Addition to Alkenes
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Module 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Hydroboration Reaction
Markovnikov
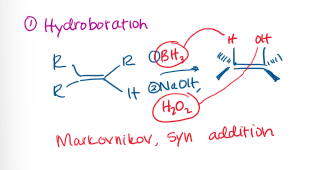
Hydroboration Reactants
Alkene +
BH3 (Boron)
NaOH, H2O2 (Sodium Hydroxide, Hydrogen Peroxide)
Oxymercuration-Demercuration Reaction
Markovnikov
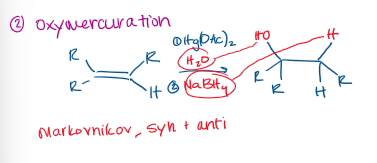
Oxymercuration-Demercuration Stereochemistry
Racemic, if chiral centers are created.
⭐ Oxymercuration–demercuration is Markovnikov hydration with no rearrangements and no stereochemical control.
⭐ You do NOT assign syn or anti in the final product.
Hydrogenation Conditions
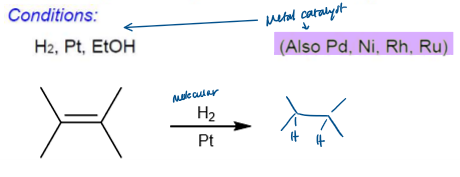
Hydrogenation Stereochemistry
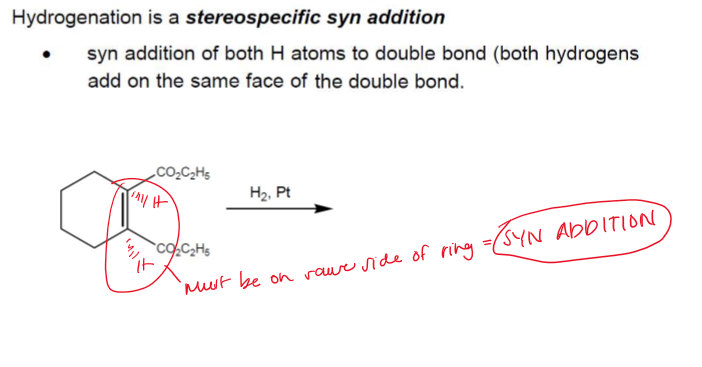
Hydrogenation Melting Point Consideration
More substitution = more stable, lower activation energy
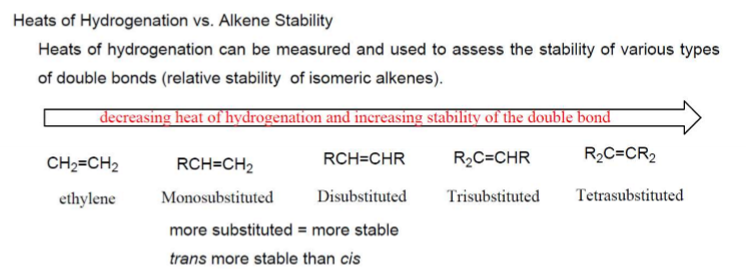
Hydrogenation Consideration
Hydrogenation is stereoselective, corresponding to addition to the less crowded face of the double bond
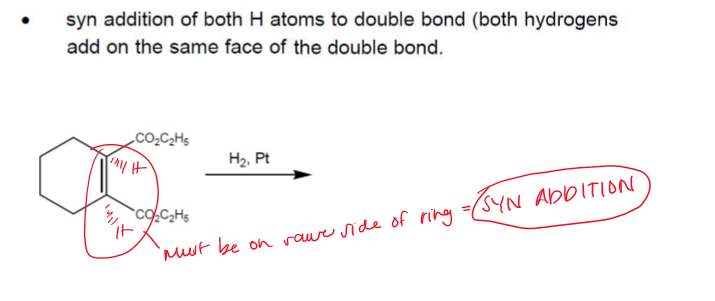
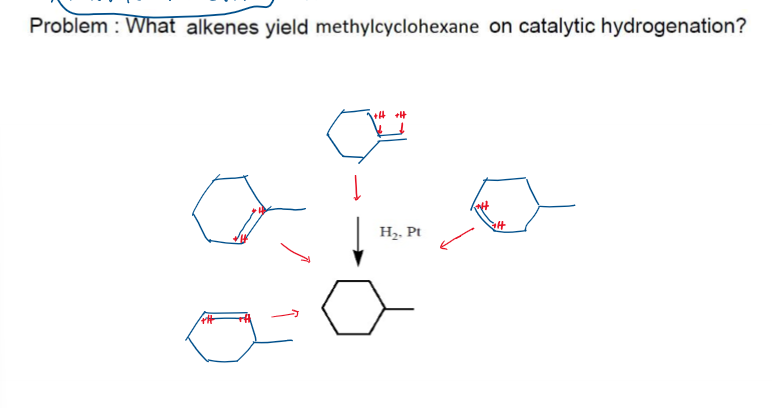
Hydrogenation Possible Reactions
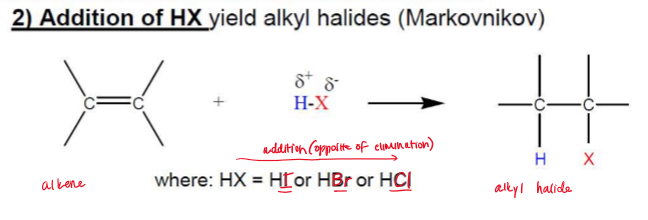
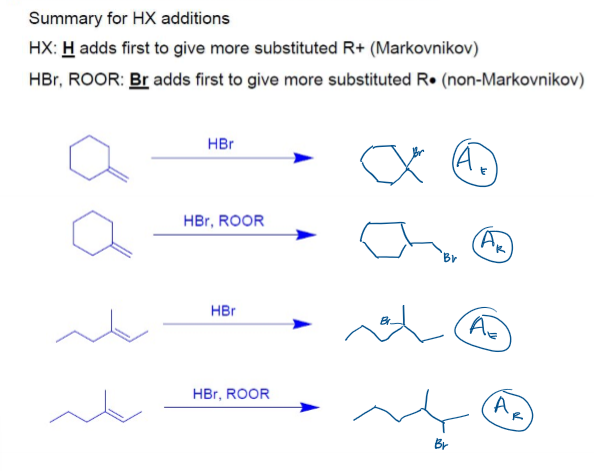
Addition of H-X (Hydrohalogenation)
Electrophilic Addition, AE
