path 8- vascular tumors
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
are hemangiomas benign or malignant
benign
most common benign tumor
hemangioma
most common type of hemangioma
capillary hemangioma
where do capillary hemangiomas occurs
skin
oral cavity
liver
spleen
kidneys

what is seen in histo for capillary hemangioma
proliferation of thin walled capillaries with scant stroma
juvenile hemangioma
strawberry type
newborns
arise in skin, grow rapidly then fade/regress by age 7
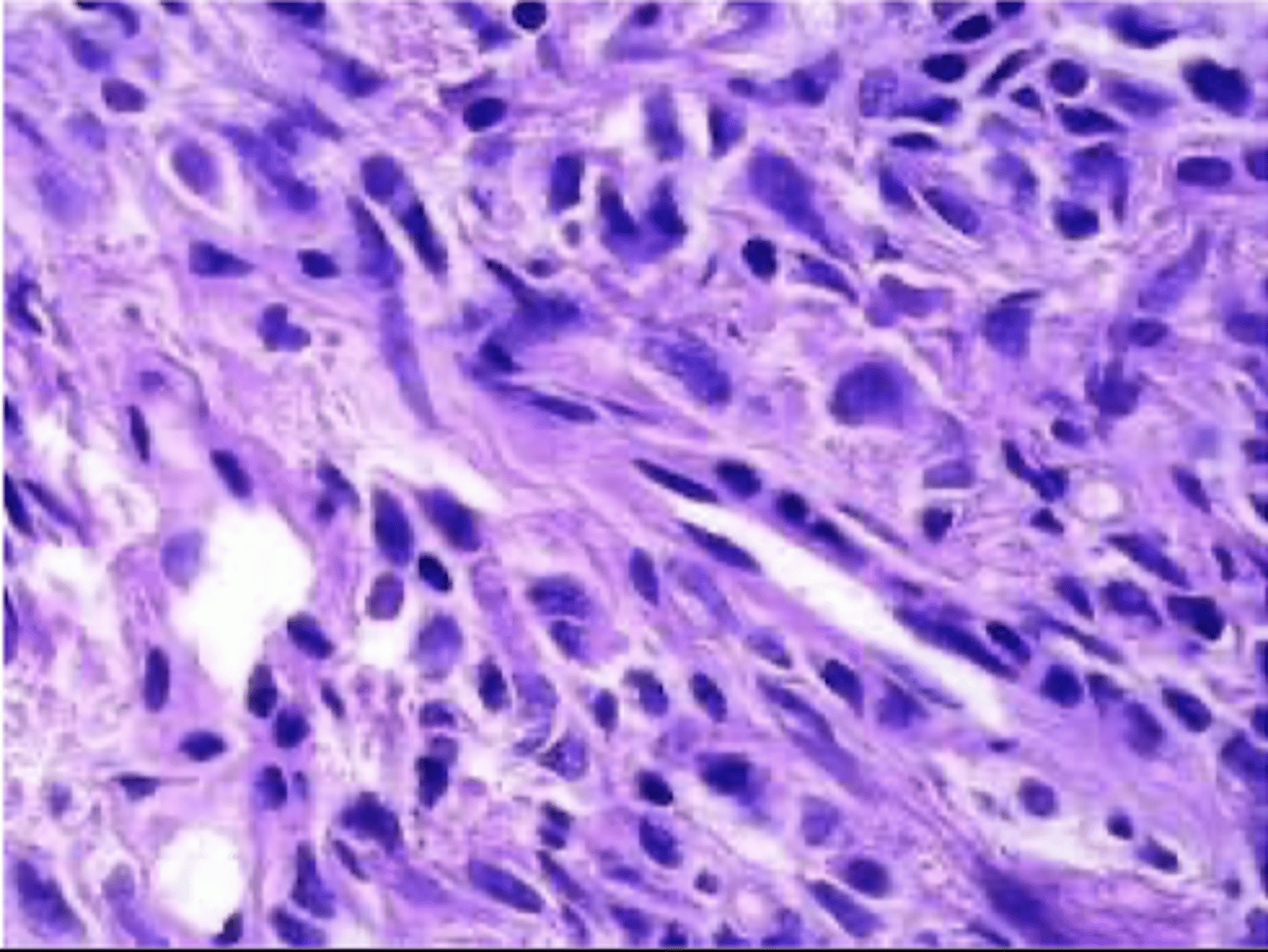
