bone disorders
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
what are the 2 main types of fibro-osseous lesions
fibrous dysplasia
cemento-osseous dysplasia (COD)
what is fibrous dysplasia
tumor-like condition, characterized by replacement of normal bone by fibrous connective tissue intermixed w abnormal bone
what does dysplasia in bone mean
disorganized growth, NOT malignant
fibrous dysplasia is a __________ condition resulting from a ___________ mutation
sporadic condition; postzygotic mutation
fibrous dysplasia may take place where depending on when and where the mutation takes place
one bone → monostotic
multiple bones → polyostotic
skin
endocrine system
is monostotic or polyostotic more common
monostotic
if you have a case of polyostotic, what may this be associated w
syndromes:
McCune-Albright Syndrome
Jaffe-Lichtenstein Syndrome
Mazabraud Syndrome
what conditions are in combination in McCune-Albright Syndrome
Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
cafe au lait spots (coast of Maine)
multiple endocrinopathies
what endocrinopathies can be associated w McCune Albright Syndrome
sexual precocity- early puberty
pituitary adenoma
hyperthyroidism
what gender is most associated w fibrous dysplasia monostotic
M = F
what age is most associated w fibrous dysplasia monostotic
teenage years (2nd or 3rd decade)
common location of fibrous dysplasia monostotic