Rearrangements possible via methyl, hydride shifts
No stereochemical control, often racemic
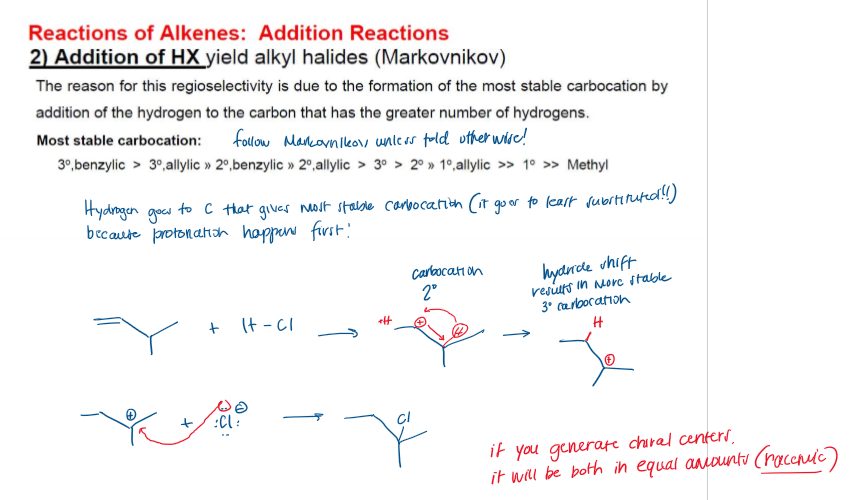
Markovnikov Hydrohalogenation Mechanism
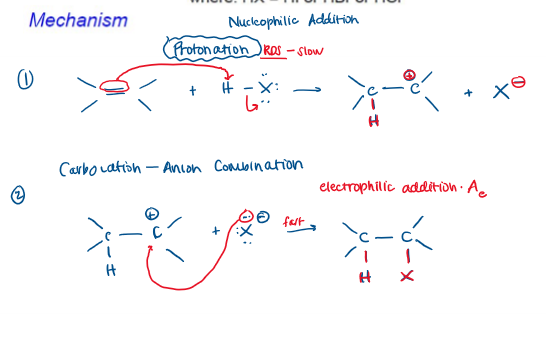
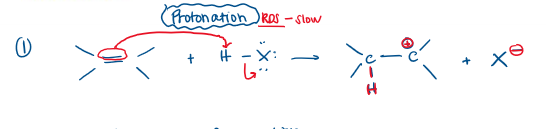
Markovnikov Hydrohalogenation Rate-Determining Step
Protonation (Step 1)
Markovnikov Rule

Hydrohalogenation Considerations
Carbocation always forms where it is most stable (tertiary > secondary > primary), this occurs through hydride shift. If chiral centers are generated, it is racemic.
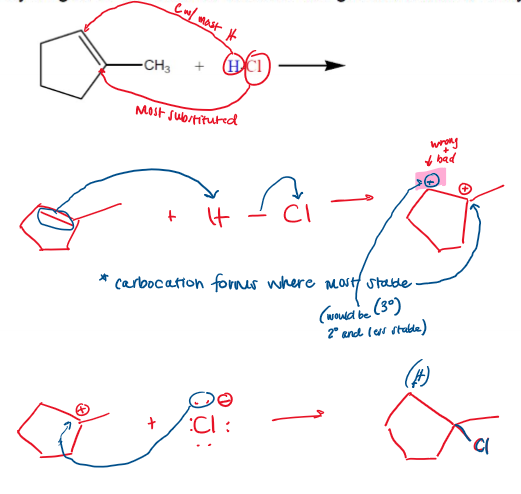
Hydride Shift Mechanism
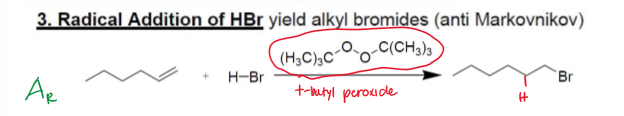
Anti-Markovnikov Hydrohalogenation (Radicalic Addition of H-Br)
Radicalic Addition, AR
Anti-Markovnikov Hydrohalogenation (Radicalic Addition of H-Br) Mechanism
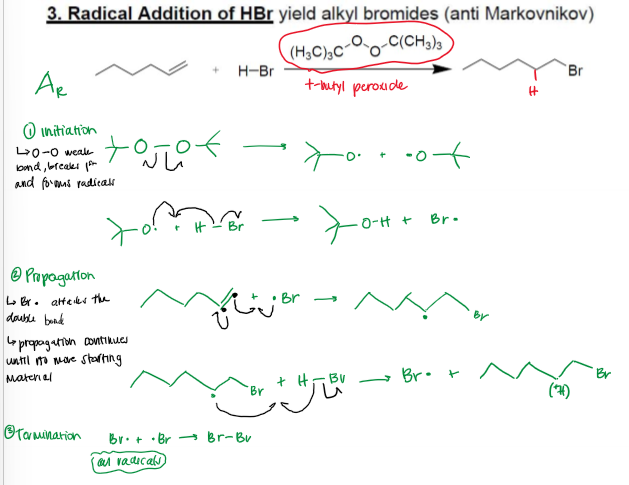
Anti-Markovnikov Hydrohalogenation (Radicalic Addition of H-Br) Conditions
H-Br, ROOR (t-Bu-O-O-t-Bu) [peroxide]
![<p>H-Br, ROOR (t-Bu-O-O-t-Bu) [peroxide]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f2318de2-7fba-428c-88b7-c92667235f92.png)
Anti-Markovnikov Hydrohalogenation Radical Stability

Markovnikov v. Anti-Markovnikov Hydrohalogenation
DIfferent Types of Hydration Reactions (Addition of H2O)
