Week 1 (Fundamentals and Immunization)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is the basis of an immune response and what can failure of the immune system lead to?
immune response: the ability of the immune system to recognize self vs non-self (foreign substances)
failure → autoimmune diseases, allergy, cancer, alloimmunization
What is the definition of immunohematology?
the study of RBC antigens and their corresponding Abs. This includes other blood cells too and their corresponding Abs
What is the difference between innate and adaptive immunity?
innate: resisting infections by normal body functions
adaptive: host adapts to kill immunogen through complex recognition process (humoral and celullar)
What is the definition of an immunogen?
a substance that triggers an immune response
What are the definitions of autoantigen, alloantigen, heteroantigen, and hapten?)
autoantigen: normal host protein that is recognized as an antigen
alloantigen: same species diff person (blood)
heteroantigen: diff species diff person
hapten: small Ag that doesn’t trigger an immune response unless in complex w/ larger protein
What is the definition of immunogenicity?
ability of the immunogen to stimulate an immune response
What are the 3 WBCs of the innate immune system and what are their functions?
neutrophil: 1st responders that perform phagocytosis
eosinophil: kills parasites and neutralizes basophils/mast cells
basophils: induce allergic reactions and stimulate B cells to produce IgE
What are the 3 tissue cells and what are their functions?
monocyte: phagocytosis and migrate to tissue to become macrophages
mast cells: enhances adaptive immune response, binds to IgE
dendritic cells: most potent phagocytes
What are the 3 WBCs of the adaptive immune system and their functions?
T lymphs (CD4 and CD8): produce cytokines
B lymphs: produce ABs
NK cells: kills viruses and cancer cells. also produces cytokines
What markers do T helper and T cytotoxic cells have?
T helper: CD4
T cytotoxic: CD8
What is opsonization and the 3 opsonins?
opsonization: when opsonins coat the pathogen to faciliate phagocytosis
3 opsonins: Abs, complement, acute phase reactants
What do PAMP and PRR stand for?
PAMP: pathogen associated molecular pattern
PRR: pathogen recognition receptors Des
Describe the process of antigen presentation
