unit 3 booklet 1 glossary
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
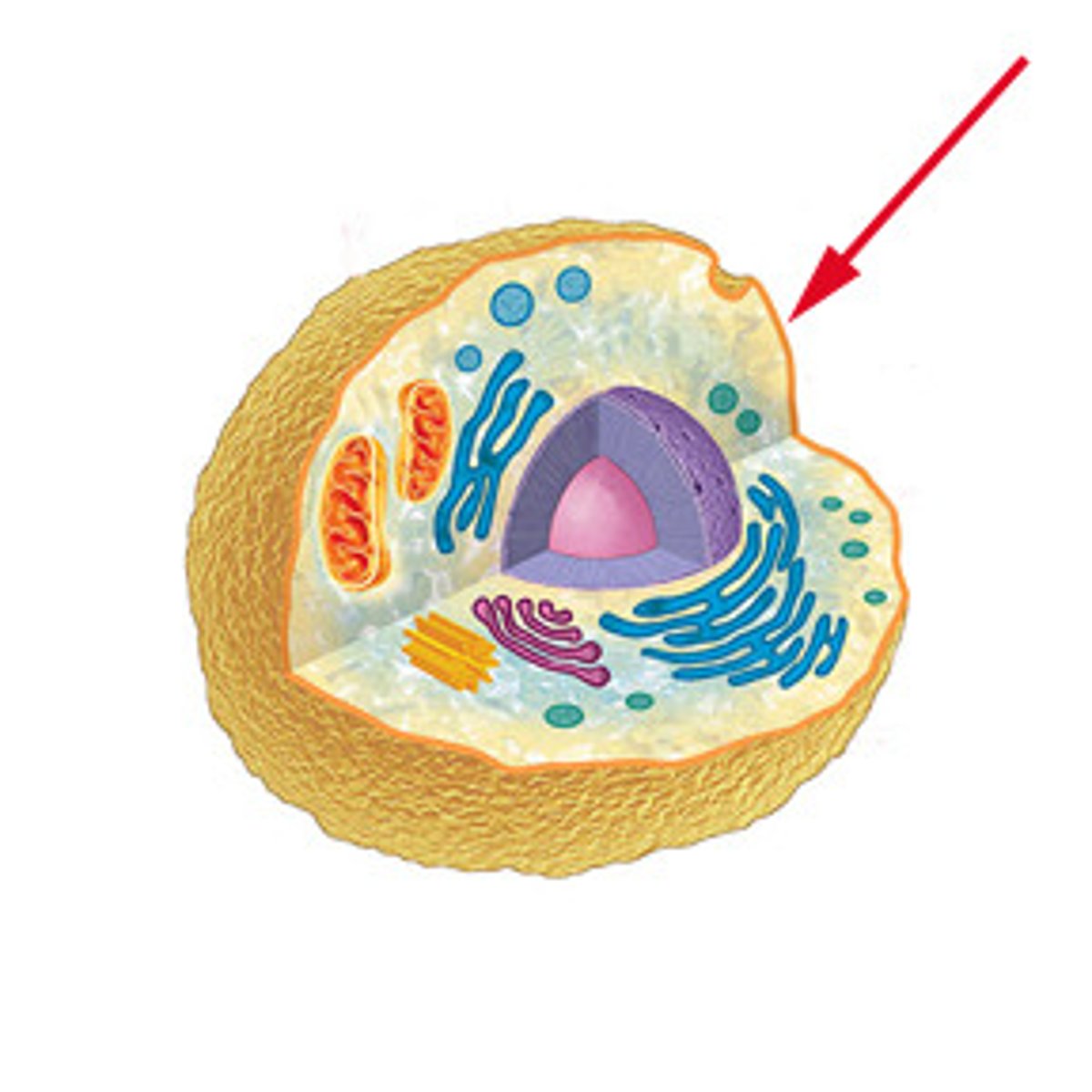
cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
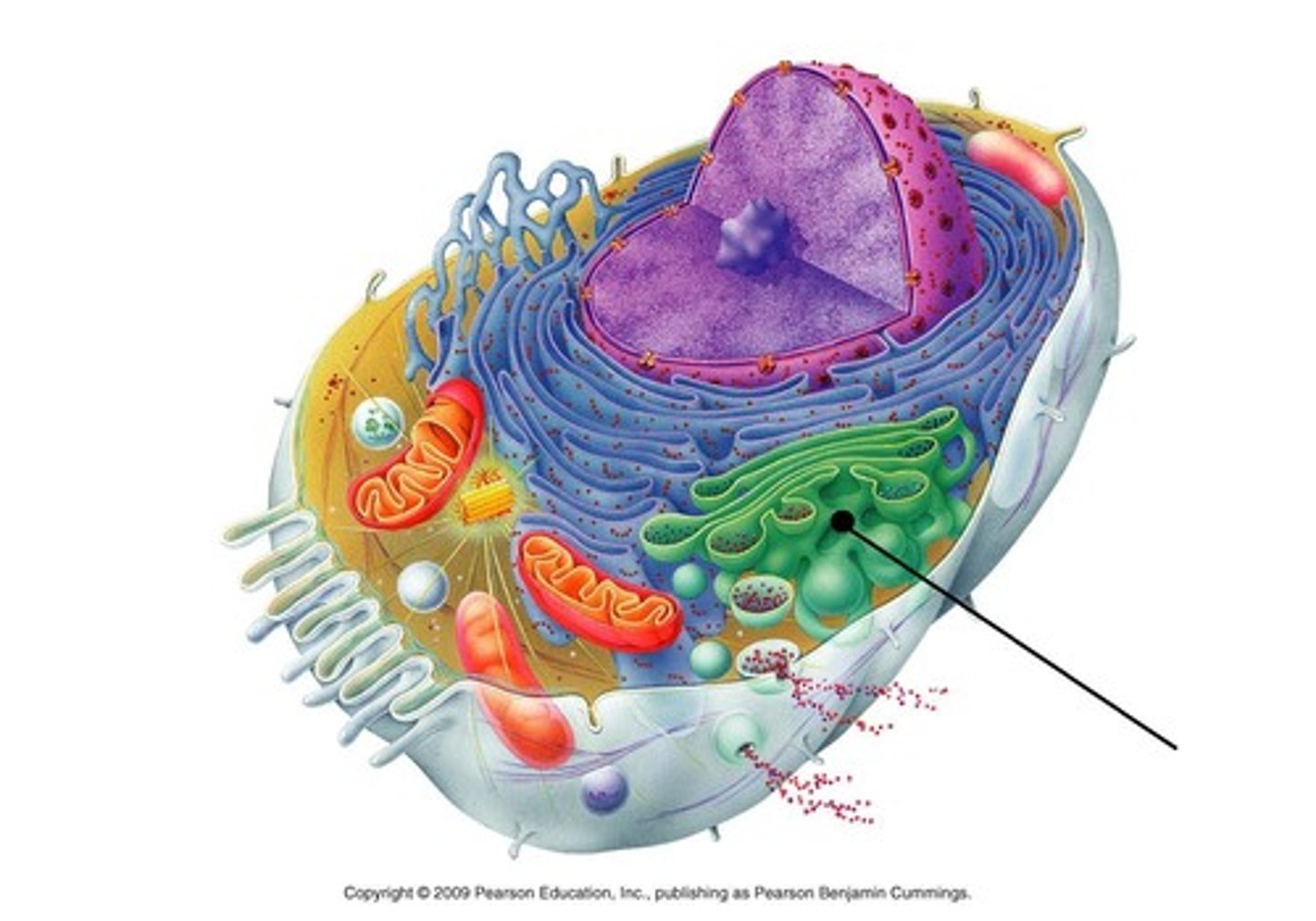
Golgi complex
a cell organelle that helps make and package materials to be transported out of the cell
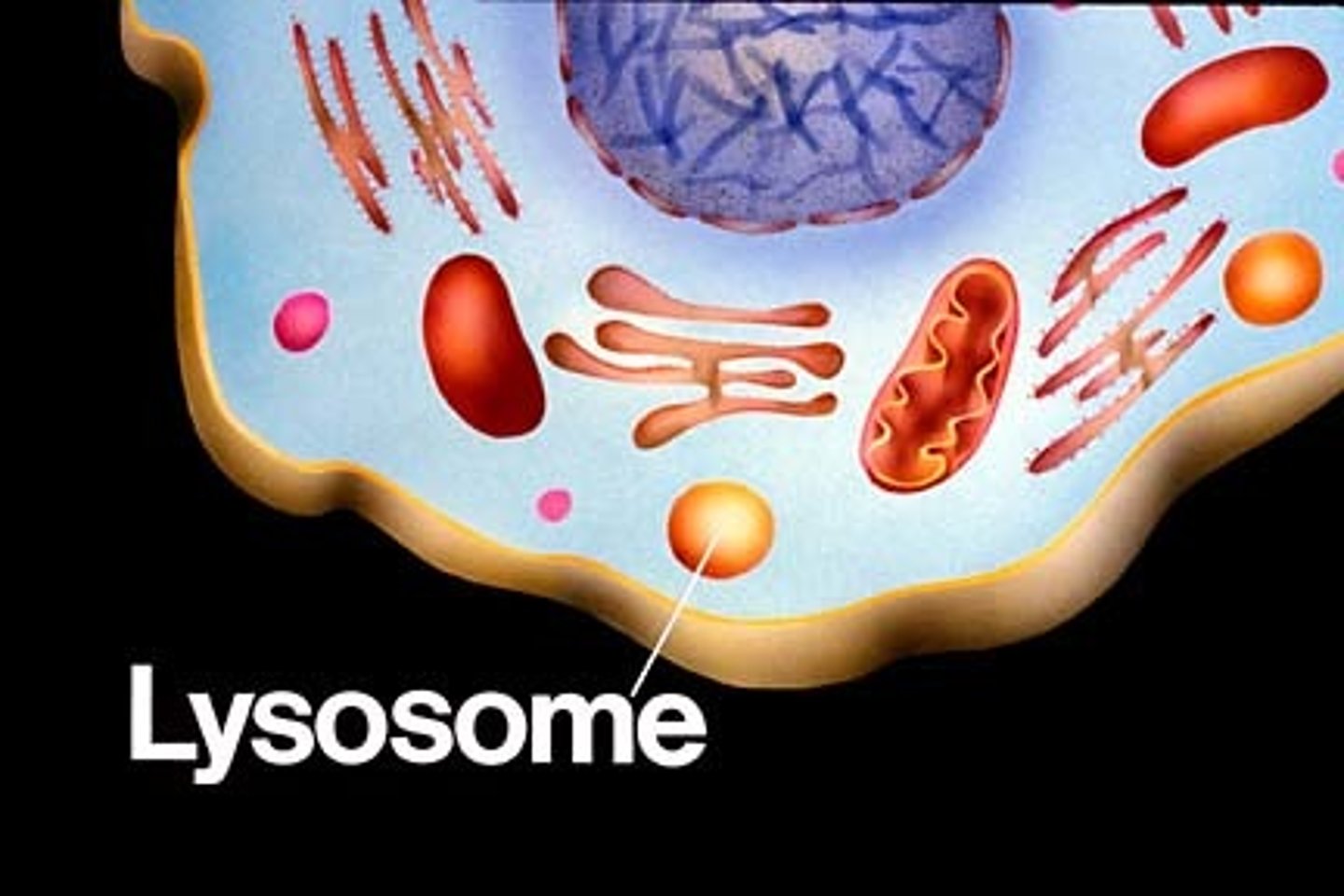
Lysosomes
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
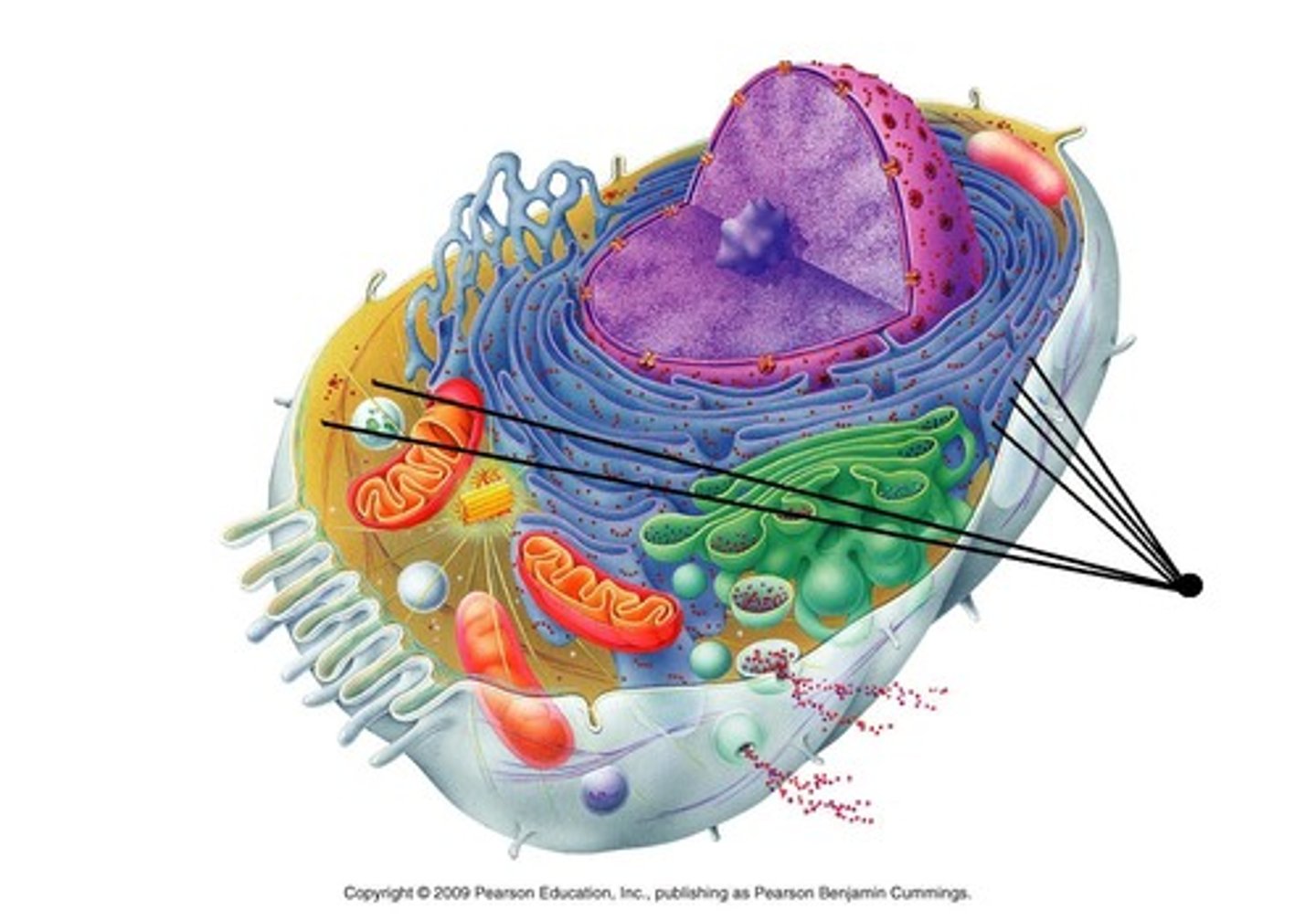
vesicle
Small membrane-bound sac that functions in moving products into, out of, and within a cell.