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration (rearrangement allowed), Markovnikov
50% H2SO4 + 50% H2O
Oxymercuration-Demercuration Hydration (rearrangement prohibited), Markovnikov
Hg(OAc)2 + H2O
NaBH4
Hydroboration-Oxidation Hydration, anti-Markovnikov
BH3 + THF complex, hydroboration
H2O2 + KOH + H2O
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration summary
Markovnikov
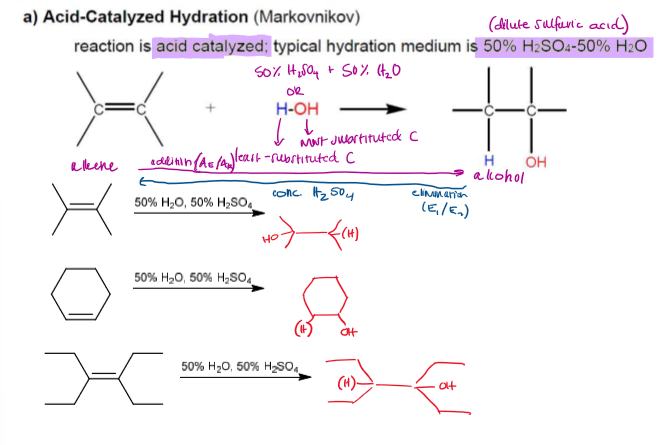
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration (Markovnikov, rearrangement allowed) Mechanism
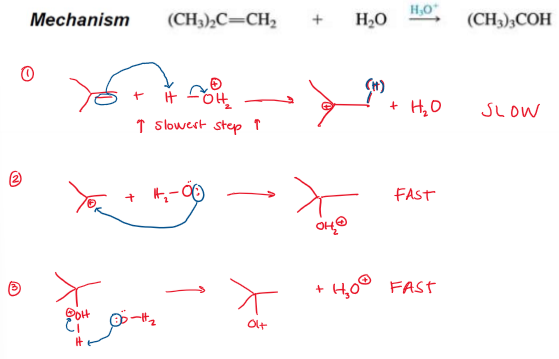
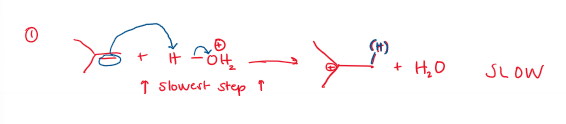
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration (Markovnikov, rearrangement allowed) Rate-Determining Step
The more stable the carbocation, the faster it is formed. Rearrangement is allowed.
Oxymercuration-Demercuration Hydration (Markovnikov, no rearrangement)
don’t have to know mechanism!
Oxymercuration-Demercuration Hydration (Markovnikov, no rearrangement) Conditions
Hg(OAc)2 + H2O
NaBH4
Hydroboration-Oxidation Hydration (anti-Markovnikov) Conditions
BH3 + THF Complex (Borane, Tetrahydrofuran)
H2O2 + KOH + H2O (Hydrogen Peroxide, Potassium Hydroxide, Water)
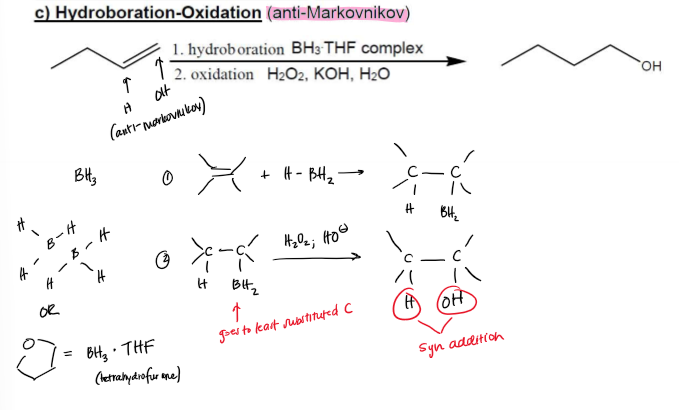
Hydroboration-Oxidation Hydration (anti-Markovnikov) Mechanism
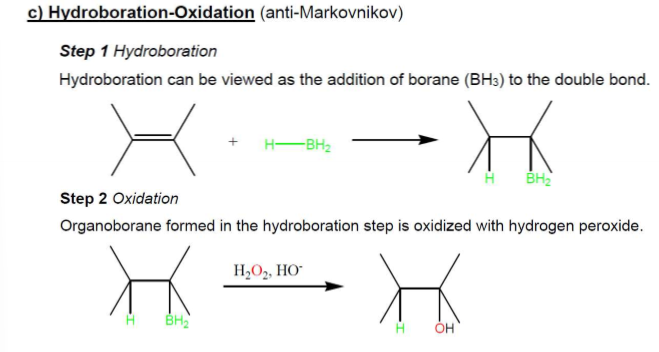