phagocyte eats the bacteria
bacteria antigen goes to surface of phagocyte
phagocyte presents antigen to T helper cell
T helper cell activated
What does the activation of a T helper cell do?
results in activation of B cells and proliferation of more T helper cells
What are the 2 types of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and where are they found?
MHC I: found in most nucleated cells
MHC II: found in antigen presenting cells (APC) aka phagocytes that present antigen (neutrophils, monocytes/macrophages, dendritic cells)
What are the general differences between the cellular and humoral elements of the adaptive immune response?
cellular: T cells that either release cytokines to activate B cells or attack cells
humoral: B cells that produce antibodies
What is an immunoglobulin and what are its 4 roles?
definition: Abs produced by plasma cells with specificity to an antigen
roles: bind Ag, activate complement, facilitate phagocytosis, neutralize toxic substances
Describe the structure of an Ab (Ig)
2 heavy chains and light chains
constant region in bottom and variable region on top
Fab region consists of heavy/light chain
Fab: binds to Ag
Fc: site of complement fixation and binds to monocytes
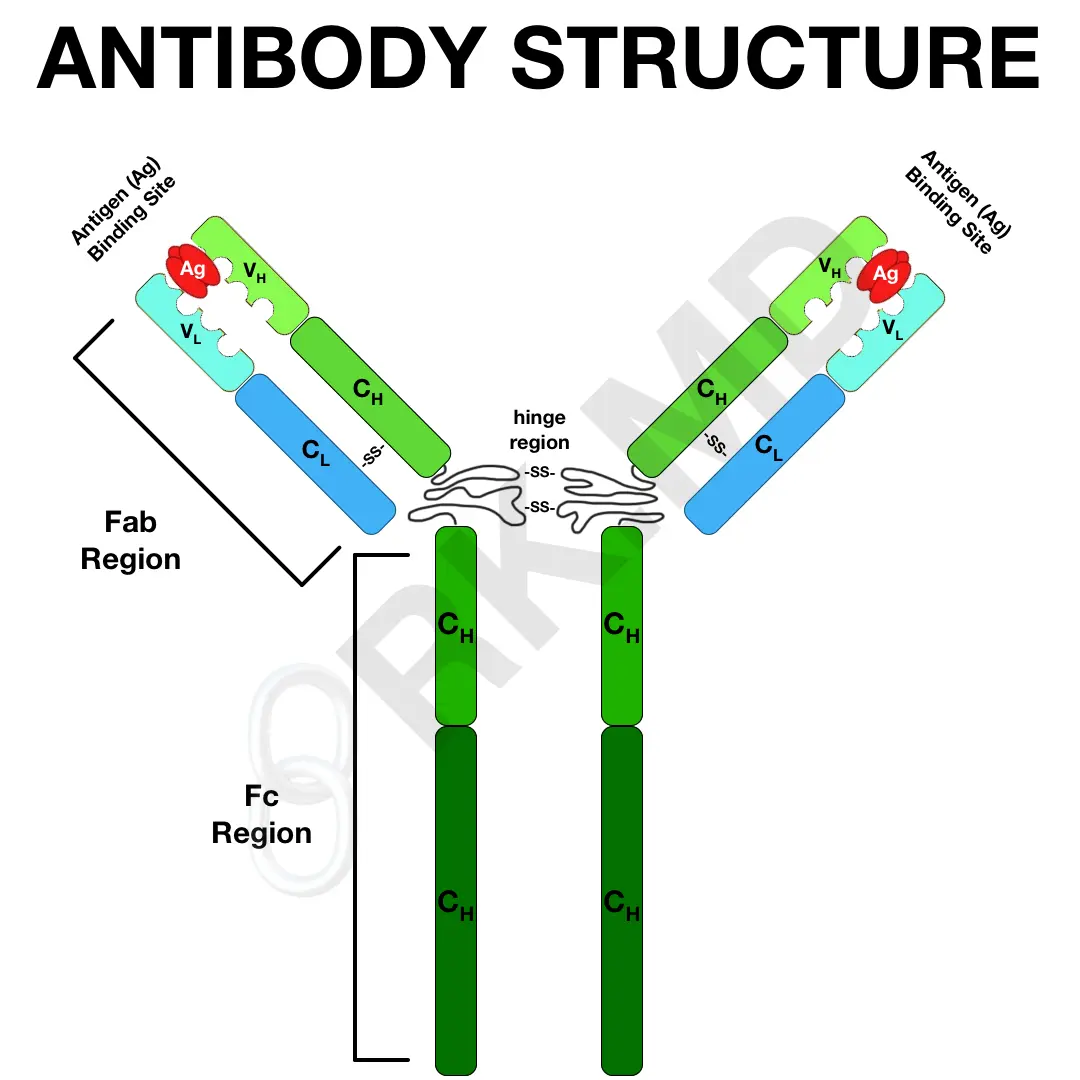
What is the difference between isotype, allotype and idiotype of Abs?
isotype: IgM, A, D, G from different type of heavy chain
allotype: genetic variation in heavy chain
idiotype: variable region has diff Ab specificity
What are the 3 key characteristics of IgG? (Fc region, can cross?, can activate?)
Fc region of IgG can bind to monocyte, macrophages, and neutrophil receptors
It can cross the placenta
Can activate complement
What are the key characteristics of IgM? (response, can cross?, can activate?, phag/tox)
primary response Ab that has no memory cells
cannot cross placenta
only 1 molecule of IgM needed to activate complement
enhances phagocytosis and neutralizes toxins
What are the key characteristics of IgA? (where found, can cross?, can activate?, regulates/deficiency )
found in bodily fluids and is an anti-inflammatory agent
cannot cross placenta
does not activate complement
regulates igG and deficiency → anaphylactic shock due to anti-igA development
What is the complement system and its 3 primary roles?
complex group of circulating cell membrane proteins.
