Biology Semester 2 Freshman Year - Unit 10: Genetics
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
somatic cells
body cells
somatic cells = diploid or haploid
diploid (2n = 2 sets of chromosomes)
gametes
sex cells
gametes = diploid or haploid
haploid (n = 1 set of chromosomes)
2 types of chromosomes that our bodies contain
Autosomes and Sex Chromosomes
Autosomes
Chromosomes that carry traits that make you who you are
Ex: 1st 22 pairs of chromosomes
Sex Chromosomes
chromosomes that carry traits that make who you are and determine your biological sex (male or female)
Ex: the 23rd pair of human chromosomes (X or Y)
meiosis
process of cell division that makes gametes
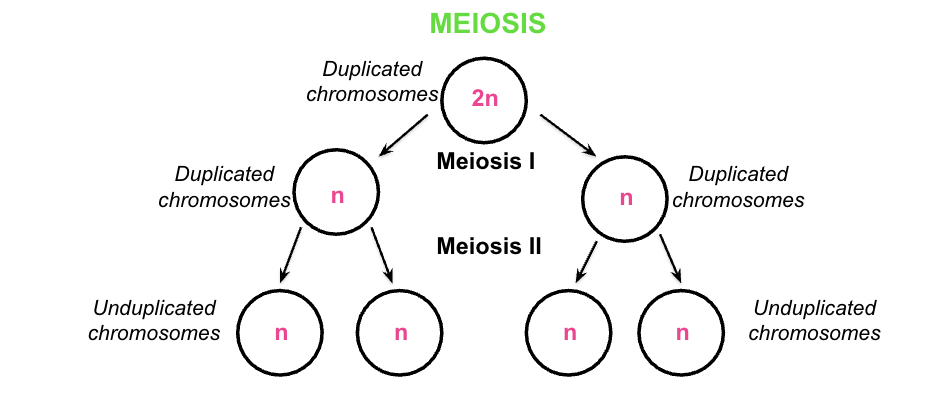
meiosis results in production of….
four haploid sex cells / gametes (egg = female or sperm = male)
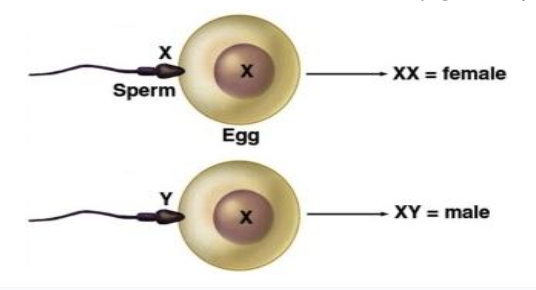
fertilization
actual fusion of egg and sperm to form a zygote
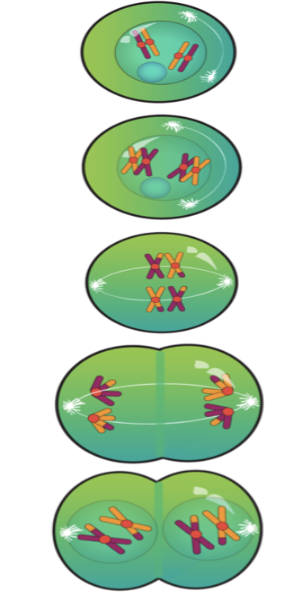
homologous chromosomes
chromosome pairs that have the same types of genes
(one from mom, one from dad)
sister chromatids
identical copies of the same chromosome
purpose of meiosis
make gametes HALF the normal number of chromosomes (only 1 set)
meiosis make gametes/sex cells that have half the normal number of chromosomes (only 1 set rather than 2). How?
