Glymphatic System
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Glial cells
Most abundant cells in the central nervous system; originally thought to be purely non-functional "glue" for neurons
Glial cells function
Perform a variety of functions including neuronal insulation, communication between neurons, nutrient transport, and waste transport
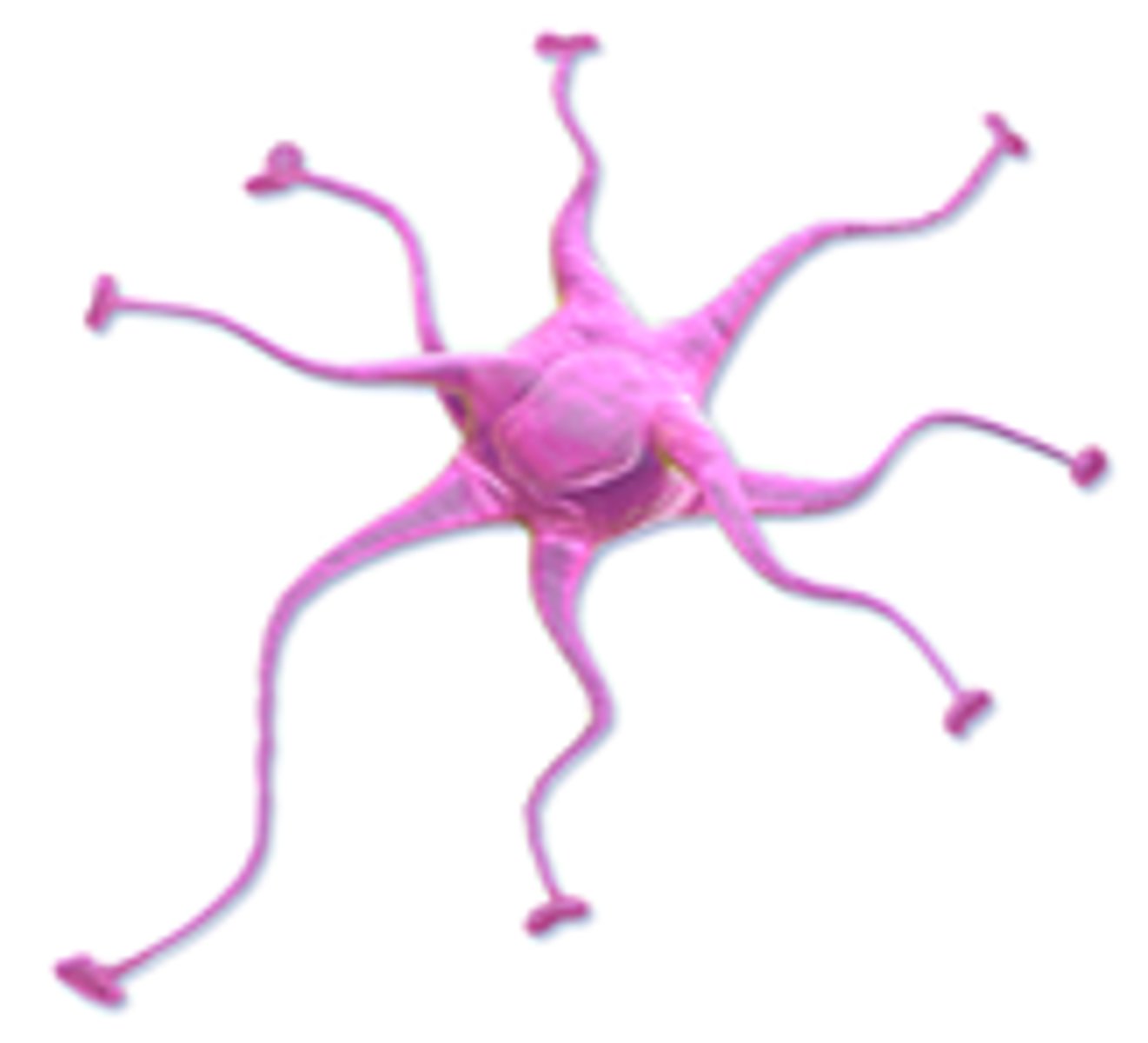
Astrocytes function
