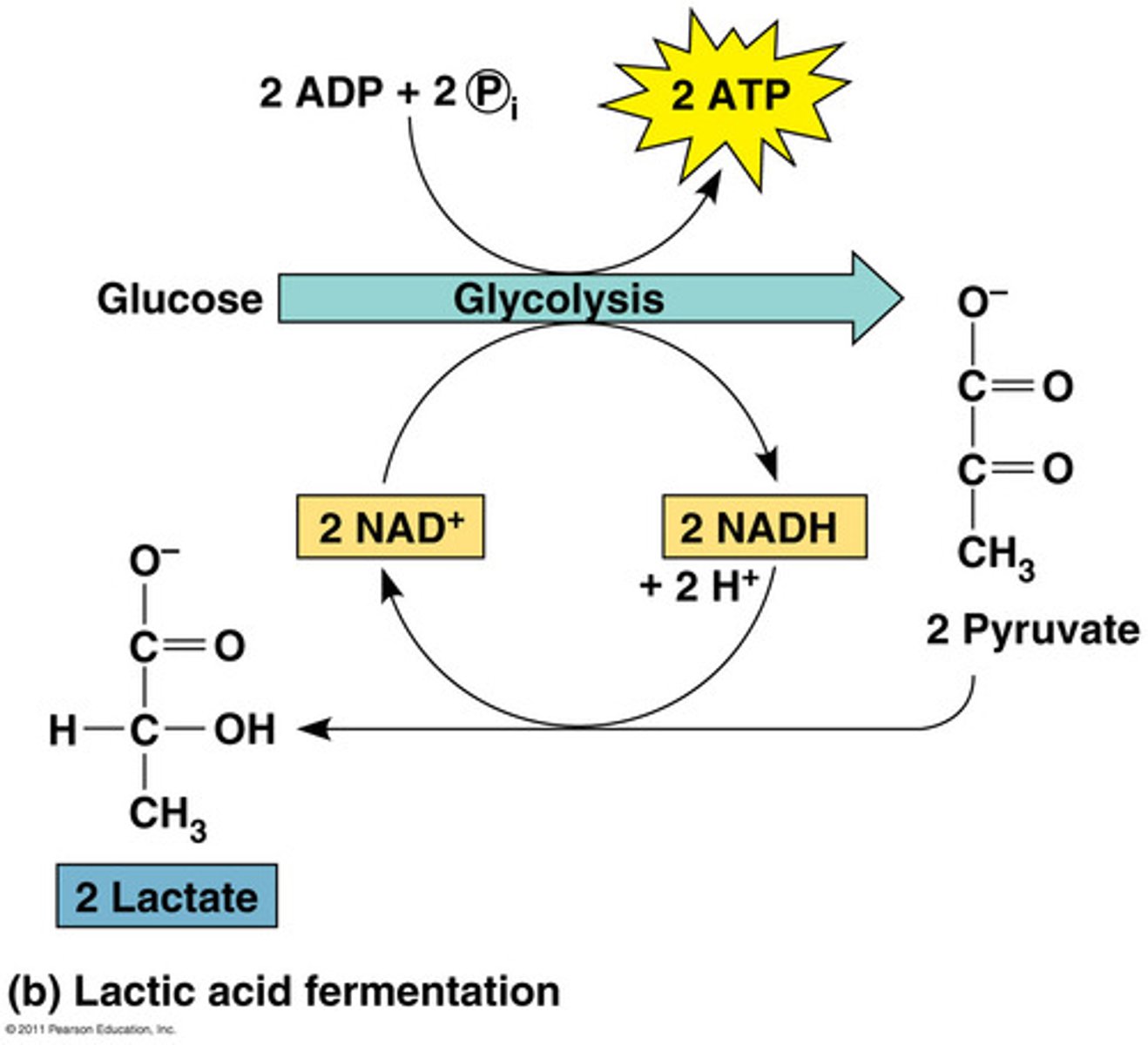
lactic acid fermentation
Anaerobic series of reactions that convert glucose to lactic acid, in some bacteria and animal cells.