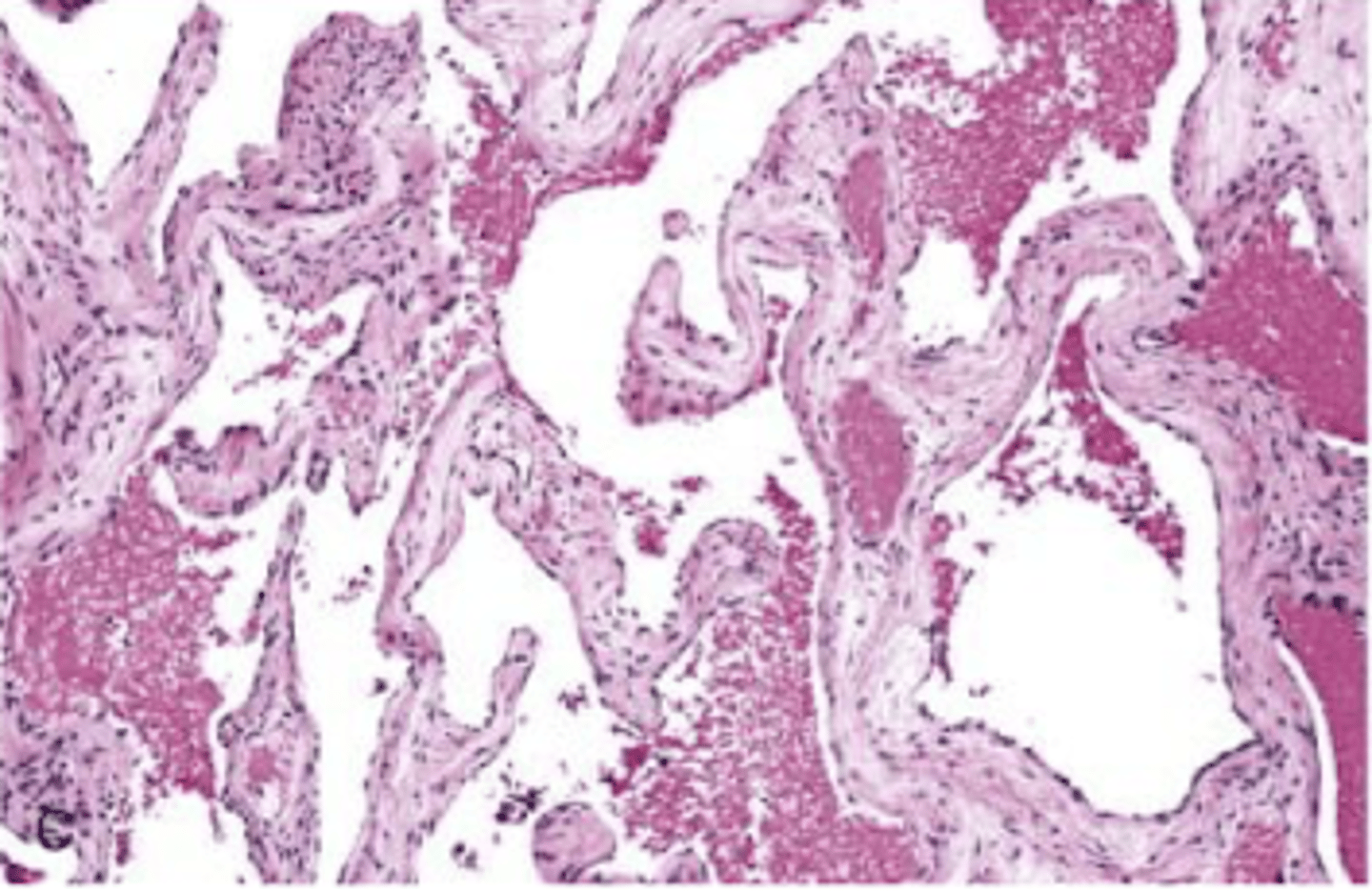
cavernous hemangioma
large blood filled dilated vascular changes with CT stroma
do not regress
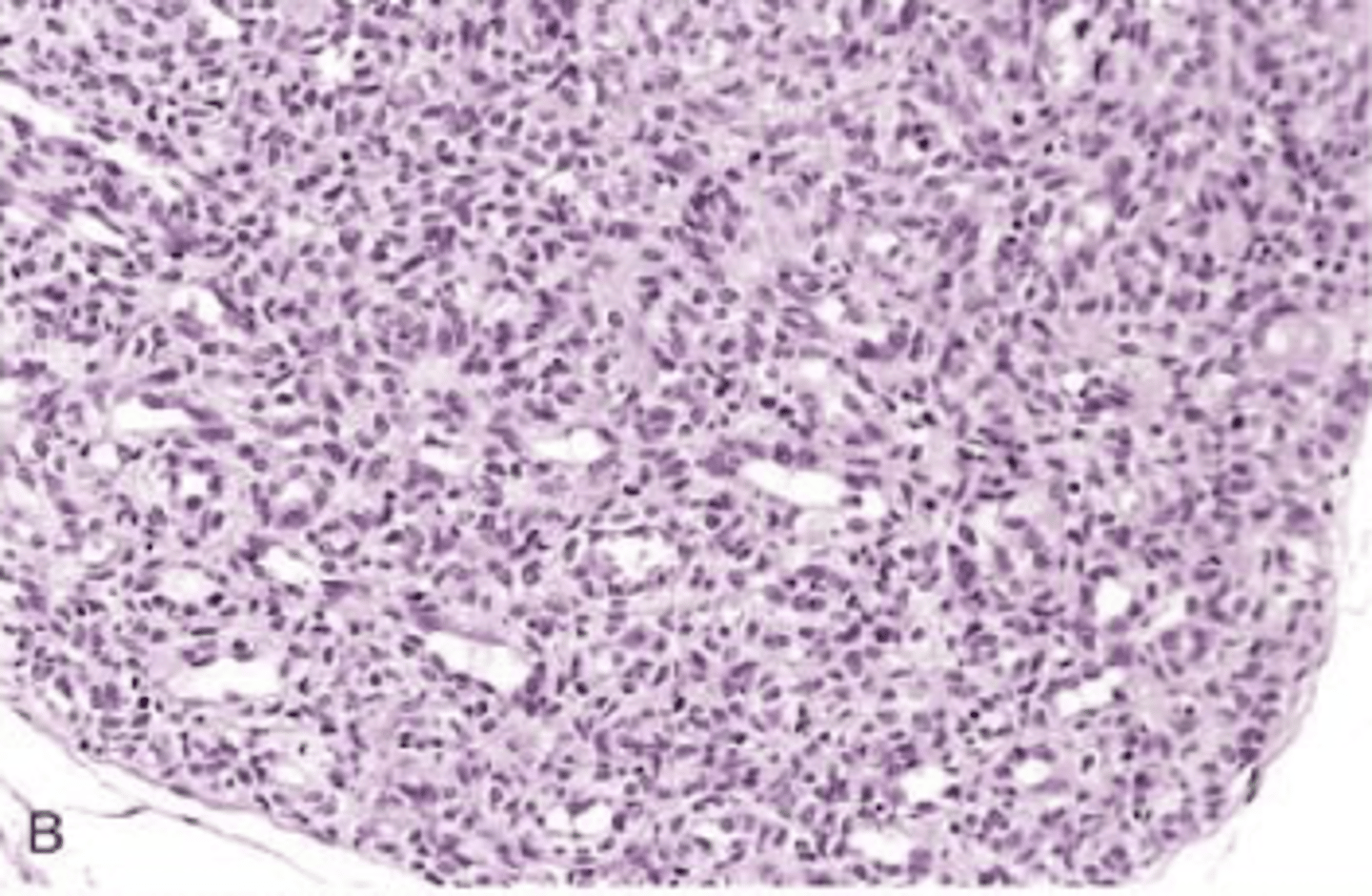
pyogenic granuloma
rapidly growing reed lesion on skin, gingival, or oral mucosa
occur following trauma
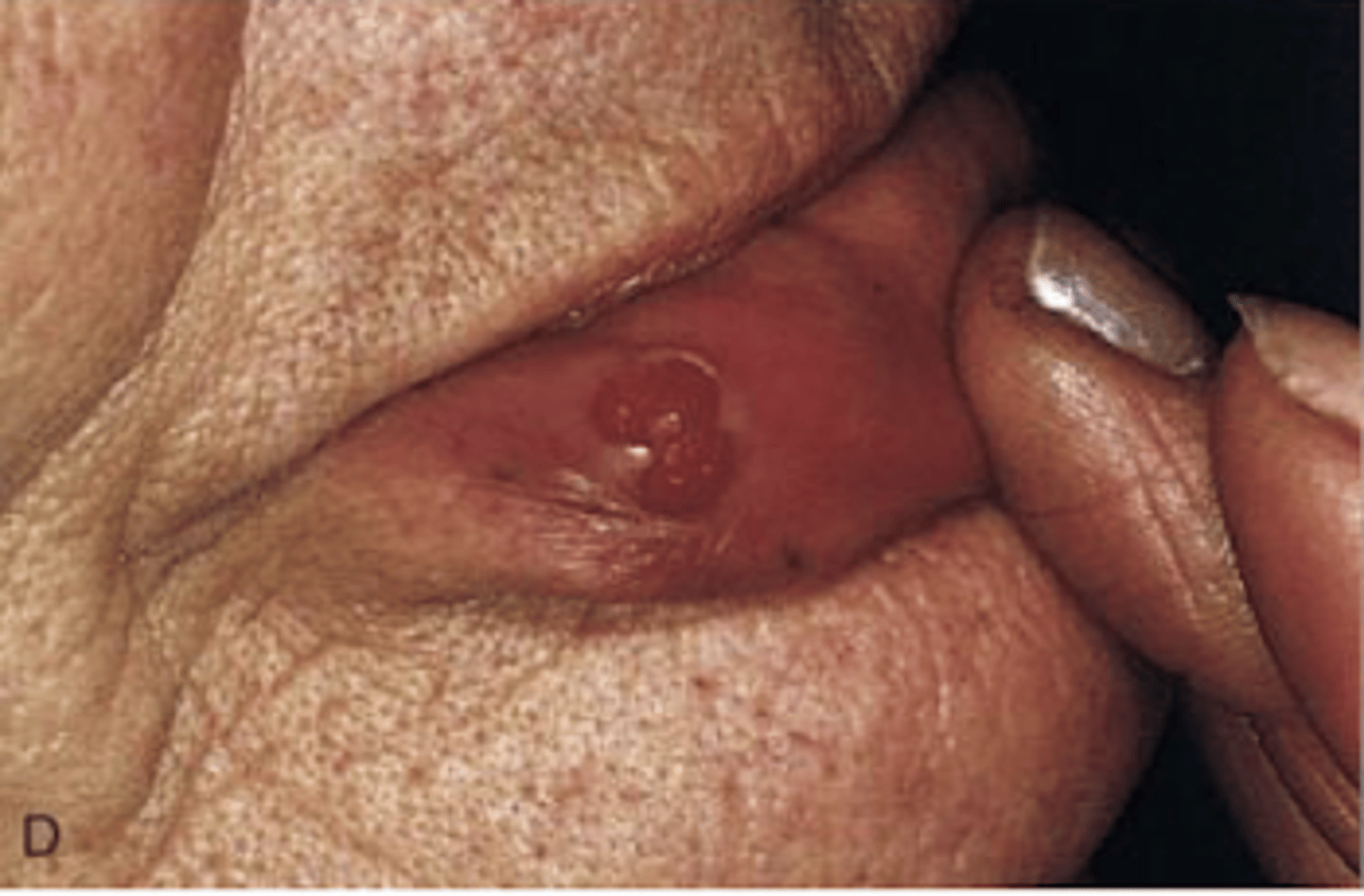
granuloma gravidarum
A pyogenic granuloma arising in the mouth of a pregnant female
lymphangioma
benign lymphatic counterpart of hemangioma
simple lymphangioma
