Lecture 10: Cashflow of stocks (dividends), common shares, preferred shares,intrinsic value
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
What are the 2 types of equity securities?
Common shares: dividends after preferred, but control over firm’s decisions (voting rights)
Preferred shared: priority in dividend payments & liquidation but have no voting rights
shares have no maturity date (dividends as long as company exists)
How do you find the value of common stock?
The value (intrinsic value) of any asset is the present value of its expected future cash flows
Value of asset = PV of future cashflow
What is case 1: zero growth?
Assume that company pays a constant dividend forever
PV of a perpetuity
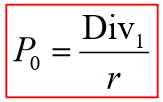
What is case 2: constant growth?
Assumes that the dividends grow at a constant rate forever
Growing perpetuity formula
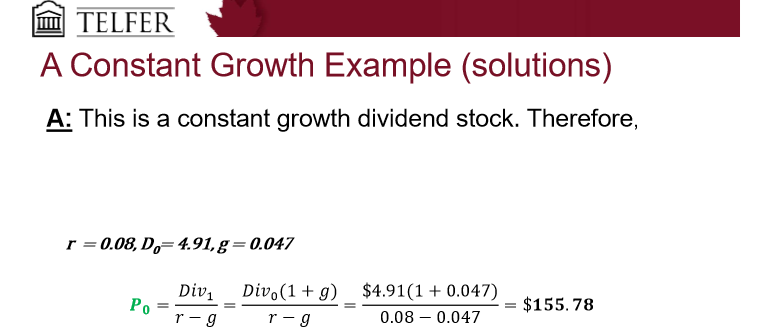
What is the general formula for differential growth?
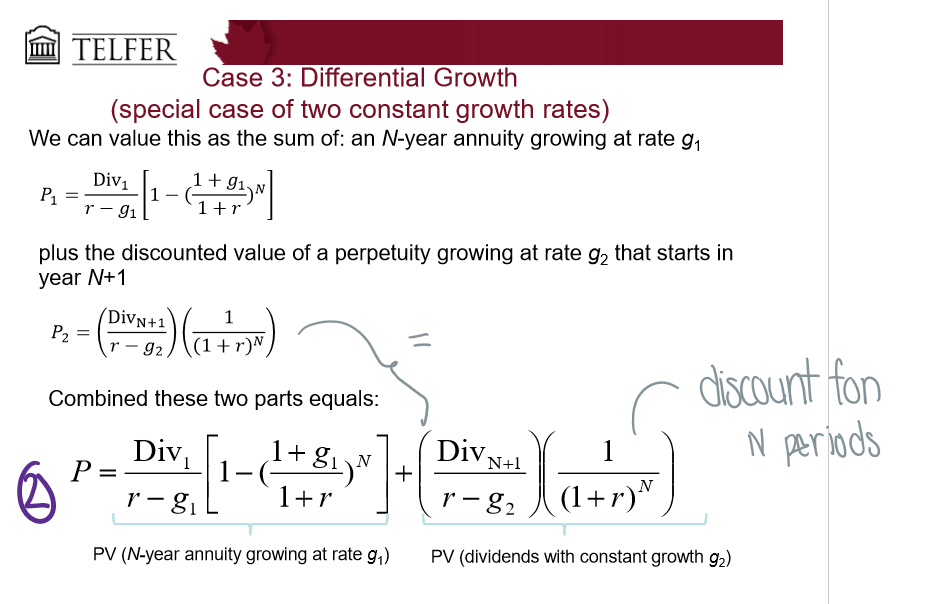
What is case 3: differential growth?
Assume that dividends grow at different rates in the near future, but then will grow at a constant rate after
estimate future dividends in the future
estimate future stock price when stock becomes a constant growth stock
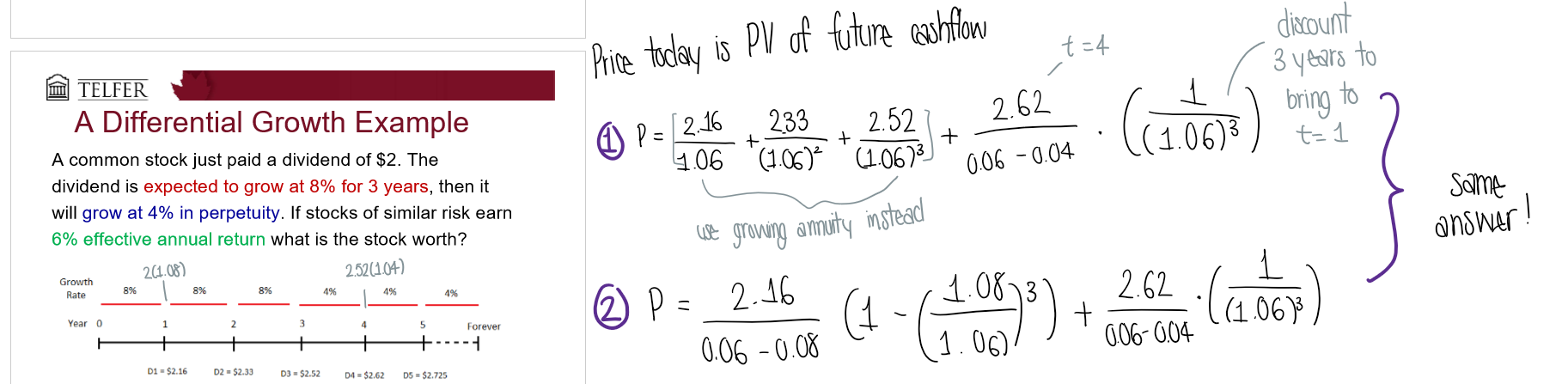
How do you estimate the growth rate g?
Growth rate = retention ratio x return on earnings
How do you estimate the discount rate r?
Re-arrange the constant dividend growth formula

What are some concerns of the dividend discount model?
Many things are hard to estimate
what if firms don’t pay dividends?
growth rate must be LESS than the return rate