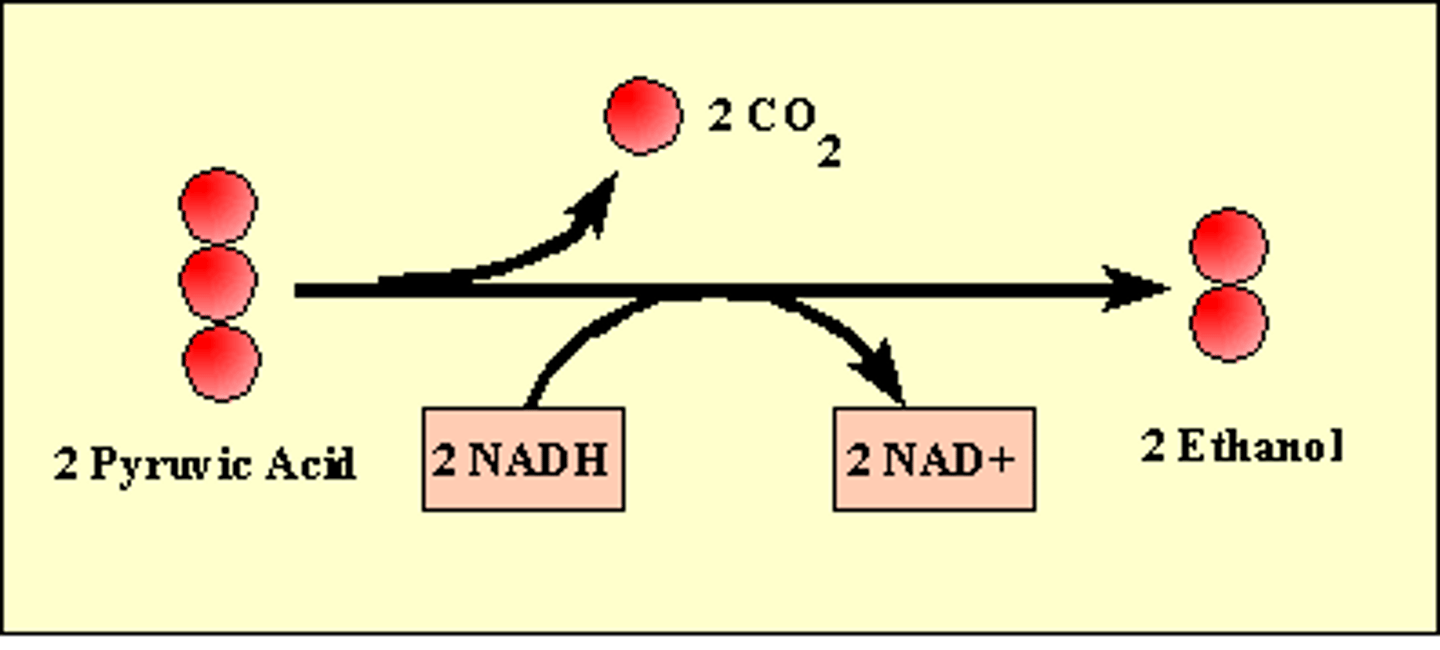
alcoholic fermentation
Anaerobic series of reactions that convert glucose to ethyl alcohol (ethanol) and carbon dioxide in some plants and yeast cells.
photosynthesis
photosynthesis: Metabolic processes carried out by green plants and cyanobacteria, by which visible light is trapped and the energy used to convert CO2 into organic compounds.