network of endothelium lined channels w/ no RBC's
head, neck, axilla
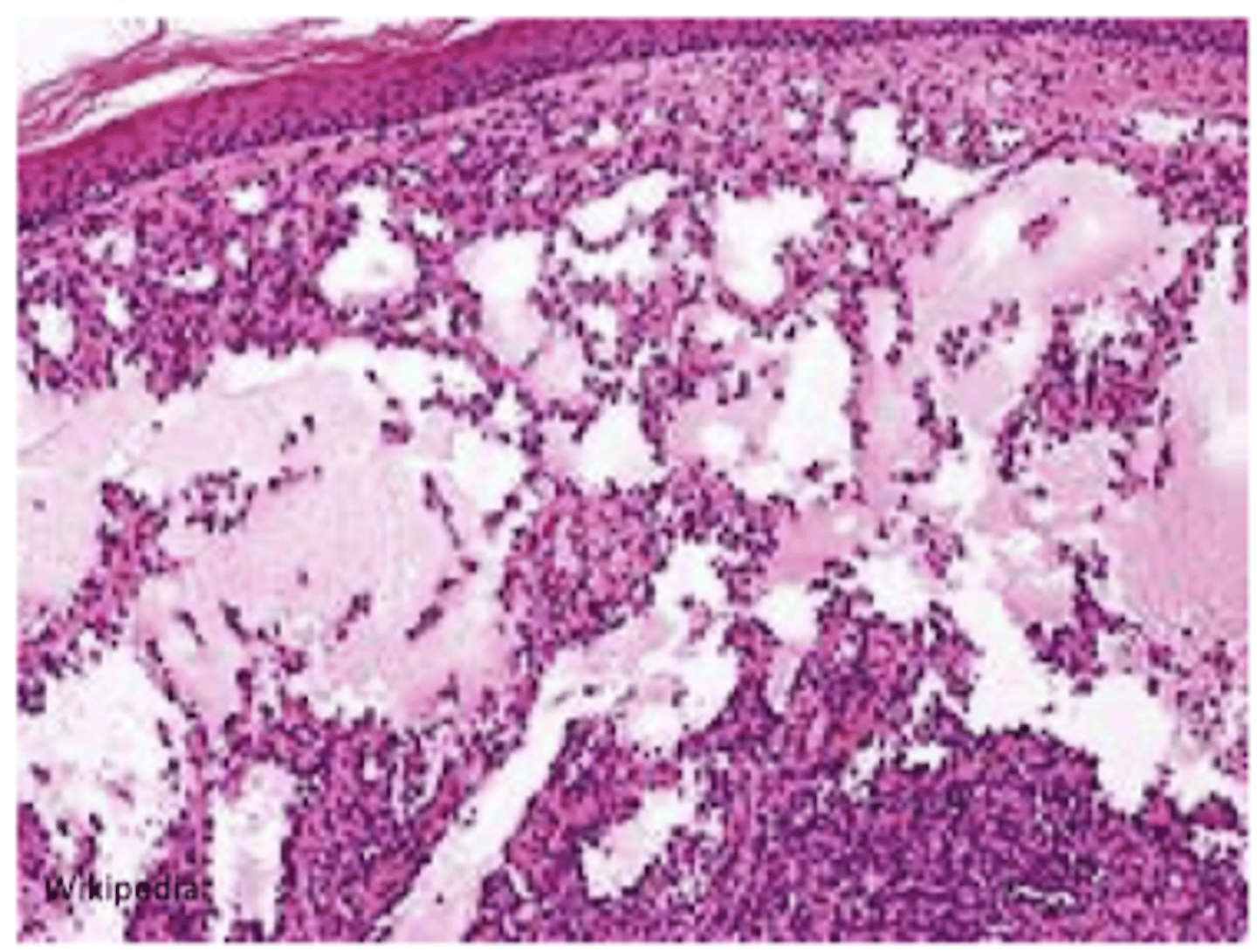
cavernous lymphangioma
neck or axilla of children
massively dilated spaces with CT stroma and lymphoid aggregates
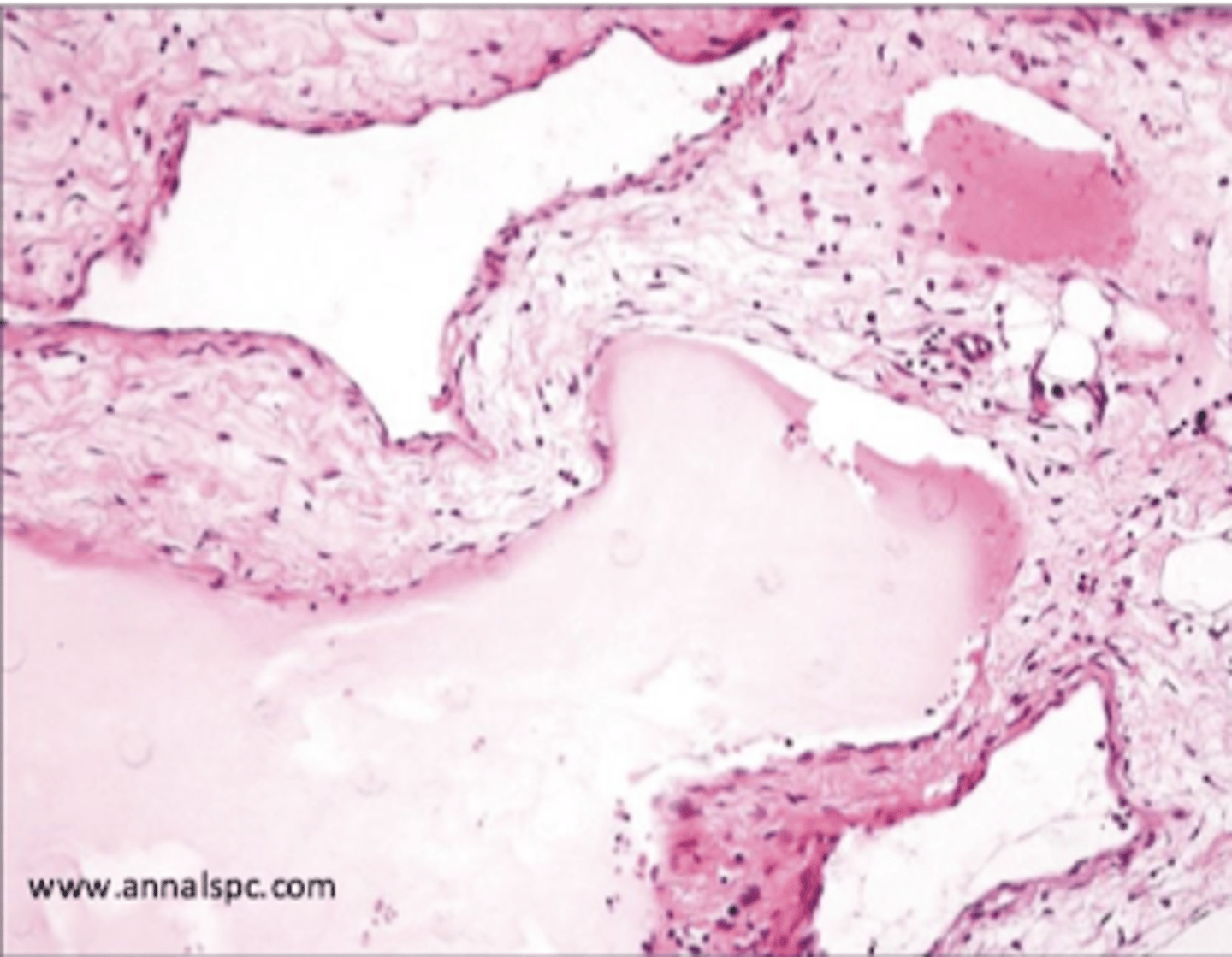
glomus tumor
super painful
arises from modified smooth muscle cells of glomus body
bacillary angiomatosis
vascular proliferation in immunocompromised hosts caused by bartonella infection
driven by VEGF production
bartonella henselae
cat scratch disease
