Kailyn Master Thesis - Introduction
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What are the differences between motor and non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease? [type of function, common symptoms, affected systems, timing]
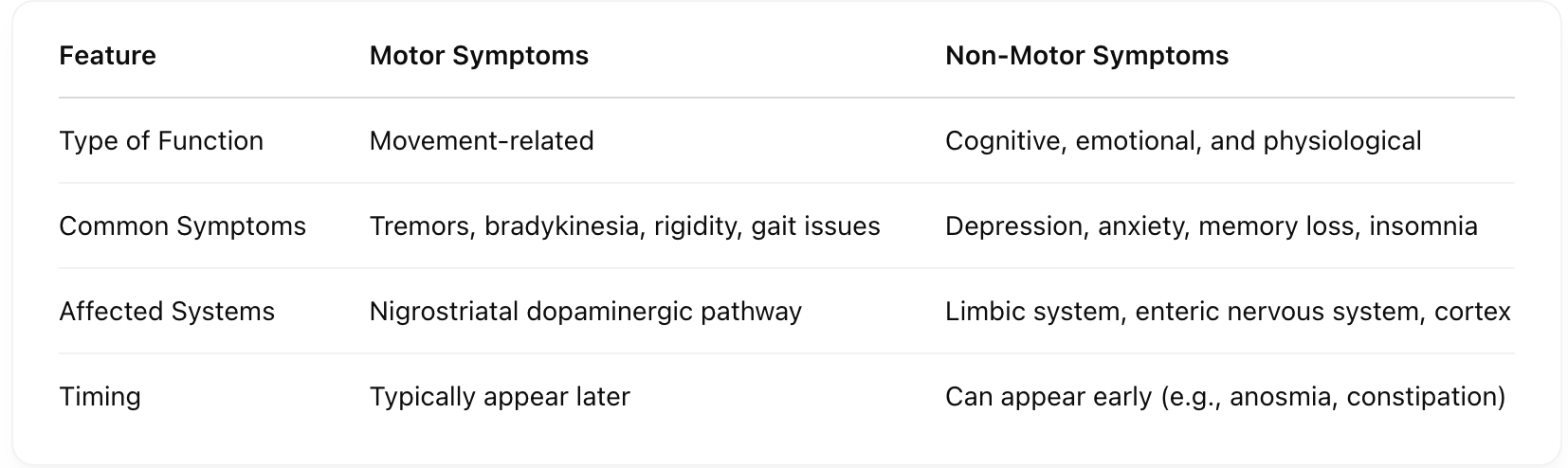
How do MPTP and 6-OHDA models differ in mimicking Parkinson’s Disease? [Blood Brain barrier, conversion process, method of entry, mechanism of damage, symptom representation, experimental use]
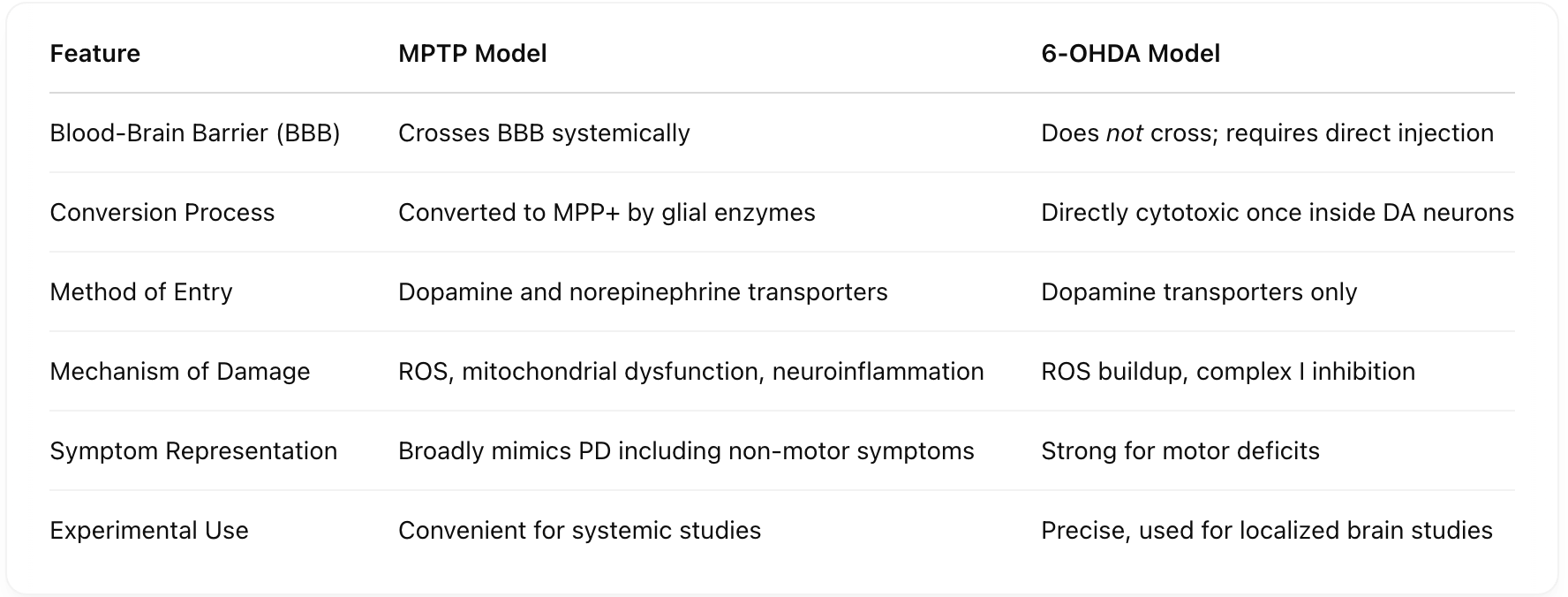
How does Lewy body distribution relate to different symptoms in PD? [Basal Ganglia & Substantia Nigra, Spinal Cord, Olfactory Bulb, Enteric Nervous System, Locus Coeruleus & Cortex]
What are the contrasting roles of N/OFQ-NOP signaling in health vs. PD conditions? [Normal physiology, inflammation regulation, PD pathology, anti-inflammatory function, expression sites]

What is the sequence from dopamine neuron degeneration to PD symptom onset, starting from an SN neuron death and ending with PD symptoms?
SN neuron death → ↓ dopamine → impaired motor/cognitive function → PD symptoms (motor and non-motor).
What is the sequence of MPTP’s neurotoxic effects?
MPTP → crosses BBB → converted to MPP+ → enters DA/NE neurons via transporters → oxidative stress & mitochondrial dysfunction.
How does 6-OHDA cause dopaminergic damage?
6-OHDA → stereotaxic brain injection → binds DAT → enters DA neurons → ROS accumulation & complex I inhibition → cell death.
How might oxidative stress contribute to Parkinson’s Disease?
ROS buildup damages neurons when clearance is impaired, leading to neurodegeneration.
What does the distribution of Lewy bodies across the CNS suggest about PD symptoms?
It explains motor, cognitive, and early non-motor symptoms depending on the affected region (e.g., basal ganglia vs. gut or olfactory bulb).
How could N/OFQ-NOP signaling exacerbate PD symptoms?
Under dopaminergic dysfunction, N/OFQ overexpression may prolong inflammation via microglial activation, worsening motor symptoms.
Why does DJ-1 dysfunction increase vulnerability to Parkinson’s Disease?
DJ-1 normally protects against oxidative stress; its inhibition promotes DA neuron death due to unchecked ROS.