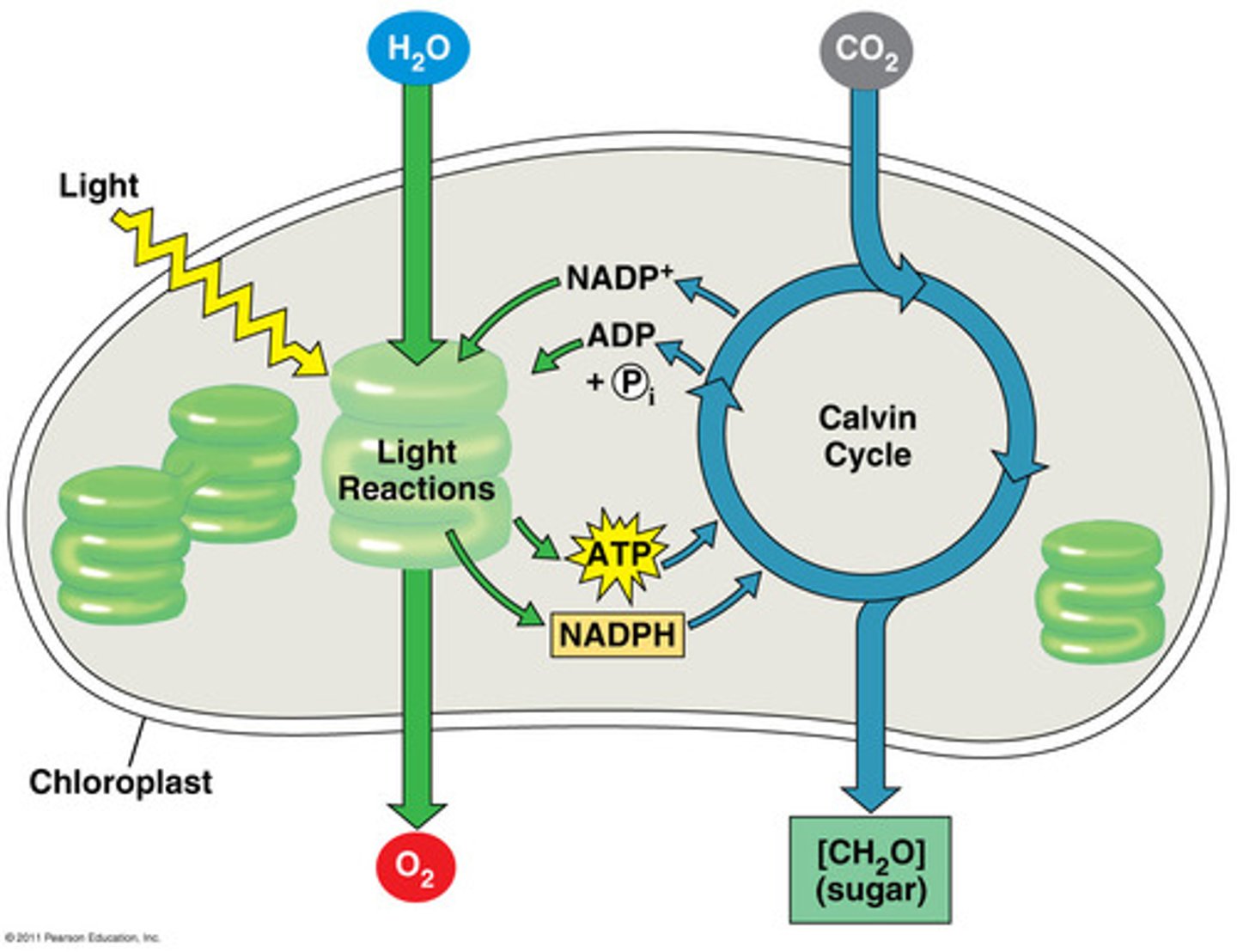
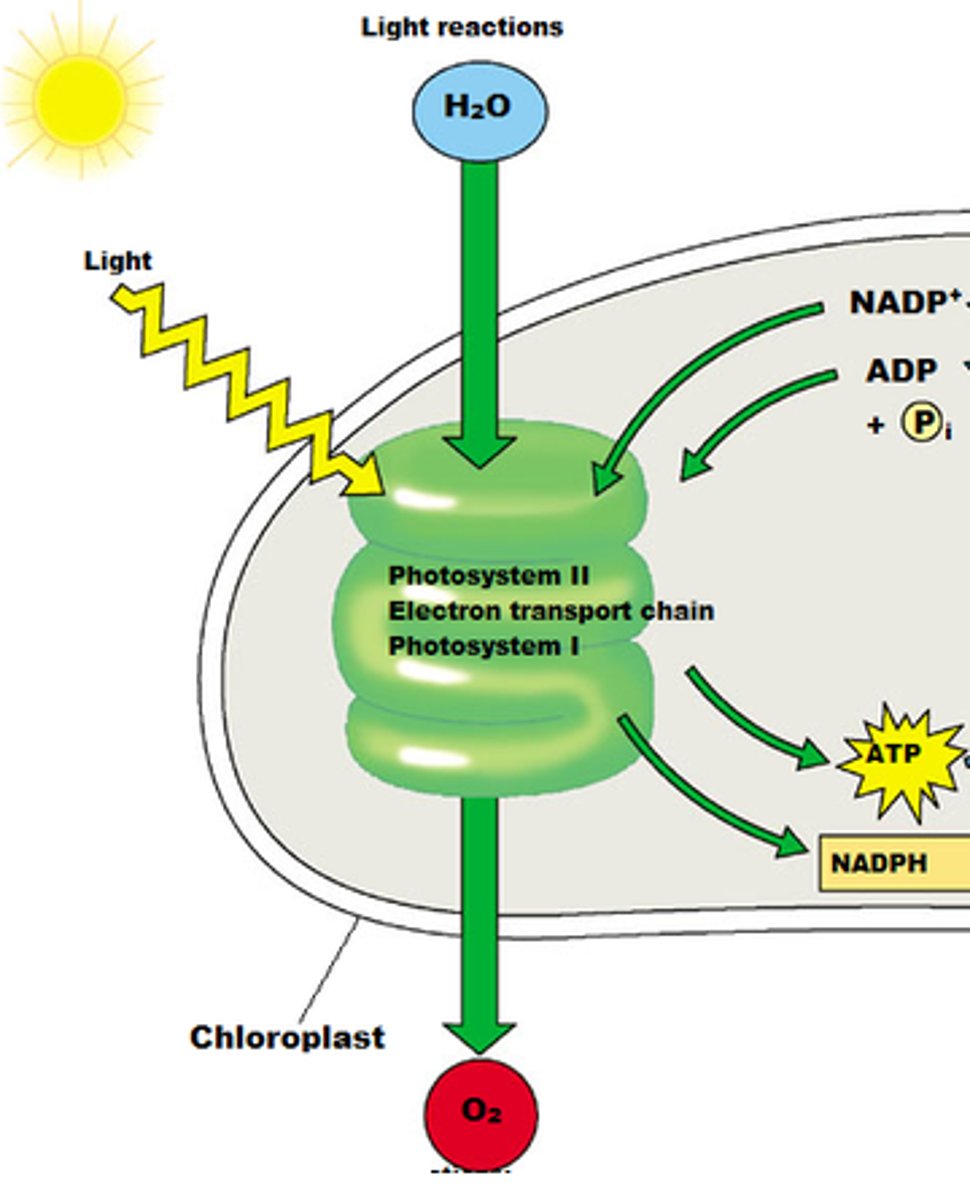
light reactions
The initial phase of photosynthesis, in which light energy is converted into chemical energy.