maxilla > mandible
what is the common feature of the affected area in fibrous dysplasia monostotic
painless, slowly growing swelling of the affected area
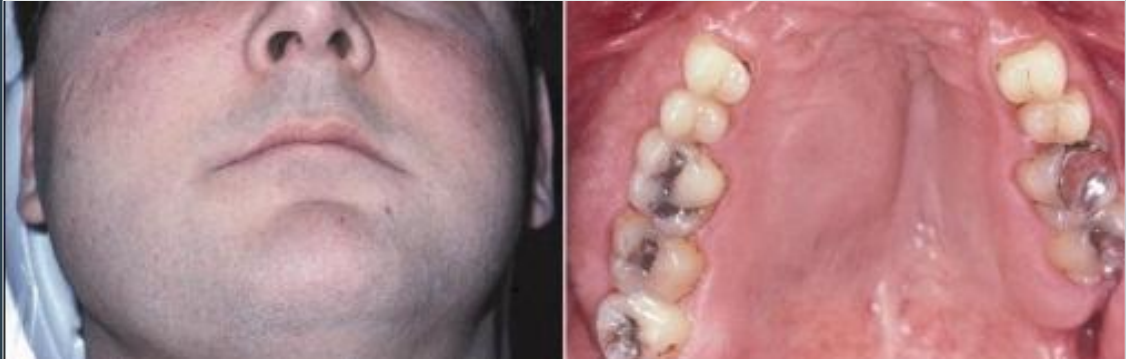
how does fibrous dysplasia appear on a radiograph in
ground glass opacification
not well demarcated, blending
narrow PDL
ill-defined lamina dura
Obliteration of the maxillary sinus
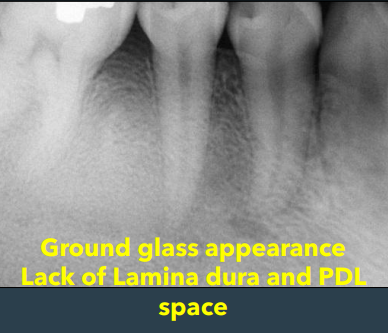
how does fibrous dysplasia progress from the early stage, then how does it progress
may be radiolucent but w time becomes radiopaque
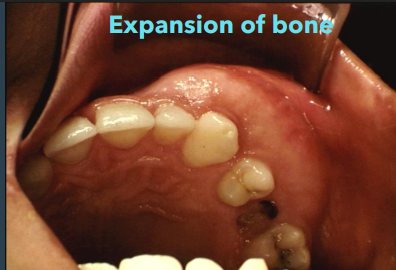
what might you see clinically in fibrous dysplasia
expansion of both the buccal and lingual plates
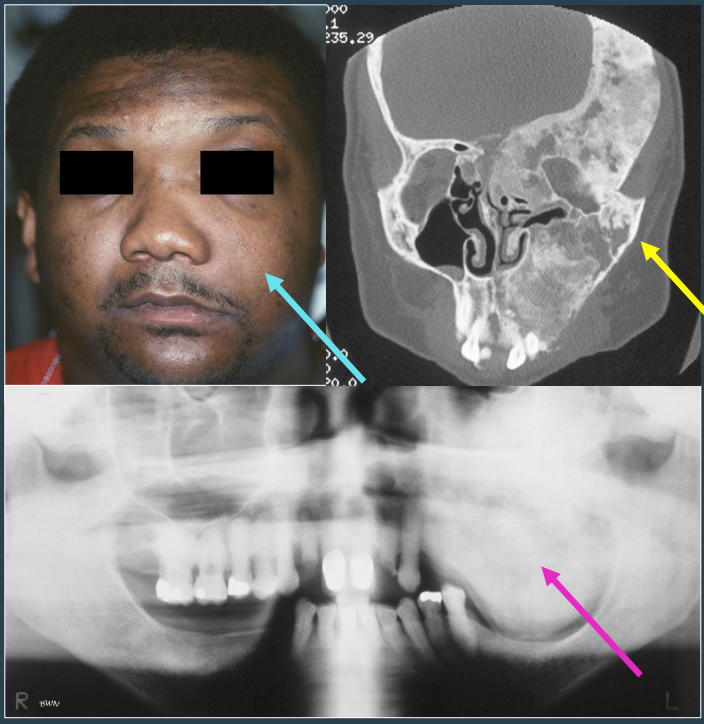
dx
fibrous dysplasia
what is fibrous dysplasia- polyostotic
involvement of two or more bones → can involve up to 75% of skeleton
age most associated w fibrous dysplasia-polyostotic
before 10 yrs- children
how can fibrous dysplasia- polyostotic present
if jaw involved, facial asymmetry may result
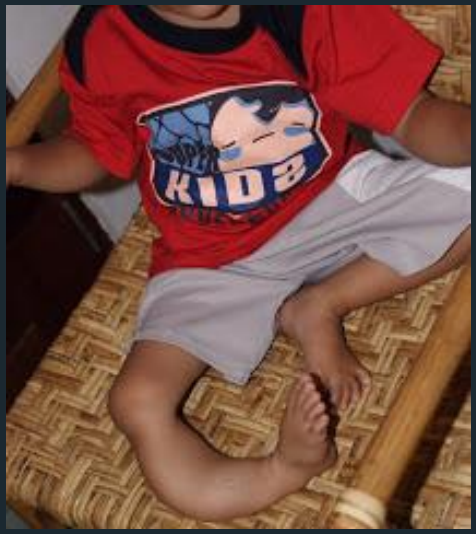
pain, due to pathologic fracture of the long bones
hockey stick deformity- leg length discrepancy
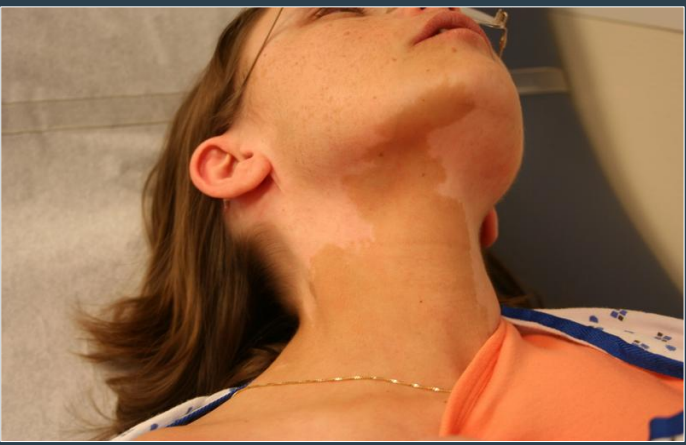
how do lesions of neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) appear clinically
cafe au lait spots are smaller and higher in number