necrotizing granulomatous disorder of lymph nodes in immunocompetent host
bartonella quintina
trench fever (shin bone disease)
acute recurring febrile illness
transmitted by human body lice
treatment for bacillary angiomatosis
macrolides
vascular ectasias
tumor like conditions
what are the vascular ectasias
nevus flammeus
spider telangiectasias
hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasias
nevus flammeus
aka birthmark
light pink to deep purple flat lesion on head or neck
usually regresses
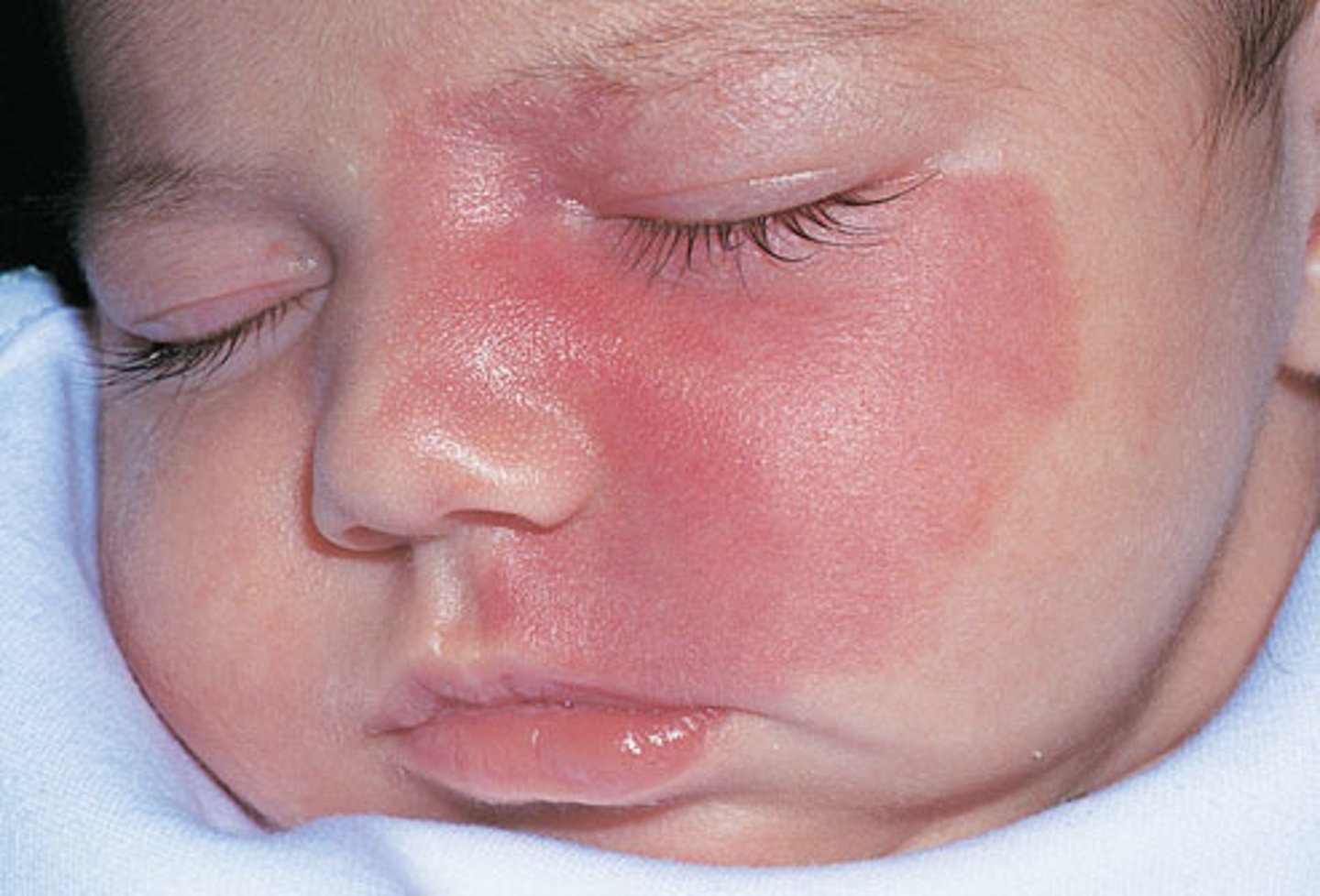
nevus flammeus is composed of
dilated vessels
port wine stain
type of nevus flammus that grows during childhood, thickens the skin and does not fade
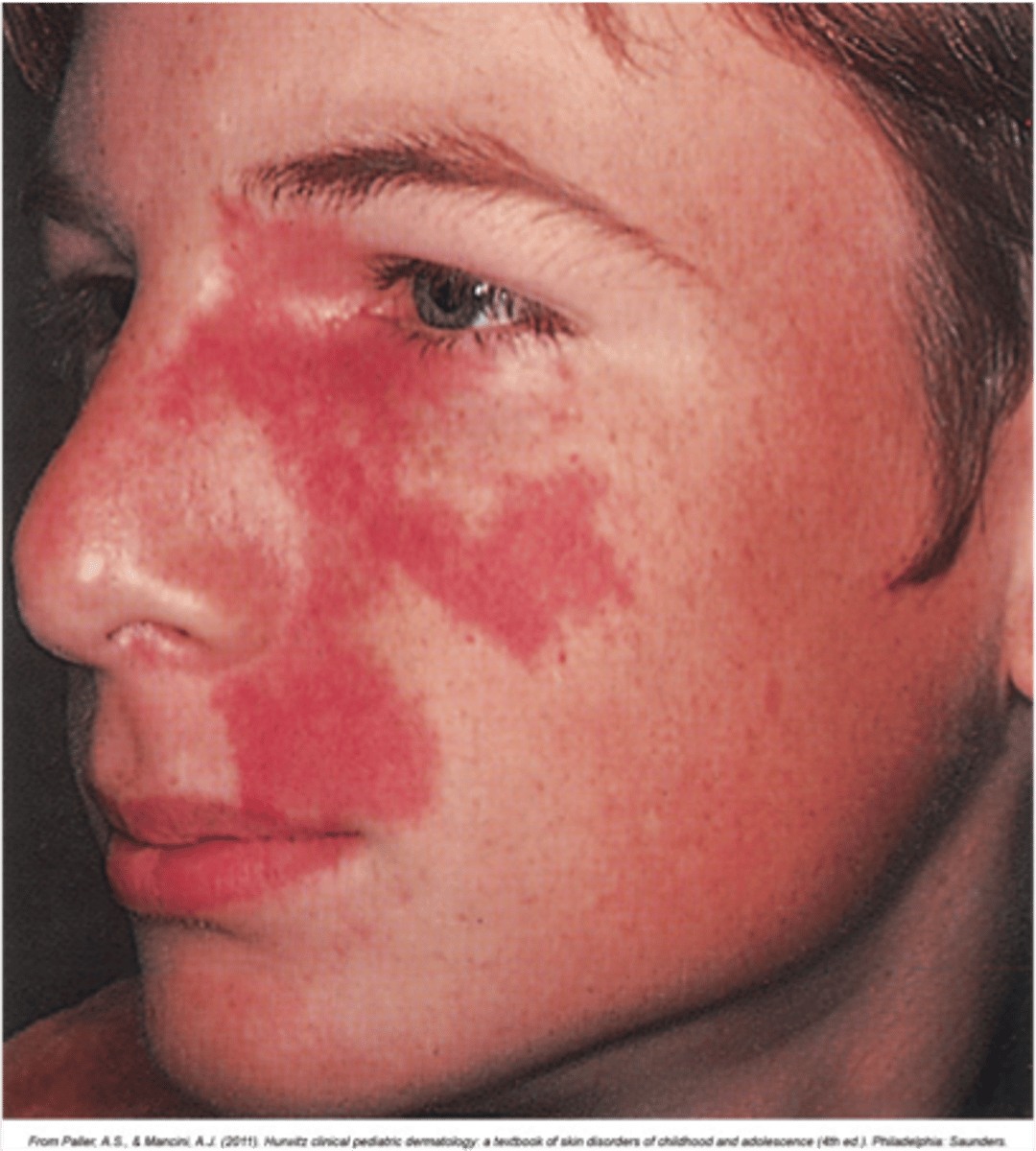
port wine stain in trigeminal distribution
Sturge-Weber syndrome
sturge-weber syndrome
large facial port wine stain in a child + mental deficiency
spider telangiectasia is associated with
hyperestrogenic states
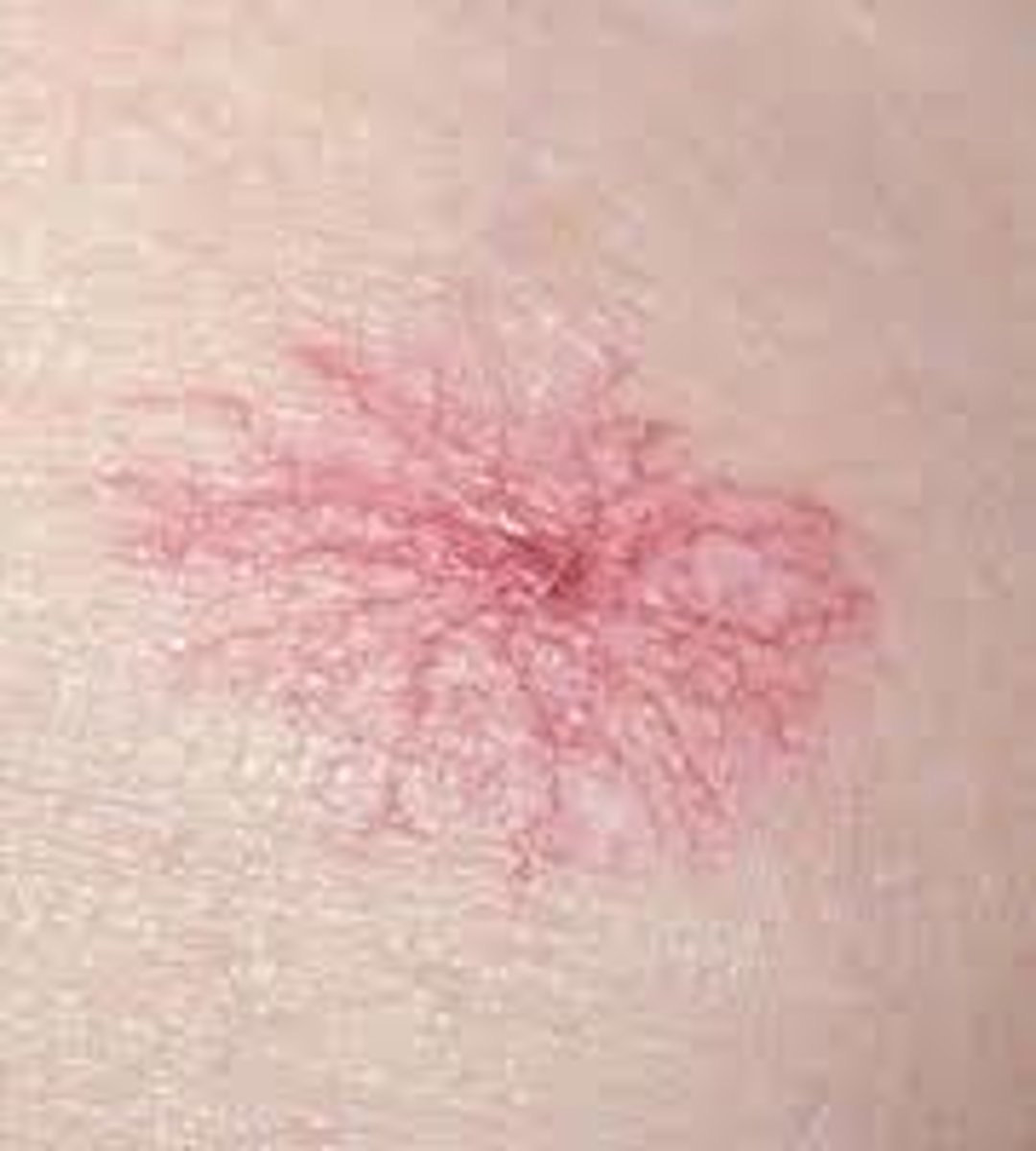
hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