pigment
A substance that absorbs visible light.

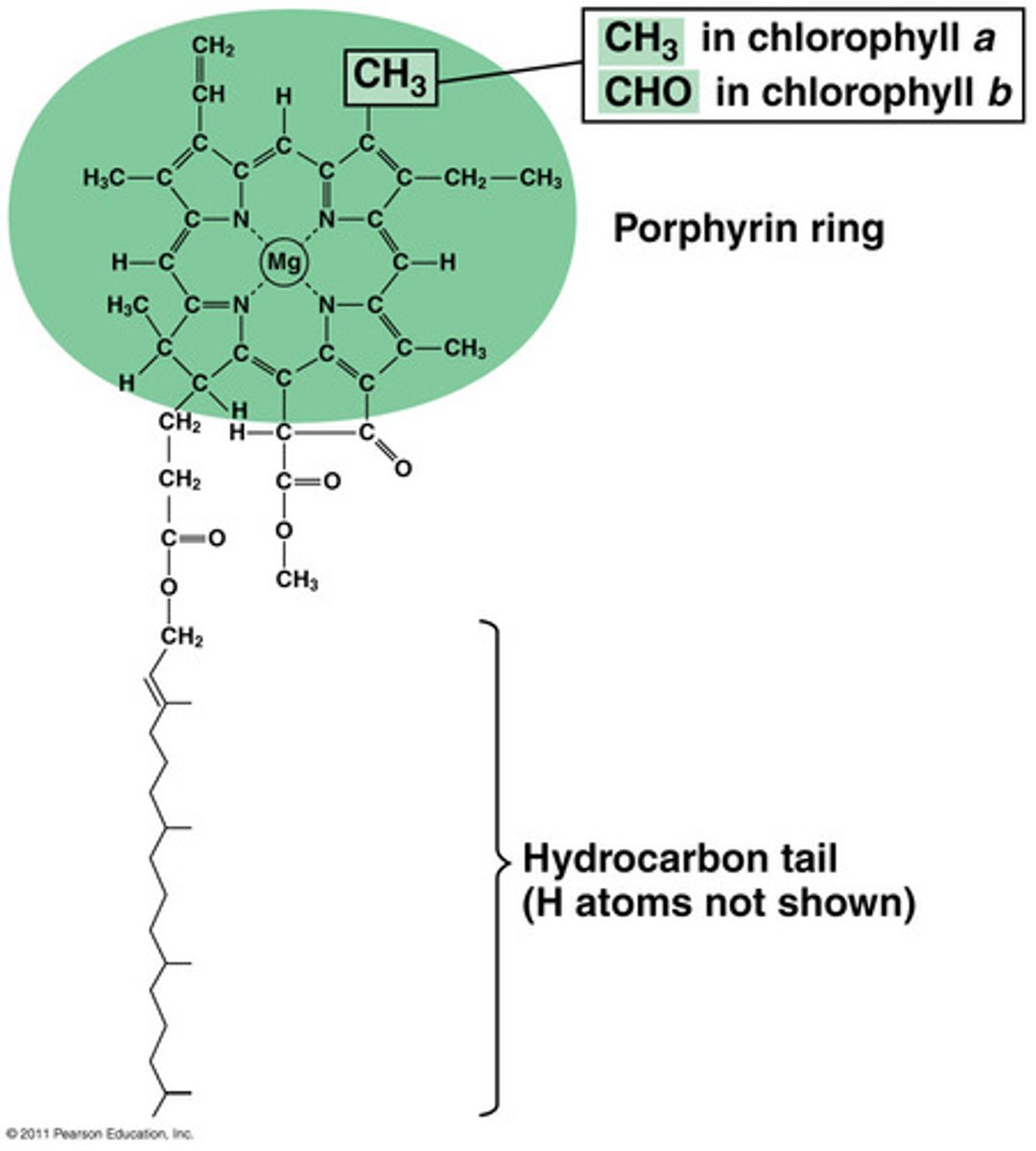
chlorophyll
Any of several green pigments associated with chloroplasts or with certain bacterial