borders are smooth and ovoid shape→ “coast of california”
cross the midline
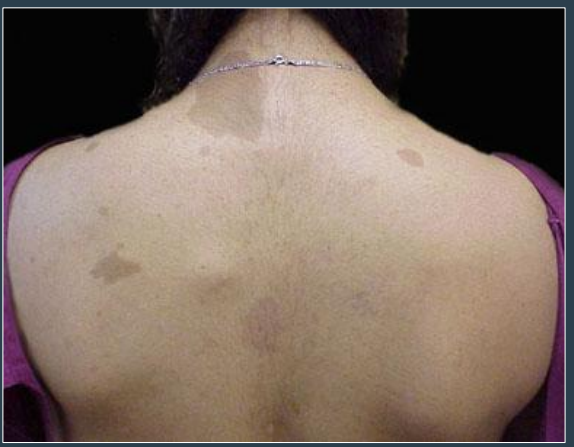
how do lesions of McCune Albright Syndrome appear clinically
cafe au lait spots are larger and fewer in number
borders are jagged and irregular → “coast of Maine”
found in midline and does NOT cross the midline
prognosis of fibrous dysplasia
disease tends to stabilize and stop growing at skeletal maturity
up to 50% recur
fibrous dysplasia tx
varies: medication, pain management, physical therapy, and in some cases- surgery
what is the most common fibro-osseous lesion encountered in clinical practice
cemento-osseous dysplasia (COD)
what is COD
abnormal bone mixed w soft tissue
location associated w COD
tooth-bearing areas of the jaw → apex
people most associated w COD
african american, middle-aged females
what are the three types of COD
focal
periapical
florid
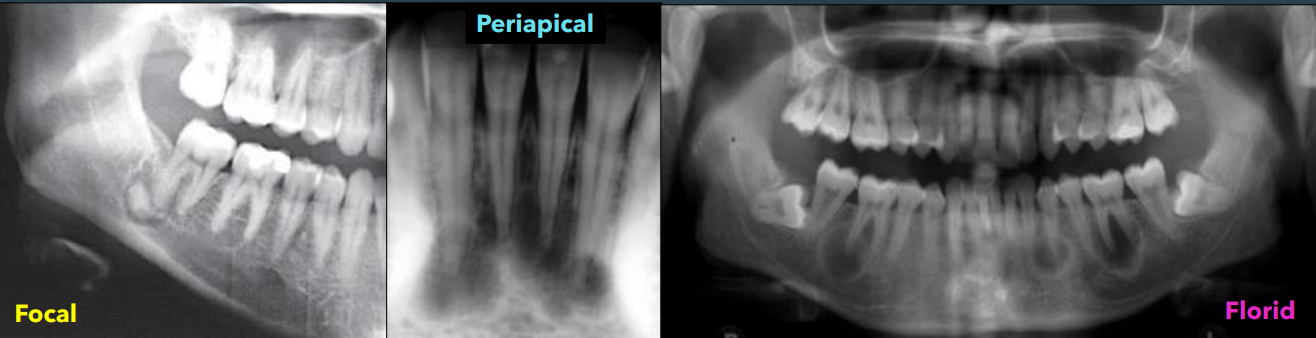
people most associated w periapical COD
90% are female
70% in african americans
middle aged (40s)
location associated w periapical COD
periapical region of anterior mandible
how to teeth present in periapical COD
teeth are invariably vital and asymptomatic
how periapical COD present on a radiograph
multiple foci are usually present
early lesions are circumscribed areas of radiolucent involving the apex of a tooth- looks identical to periapical granuloma or cyst