malformations of capillaries and veins that are present at birth
s/s of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
spontaneously rupture and bleed causing nosebleeds, GI bleed, or hematuria
kaposi sarcoma
vascular neoplasm caused by HHV-8
kaposi sarcoma is associated with
AIDS
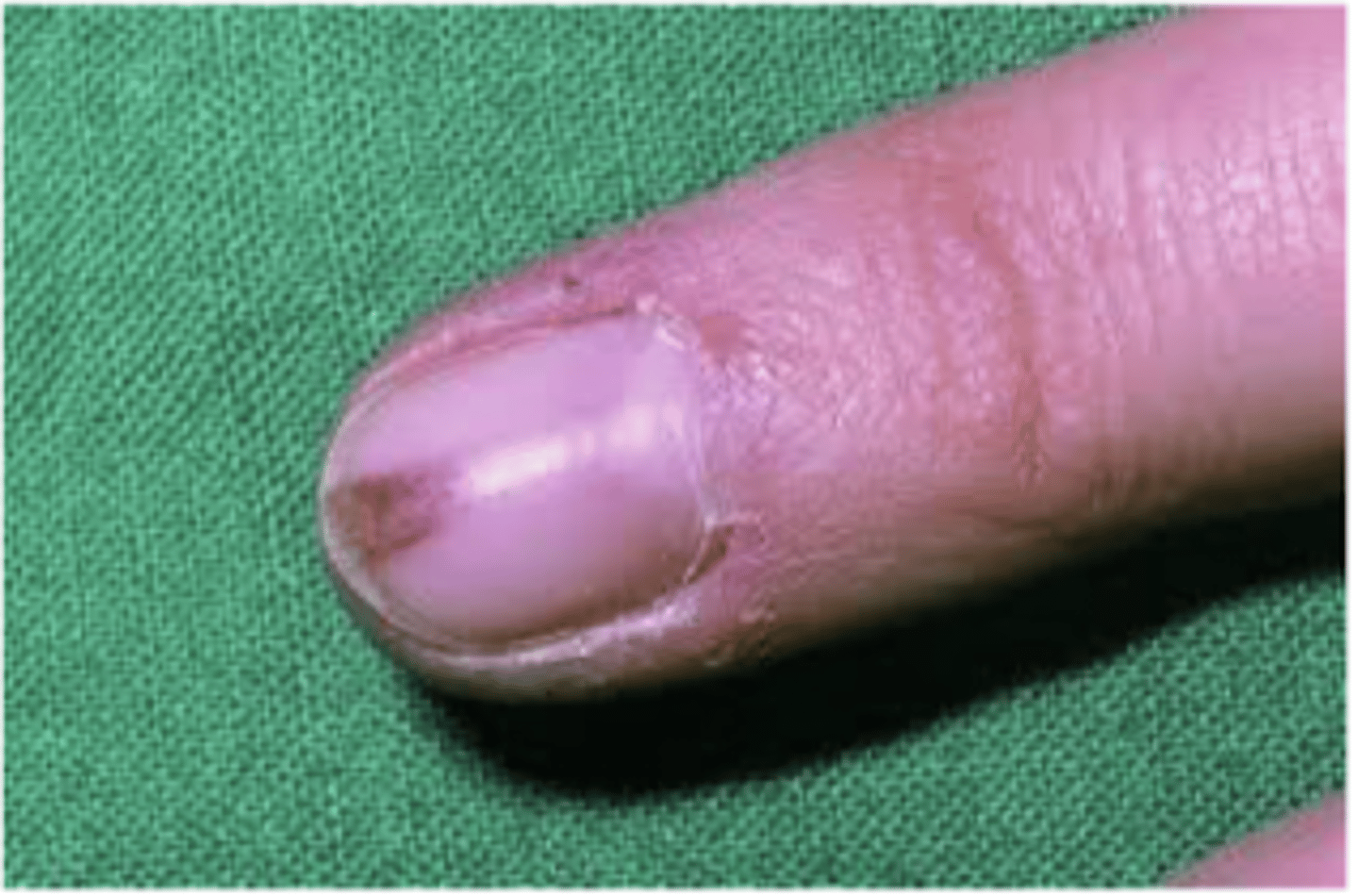
s/s of kaposi sarcoma
3 stages of cutaneous lesions in LE
1. patches
2. raised plaques
3. nodular
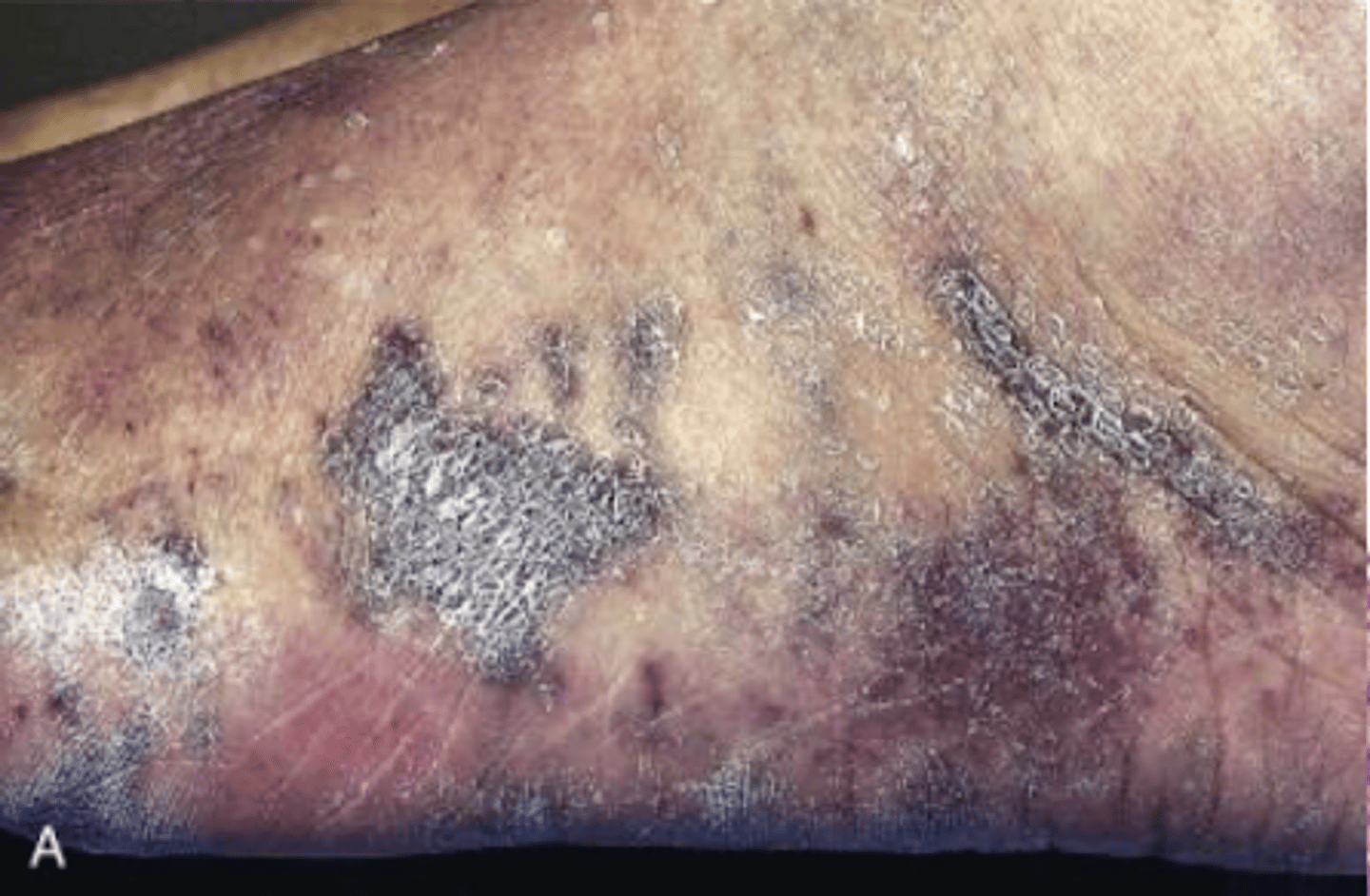
classic KS