membranes; responsible for trapping light energy for photosynthesis.
light-harvesting complex
in photosynthesis, a group of different molecules that cooperate to absorb light energy and transfer it to a reaction center. Also called antenna system.
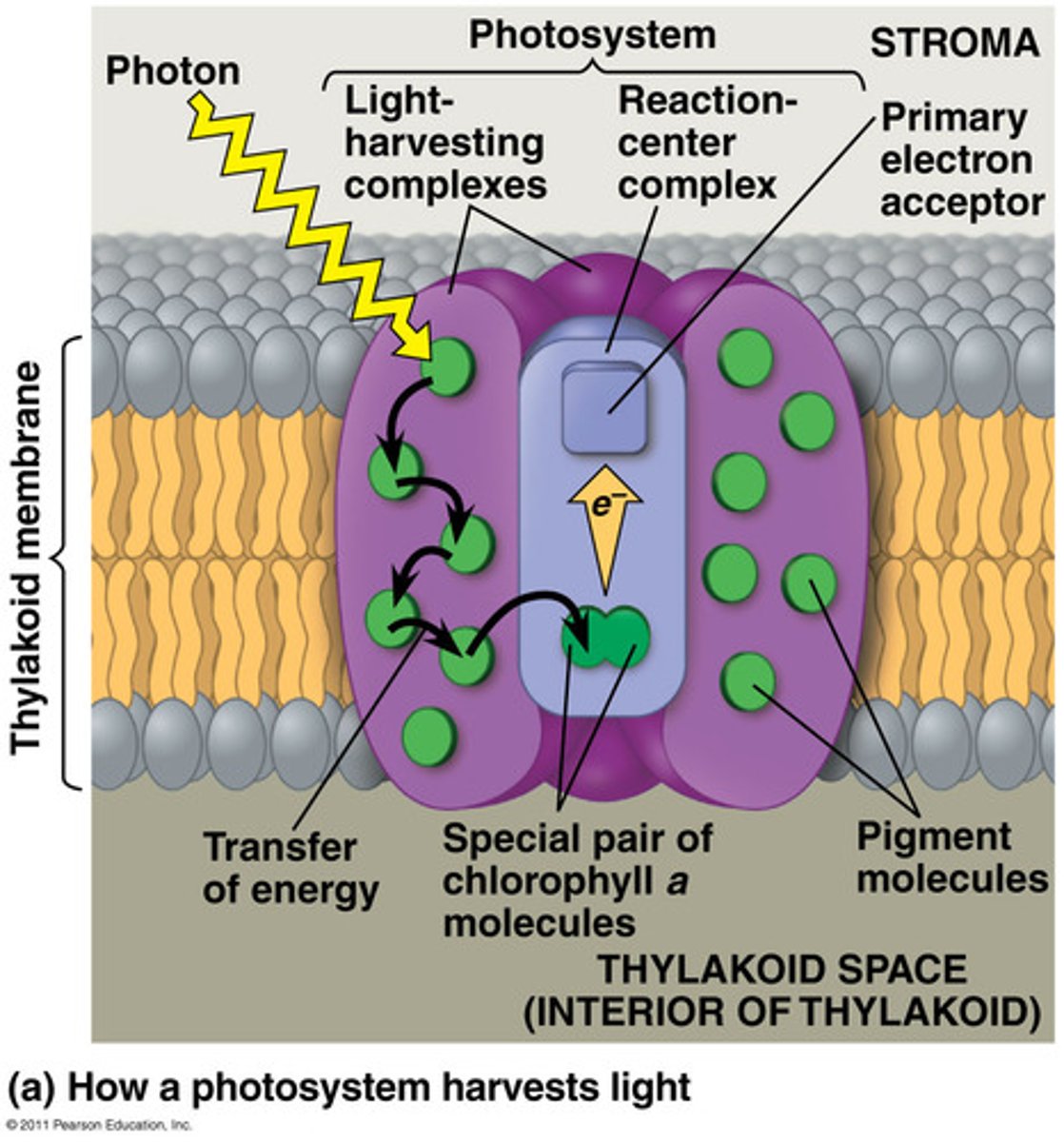
photosystem
A light-harvesting complex in the chloroplast thylakoid composed of pigments and proteins.