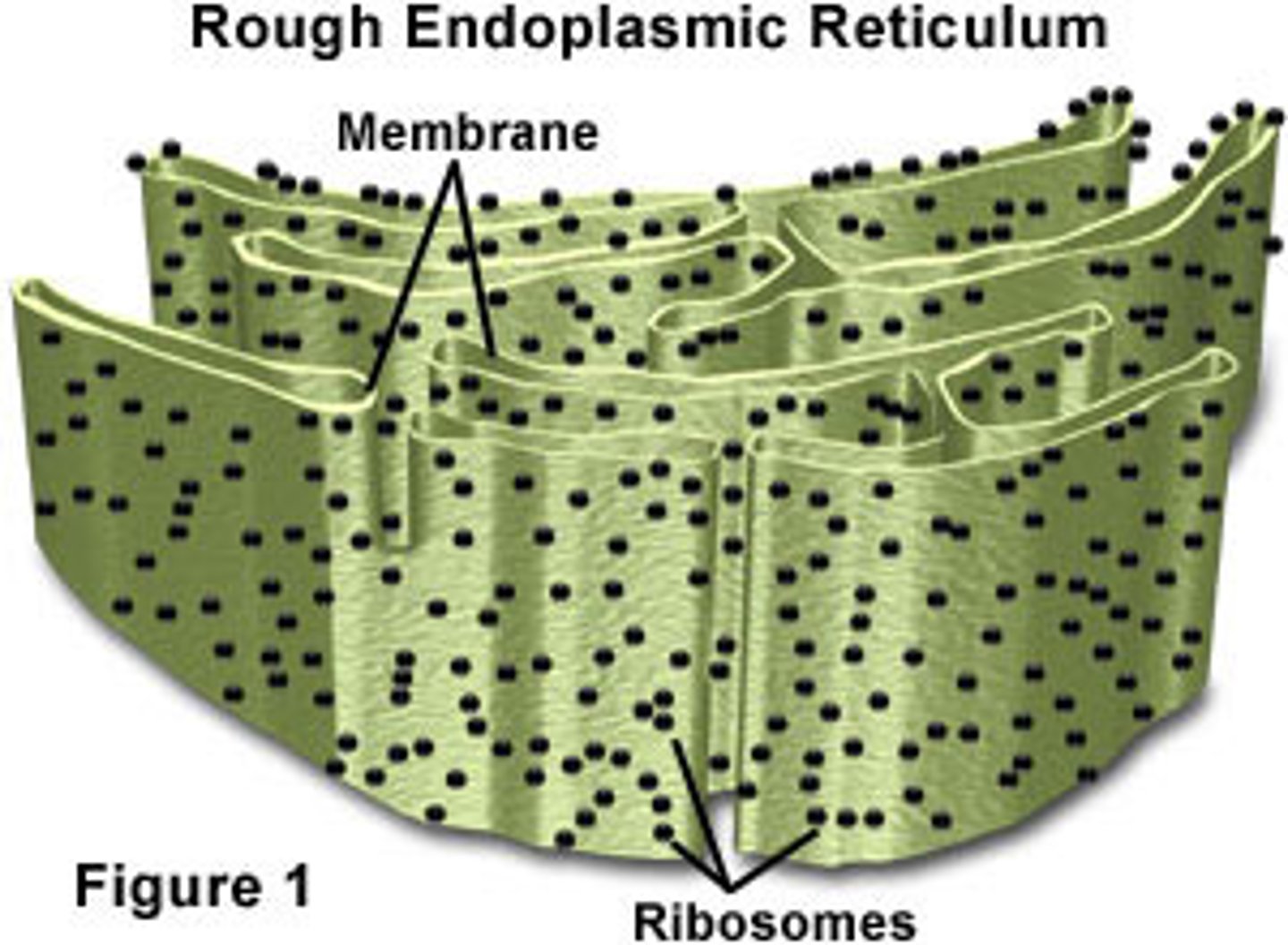
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
System of internal membranes within the cytoplasm. Membranes are rough due to the presence of ribosomes. functions in transport of substances such as proteins within the cytoplasm
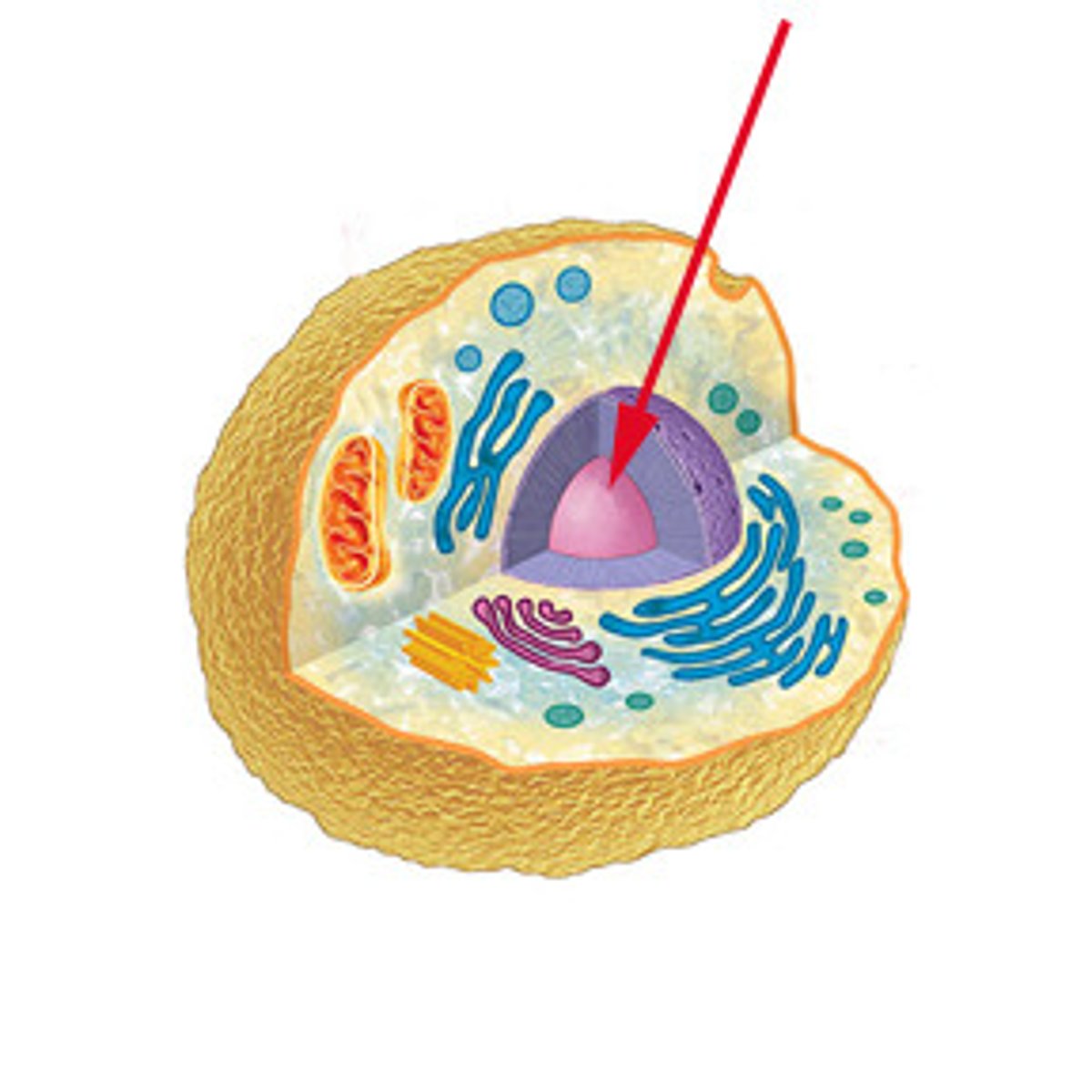
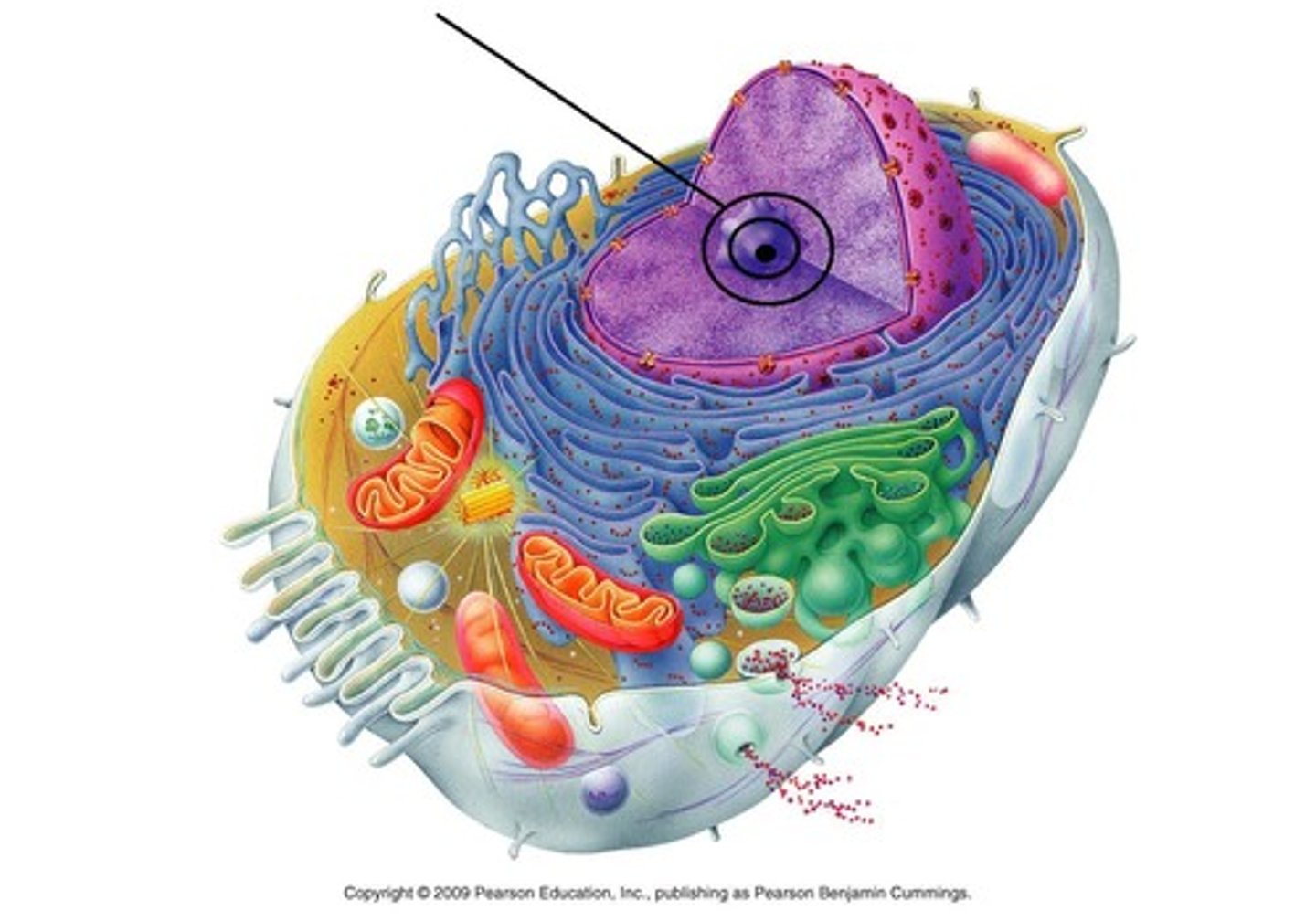
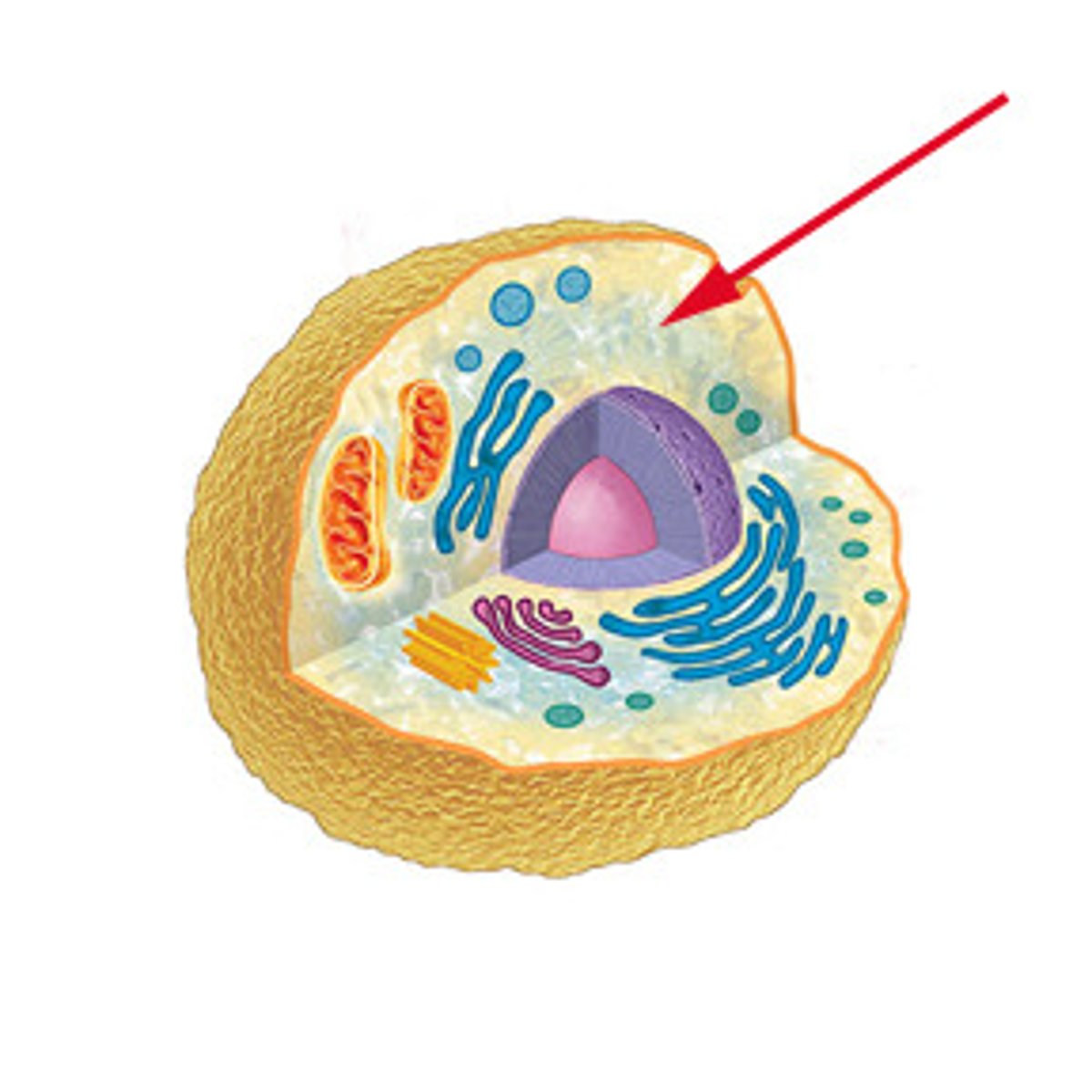
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
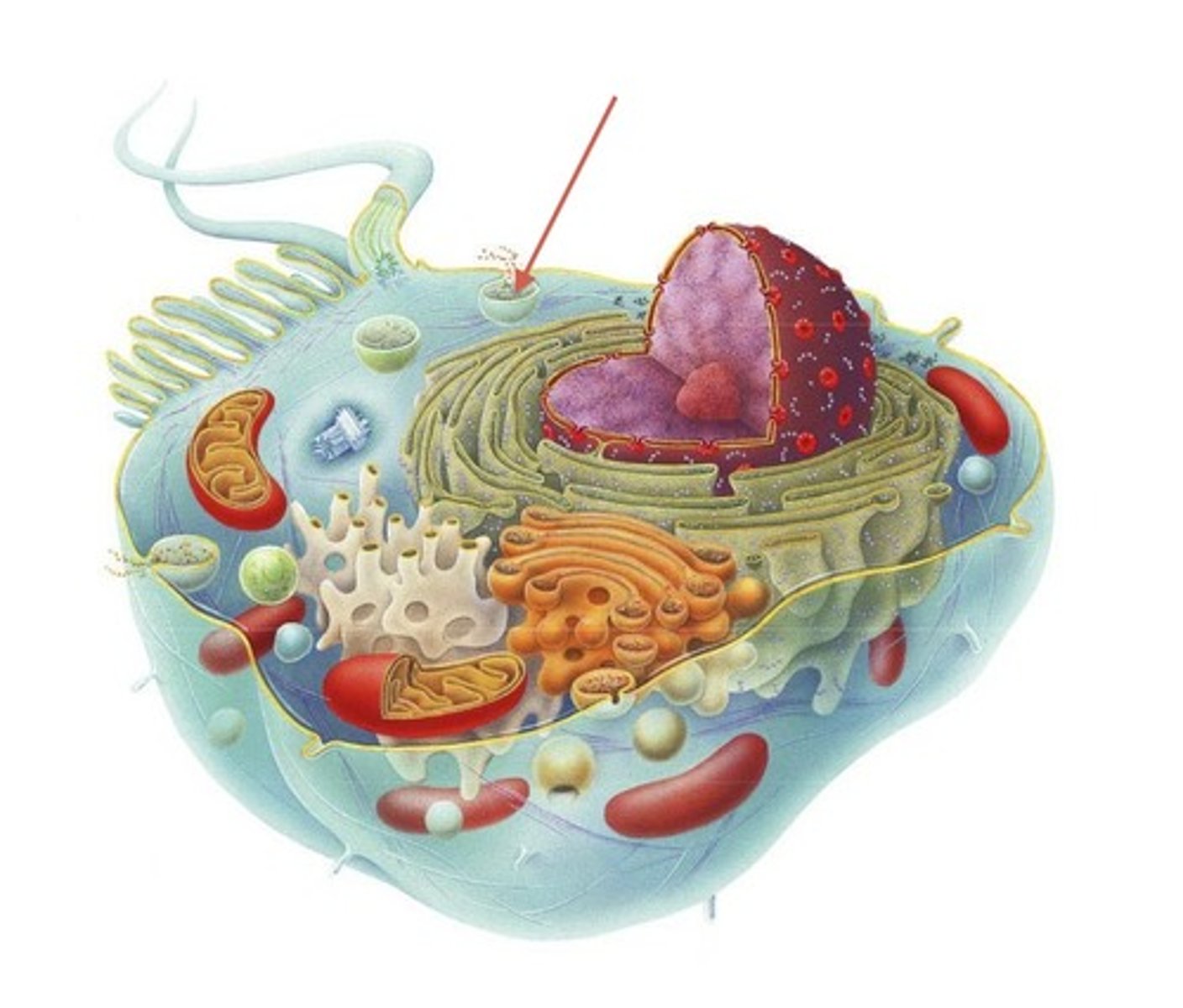
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
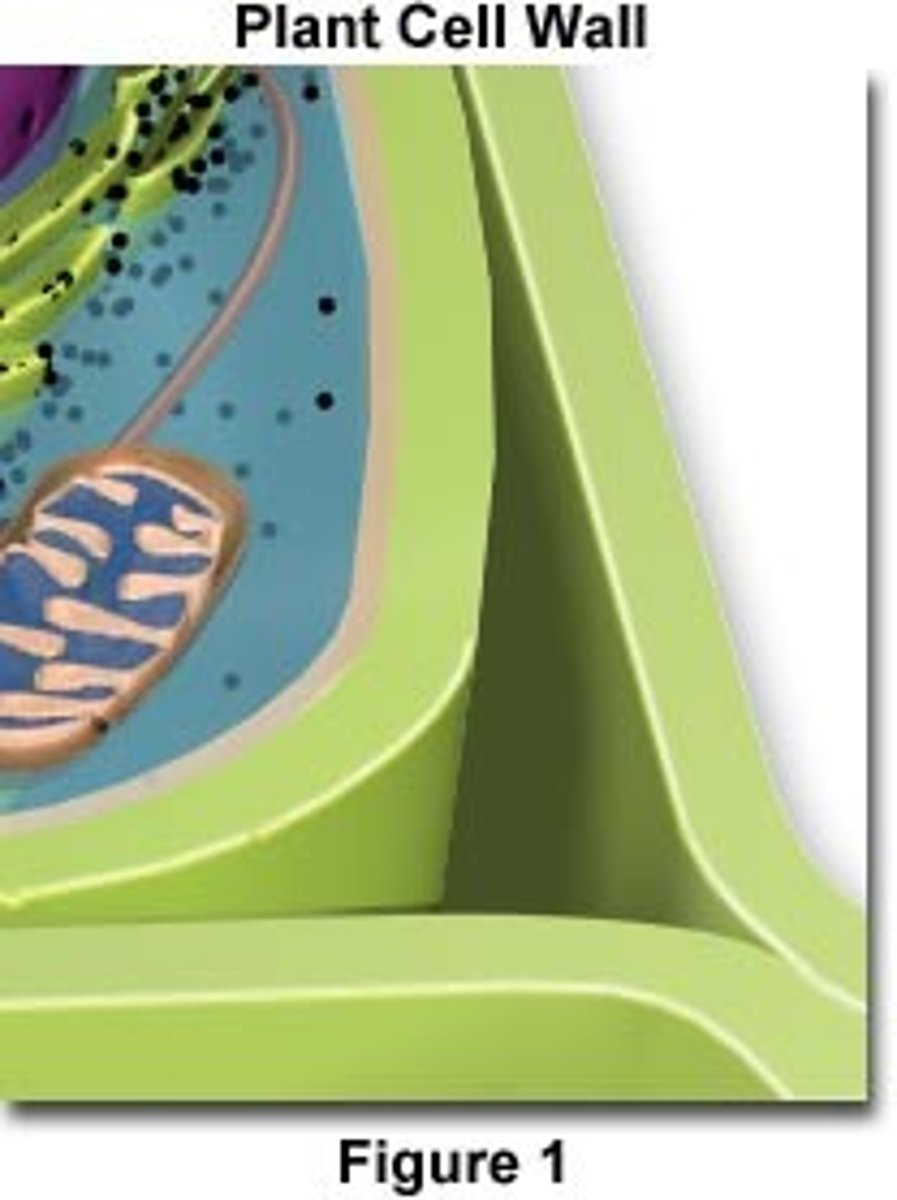
cell wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