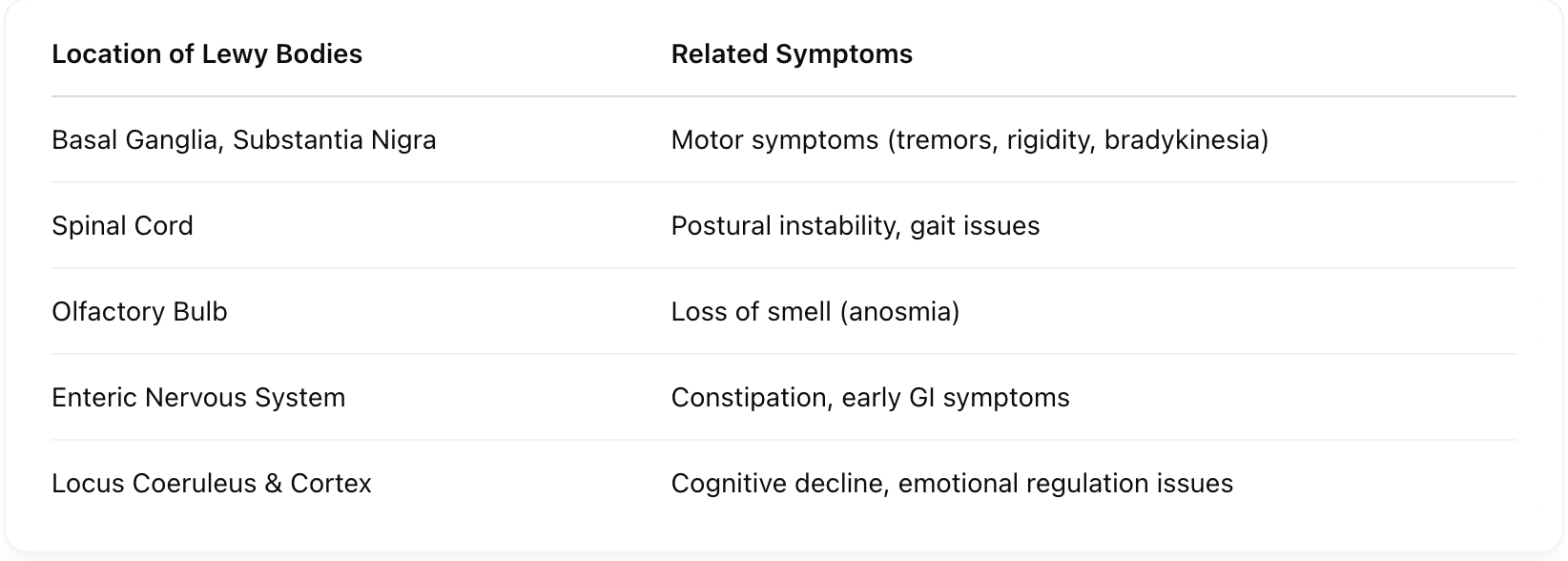
How does α-synuclein aggregation differ when caused by SNCA mutation versus oxidative stress? [Cause, Mechanism, Resulting Form, Feedback Loop]
What are the differences between DOPAL and α-synuclein in driving neurotoxicity? [origin, mechanism, interaction, toxic form]

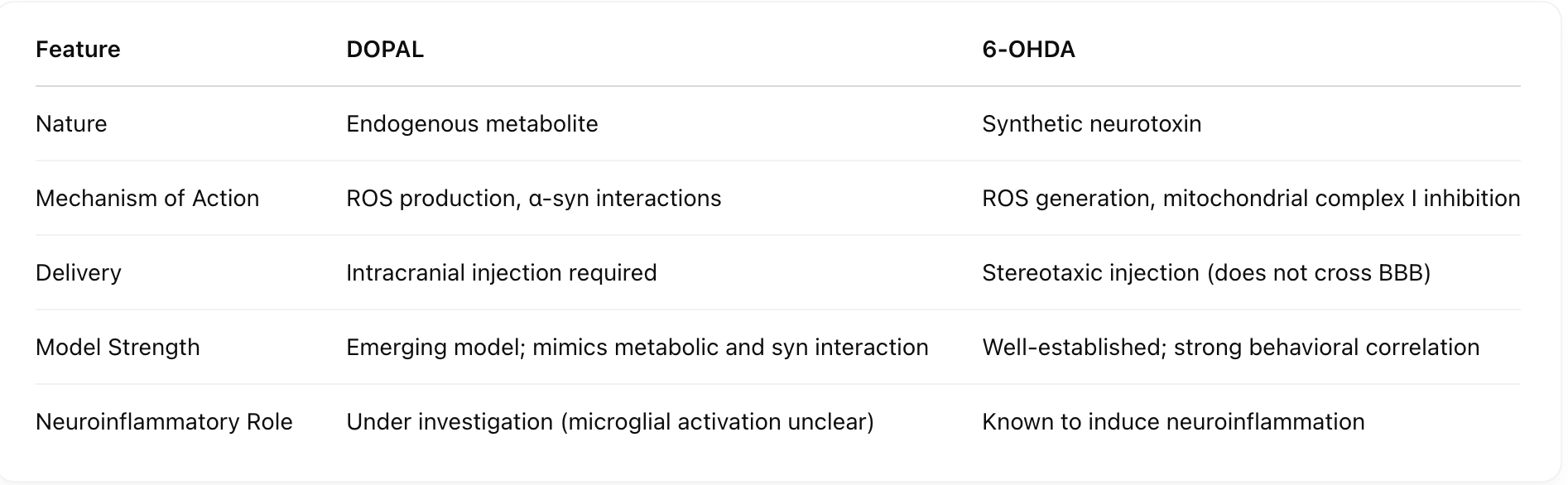
How do DOPAL and 6-OHDA differ as models of Parkinson's Disease? [nature, mechanism of action, delivery, model strength, neuroinflammatory role]
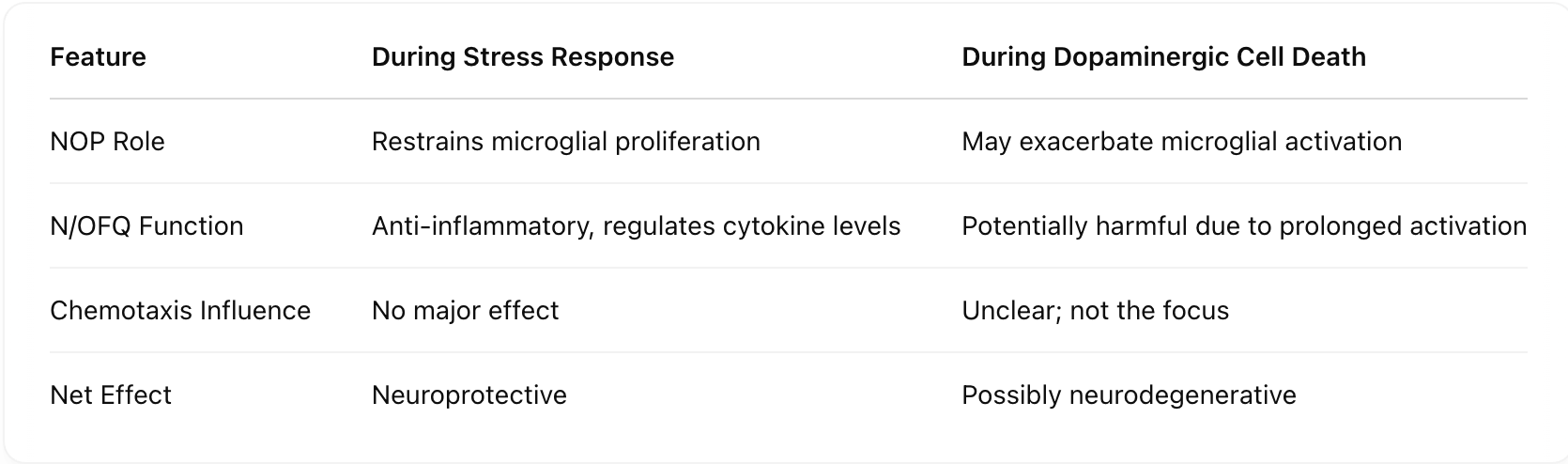
How does the NOP receptor function during stress versus dopaminergic cell death? [NOP role, N/OFQ function, Chemotaxis influence, Net effect]
What is the sequence from SNCA mutation to Lewy body formation?
SNCA mutation → α-syn overexpression → cytoplasmic accumulation → hyperphosphorylation → misfolding → aggregation → Lewy bodies.
How does DOPAL contribute to neurotoxicity, starting from dopamine?
Dopamine → converted by MAO-A to DOPAL → ALDH inhibition prevents DOPAC conversion → DOPAL buildup → ROS, 4-HNE production → α-syn oligomerization and toxicity → Lewy Bodies.
What is the signaling sequence involving N/OFQ–NOP in inflammation regulation, starting from a neural injury?
Neural injury → N/OFQ release → NOP activation → microglial chemotaxis (unaffected) → proliferation restrained (in normal stress) or enhanced (during cell death).
What happens when ALDH activity is impaired in dopamine metabolism?
DOPAL accumulates, increasing ROS and lipid peroxidation, leading to neuronal damage and sustained oxidative stress.
How might a feedback loop between DOPAL, ROS, and 4-HNE worsen PD?
ROS and 4-HNE from DOPAL buildup inhibit ALDH further, increasing DOPAL and sustaining neurotoxic conditions.
Could DOPAL serve as a model for PD neurotoxicity? Why?
Yes; its accumulation induces motor deficits, ROS, and α-syn interactions, making it a candidate for modeling PD pathology.
What effect might NOP knockout have on dopaminergic cell survival after toxin exposure?
NOP KO mice may show altered survival due to lack of NOP-mediated inflammatory modulation, revealing NOP’s role in neurodegeneration.
Is N/OFQ signaling protective or harmful in advanced PD?
Hypothetically harmful—although initially anti-inflammatory, N/OFQ may enhance microglial activity during cell death, worsening neuron loss.