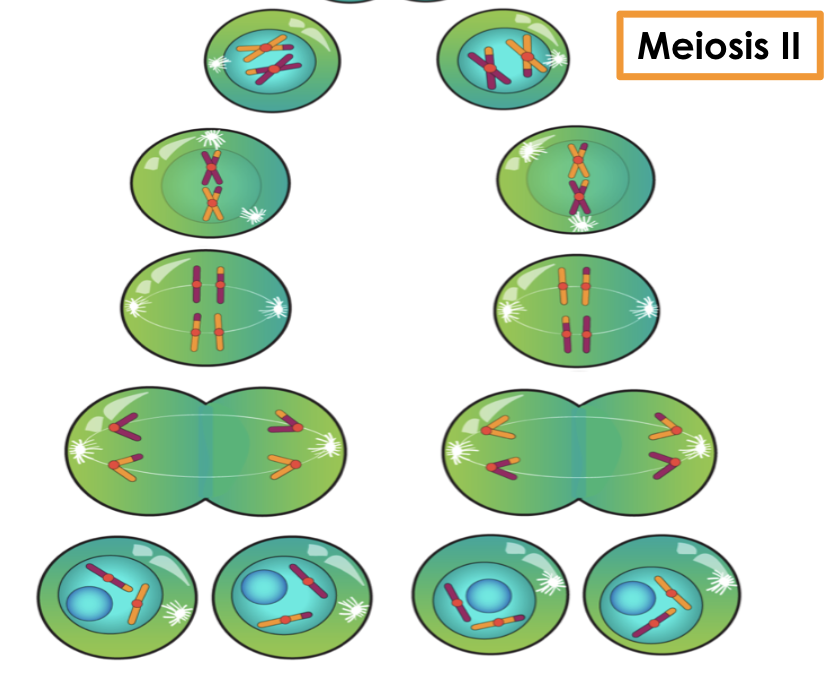
cell division happens twice in Meiosis
Meiosis I results in…
separation of homologous chromosomes
Meiosis II results in…
separation of sister chromatids
Duplicated chromosomes from Meiosis I divide into individual chromosomes.
DNA replicates during…
S phase (interphase)
Prophase in Meiosis 1
Each replicated chromosome pairs with its homologous chromosome, and crossover happens
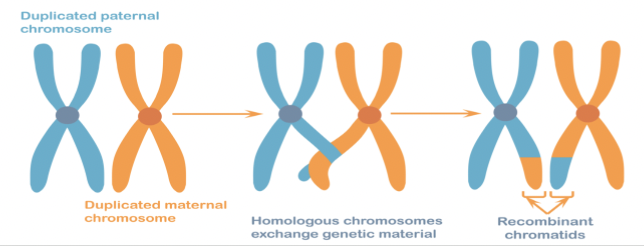
crossover
swapping of DNA between the homologous chromosome pairs
crossover happens during..
prophase 1 of meiosis
is there any DNA replication prior to meiosis 2?
no
in meiosis 2, …
sister chromatids are pulled apart
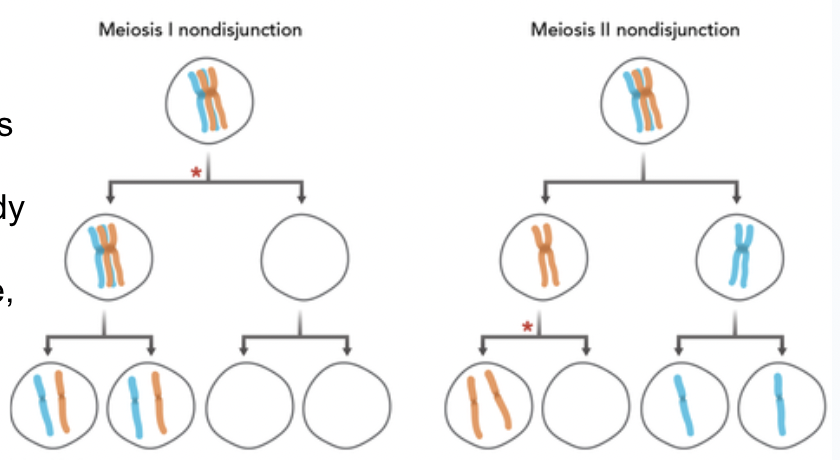
Nondisjunction
Failure of chromosomes to separate in meiosis; leads to aneuploidy (extra or missing chromosomes)
gene
section of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein
Alleles
different versions of the same gene
Gregor Mendel
Austrian monk who used pea plants to learn about genetics. He is known as the “father of genetics”.
Three laws of inheirtance
Law of Dominance, Law of Segregation, Law of Independent Assortment
Law of Dominance
Dominant trait always expresses itself over the recessive
Law of Segregation
When chromosomes separate in meiosis, each gamete will receive only one chromosome from each pair.