Hydroboration-Oxidation Hydration (anti-Markovnikov) Examples
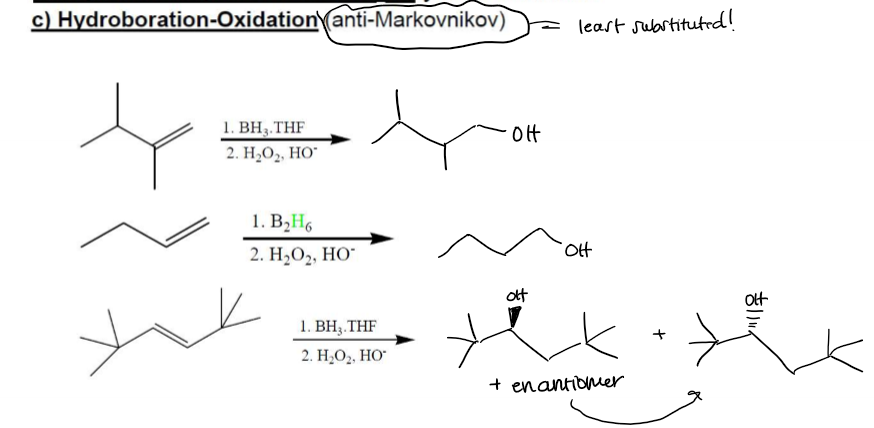
Hydroboration-Oxidation Hydration (anti-Markovnikov) Regioselectivity
Anti-Markovnikov, no rearrangement allowed
Hydroboration-Oxidation Hydration (anti-Markovnikov) Stereochemistry
stereospecific syn addtition, —H and —OH attach to same face of double bond
Halogenation of Alkenes (Addition of Cl2 and Br2)
Electrophilic addition, Ae, forms vicinal dihalide (neighboring carbons get halides), only uses Br and Cl because F is explosive and I is endothermic, -anti addition
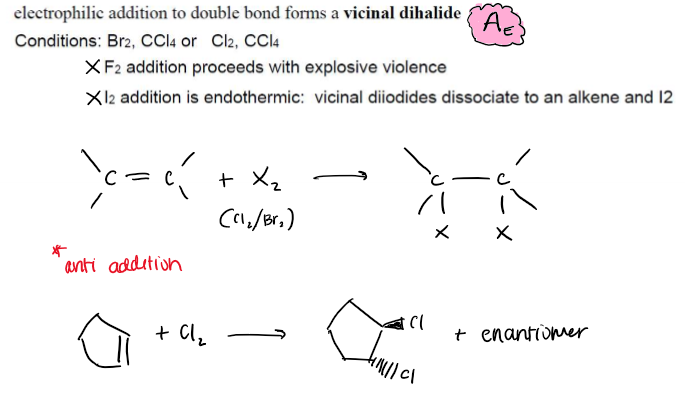
Halogenation of Alkenes (Addition of Cl2 and Br2) Stereochemistry
anti addition only, syn products NOT formed
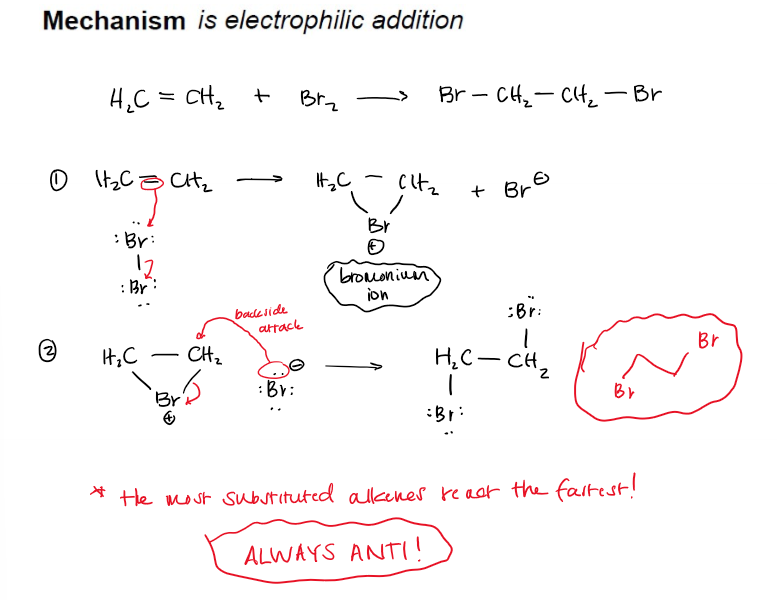
Halogenation of Alkenes (Addition of Cl2 and Br2) Mechanism
*the most substituted alkenes react the fastest!
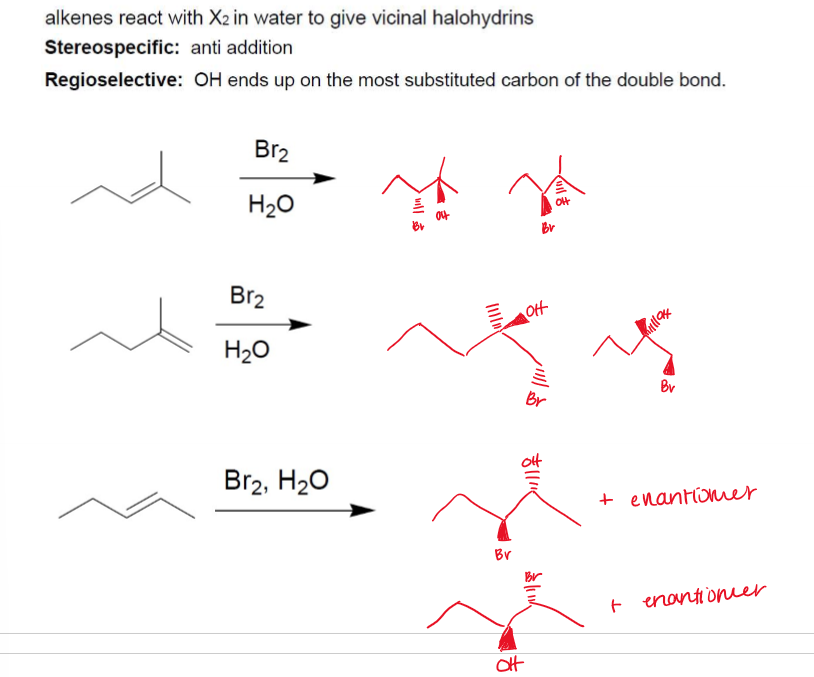
Halohydrin Formation (alkene → alkane + —OH, —X)
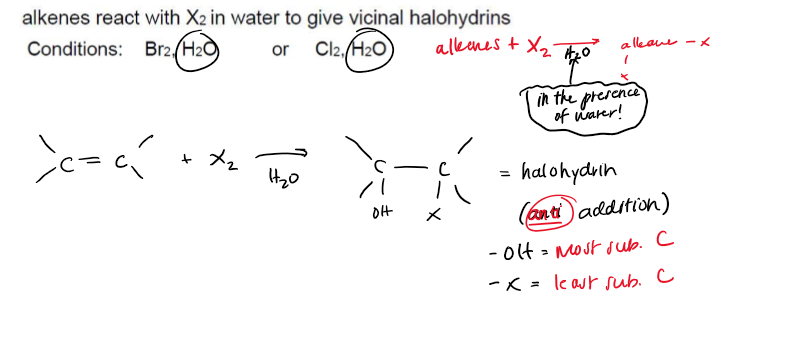
Halohydrin Formation (alkene → alkane + —OH, —X) Conditions
Elemental Halide (Cl2 or Br2), in the presence of H2O
Halohydrin Formation (alkene → alkane + —OH, —X) Stereochemistry
Stereospecific, -anti addition; Regioselective: —OH ends up on the most substituted C of the double bond.