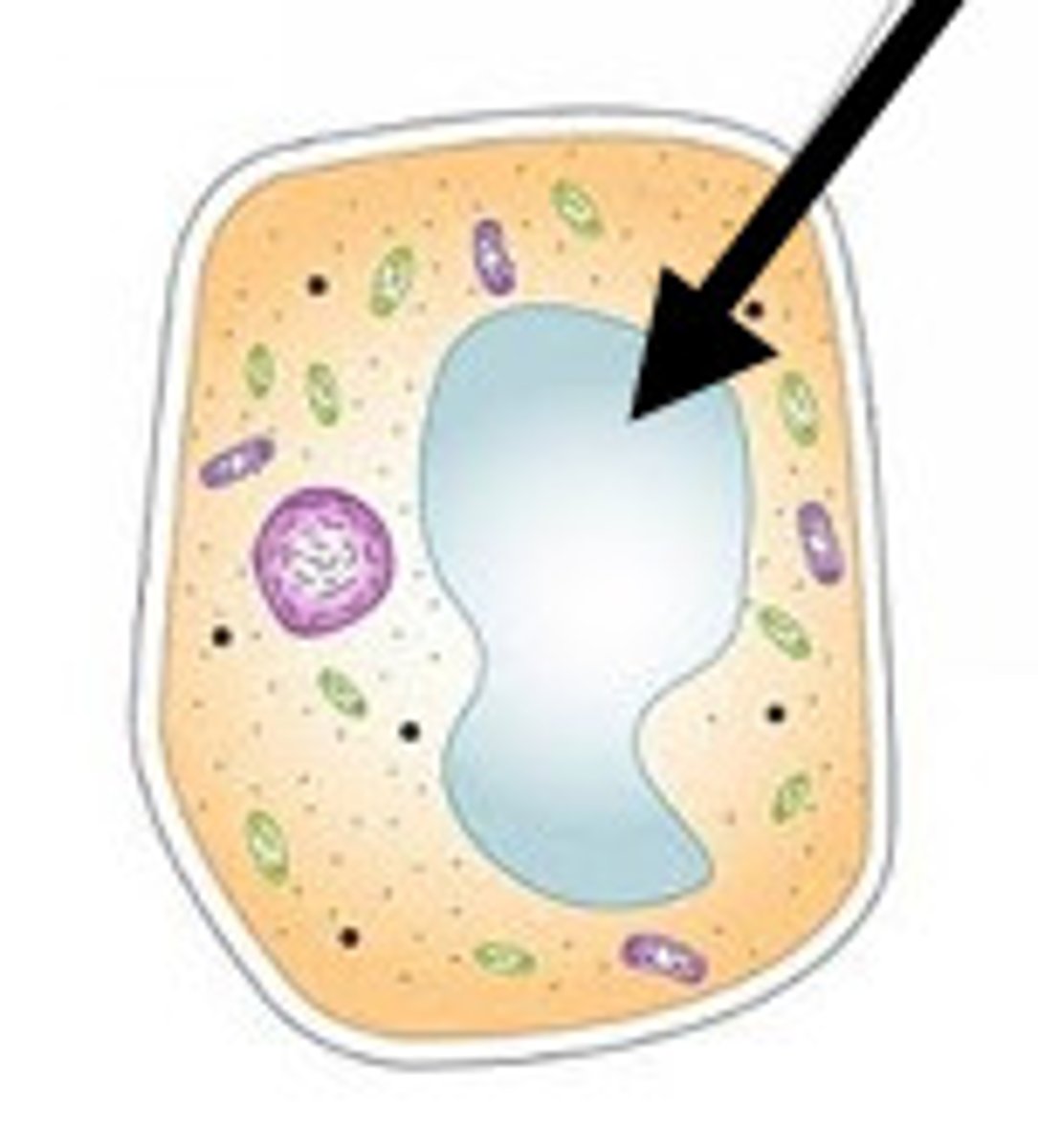
Vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
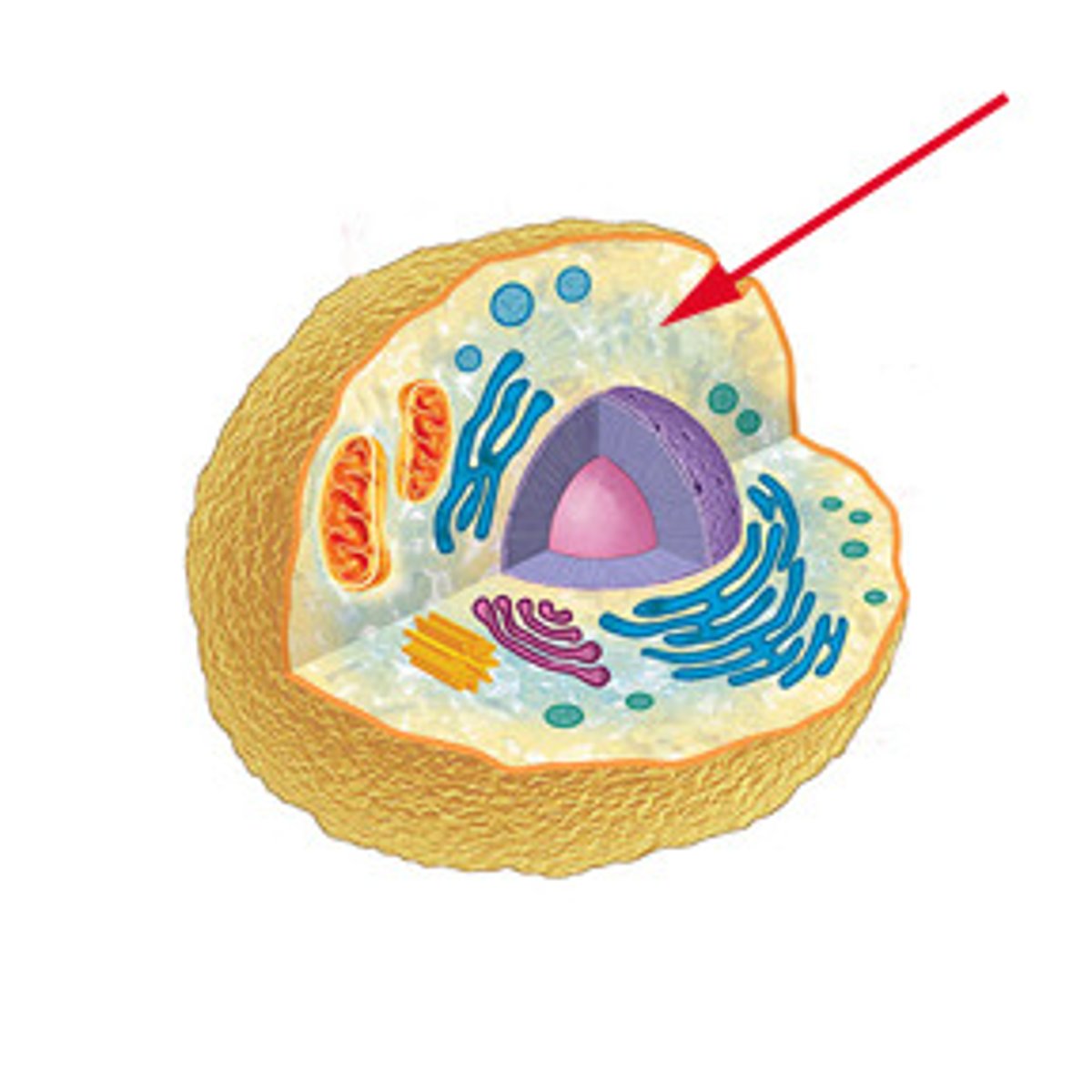
cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
Cytosol
The soluble portion of the cytoplasm, which includes molecules and small particles, such as ribosomes, but not the organelles covered with membranes.
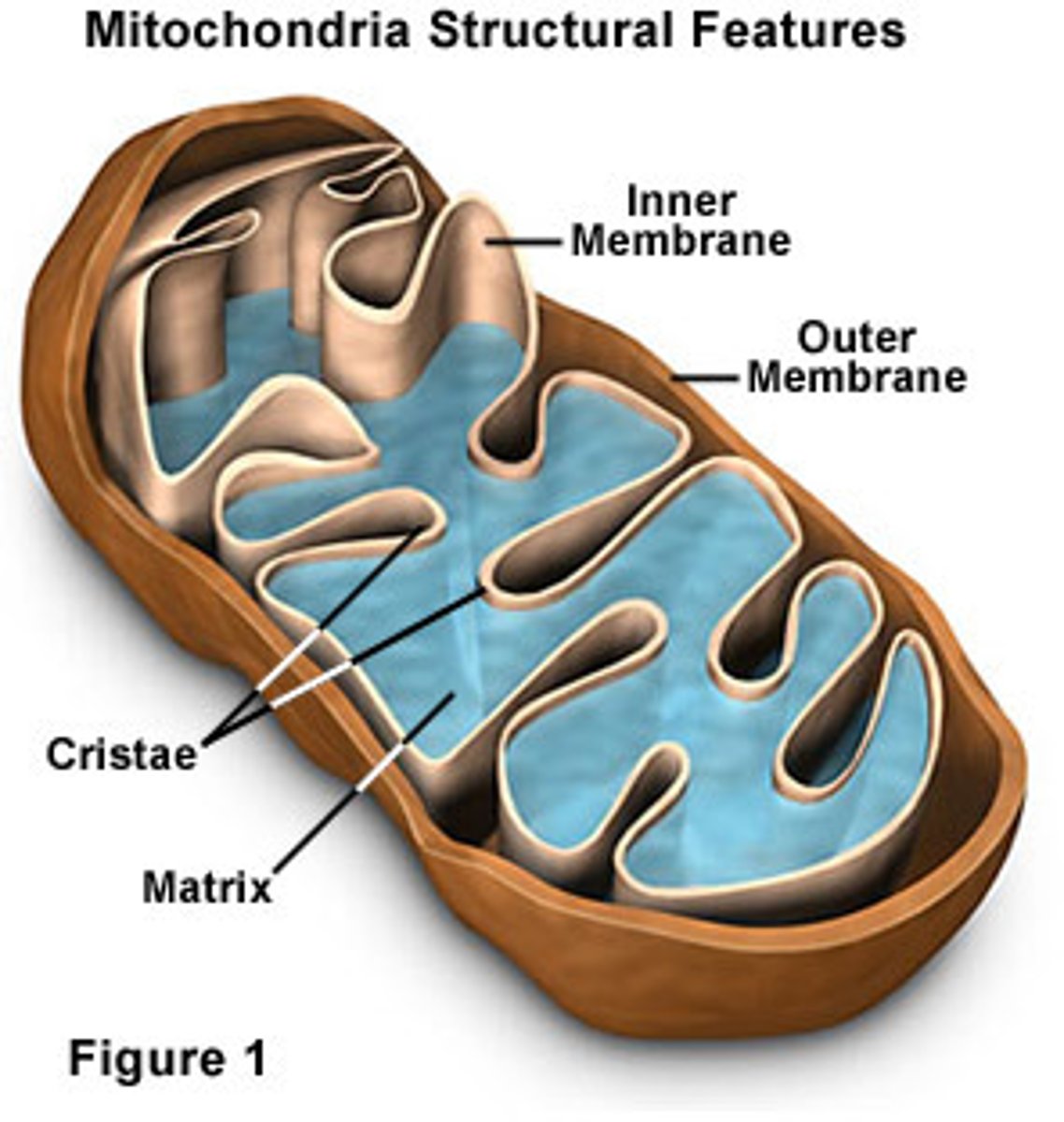
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
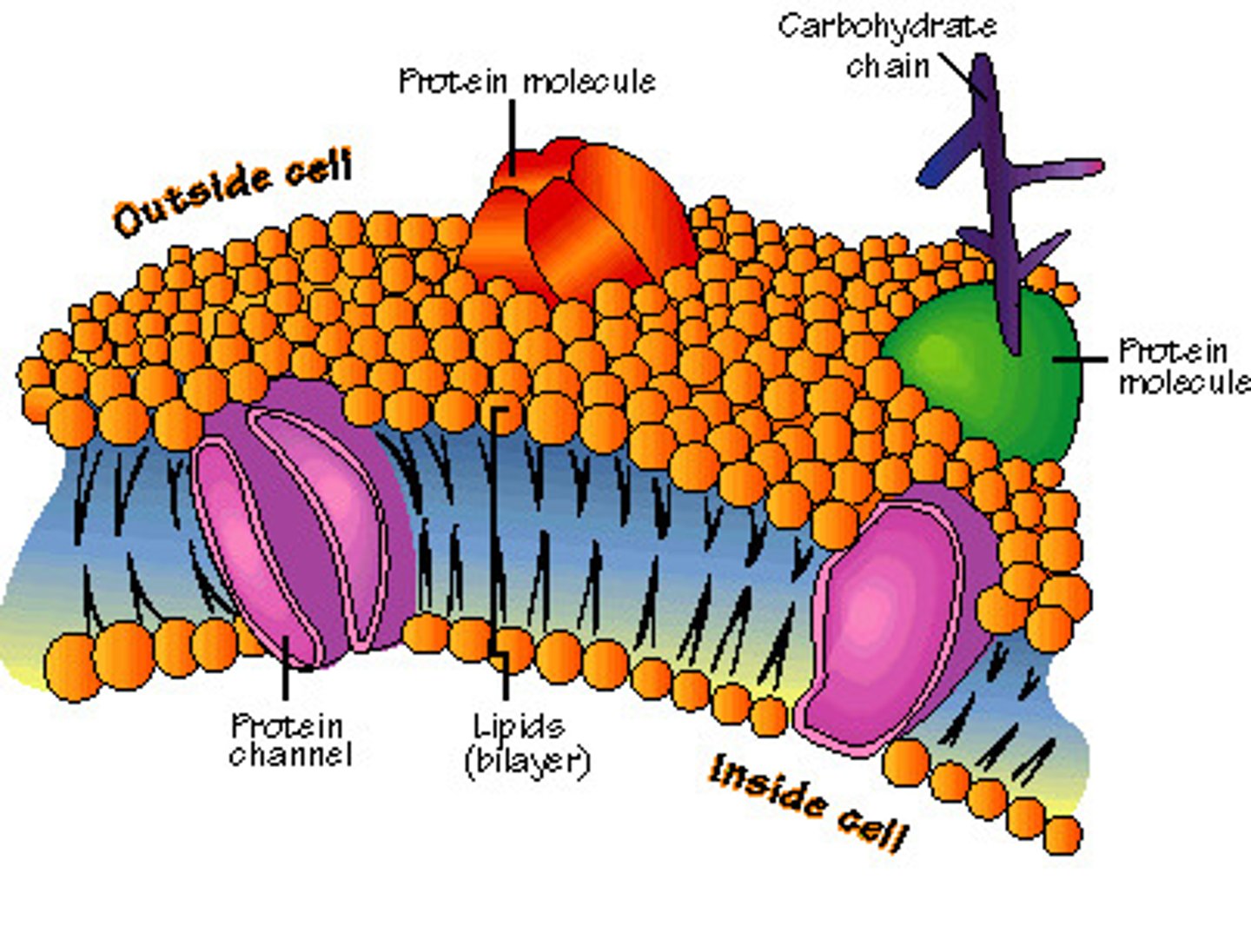
Hydrophilic
Attracted to water
Hydrophobic
Having an aversion to water; tending to coalesce and form droplets in water.