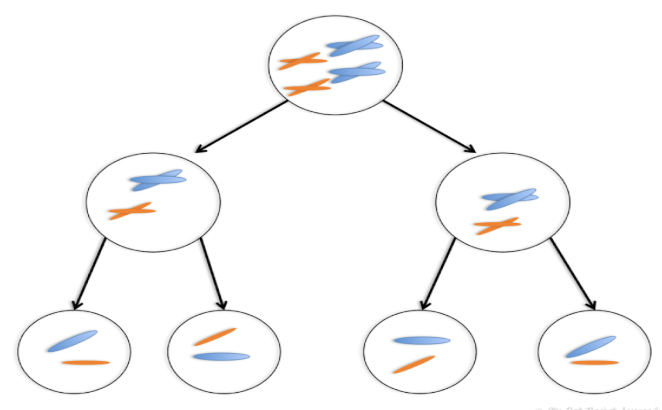
Law of Independent Assortment
the assortment of chromosomes for one trait doesn’t affect the assortment of chromosomes for another trait
Punnet Square
a diagram that shows the probability of inheriting traits from parents with certain genes
Monohybrid cross
a cross between two organisms looking at one trait
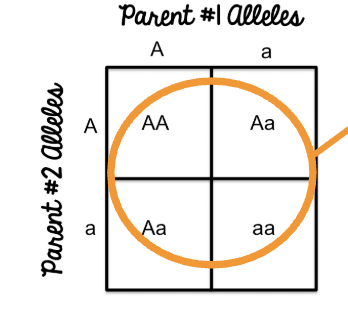
Dihybrid crosses
Used when finding the possible genotypes for offspring when considering two traits at the same time
Probability
Can be used to determine the outcome of genetic crosses

Incomplete Dominance
neither allele is completely dominant or recessive
example = red + white flowers make pink flowers
Co-dominance
both traits are expressed; Ex. red + white flower = red & white flower
Multiple Alleles
Having more than 2 alleles for one gene
Blood type inheritance pattern
Co-dominance and multiple alleles
Polygenic Inheritance
a trait produced by two or more genes
Epistasis
when one gene overshadow all of the others
ex. Labrador retriever fur colors, eye color, Albinism
linked genes
genes that are physically located on the same chromosome and will be inherited together
the only time linked genes can be separated or broken apart is during…
crossover
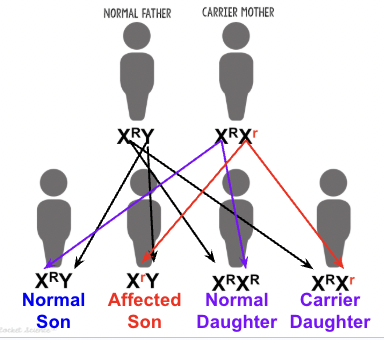
Sex-linked genes
genes on the sex chromosomes
carrier