Contribute to the formation of the blood-brain barrier; physically and metabolically support and communicate with neurons; regulate the formation and functions of synapses; maintain water homeostasis and the microenvironment in the brain
Astrocyte image
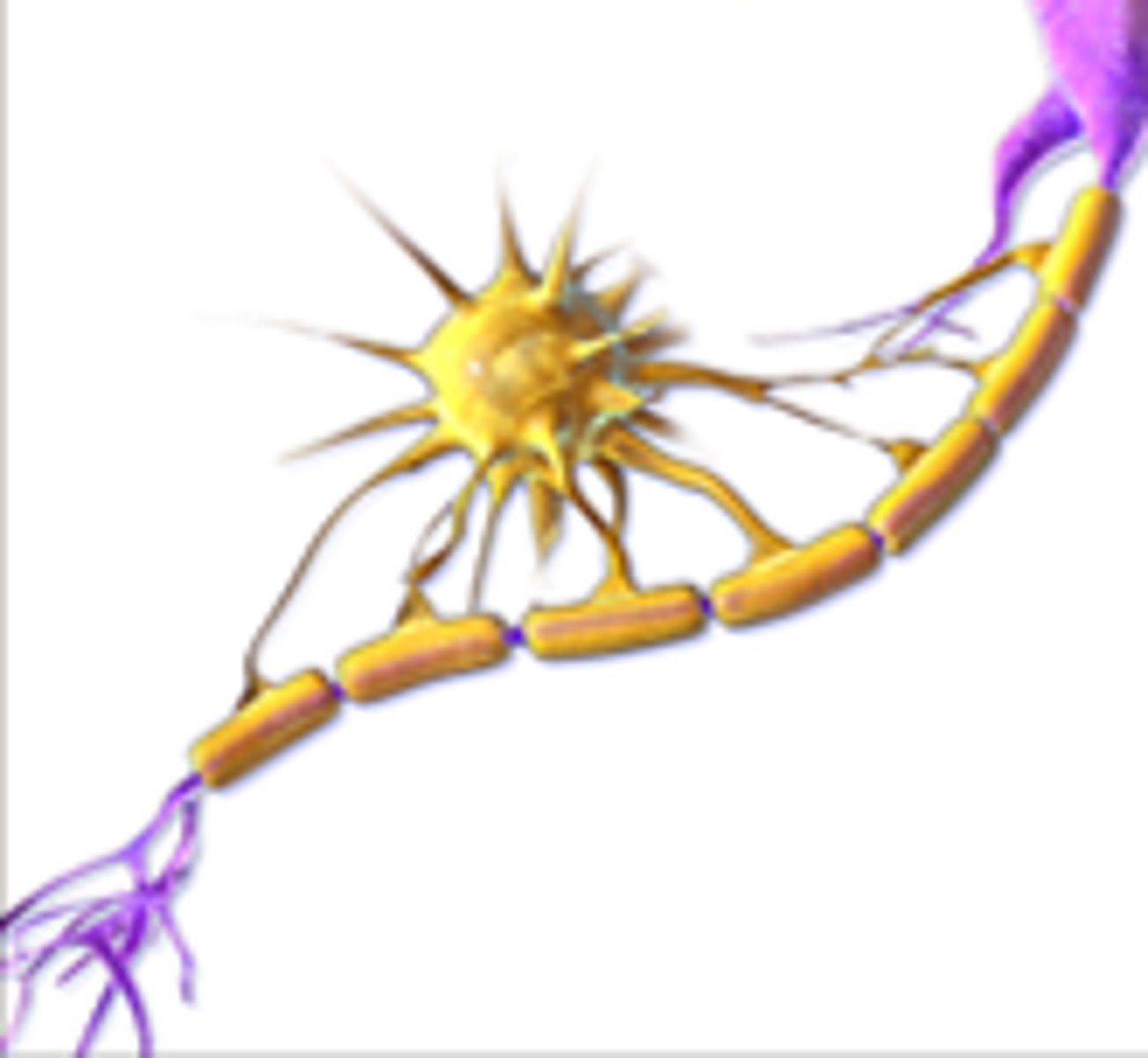
Oligodendrocyte function
Produces myelin sheathes to ensure to saltatory action potential propagation along the axons.