protein channels
proteins in the membrane whose role it is to pass molecules that cannot go through the membrane
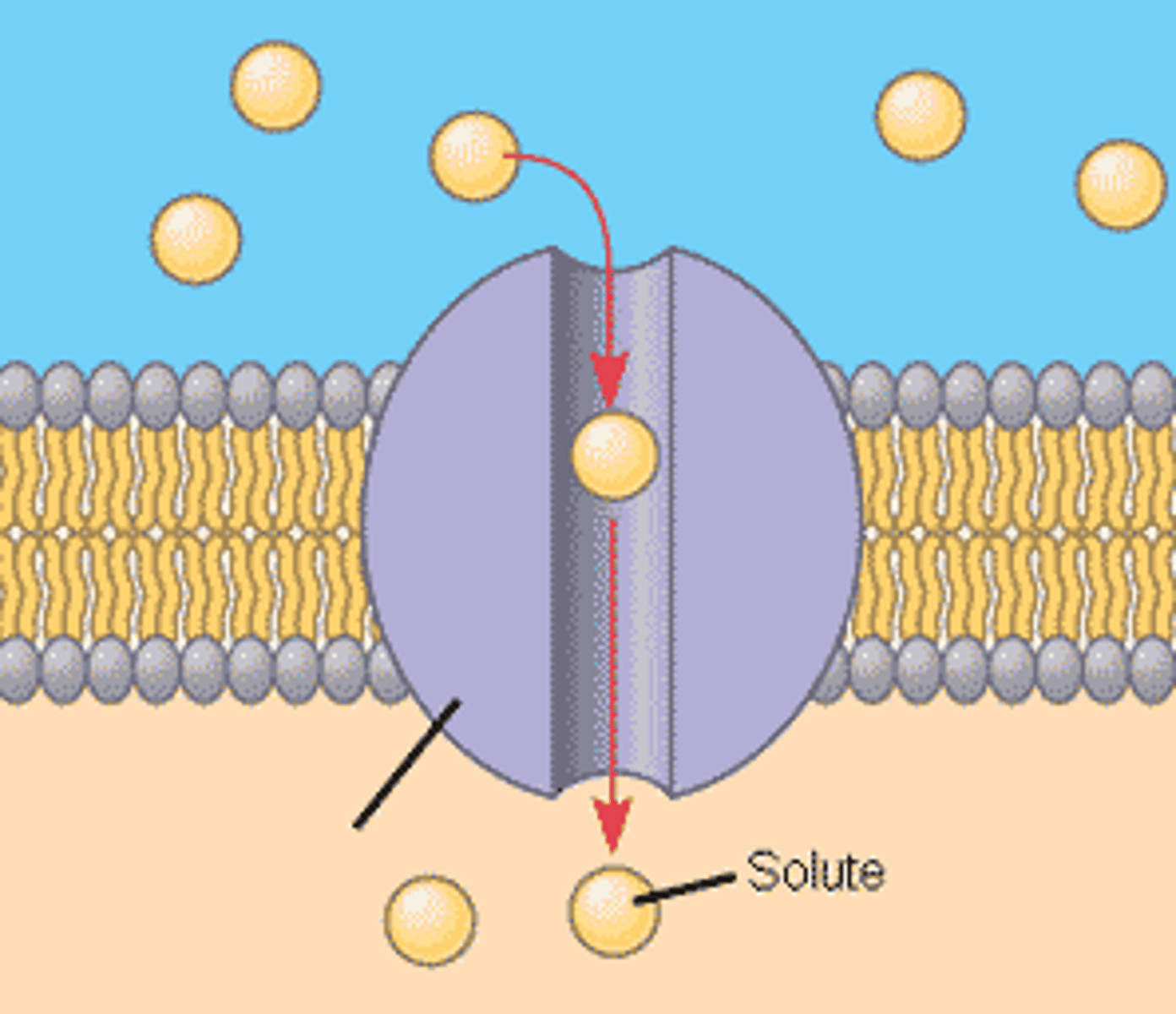
bulk transport
The process by which large particles and macromolecules are transported through plasma membranes. Inc. exocytosis and endocytosis
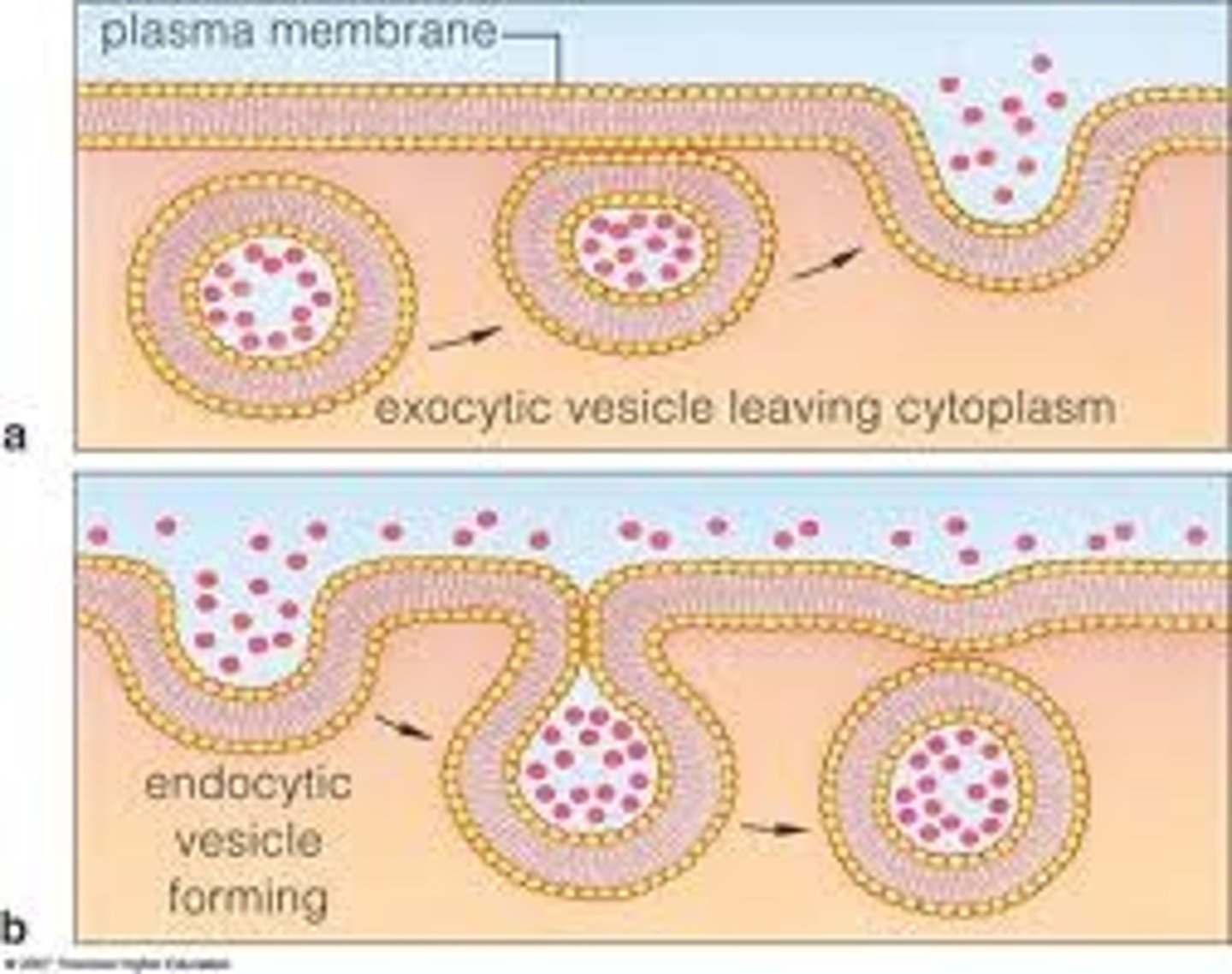
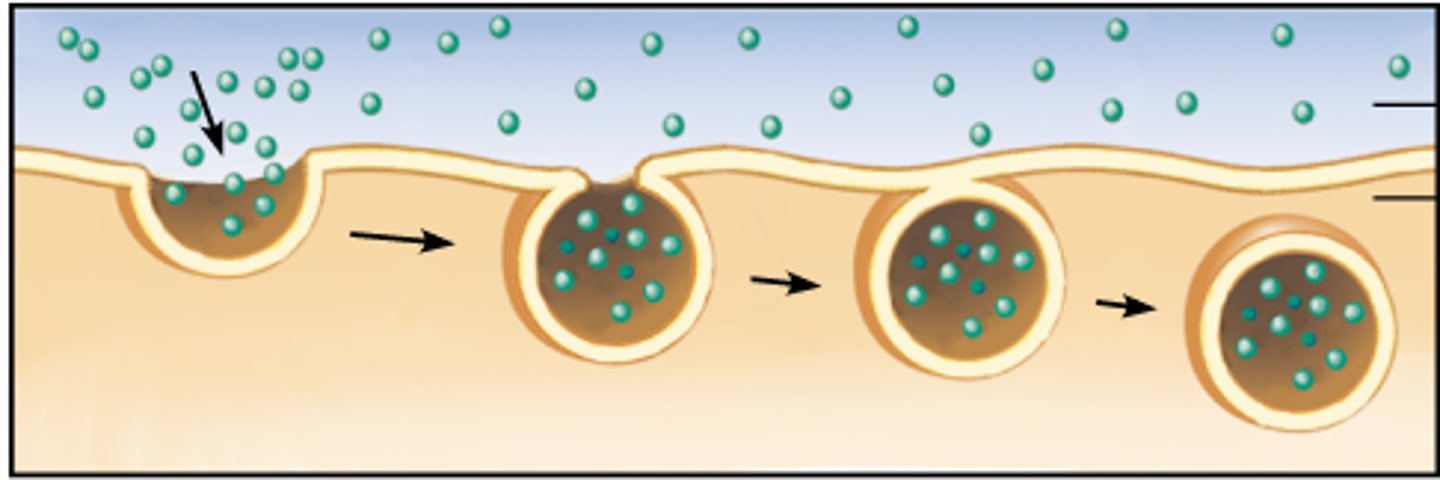
Endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
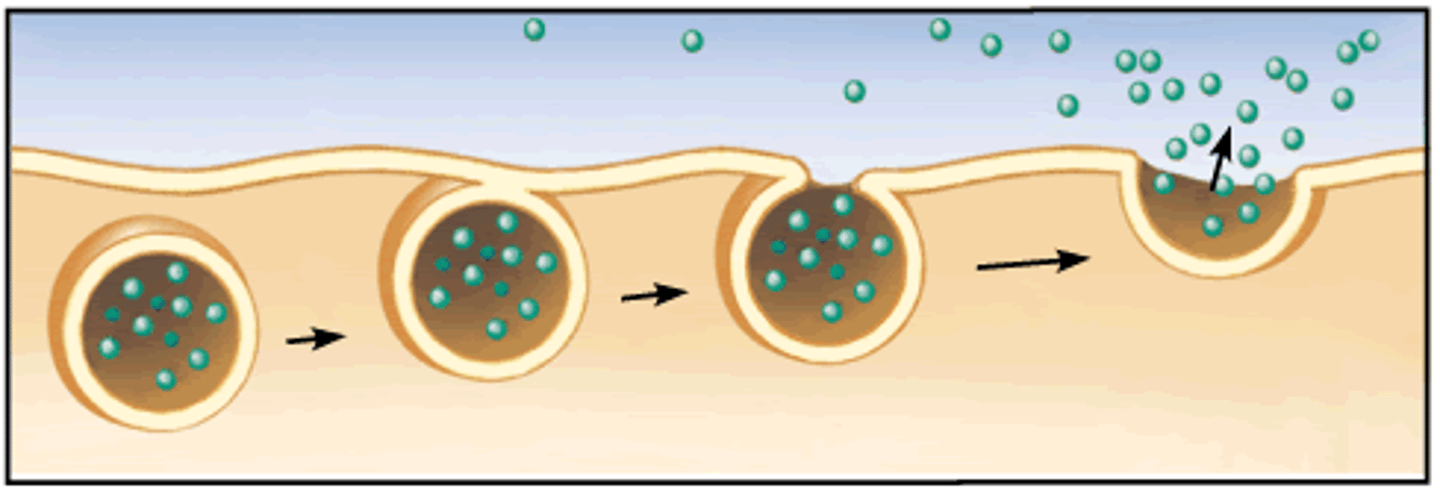
Exocytosis
a process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane.