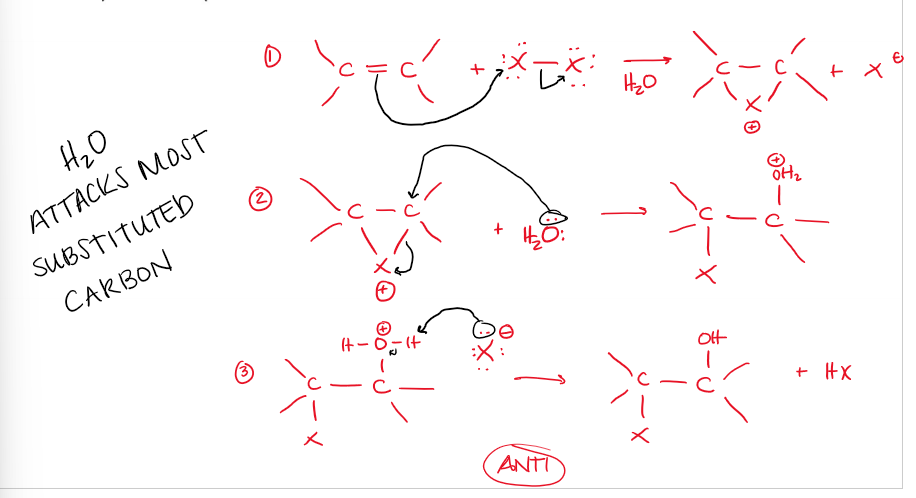
Halohydrin Formation (alkene → alkane + —OH, —X) Mechanism
electrophilic addition, Ae.
Br attaches to both C, removing the pi bond
H2O attacks the most substituted C and that C detaches from Br
Result is -anti addition of H2O and Br across a double bond
H2O deprotonates into the final halohydrin product (+—OH, —X)
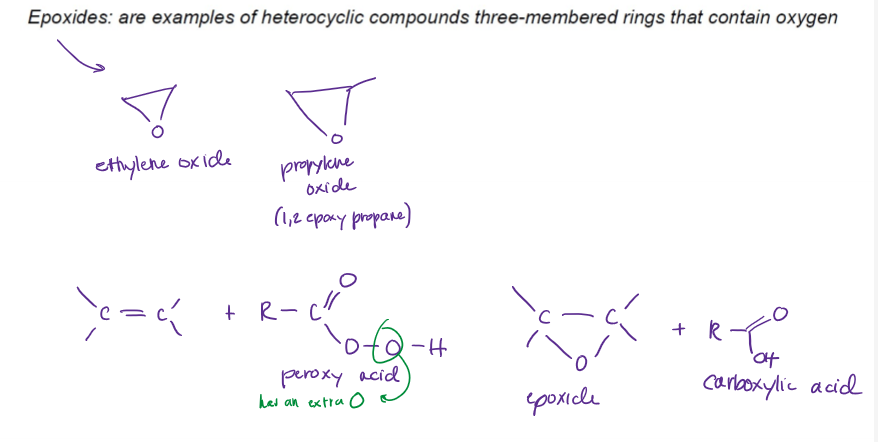
Epoxidation of Alkenes