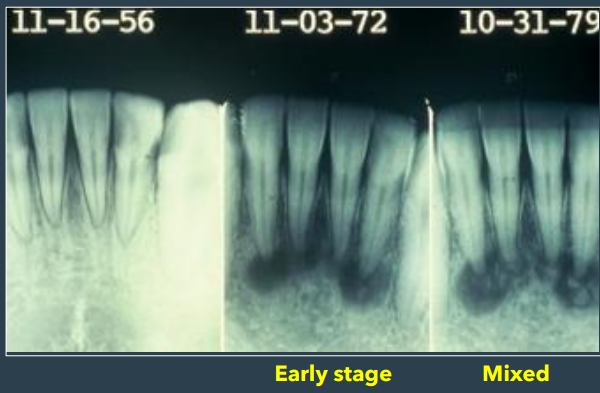
what are the 3 stages of periapical
early stage
mixed stage
late stage
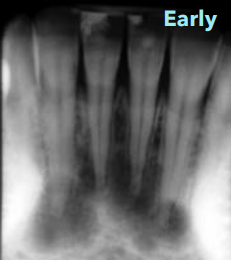
how does the early stage of periapical COD stage present
radiolucent lesions
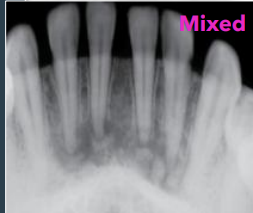
how does the mixed stage of periapical COD stage present
radiolucent-radiopaque appearance
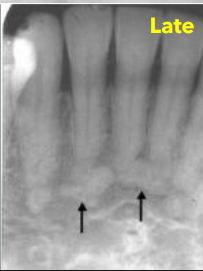
how does the late stage of periapical COD stage present
densely radiopaque w a radiolucent rim
prognosis of periapical COD
lesion is typically non-expansile, self-limiting → will stop growing and expanding, biopsy not rlly recommended
people associated w focal COD
90% occur in african american females
middle aged
location associated w focal COD
posterior mandible
how focal COD will appear radiographically
single lesion
radiolucent to radiopaque
in tooth-bearing areas of the jaw
well-defined rim during mixed stage
smaller than 1.5 cm
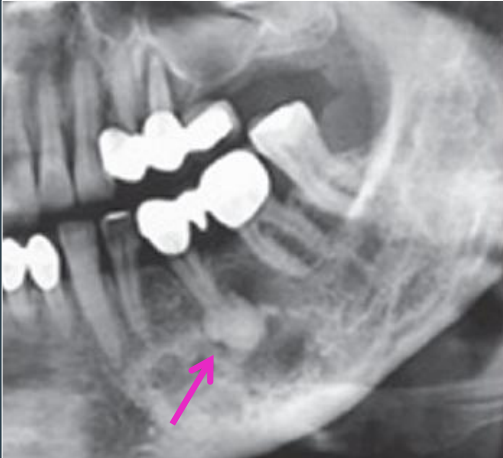
would you expect pt to symptomatic or asymptomatic in focal COD
asymptomatic
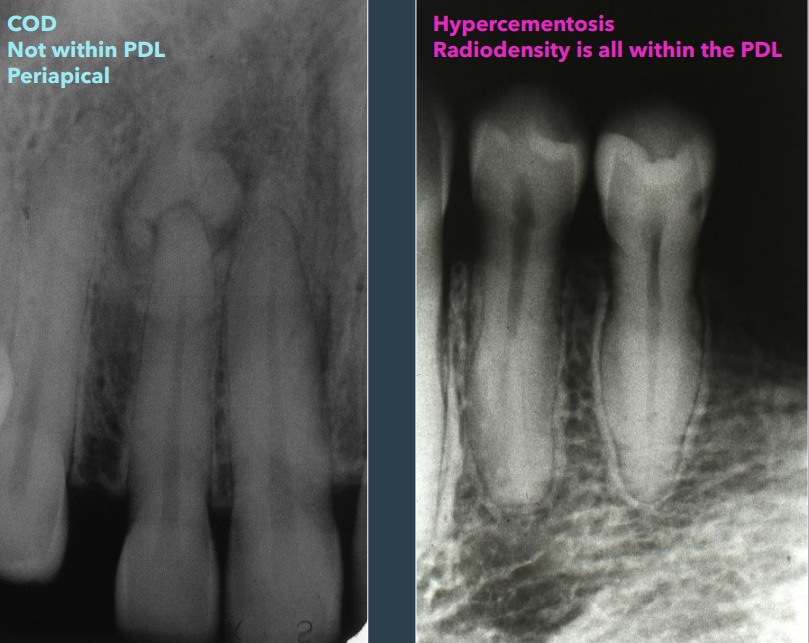
how to differentiates COD and hypercementosis
COD: not within PDL space
hypercementosis: within PDL space
people associated w florid COD
90% are female and african american
middle aged or older adults
location associated w florid COD