opsonization: C3b attached to antigen recognized by phagocytes
promotes assembly of MAC
participates in acute inflammatory response
What are the 3 complement activation pathways?
classical: Ab directed mechanism
lectin: recognition unit used by mannose binding lectin
alternative: mainly to stabilize C3 convertase
What is the common pathway for all?
cleavage of C3 to C3b and assembly of MAC
Describe the classical complement pathway
C1qrs is activated
C4 and C2 are cleaves into C4a,C4b,C2a,C2b → C4b2a complex
C4b2a cleaves C3 into C3a,C3b → C4b2a3b
C4b2a3b cleaves C5 into C5a,C5b → C5b combines with C6,C7,C8,C9 → C5b6789
yellow = recognition, blue = activation, red = MAC
What complex is known as C3 convertase? C5 convertase?
C4b2a, C4b2a3b
Describe the lectin pathway
Mannose binding lectin binds to bacterial cell wall to activate complement
No C1, starts pathway with C4b2a and follows same pathway afterwards like classical pathway
Describe the alternative pathway
Factor C3 is hydrolyzed by water → C3b, which binds to factor B and both attach to target cell surface
Factor D cleaves B → Ba and Bb. Bb + C3b→ C3bBb, which has C3 convertase activity and is stabilized by properdin
Follows the rest of classical pathway
unique to this pathway are properdin, Factor B and D
What are the 3 functions of interleukins?
inflammation and fever
initiation of acute phase reactants
activation/growth of B/T lymphs
What are the 2 roles of tumor necrosis factors (TNF)?
induce lysis of tumor cells
activates T cells
What are the 3 roles of transforming growth factors? (TGF)
anti-inflammatory
inhibit T/B cell proliferation
inhibit macrophages
What are the 5 roles of interferon?
activate NK cells
increase MHC class I expression
increases Ag presentation
activates macrophages
protects host from viruses
What is the role of colony stimulating growth factors (CSGF)?
stimulate proliferation/differentiation of hematopoietic stem cell
What is hypercytokinemia (cytokine storm) and what can it cause?
it is the overproduction/stimulation of cytokines → septic shock and death
What are acute phase reactants and when are they released?
they are proteins (CRP, haptoglobin, fibrinogen, etc) that bind to microorganisms to promote phagocytosis (opsonins) and are released by liver cells when there is an increased level of cytokines
What is the difference between immunity and immunization?
immunity: condition of being resistant to a disease
immunization: process by which immunity is acquired
What is the mechanism, advantage, and limitation of active immunity?
mechanism: activation of humoral/cell mediated response by exposure to an antigen
advantage: long term memory against antigen
limitation: delay in the initiation of immune response
What is the mechanism, advantage, and limitation of passive immunity?
mechanism: transfer of Ab from immunized host → non-immunized person
advantage: provides immediate protection to the recipient
limitation: only temporary immunity, no memory, and hypersensitivity can be developed
What are some examples of passive immunity?
maternal IgG to fetus via placenta
maternal IgA to infant via breast milk
Rhogam
monoclonal Abs
human serum globulins
What is the mechanism, advantage, and limitation of the adoptive immunity?
mechanism: transfer of immune system cells to non-immune person
advantage: can transfer cell-mediated immunity
limitation: patient’s own cells must be depleted and allogeneic cells may be rejected
What is the composition of attenuated, inactivated, and subunit vaccines?
attenuated: live pathogens weakened by growth under modified culture conditions
inactivated: killed microorganisms
subunit: derived from 1 or more components of the pathogen
What are the 3 adverse effects of vaccines?
local inflammatory response @ site of injection
systemic inflammatory reactions (fever, nausea, etc.)
hypersensitivity reactions
What is the antigenic variation that allows a pathogen to escape immunity?
antigenic drift and shift
What are 3 scenarios of a failure in the host defense mechanism?
some viruses persist in vivo and stop replicating until immunity drops
some pathogens resist destruction and use host to survive
pathogens can cause immunosuppression