epoxides are heterocyclic compounds, three-membered rings that contain oxygen, requires peroxyacetic acid or MCPBA
Epoxidation of Alkenes Stereochemistry
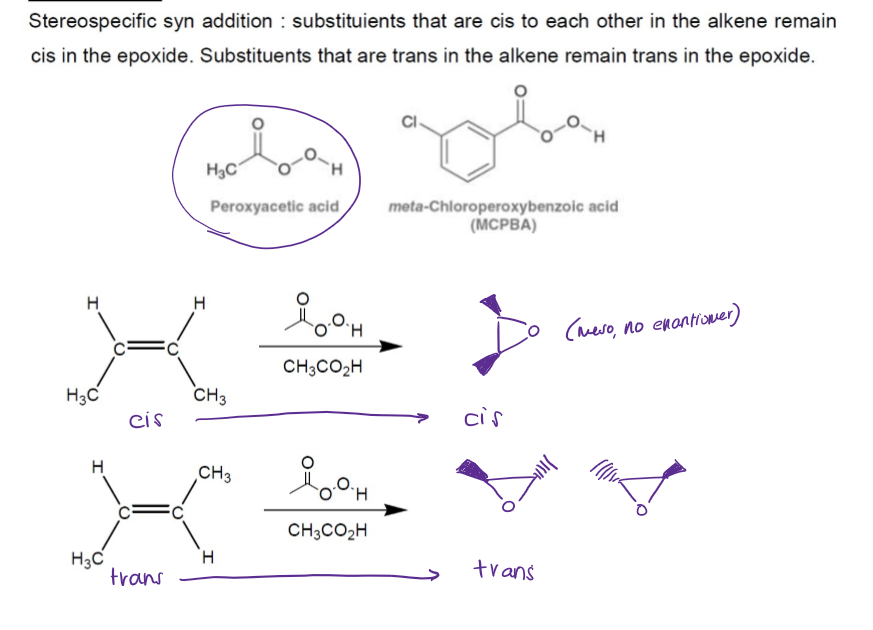
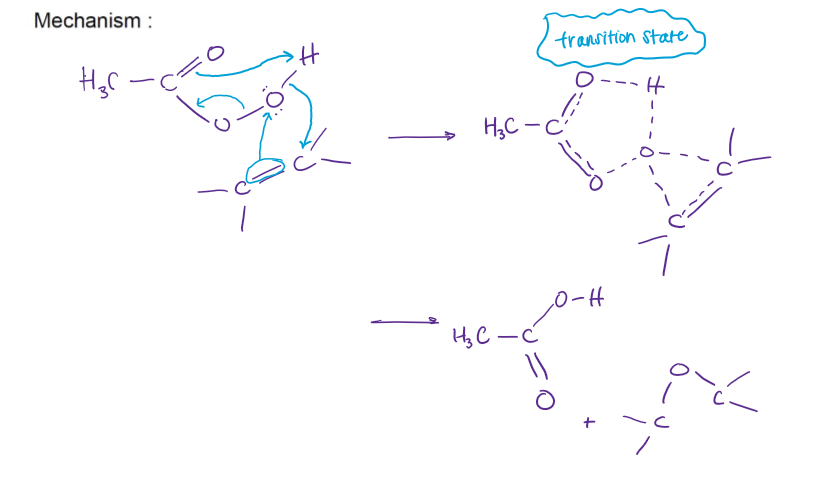
Epoxidation of Alkenes Mechanism
-Anti Dihydroxylation (epoxide first, then anti dihydroxylation)
Epoxidation first, followed by subsequent treatment with H3O+, yields trans-diol
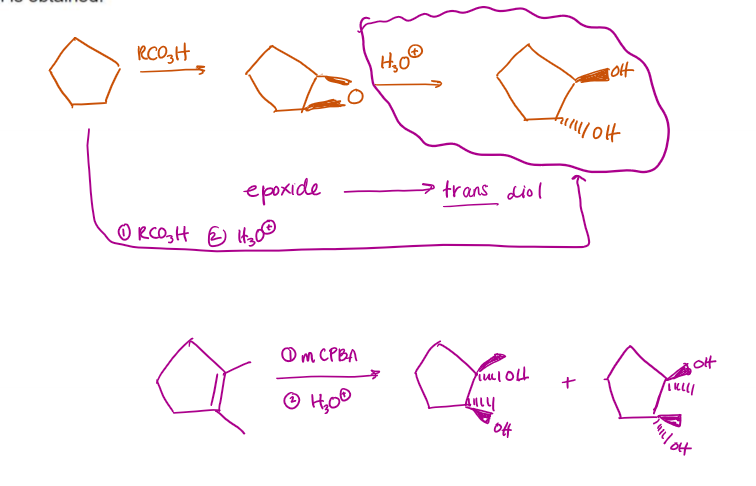
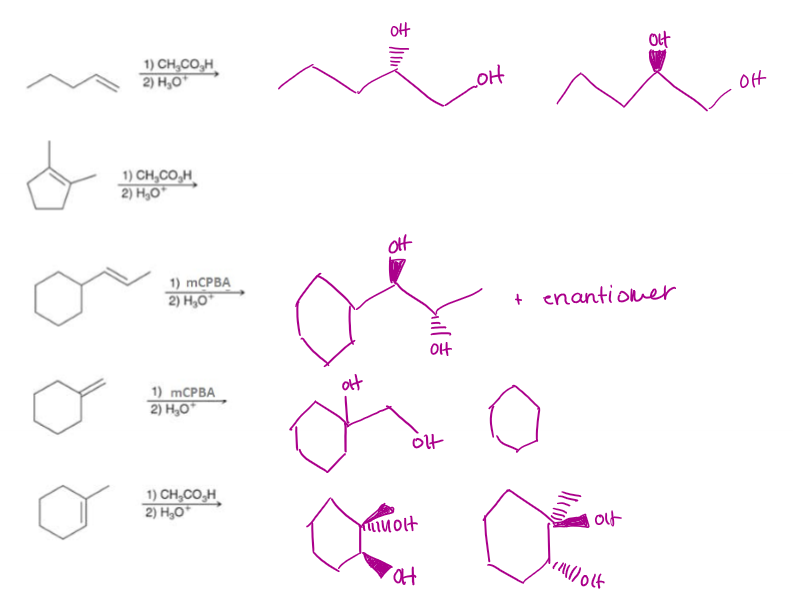