older men of mediterranean, middle eastern or eastern European descent
red-purple skin plaques on distal LE
endemic African KS
HIV negative individuals < 40
inversely related to wearing shoes
transplant associated KS
solid organ transplant with T cell immunosuppression
AIDS-associated KS
most common HIV related malignant worldwide
epitheliod hemangioendothelioma
adults
occur around medium to large veins
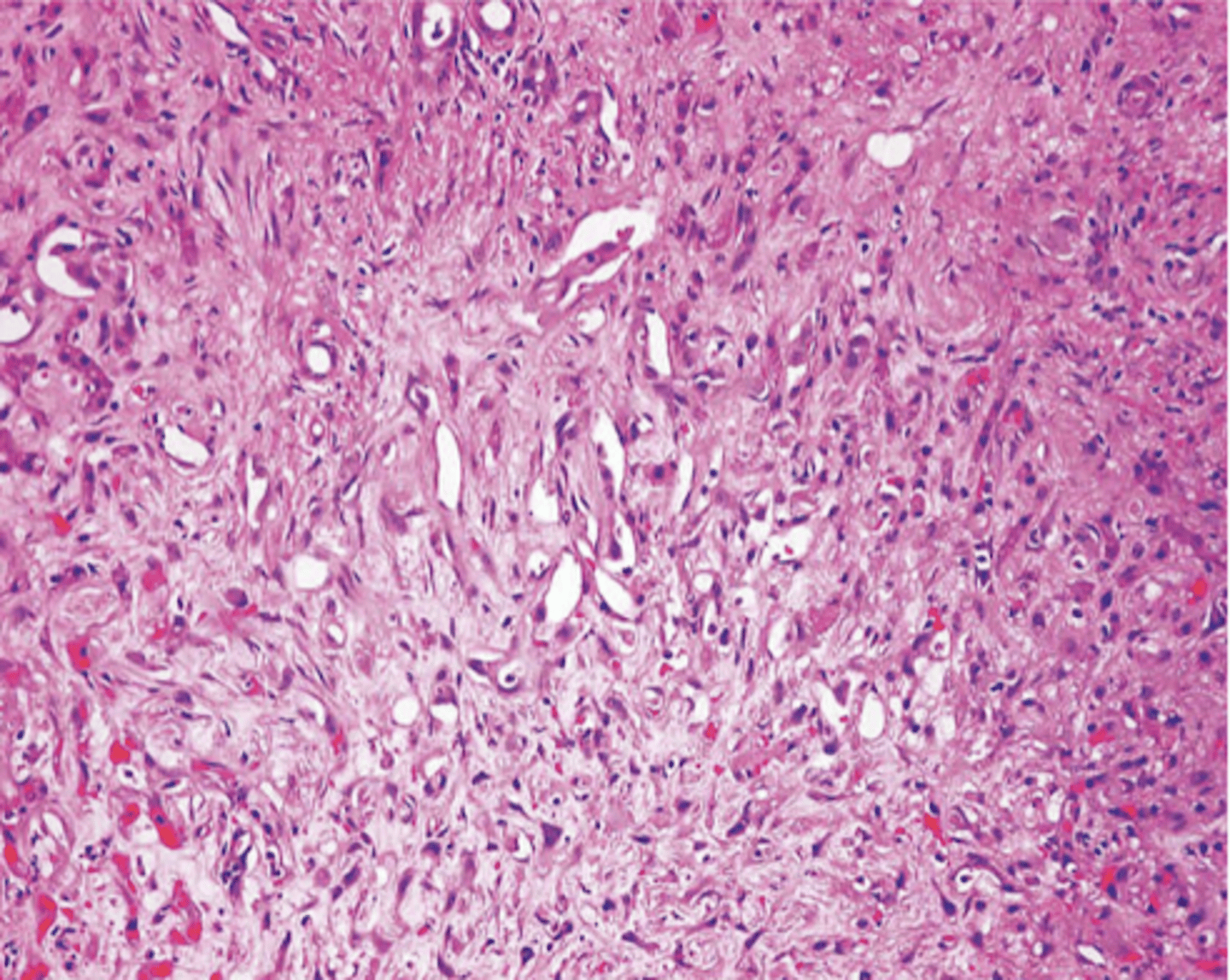
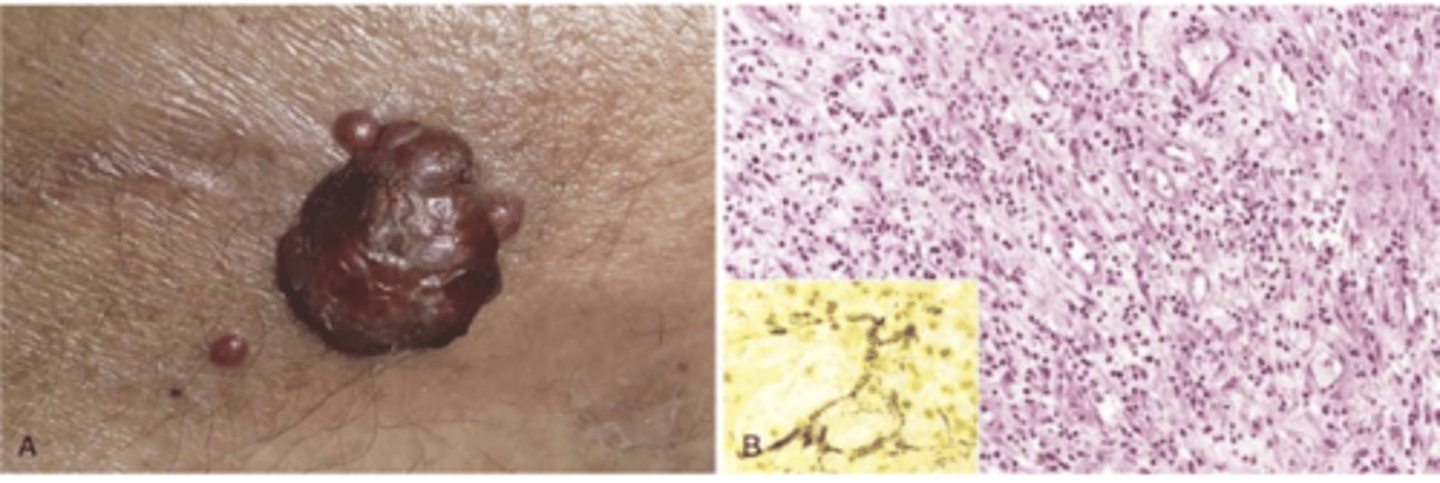
angiosarcoma
malignant endothelial neoplasm