someone who carries the recessive trait but isn’t affected by it
X-linked genes
females inherit X-linked genes as normal and the principle of dominance applies
Males inherit the gene on the X but not the Y so they will be affected if they get the recessive gene
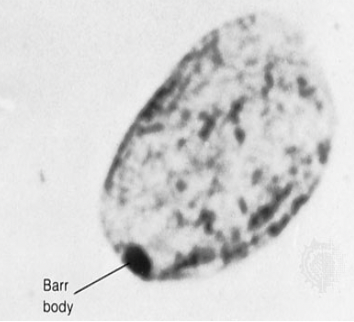
Barr Bodies
Inactive X-chromosome in females
Aneuploidy
when an organism has missing or extra chromosomes
monosomy
missing chromosome from a pair
Trisomy
three copies of a chromosome instead of two
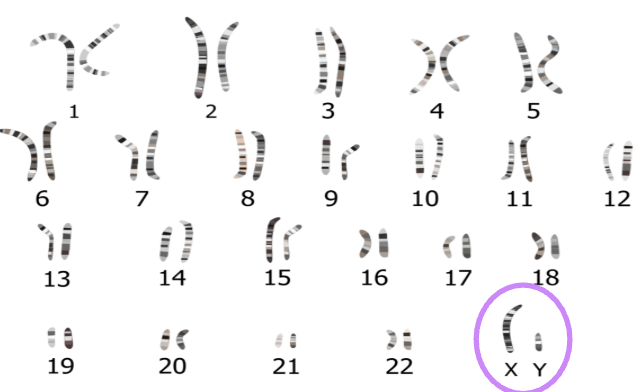
Karyotype
Visual representation of the number, size and structure of a person’s chromosomes
pedigree
chart used to trace the phenotypes and genotypes in a family to determine whether people carry diseases or traits
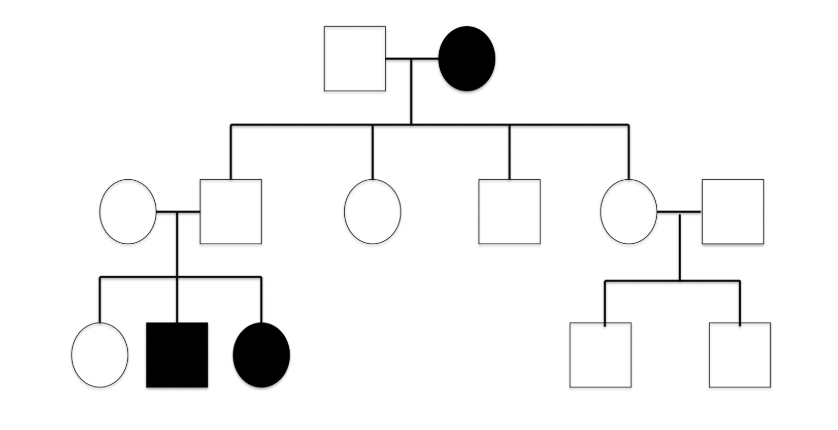
square in a pedigree represents a….
male
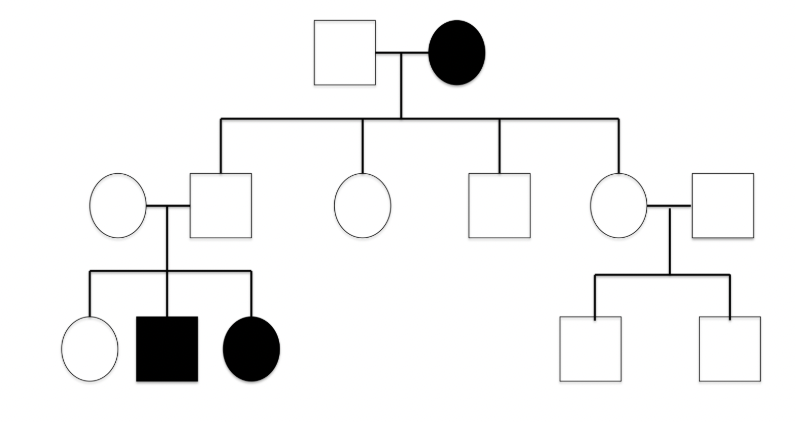
circle in a pedigree represents a…
female
Autosomal recessive trait
common inheritance pattern, the disease is rare in the family, disease skips generations, and males & females are equally likely to inherit the disease
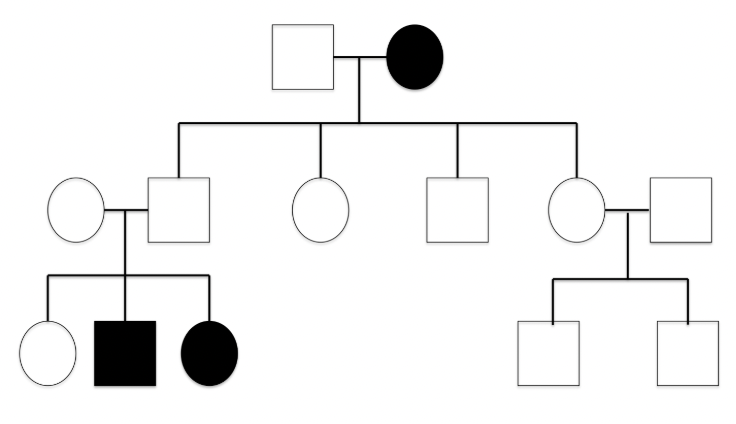
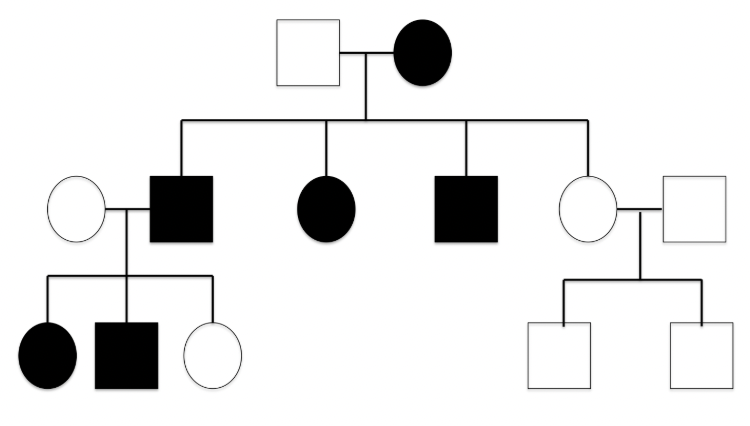
Autosomal dominant trait
disease is common in the family, it never skips generations and males & females are equally likely to inherit this disease
Sex-linked recessive trait