multiple focal involvement not limited to the anterior mandible
how does florid COD appear on a radiograph
may have lesions in post jaws, some pts have lesions throughout
bilateral and symmetrical
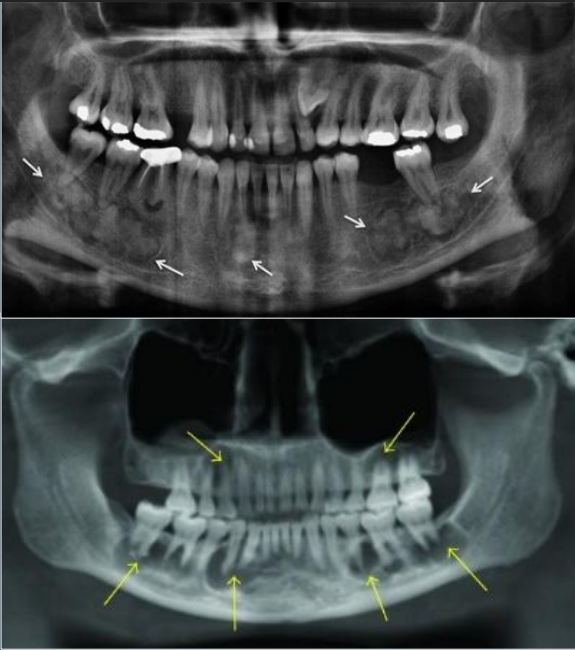
how does teeth vitality present in florid COD
vital and asymptomatic
how to dx COD
can be made from distinctive clinical and x-ray finding → do NOT need biopsy
if you biopsy COD, what can this lead to
necrosis due to hypovascularity
tx for COD
focal COD: may require surgical investigation bc features are less specific
follow up
antibiotics if osteomyelitis/infection is present
what 5 things should be on your differential dx for a radiopaque lesion at the apex
COD
condensing osteitis
idiopathic osteosclerosis
hypercementosis
cementoblastoma
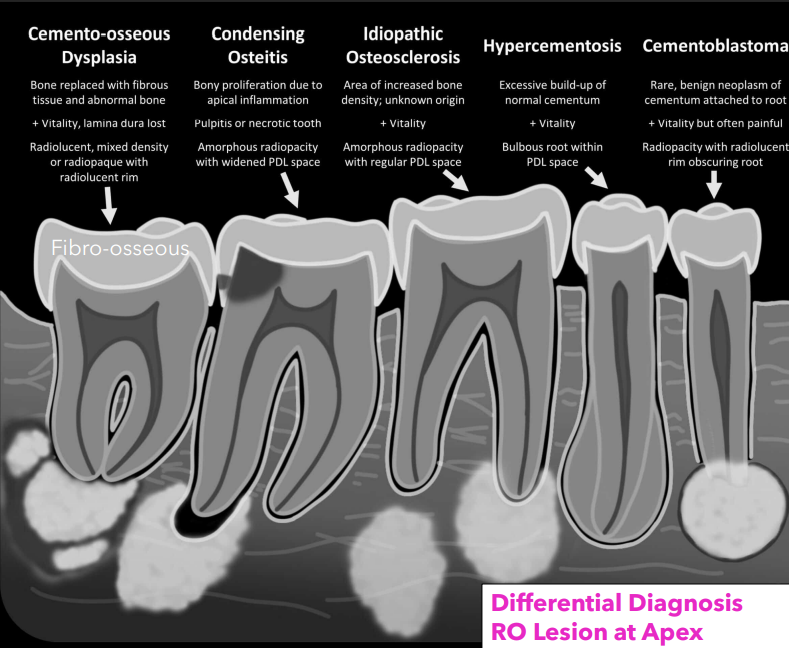
how does focal COD appear in the mixed phase on a radiograph
rim is prominent
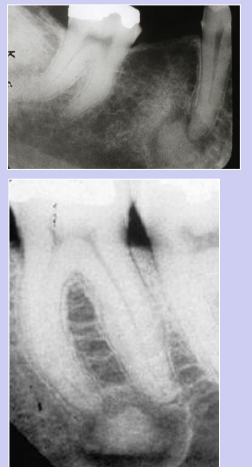
what is cementoblastoma
benign neoplasm of cementum
how does cementoblastoma present on a radiograph
radiolucent rim is contiguous w PDL and PDL is NOT in tact at involved portion of the root, effacement of root
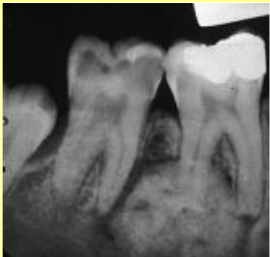
what is condensing osteitis also called
focal sclerosing osteomyelitis
how does condensing osteitis present on a radiograph
no radiolucent rim, borders blend w surrounding trabeculae; is due to pulpal involvement