angiosarcoma usually affects
older adults
appearance of angiosarcoma
starts as small papule
progresses to large, fleshy red tan to gray white lesions with blurred margins, necrosis, hemorrhage
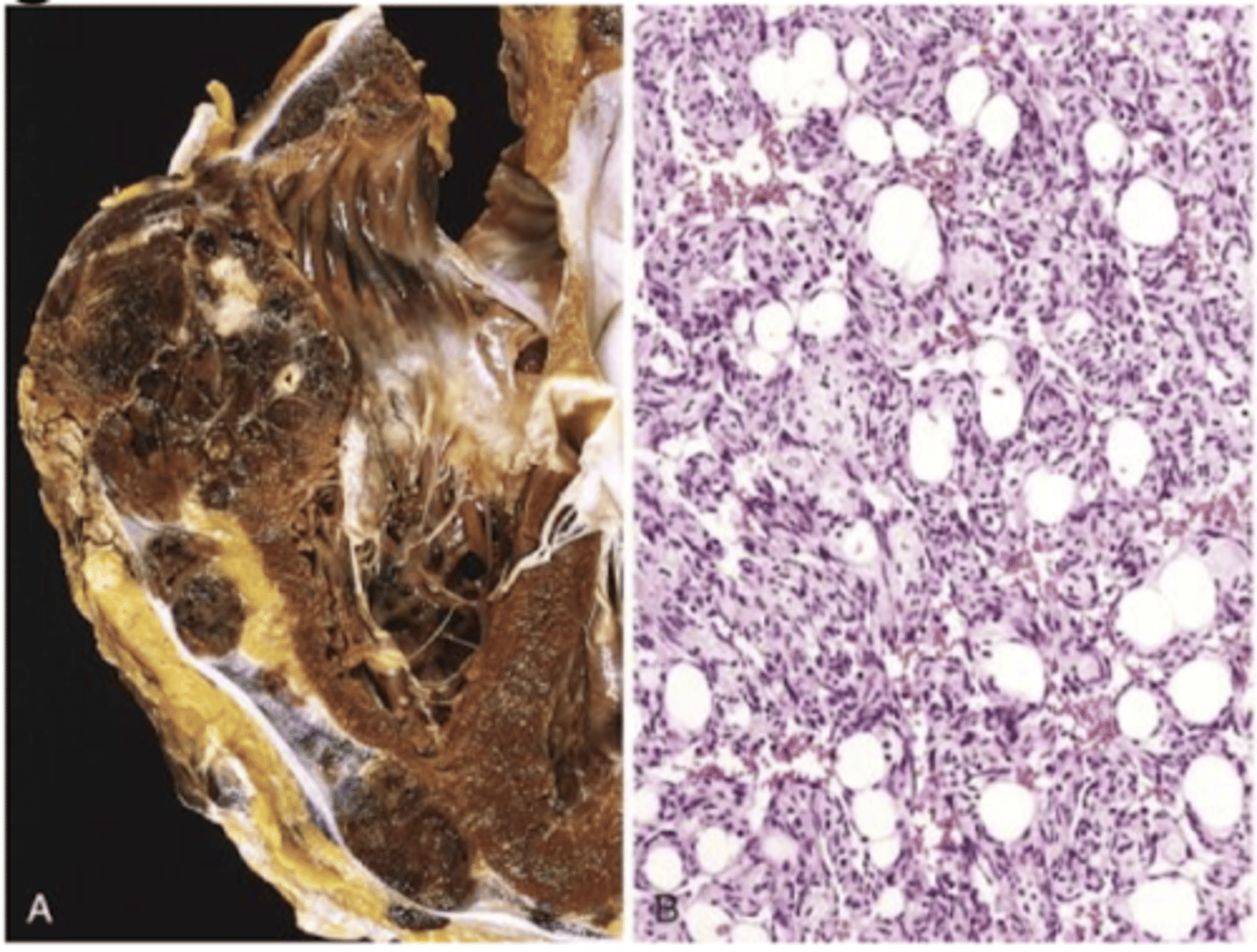
angiosarcoma can arise from
lymphedema
hepatic angiosarcoma (carcinogenic exposure)
CD31 (vWF)
endothelial origin
angiosarcoma
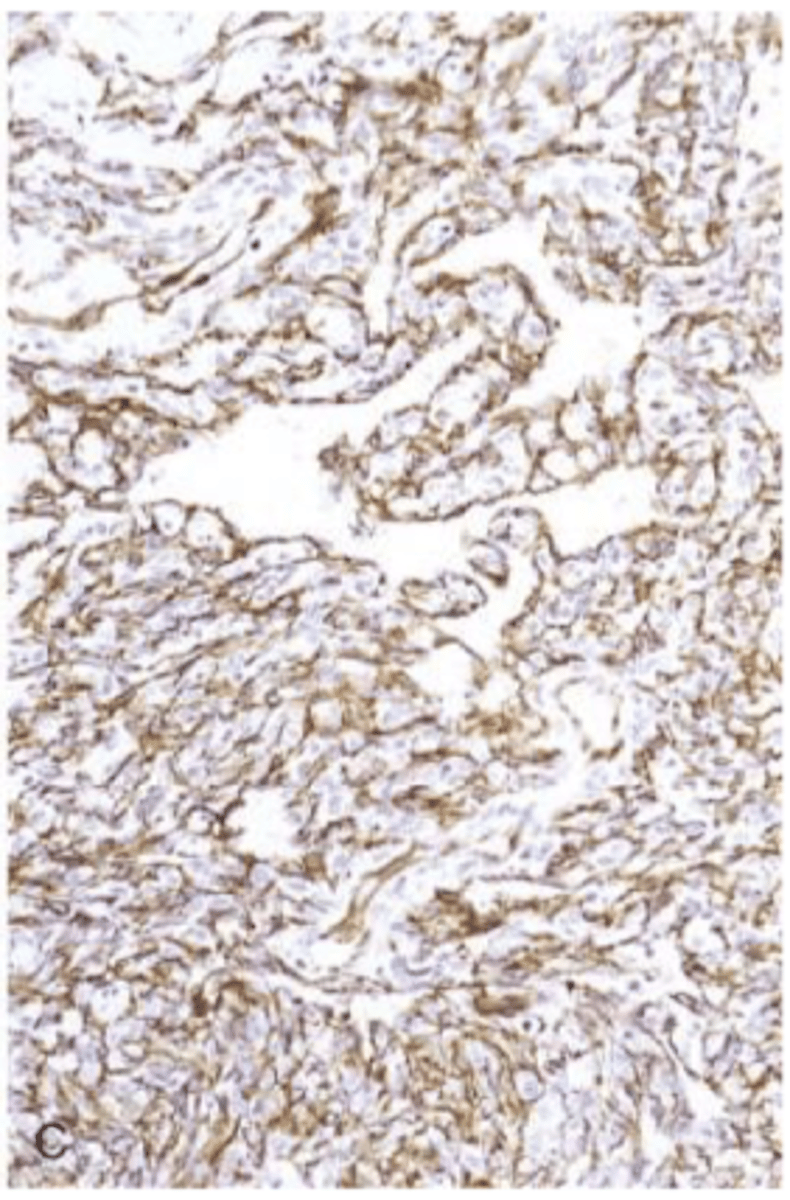
Hemangiopericytoma
arises from pericytes (myofibroblast like cells surrounding capillaries and venules)
rare