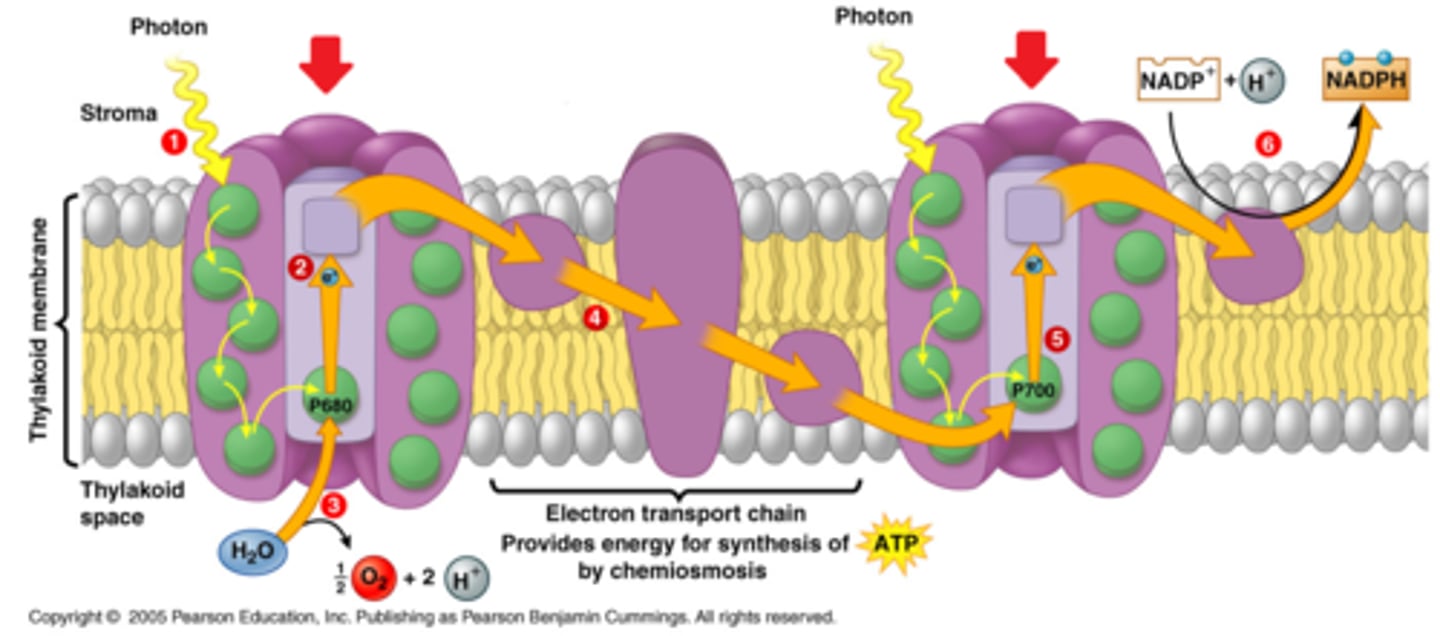
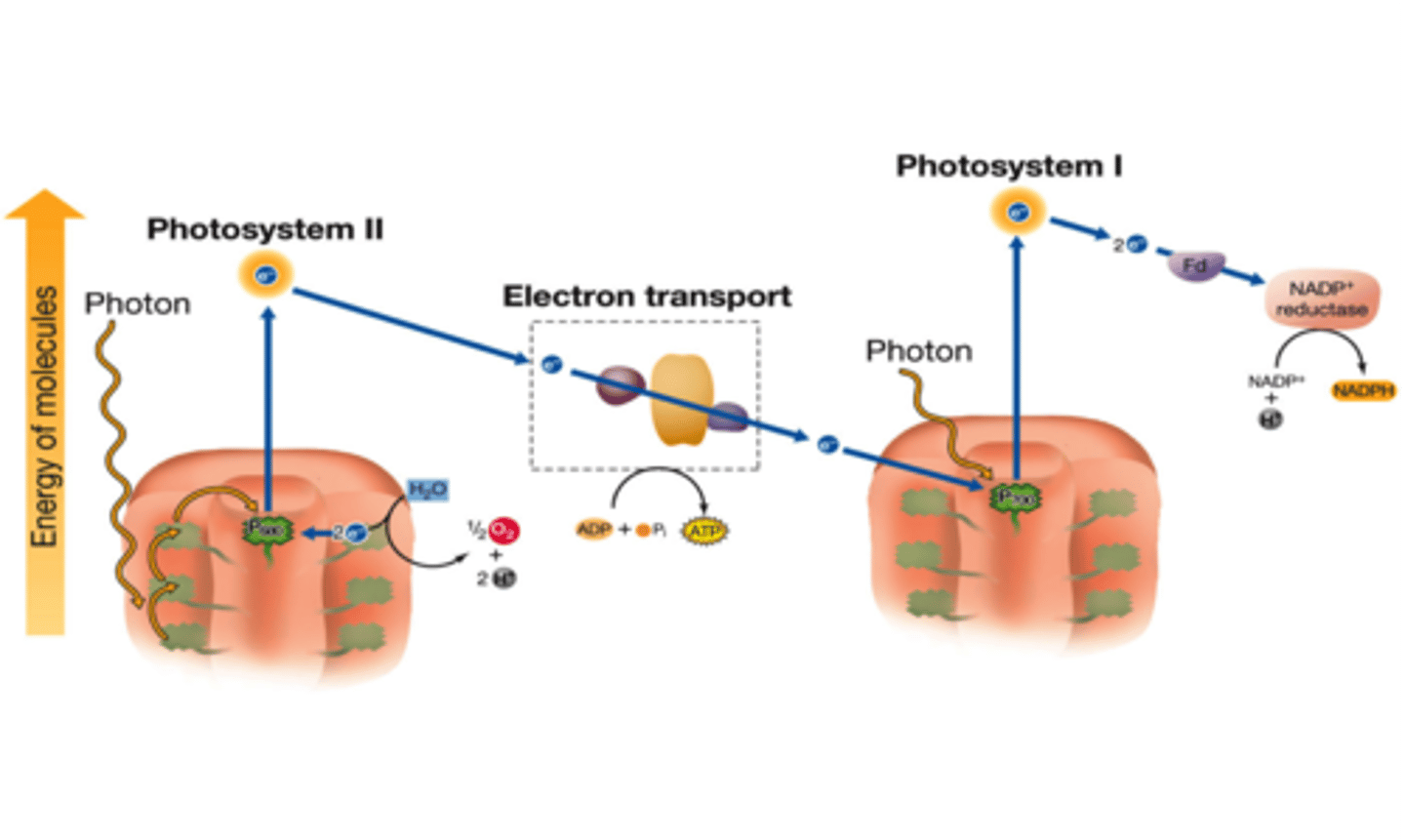
noncyclic electron transport
In photosynthesis, the flow of electrons that forms ATP, NADPH, and O2.