-Anti Dihydroxylation Examples
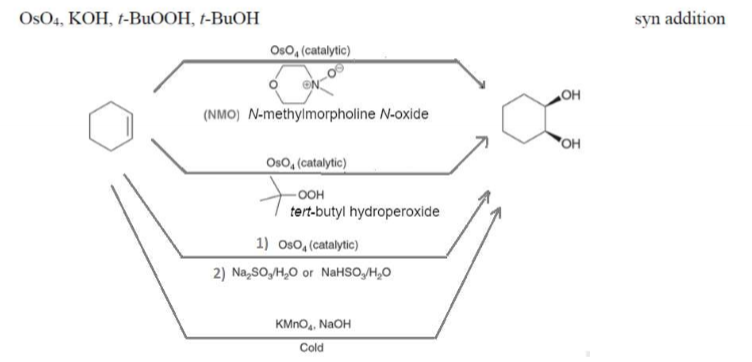
Syn Dihydroxylation Reactants
Can proceed with any of the following conditions
OsO4 (catalytic) +
NMO
tert-butyl hydroperoxide
Na2SO3/H2O or NaHSO3/H2O
KMnO4, NaOH
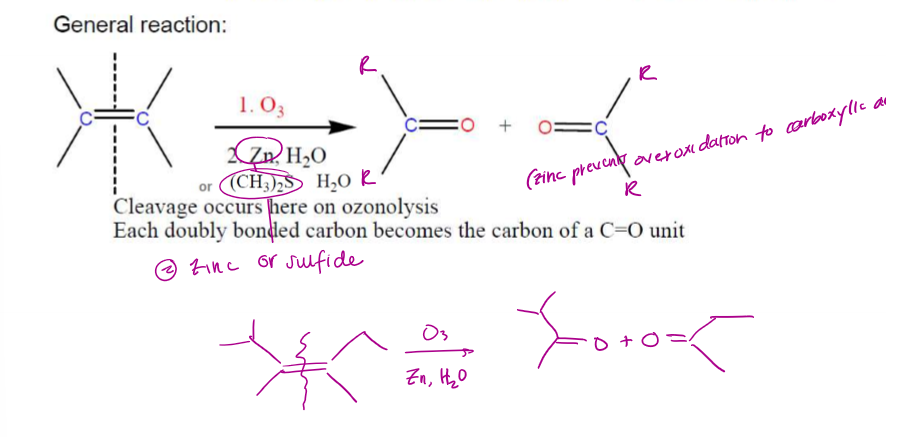
Ozonolysis
General reaction = cleaving of a C=C and the addition of O on each cleaved end, yields C=O (x2)
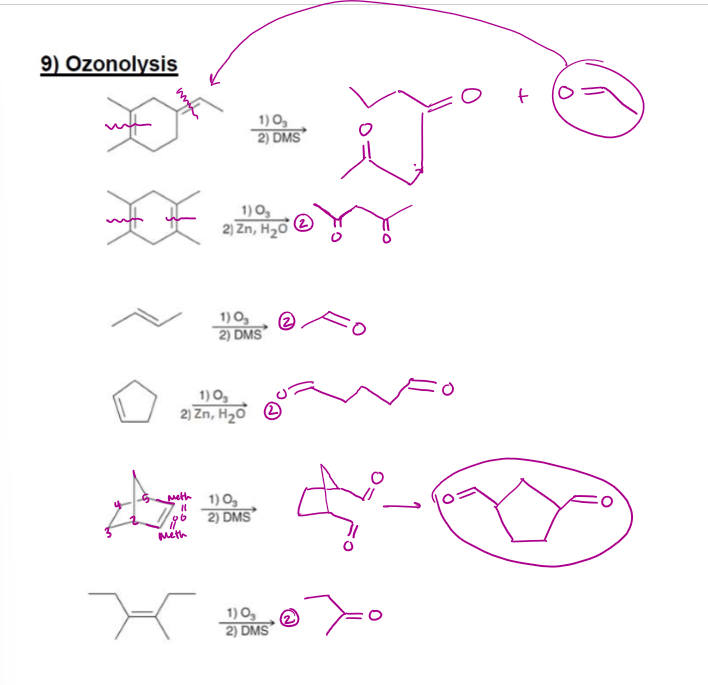
Ozonolyis Examples