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells
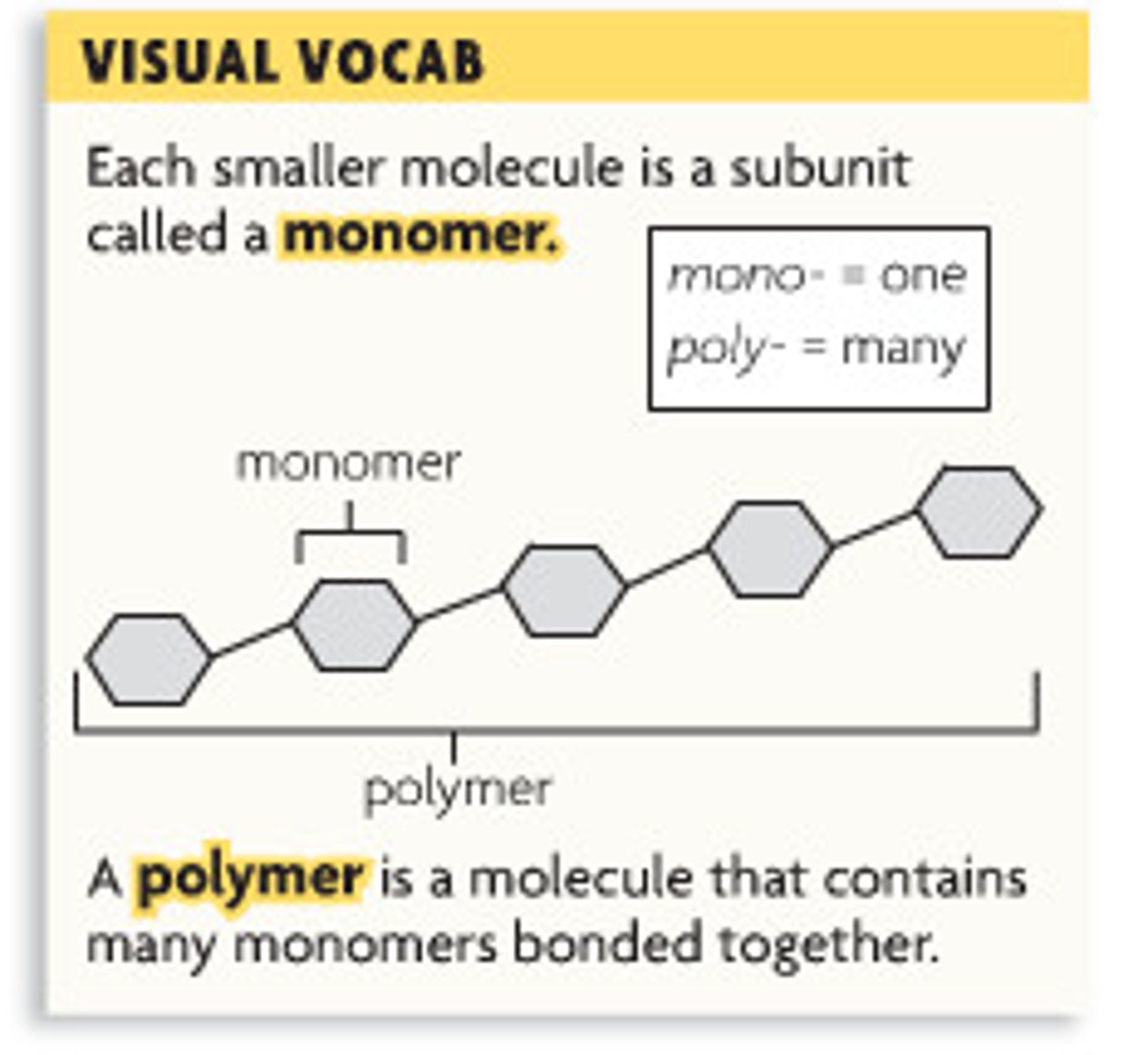
Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
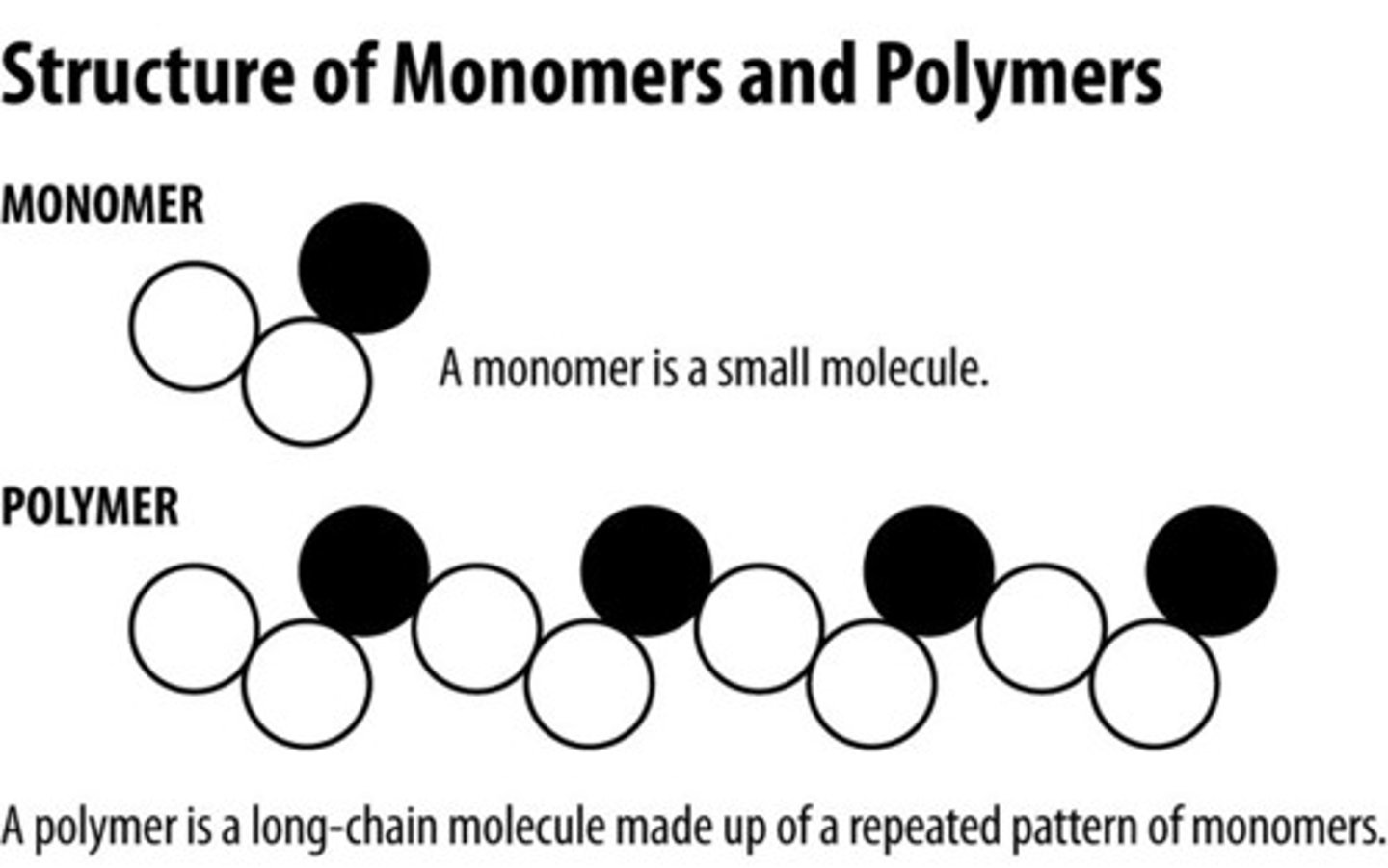
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
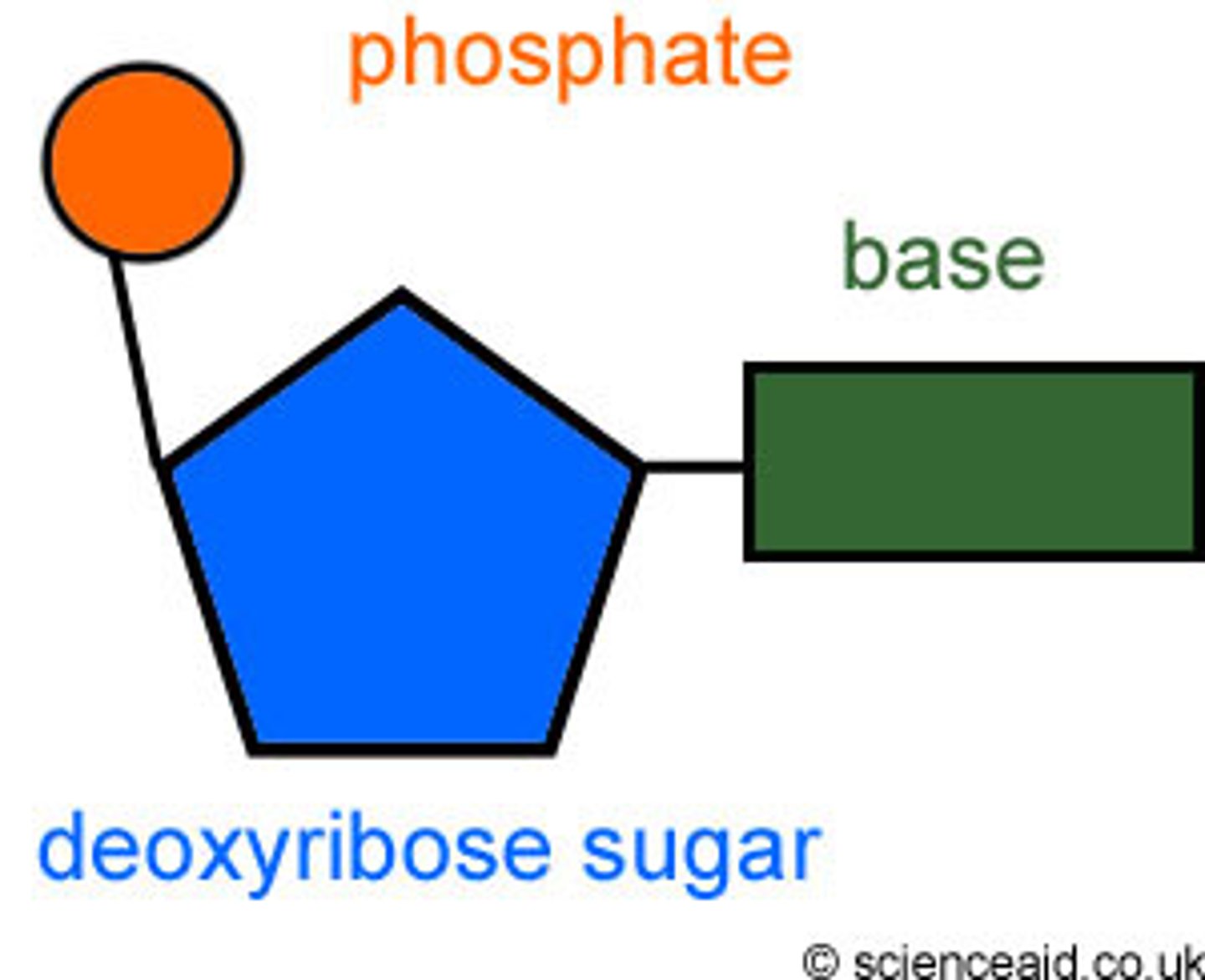
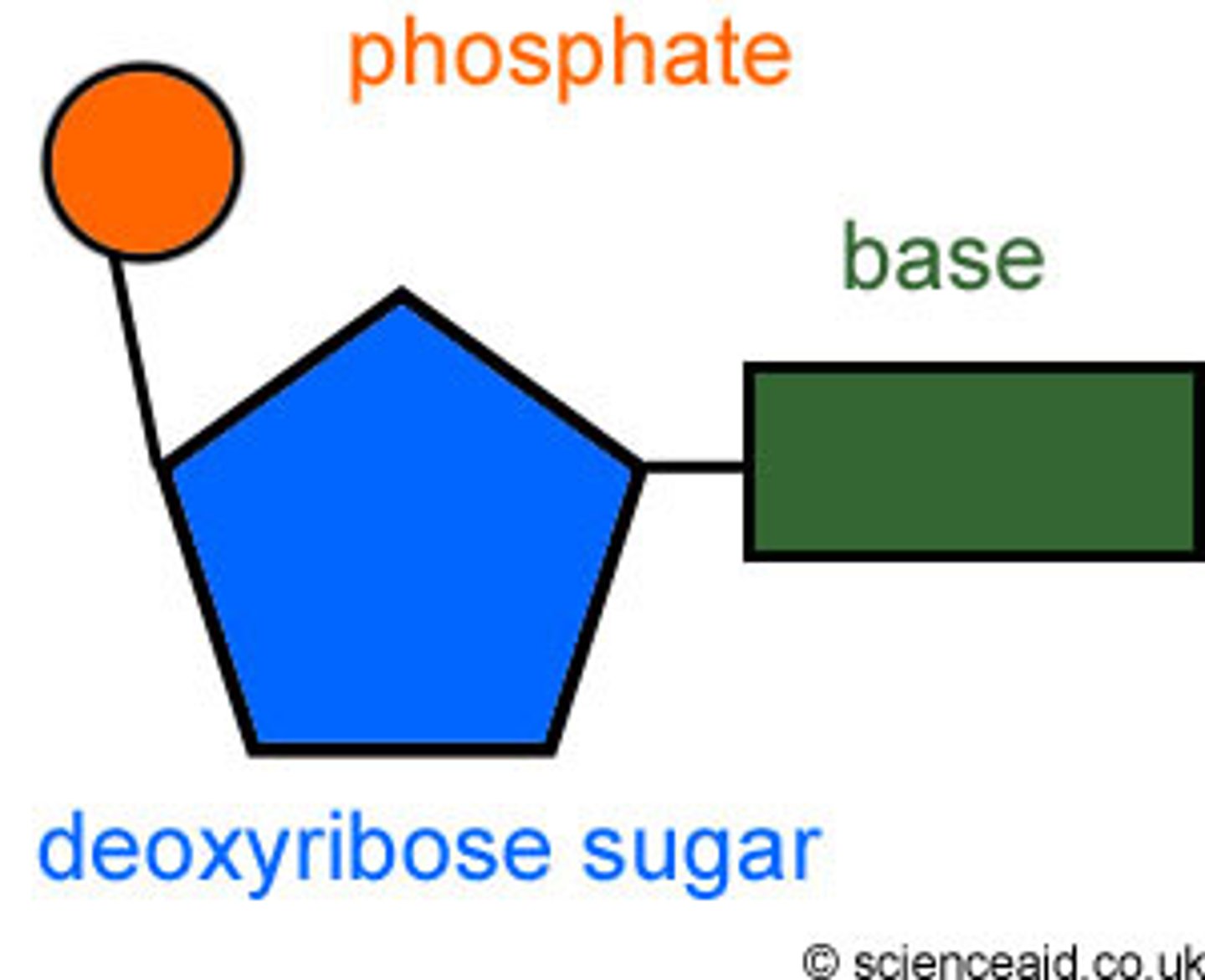
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
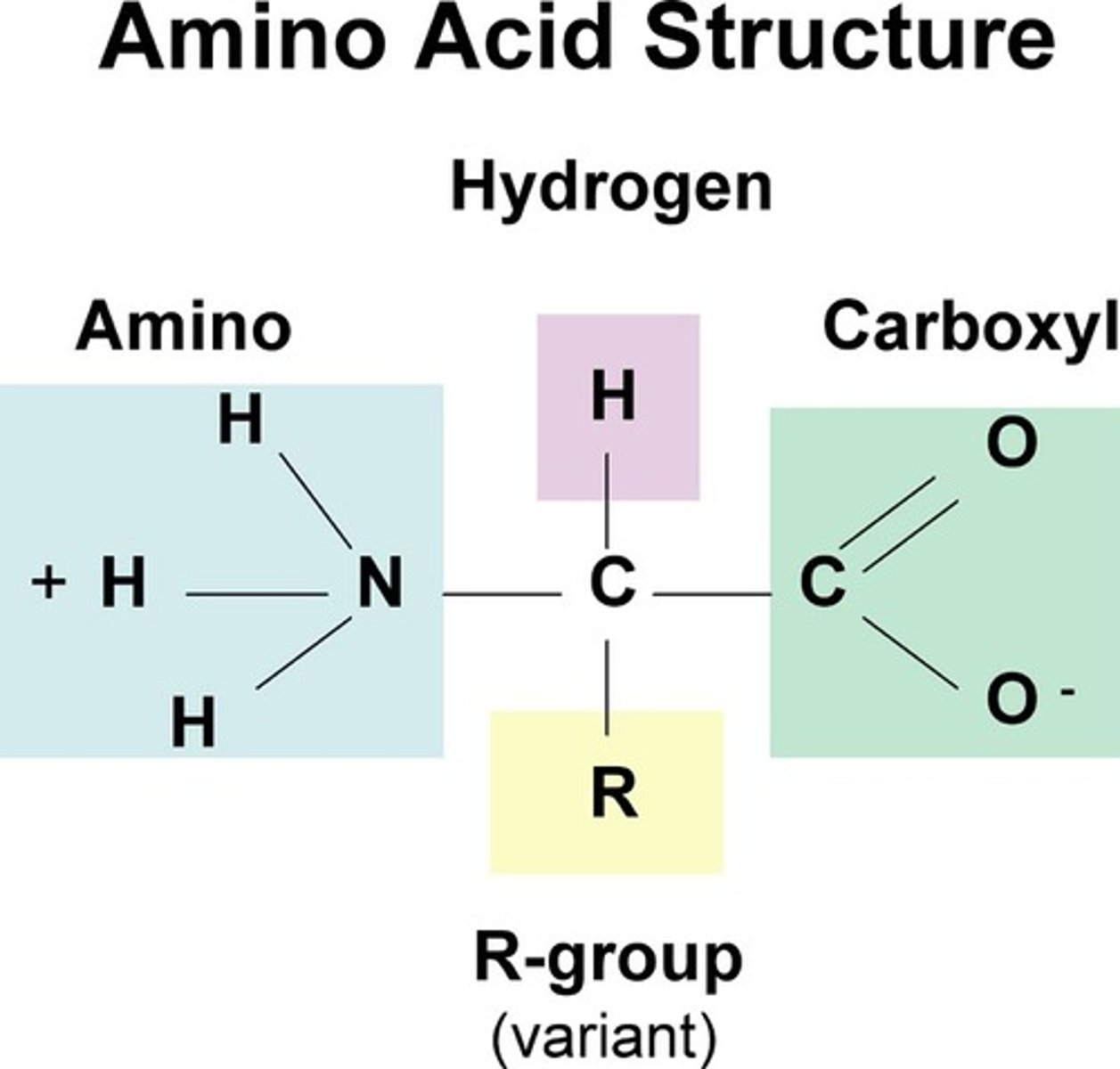
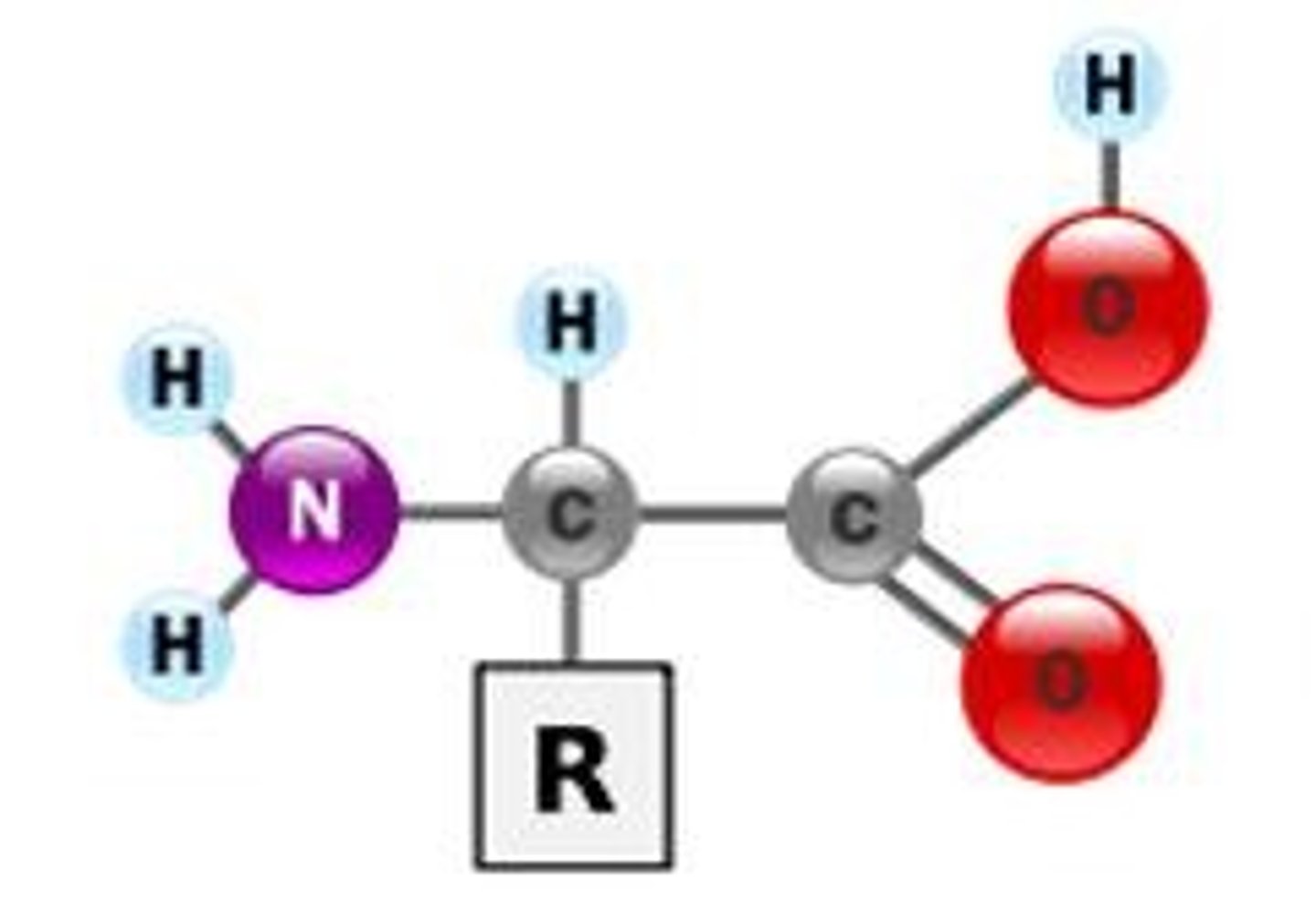
amino acids
a simple organic compound containing both a carboxyl (—COOH) and an amino (—NH2) group.