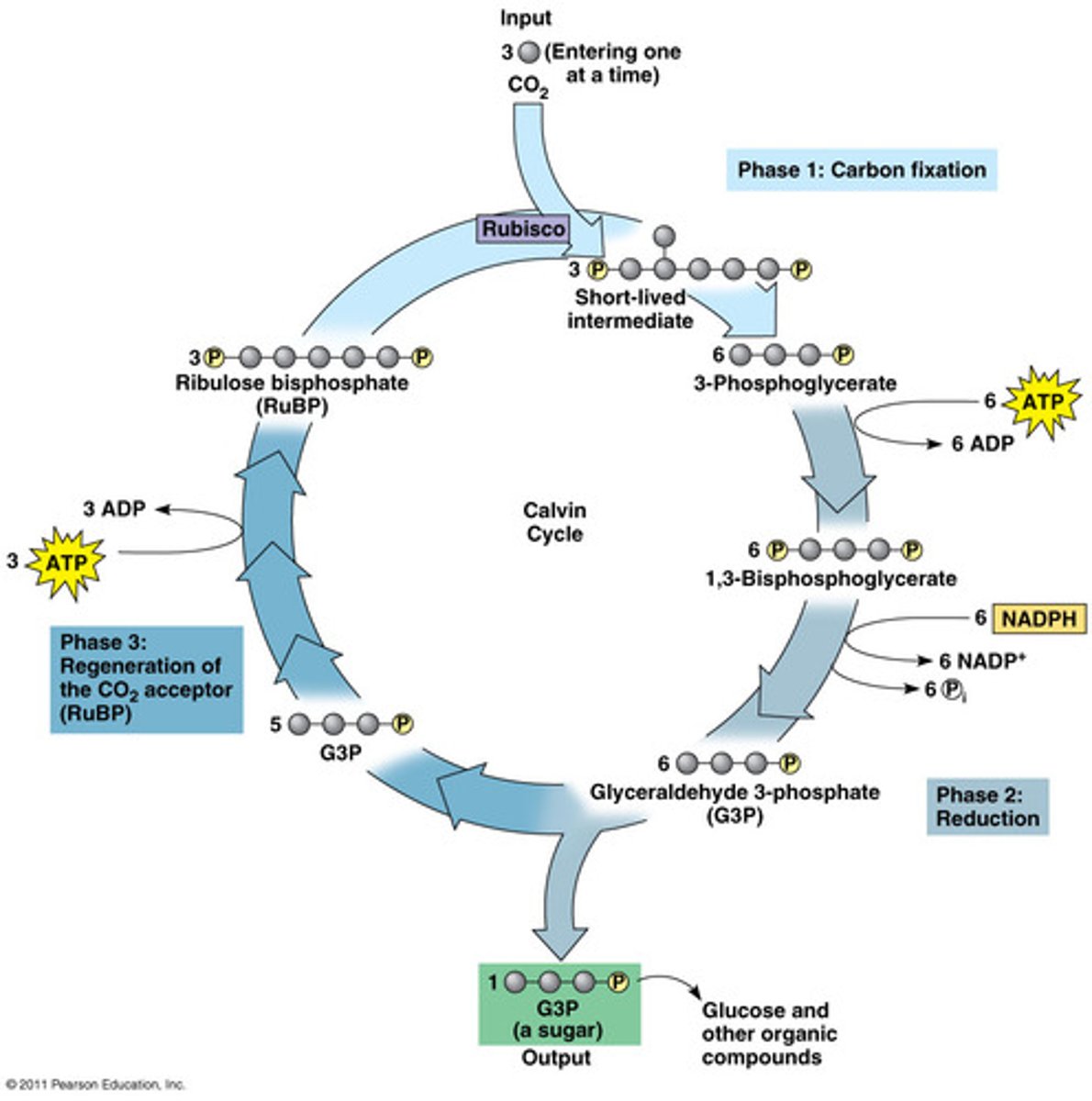
Calvin cycle
a series of enzyme-assisted chemical reactions that produces a three-carbon sugar
metabolism
The sum of the building & breaking reactions occurring in cells