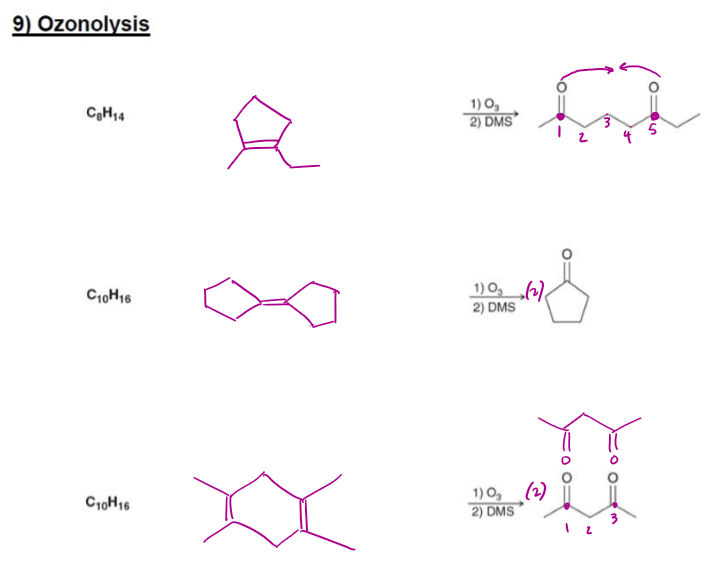
Ozonolysis Reactant Formation Examples
Polymerization Mechanism
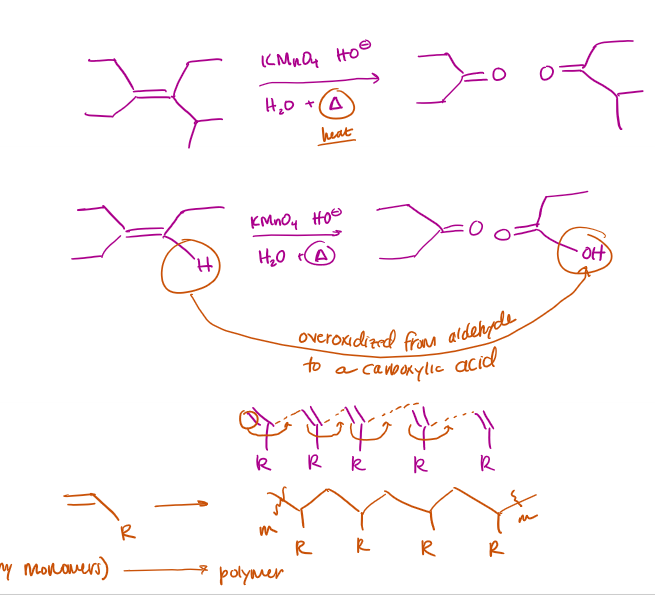
Polymerization Examples
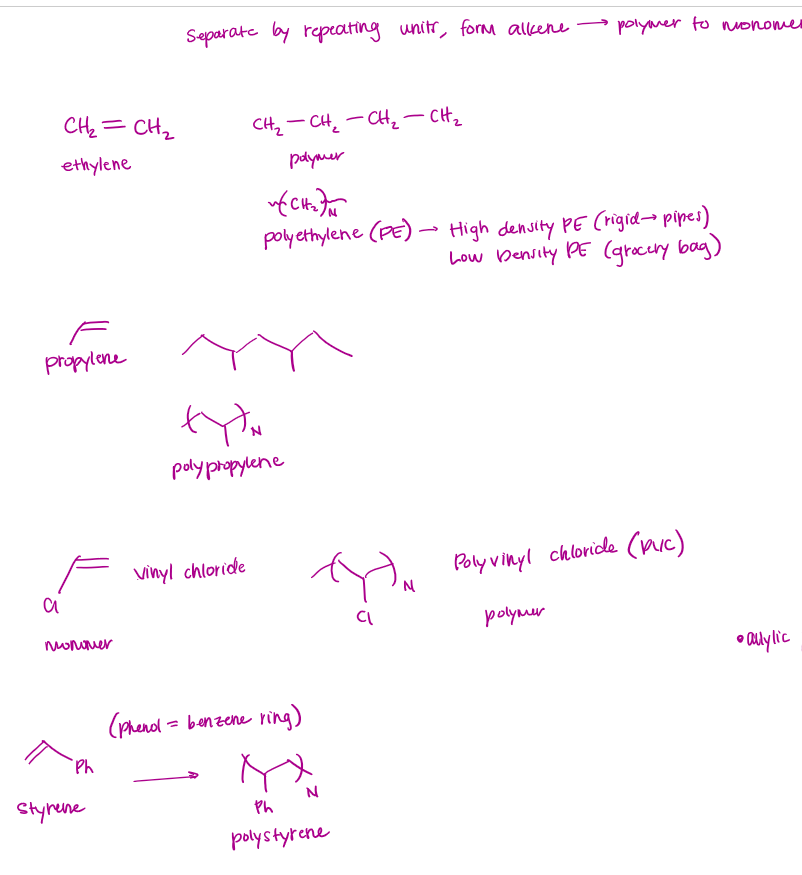
Formation of Alkenes Examples
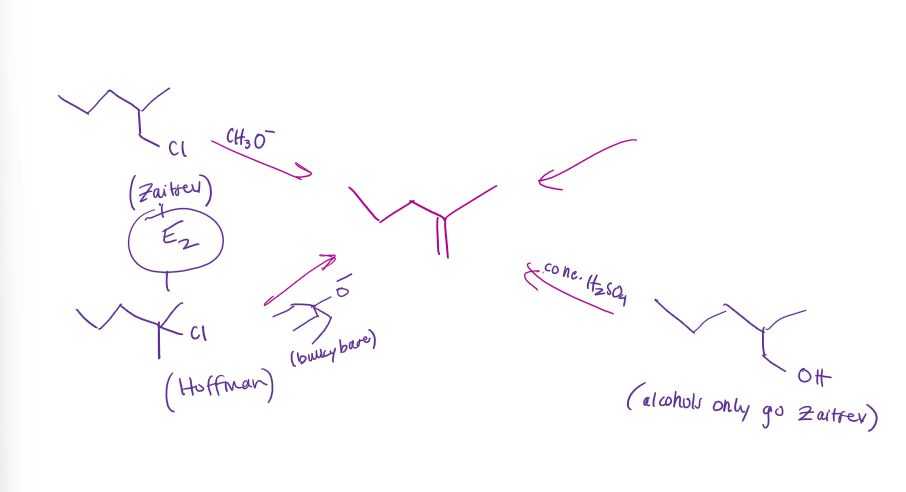
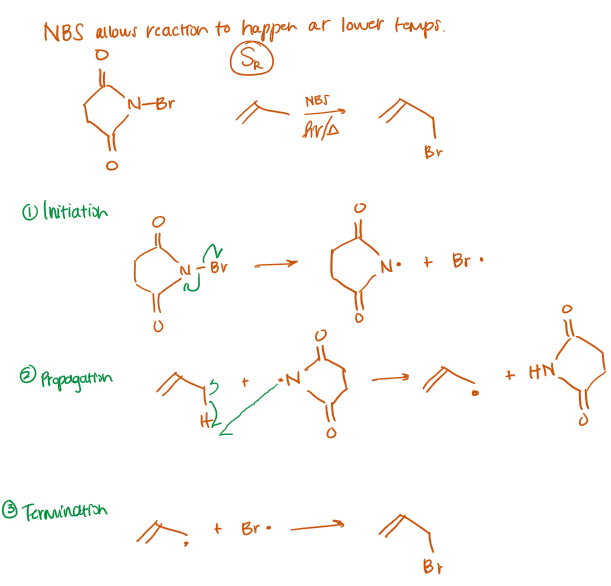
Allylic Bromination (anti-addition of X2) Mechanism
radicalic substitution, SR,
NBS allows this reaction to happen at lower temps, otherwise requires 400C