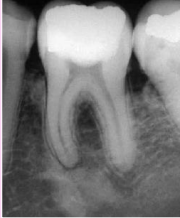
how does idiopathic osteosclerosis dense bone, enostosis, bone scar present on a radiograph
no radiolucent rim, borders blend w surrounding trabeculae
what are the 4 hereditary bone disorders
osteogenesis imperfecta (OI)
osteopetrosis
cleidocranial dysplasia
cherubism
osteogenesis imperfecta is also called…
brittle bone disease
in osteogenesis imperfecta, there is a mutation in…
type collagen 1
osteogenesis imperfecta mode of inheritance
AD: 90%
AR: 10%
some are sporadic
gender associated w osteogenesis imperfecta
M = F
age associated w osteogenesis imperfecta
infant, young children
location associated w osteogenesis imperfecta
bone, teeth, ligament, skin, sclera
what is the most common inherited bone disorder, even though it is uncommon
osteogenesis imperfecta
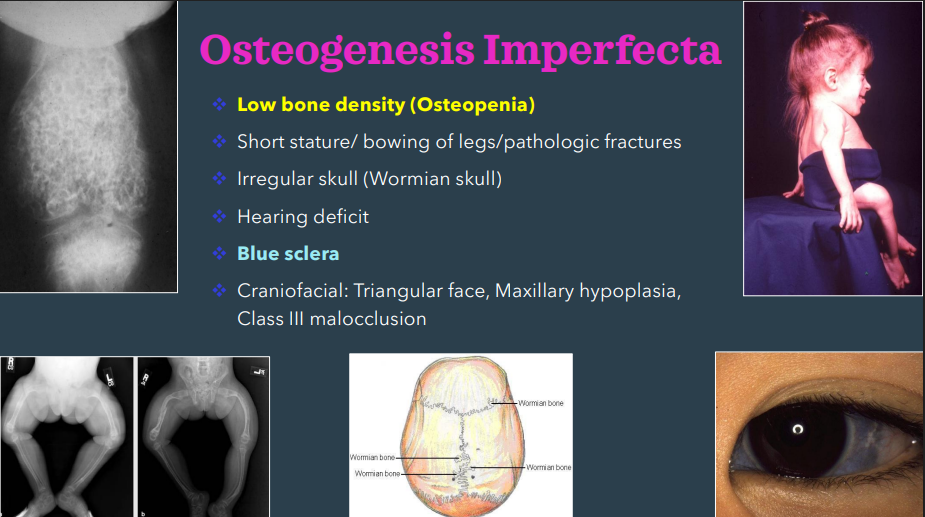
main clinical features of osteogenesis imperfecta
low bone density- osteopenia
blue sclera
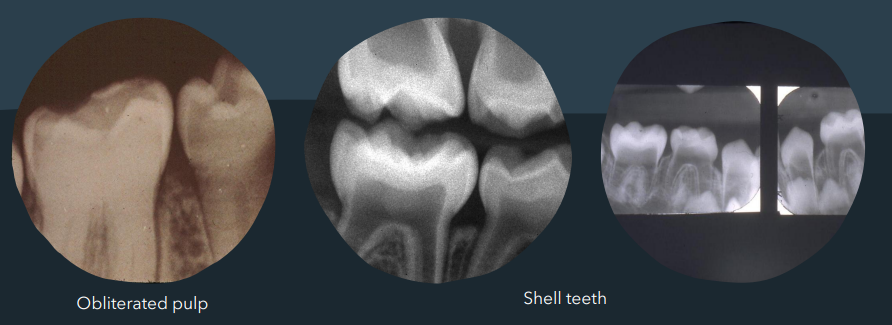
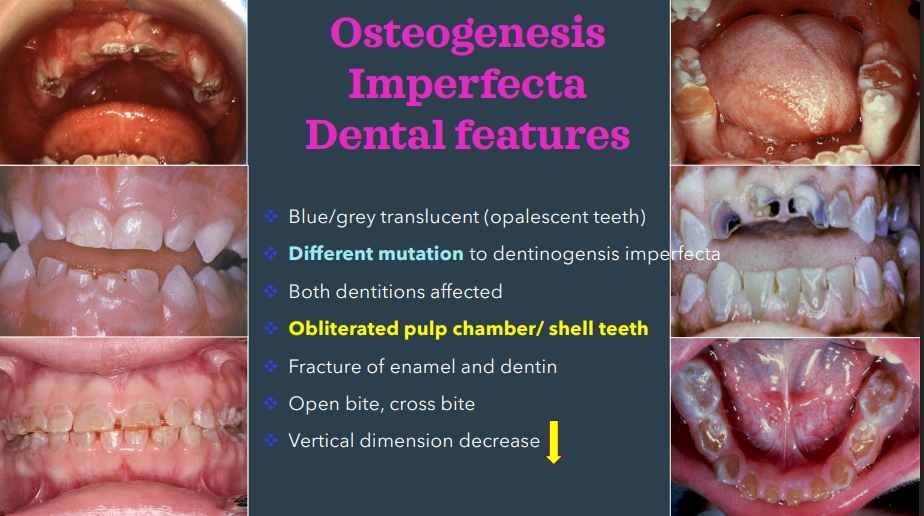
dental features of osteogenesis imperfecta
blue/grey translucent teeth
obliterated pulp chamber/ shell teeth
osteogenesis imperfecta presents similarly to…
dentinogenesis imperfecta; diff is they have diff mutations
management of osteogenesis imperfecta
restorations
osteopetrosis is also called…
albers-schonberg disease