peptide bond
The chemical bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid
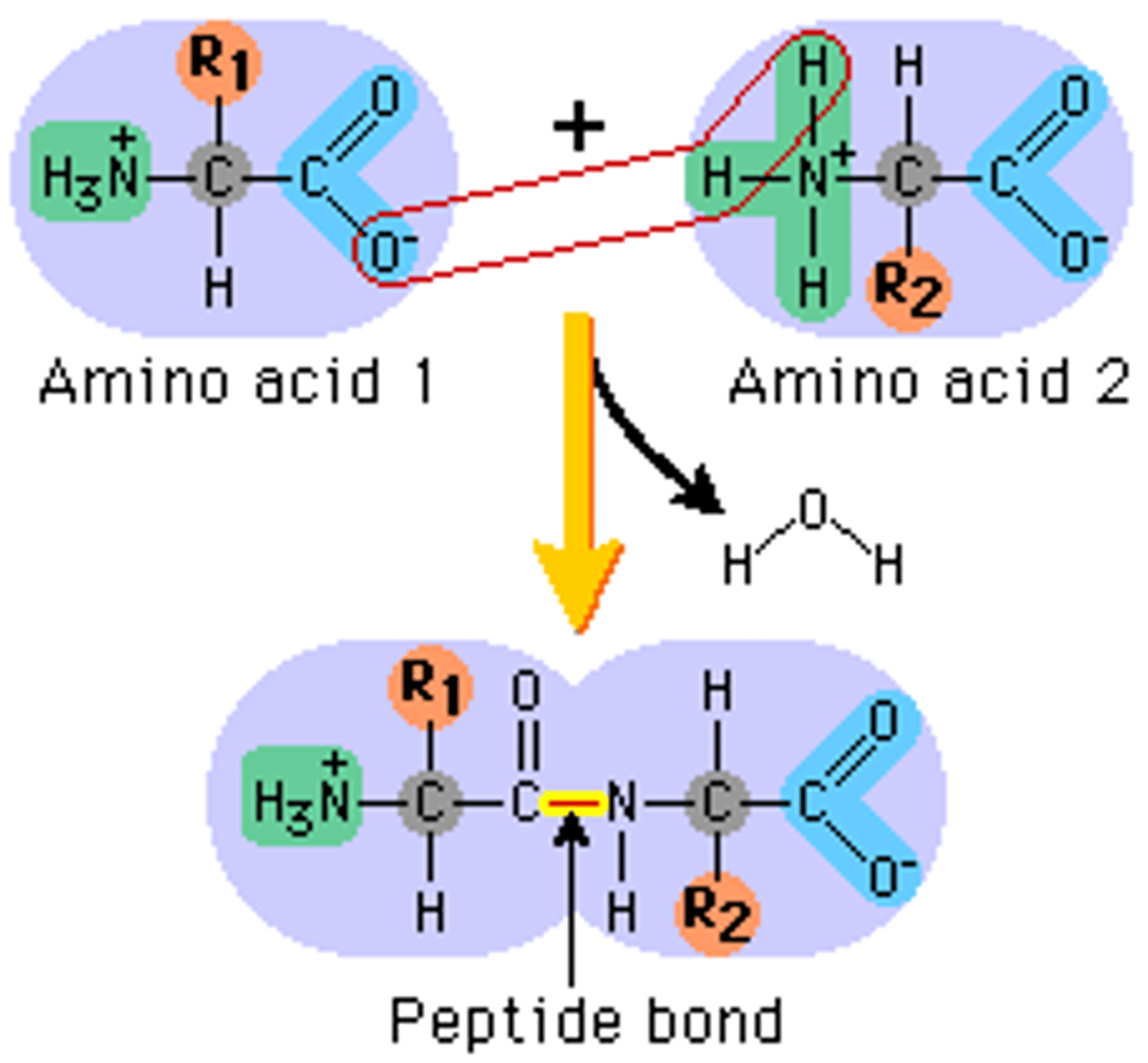
Protein
An organic compound that is made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is a principal component of all cells
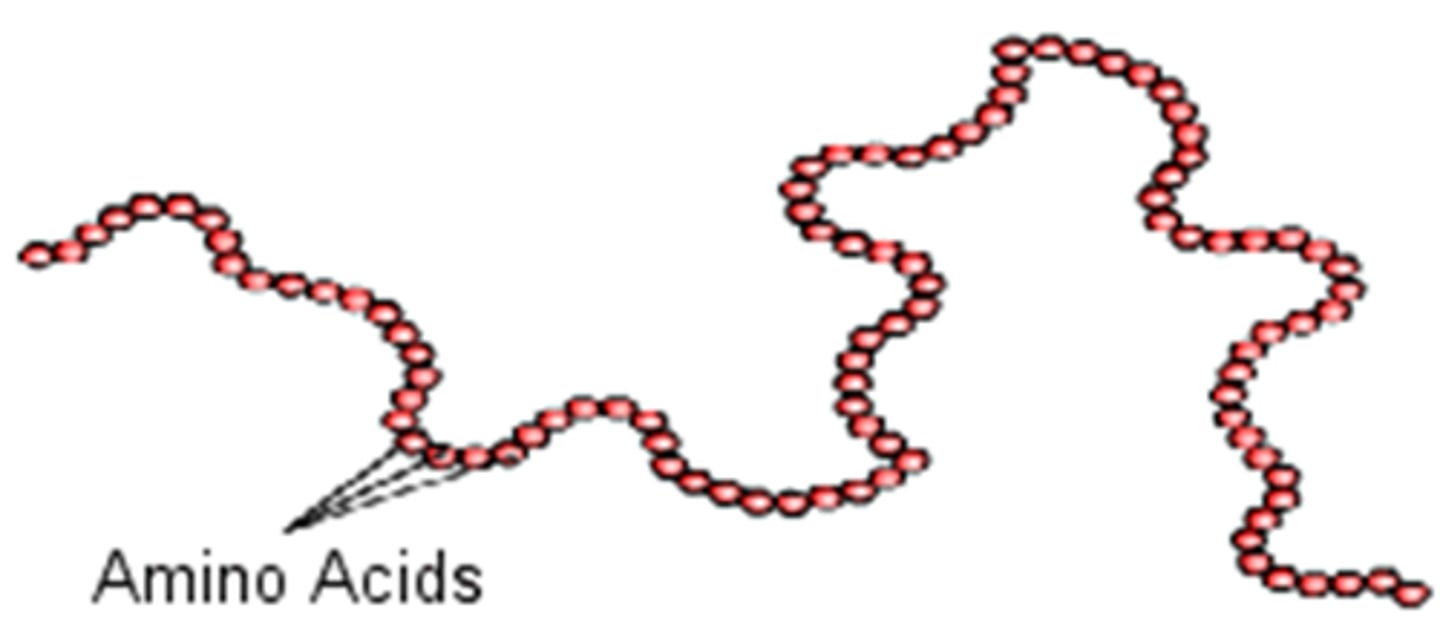
Polypeptide
A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
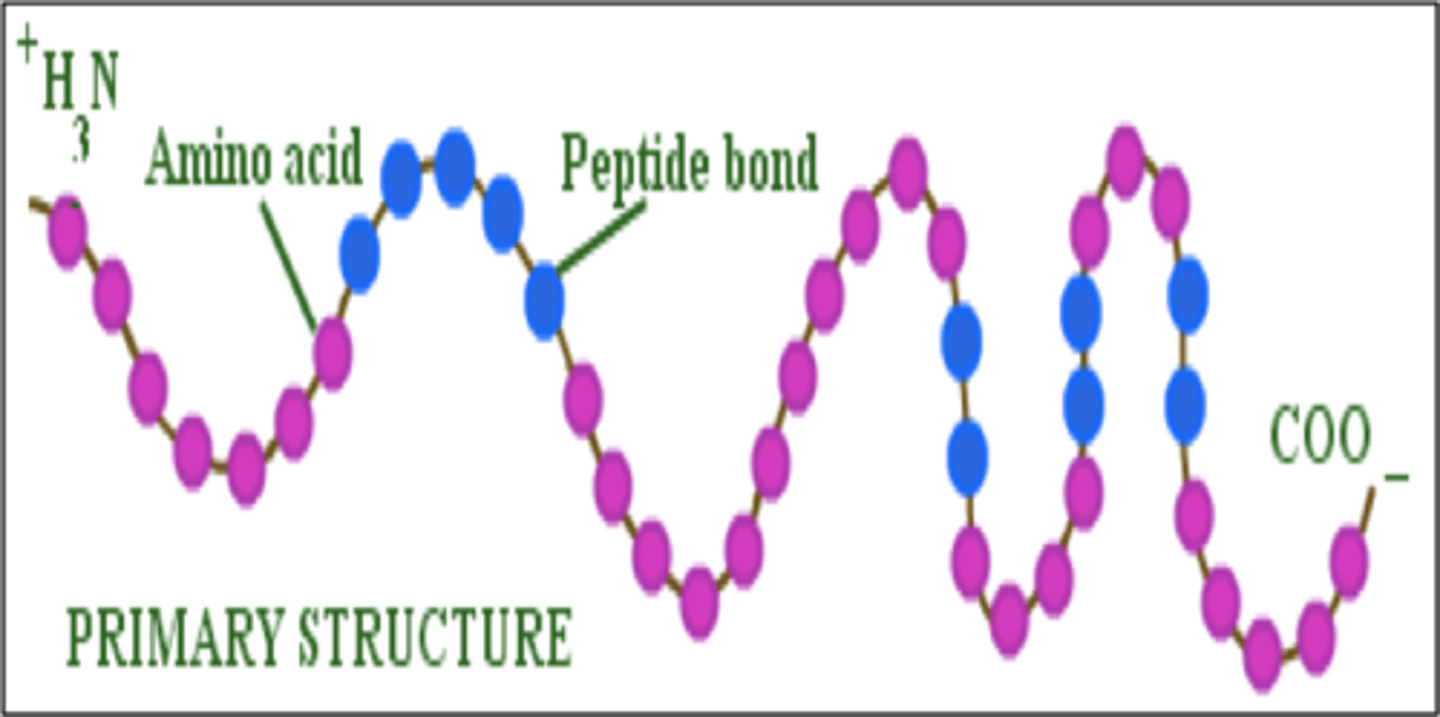
primary structure
The first level of protein structure; the specific sequence of amino acids making up a polypeptide chain.

secondary structure
The second level of protein structure; the regular local patterns of coils or folds of a polypeptide chain.
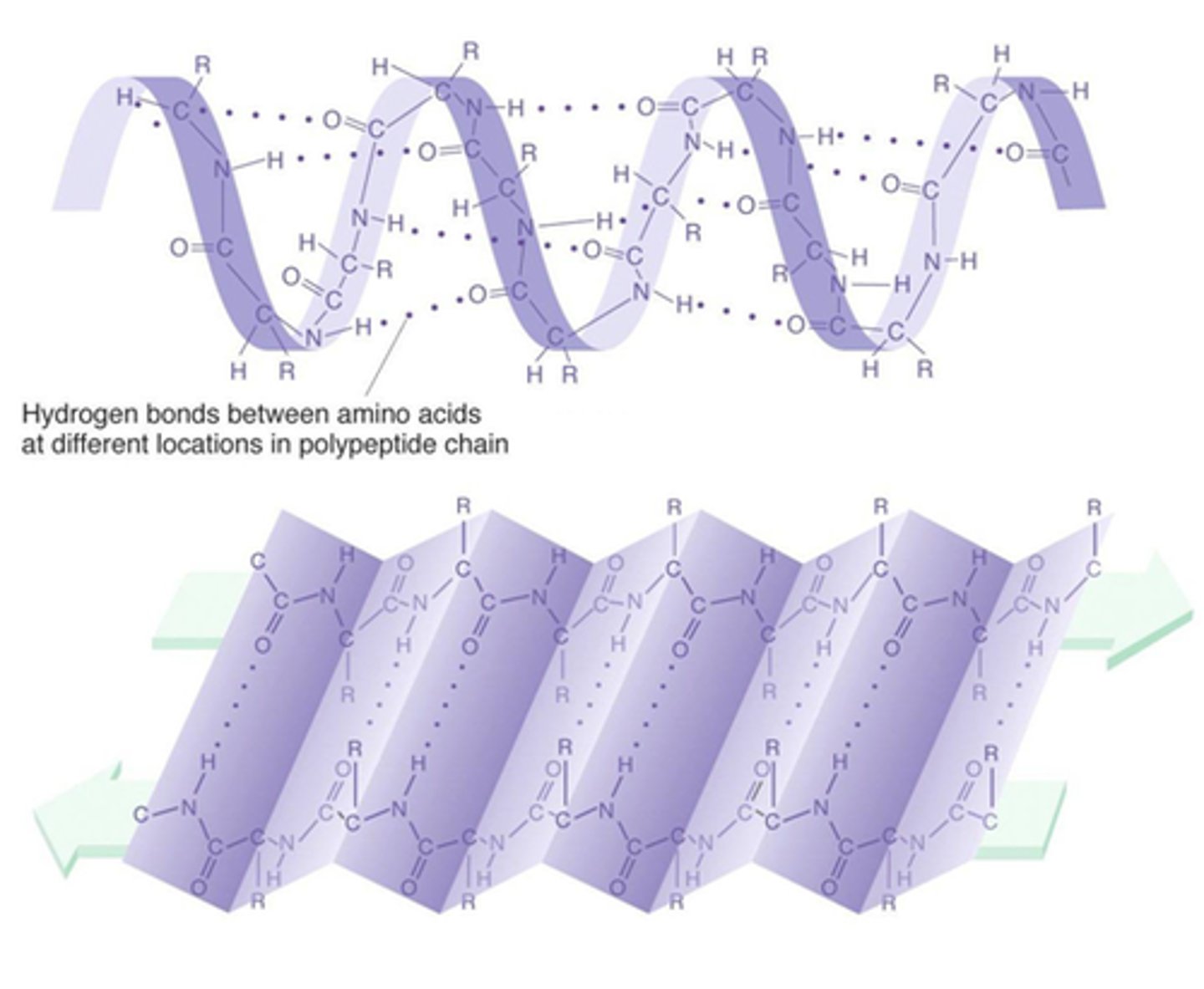
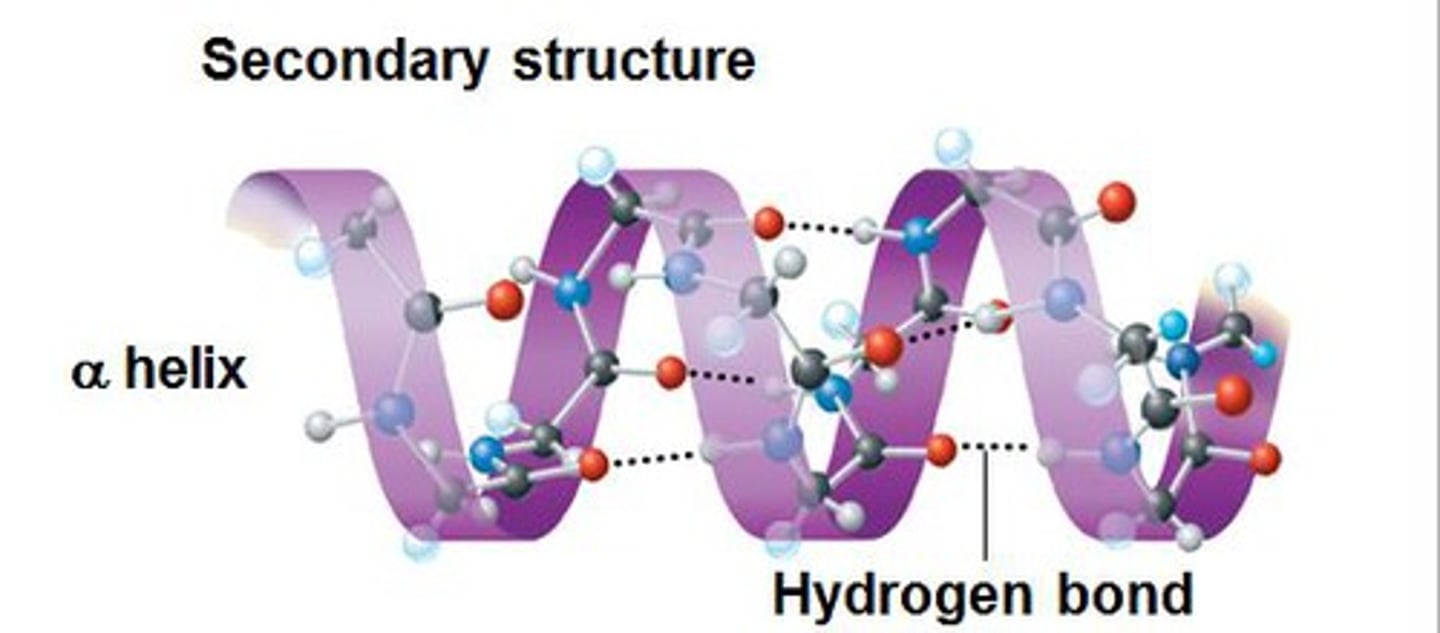
alpha helix
A spiral shape constituting one form of the secondary structure of proteins, arising from a specific hydrogen-bonding structure.
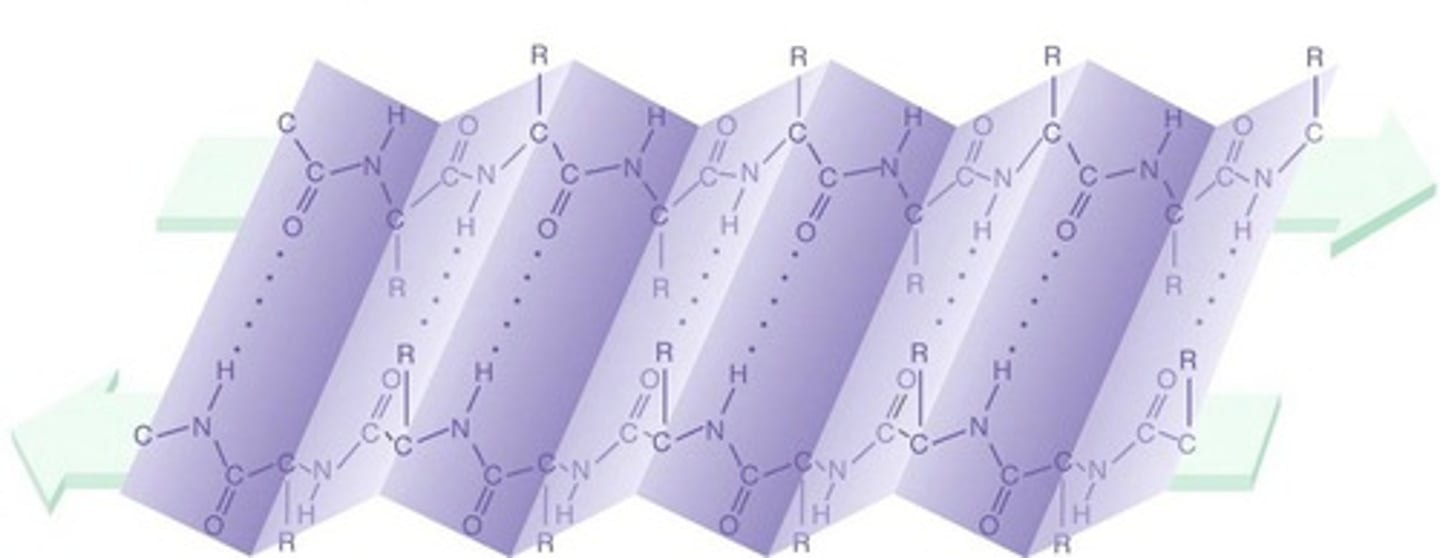
beta pleated sheet
One form of the secondary structure of proteins in which the polypeptide chain folds back and forth, or where two regions of the chain lie parallel to each other and are held together by hydrogen bonds.
hydrogen bond
A type of weak chemical bond formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of a polar covalent bond in one molecule is attracted to the slightly negative atom of a polar covalent bond in another molecule.