the disease is rare in the family, more males are affected, the disease often skips generations, and affected fathers don’t pass on their trait to their sons
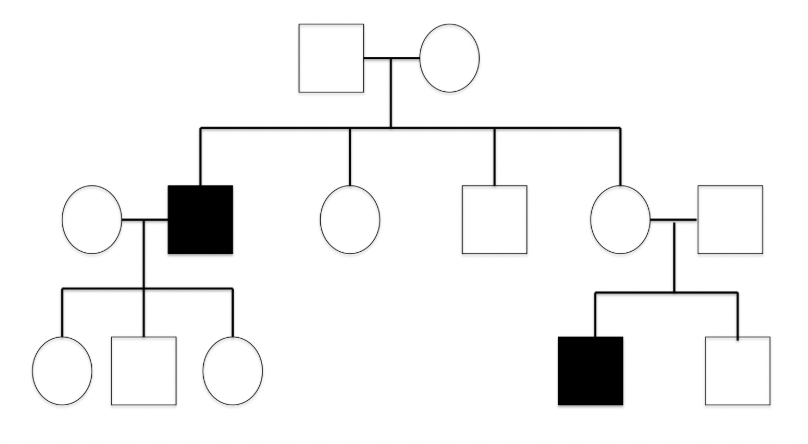
Affected fathers in a sex linked trait cannot pass their trait to their son. Why?
they only contribute the Y chromosome to the males and only pass on their X trait to the females
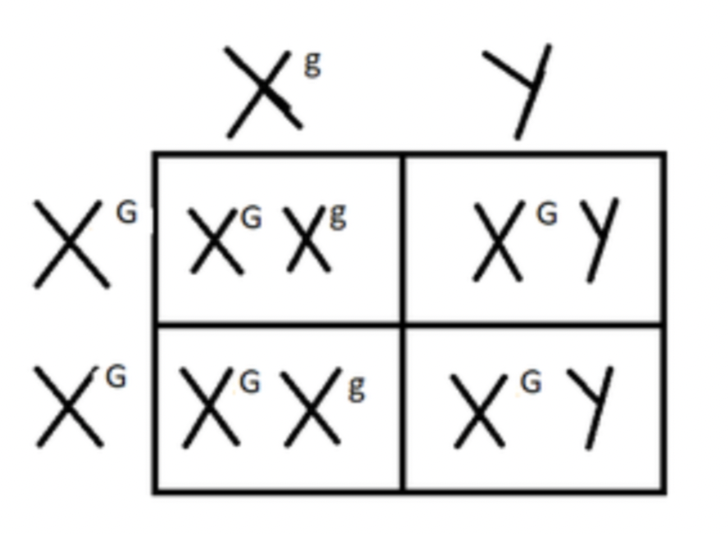
First step to find the pattern of inheritance in a pedigree
If there are way more males than females affected (shaded in) then the pedigree is tracing a Sex-Linked trait.
If not, look for two parents that are the same shade that have a child who is different from them. Label that child homozygous recessive (Ex. rr) and the parents heterozygous (Ex. Rr)
second step to determine the pattern of inheritance in a pedigree if you determine it not to be a sex linked trait
Look for two parents that are the same shade that have a child who is different from them. Label that child homozygous recessive (Ex. rr) and the parents heterozygous (Ex. Rr)
If the child was shaded, the pedigree is tracing an Autosomal Recessive trait.
If the parents were shaded, the pedigree is tracing an Autosomal Dominant trait.
phenotype
the physical traits of an organism; Ex. Purple flowers
genotype
actual alleles inherited; Ex. AA, Aa, aa