marble bone disease
what cells are affected in osteopetrosis
decreased osteoclastic activity
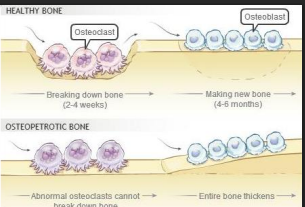
in osteopetrosis, there is an _____ (inc/dec) in bone density
inc
mode of inheritance of osteopetrosis
AD or AR-fatal
gender associated w osteopetrosis
M = F
age associated w osteopetrosis
infancy except adult form
location associated w osteopetrosis
anywhere
clinical features of osteopetrosis
anemia, pathologic fractures, infection, deafness, and blindness
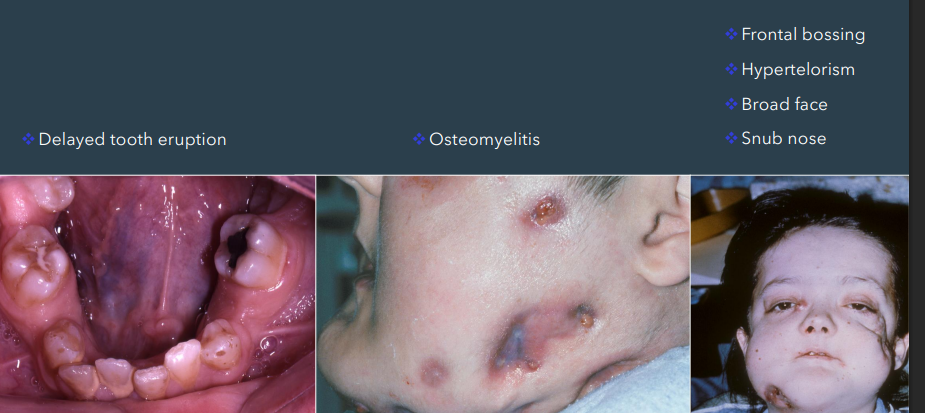
facial features of osteopetrosis
delayed tooth eruption
osteomyelitis
frontal bossing
hypertelorism
broad face
snub nose
tx for osteopetrosis
bone marrow transplant
palliative
prognosis of osteopetrosis
good for AD but fatal for AR
cleidocranial dysplasia is also called…
cleidocranial dysostosis
how is cleidocranial dysplasia characterized
by dental and clavicle abnormalities
mode of inheritance for cleidocranial dysplasia
AD
bone defects of cleidocranial dysplasia chiefly affect what bones
skull and clavicles- hypoplasia
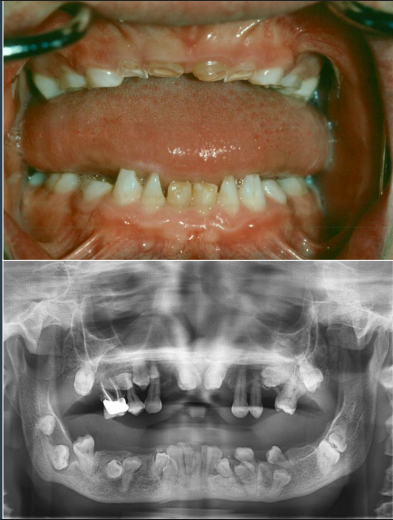
dental features associated w cleidocranial dysplasia
prolonged retention of teeth
delay or failure of eruption of permanent teeth
supernumerary teeth
numerous unerupted permanent and supernumerary teeth
supernumerary teeth can be associated w what two conditions