Oligodendrocyte image
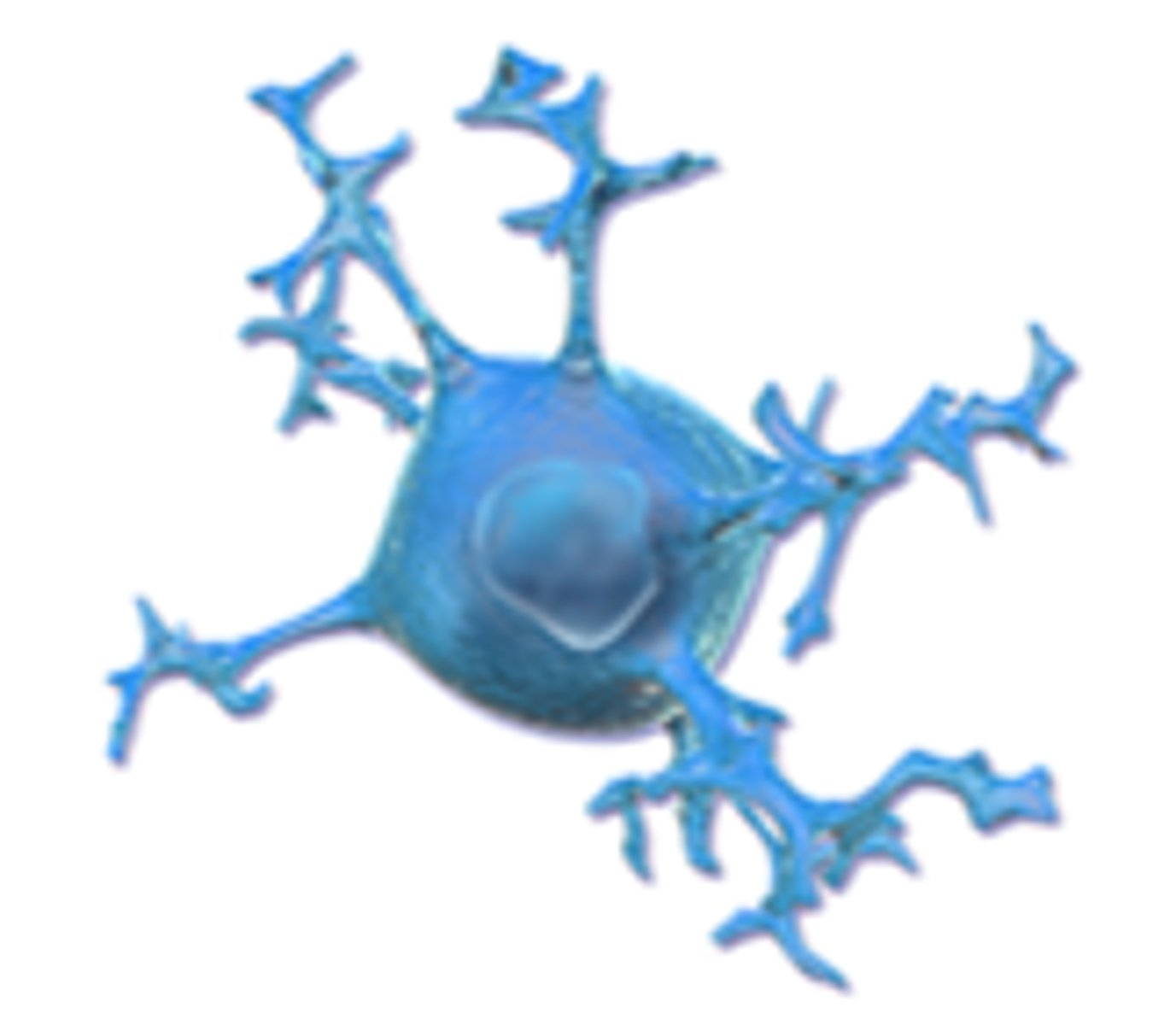
Microglia function
Responsible for the elimination of microbes, dead cells, redundant synapses, protein aggregates, and other particulate and soluble antigens that may endanger the CNS; mediators of neuroinflammation and can induce or modulate a broad spectrum of cellular responses
Microglia image
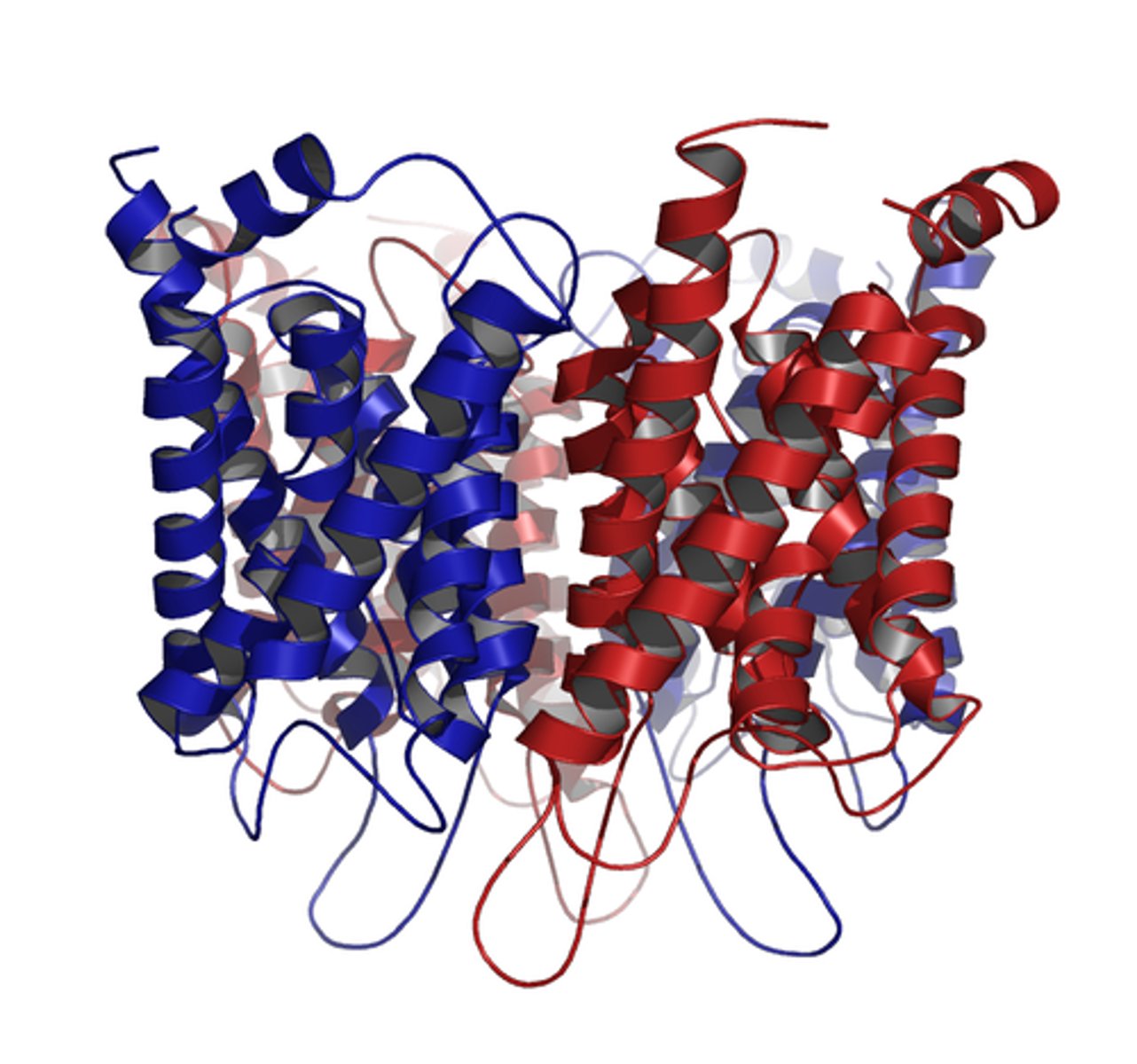
Aquaporins (AQPs) description
Diverse family of membrane proteins that are expressed predominantly in tissues in which edema and fluid imbalances are of major concern
Aquaporins (AQPs) function
Responsible for the bi-directional passage of water and small solutes across the cell membranes while preserving ion gradients
Aquaporins image
Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) description
A water-selective transporter expressed mainly by astrocytes in small processes in the proximity of the subarachnoid area, ventricular spaces, and blood vessels
Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) function
Necessary not only for water homeostasis but also to clear small molecules and metabolites, including Ab and Tau proteins, from interstitial space
What triggers AQP activity?
Interneuron release of peptides
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) description
A neuropeptide that functions as a neuromodulator and neurotransmitter
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) function
Involved in several cellular processes that are relevant to glymphatic clearance and is thought to be released during high-frequency stimulation
What frequency stimulation causes neurons to release peptides that increase glymphatic clearance of amyloid?
40Hz