tertiary structure
The third level of protein structure; the overall, three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
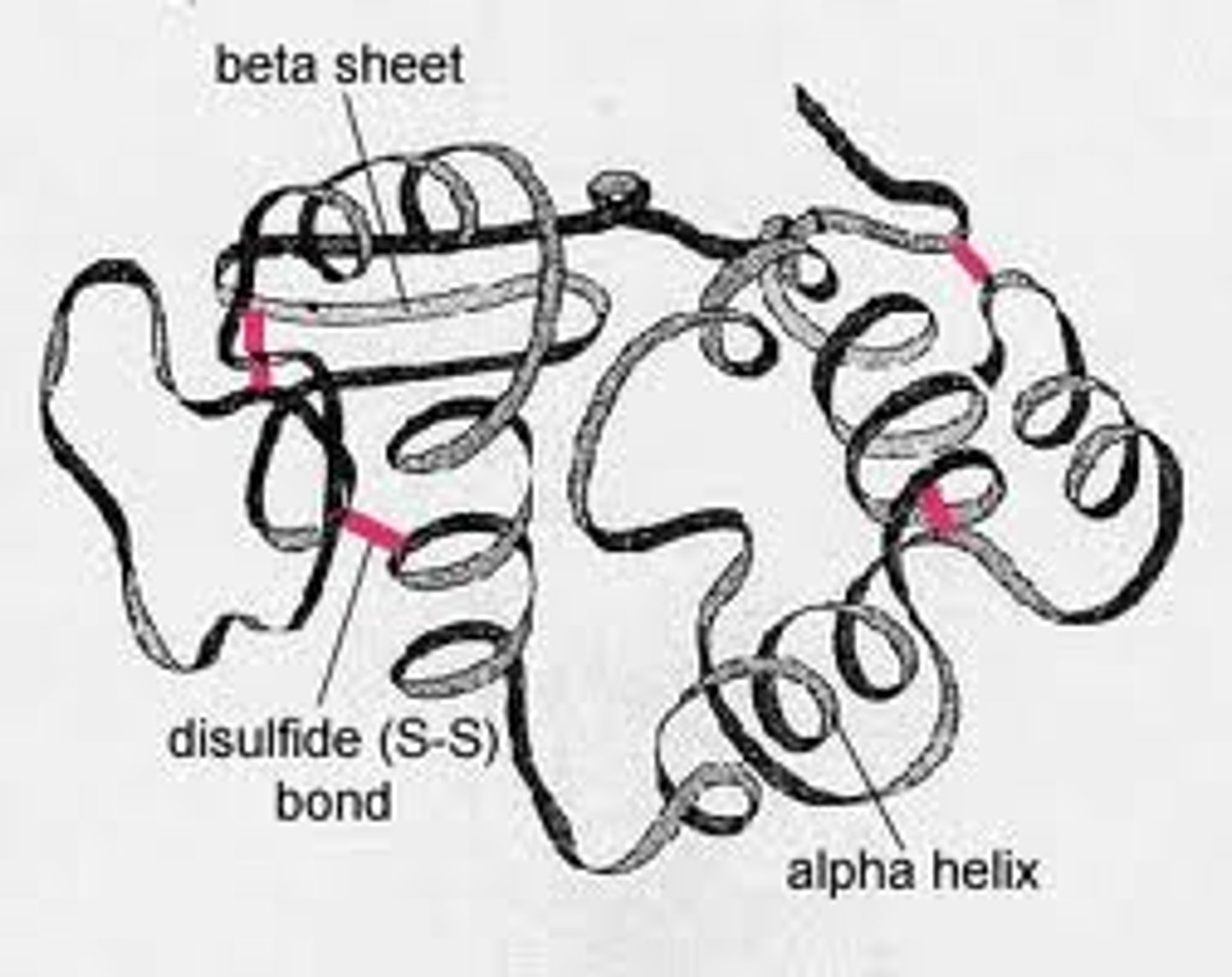
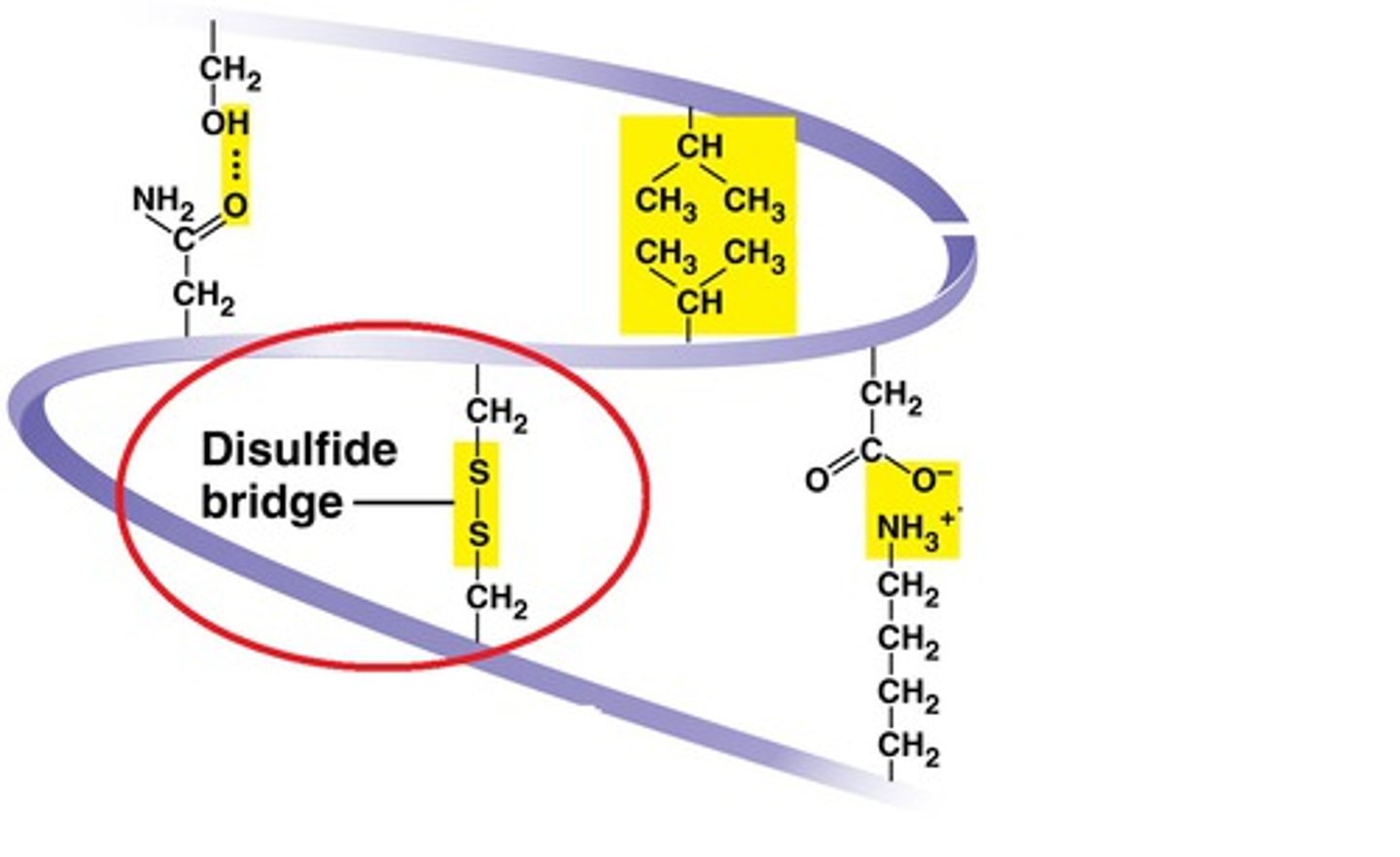
disulfide bridges
A strong covalent bond formed when the sulfur of one cysteine monomer bonds to the sulfur of another cysteine monomer.
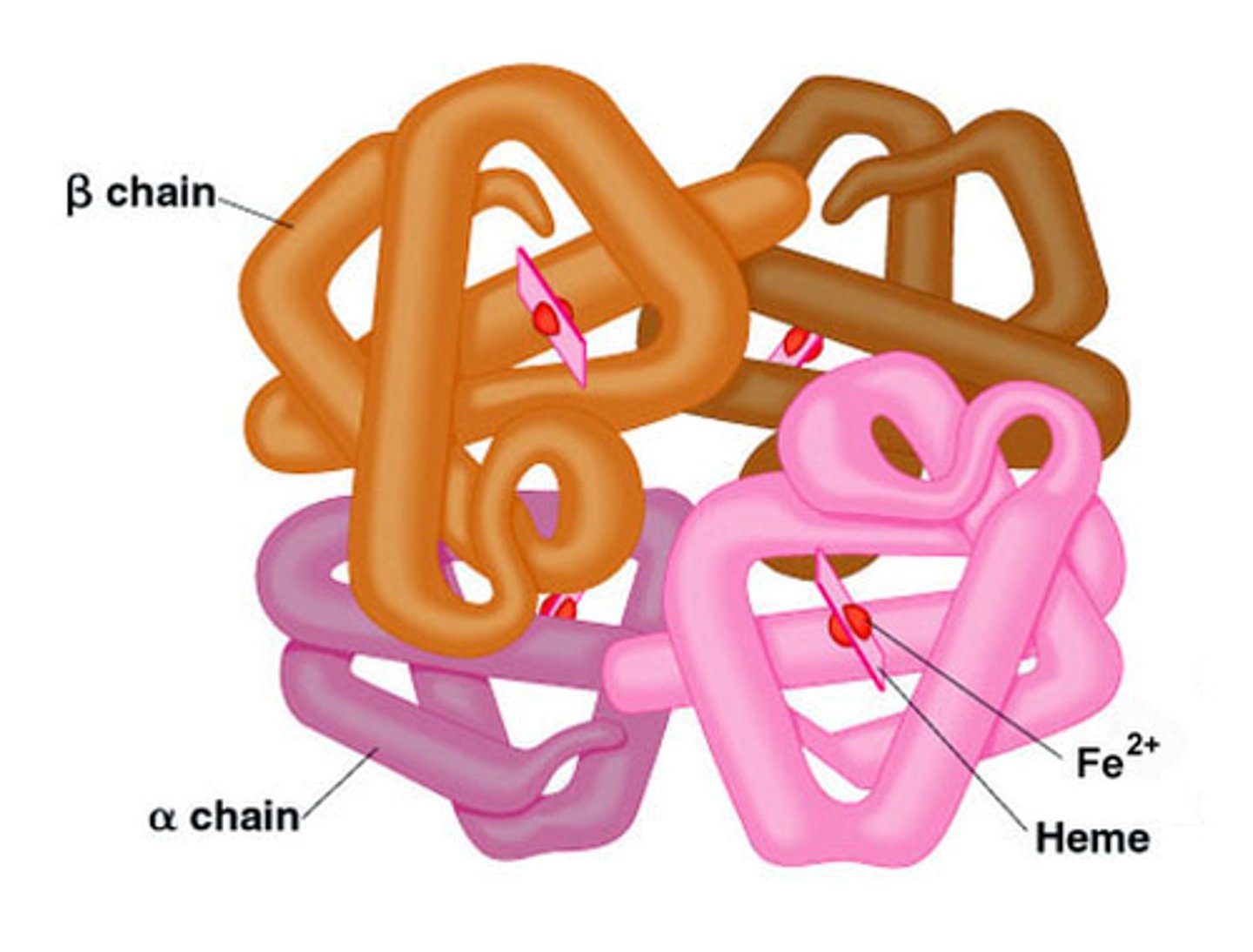
quaternary structure
The fourth level of protein structure; the shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits.
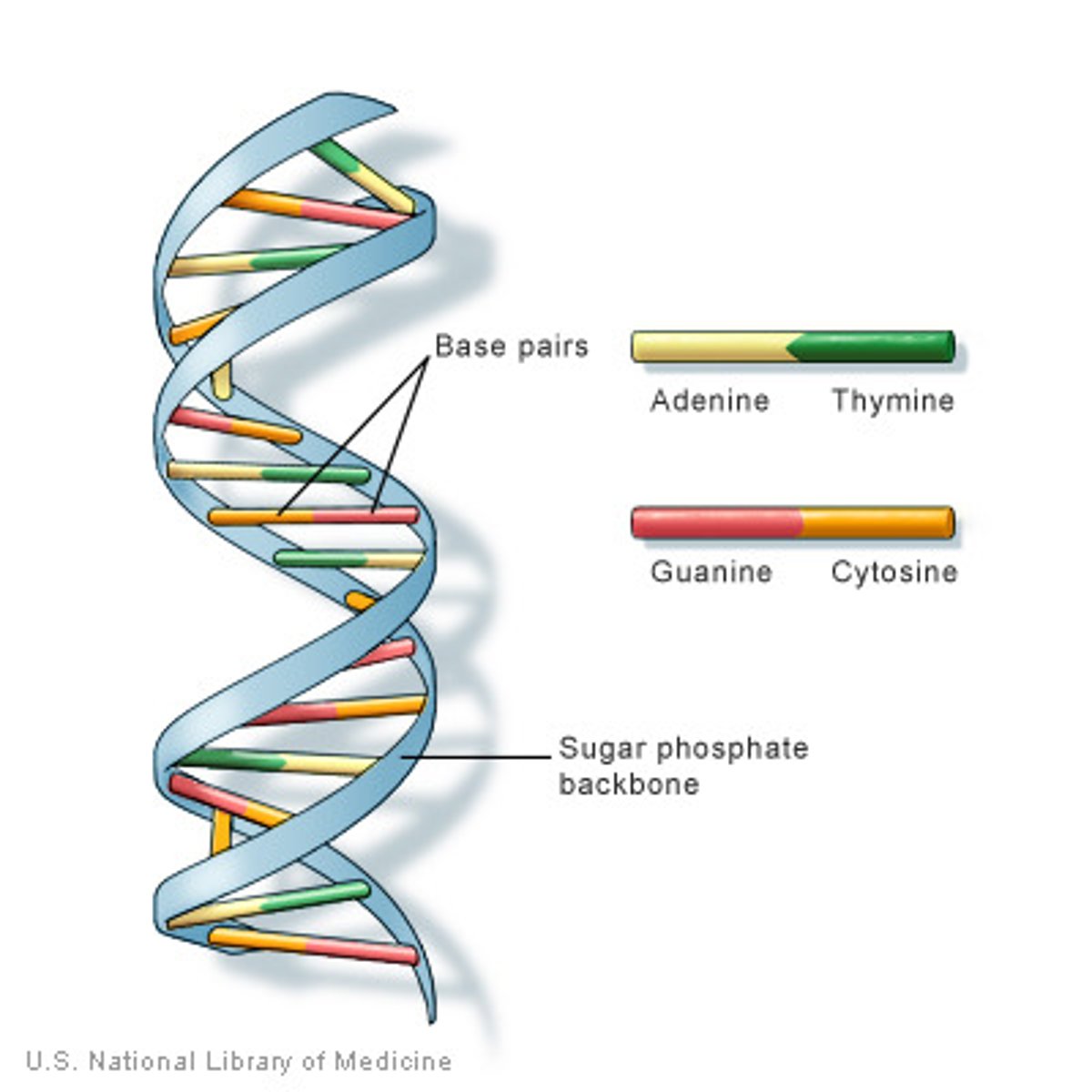
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
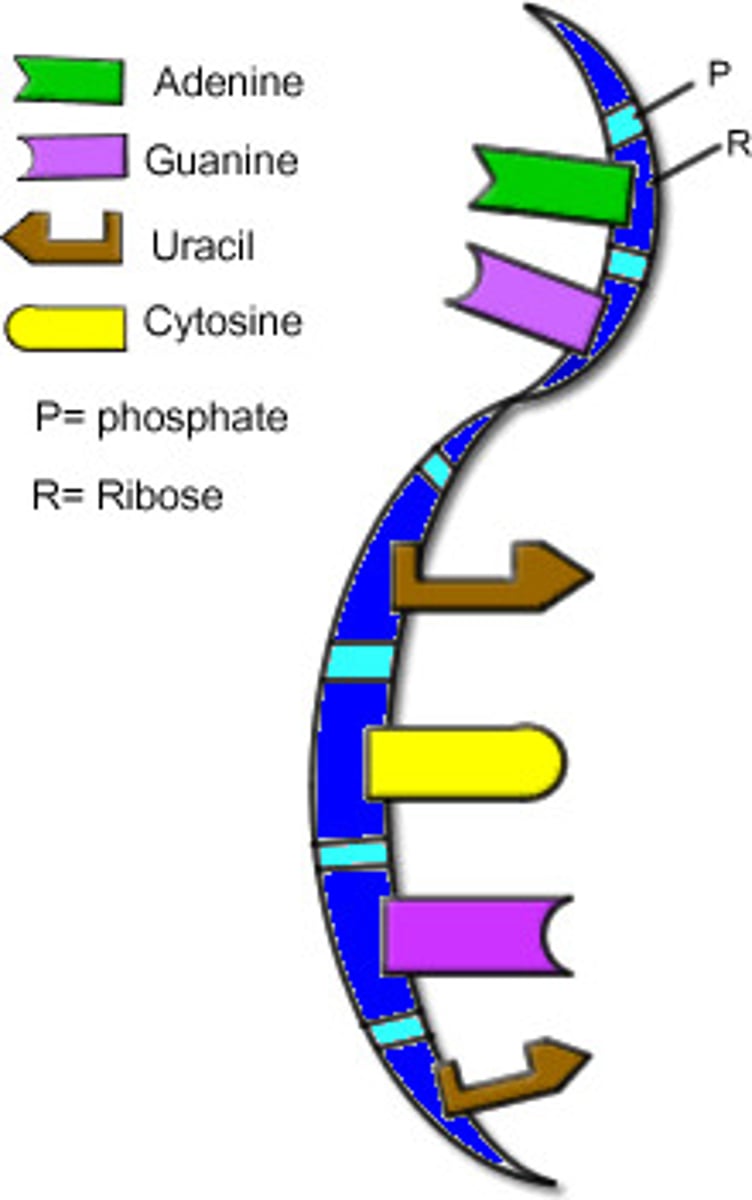
RNA