gardeners syndrome
cleidocranial dysplasia
mode of inheritance in cherubism
AD
mutation in cherubism
SH3BP2 chromosome #4p16
gender associated w cherubism
M = F
age associated w cherubism
2-5 → children
location associated w cherubism
bilateral posterior mandible (MOST COMMON), maxilla
clinical manifestations of cherubism
mandibular lesions are painless, bilateral, posterior, and expansile
distortion of alveolar ridge
may lead to failure of tooth eruption
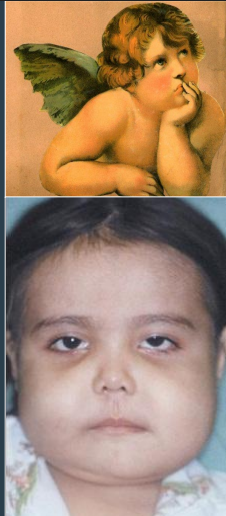
microscopic findings of cherubism are identical to those found in…
central giant cell granulomas (CGCG)
x-ray features that can be seen in cherubism
multilocular, radiolucent, expansile
prognosis of cherubism
unpredictable
varying degrees of remission and involution after puberty
tx of cherubism
early surgical intervention w curettage has lead to both good results or rapid regrowth w worsening deformity → optimal therapy hasn’t been determined
radiation therapy is contraindicated due to risk of postirradiation sarcoma
paget disease of bone is also called…
osteitis deformans
what is paget disease
a metabolic bone disease characterized by abnormal resorption and deposition of bone of unknown cause- mainly osteoclast
what are the possible causes of paget disease
30% hereditary
AD
sporadic
paramyxovirus
gender associated w paget disease of bone
M caucasians > F