A single-stranded nucleic acid that passes along genetic messages
nucleic acids
macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus
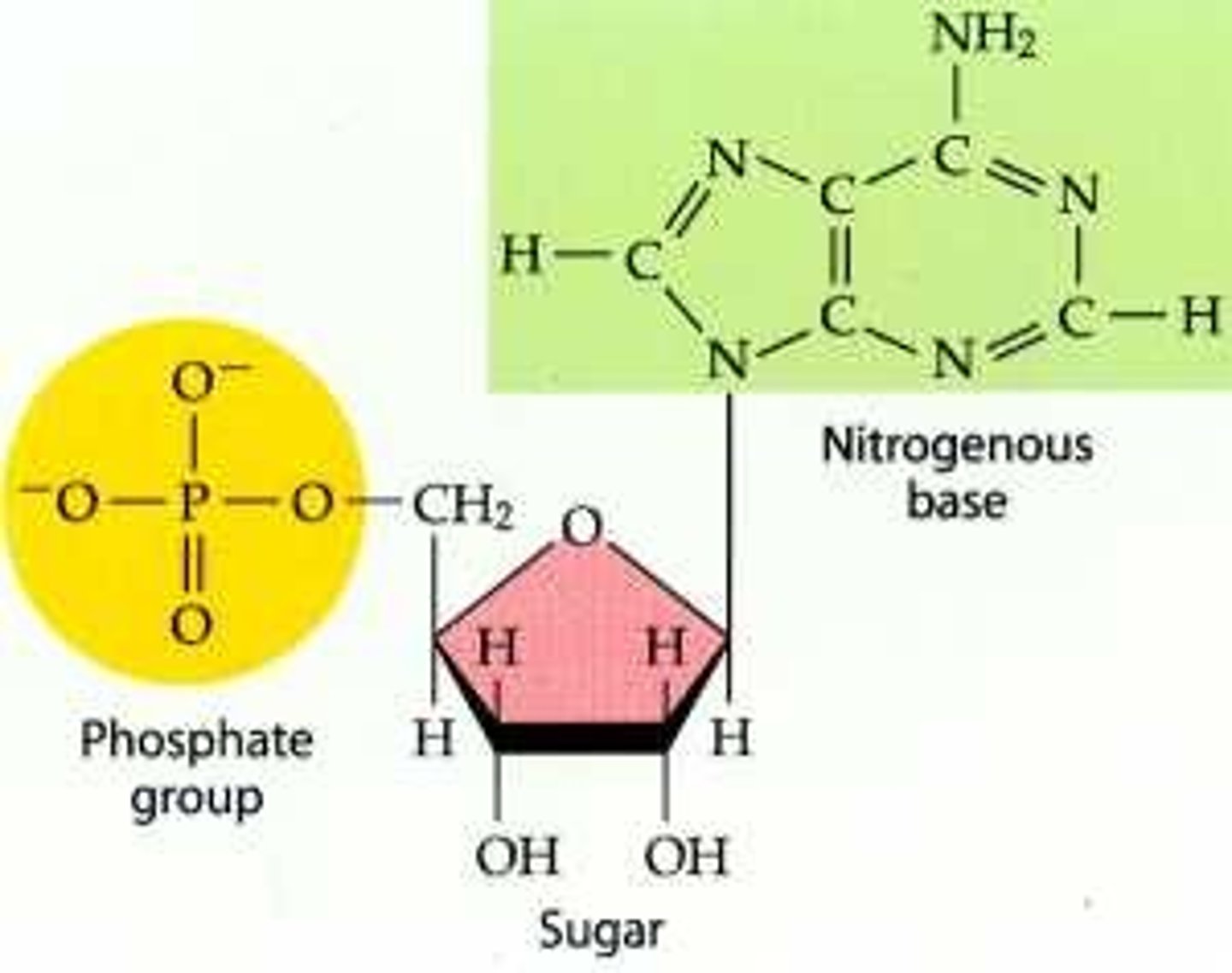
nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
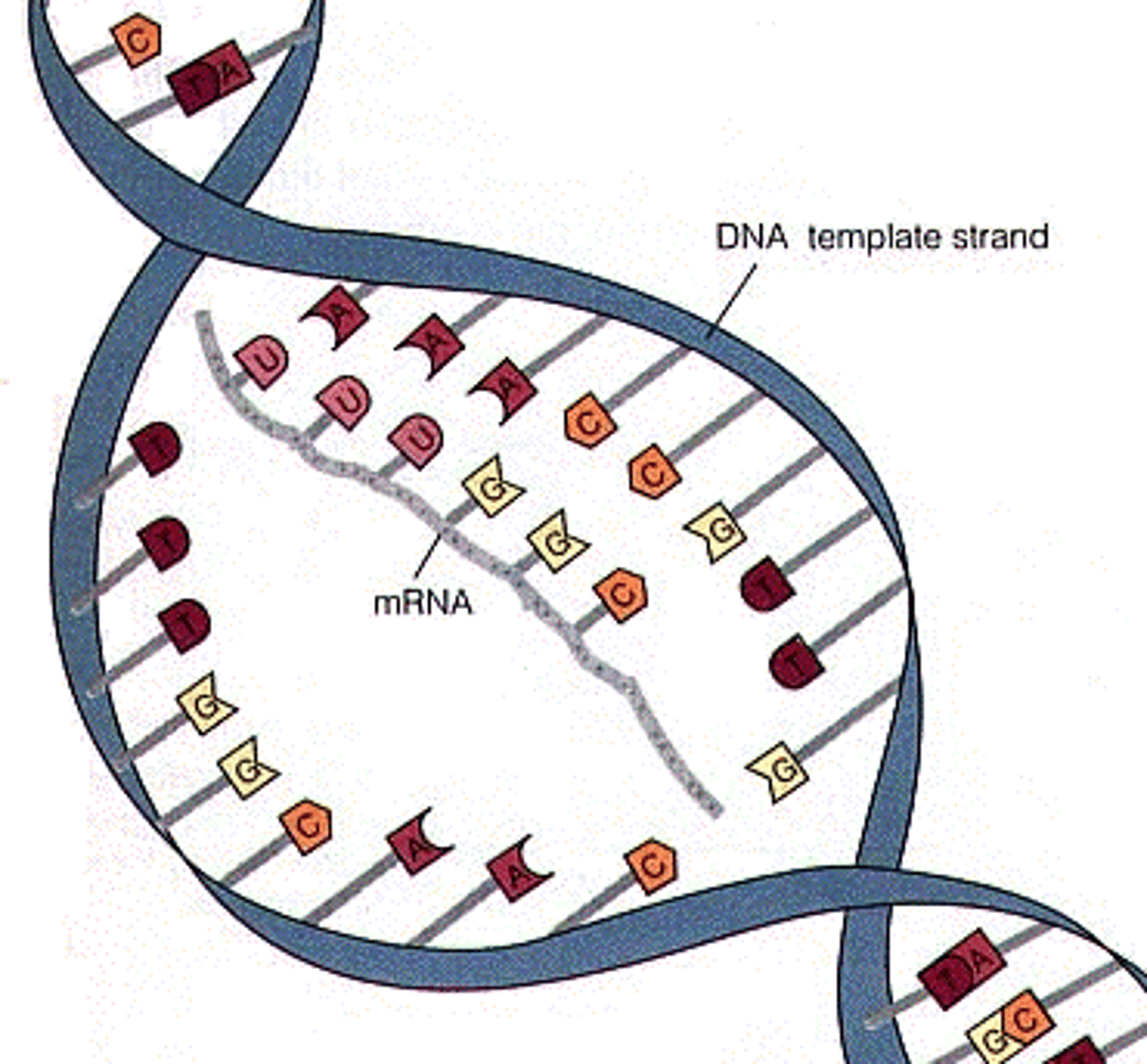
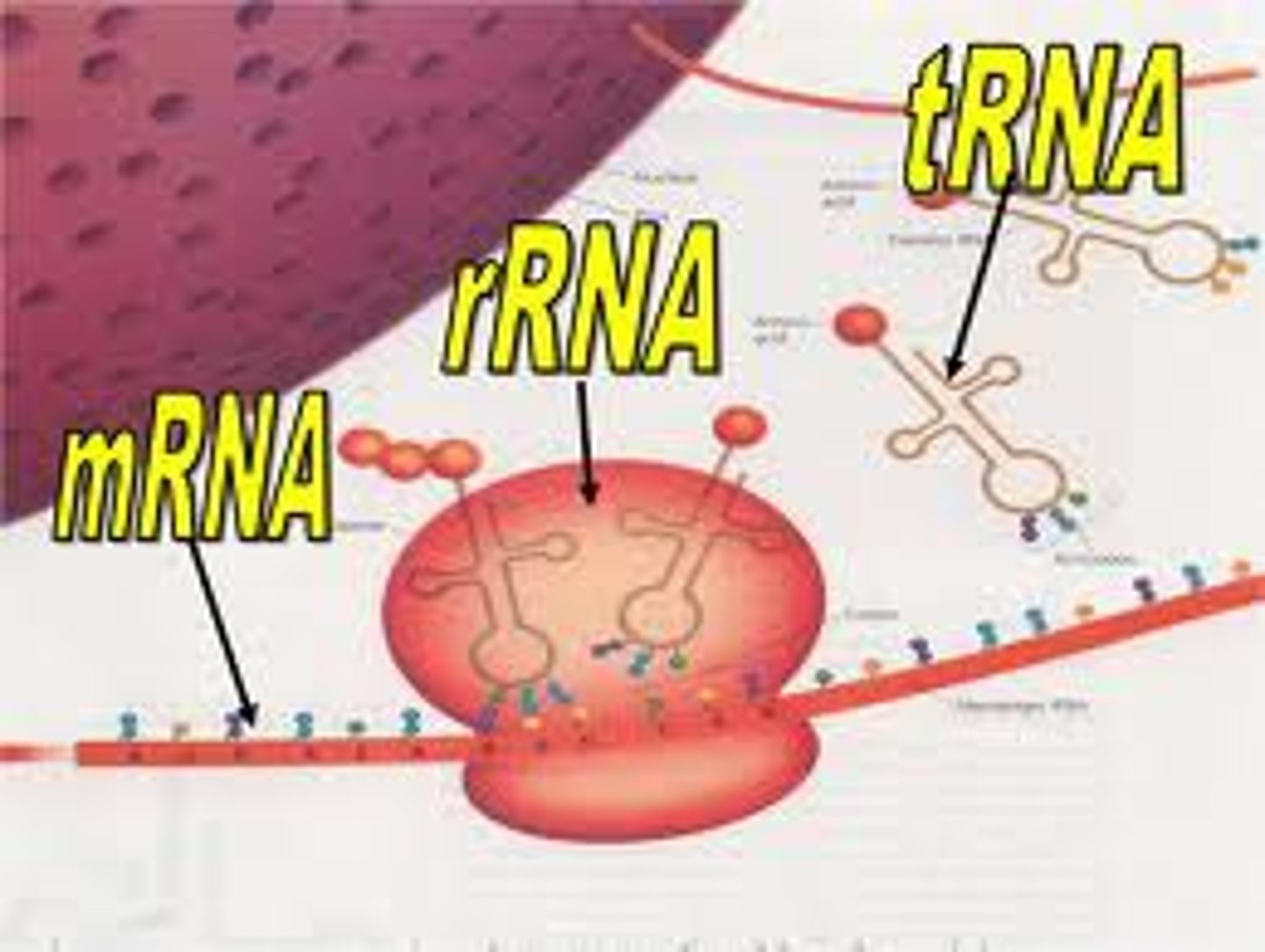
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
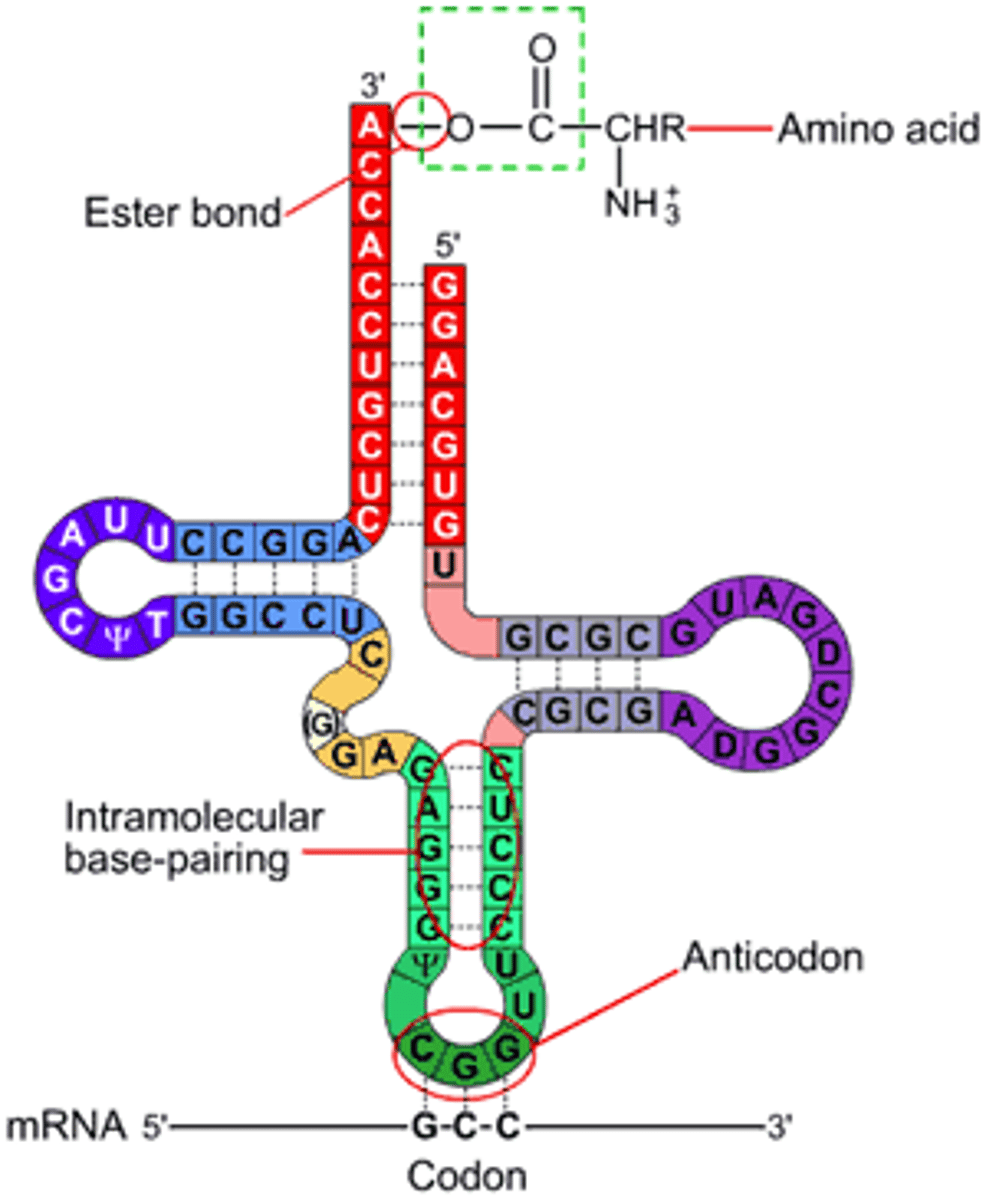
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
rRNA
ribosomal RNA; type of RNA that makes up part of the ribosome
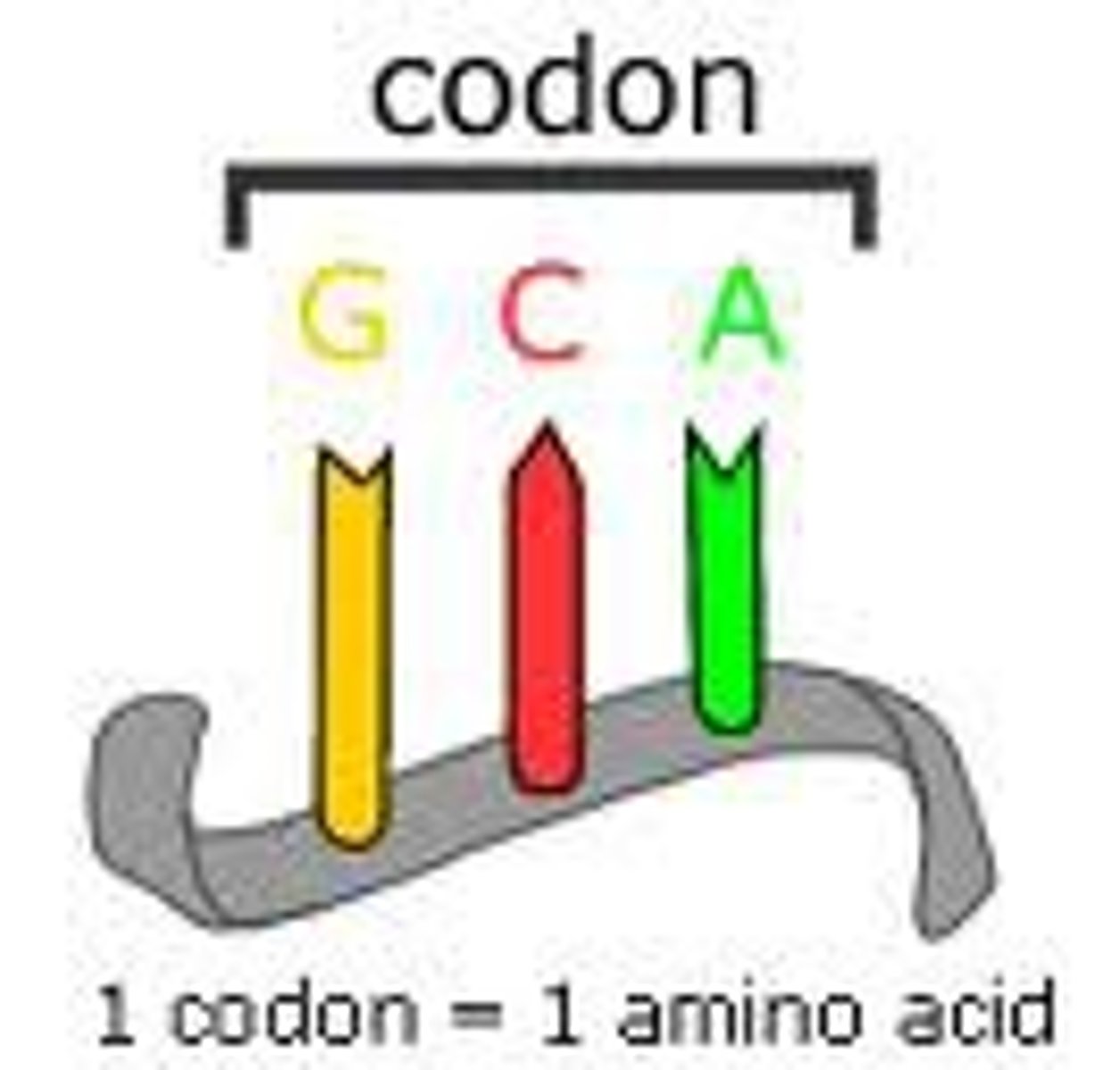
Codon
A specific sequence of three adjacent bases on a strand of DNA or RNA that provides genetic code information for a particular amino acid