4) Radical reactions INTRODUCTION
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
page 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
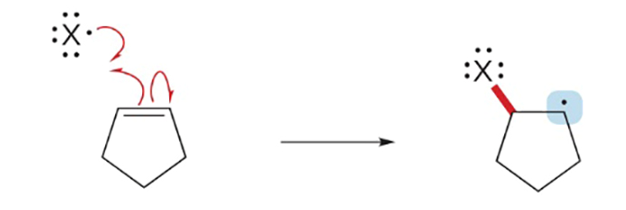
What is a radical?
Atom with a unpaired electron
Radicals are
electrophiles due to unfilled orbitals, highly reactive
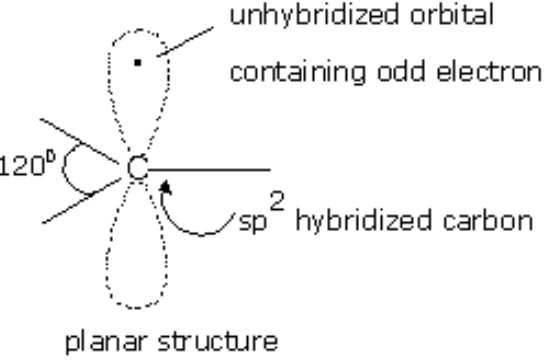
What is the e- geometry?
Trigonal planar, sp2 with a half-filled p orbital
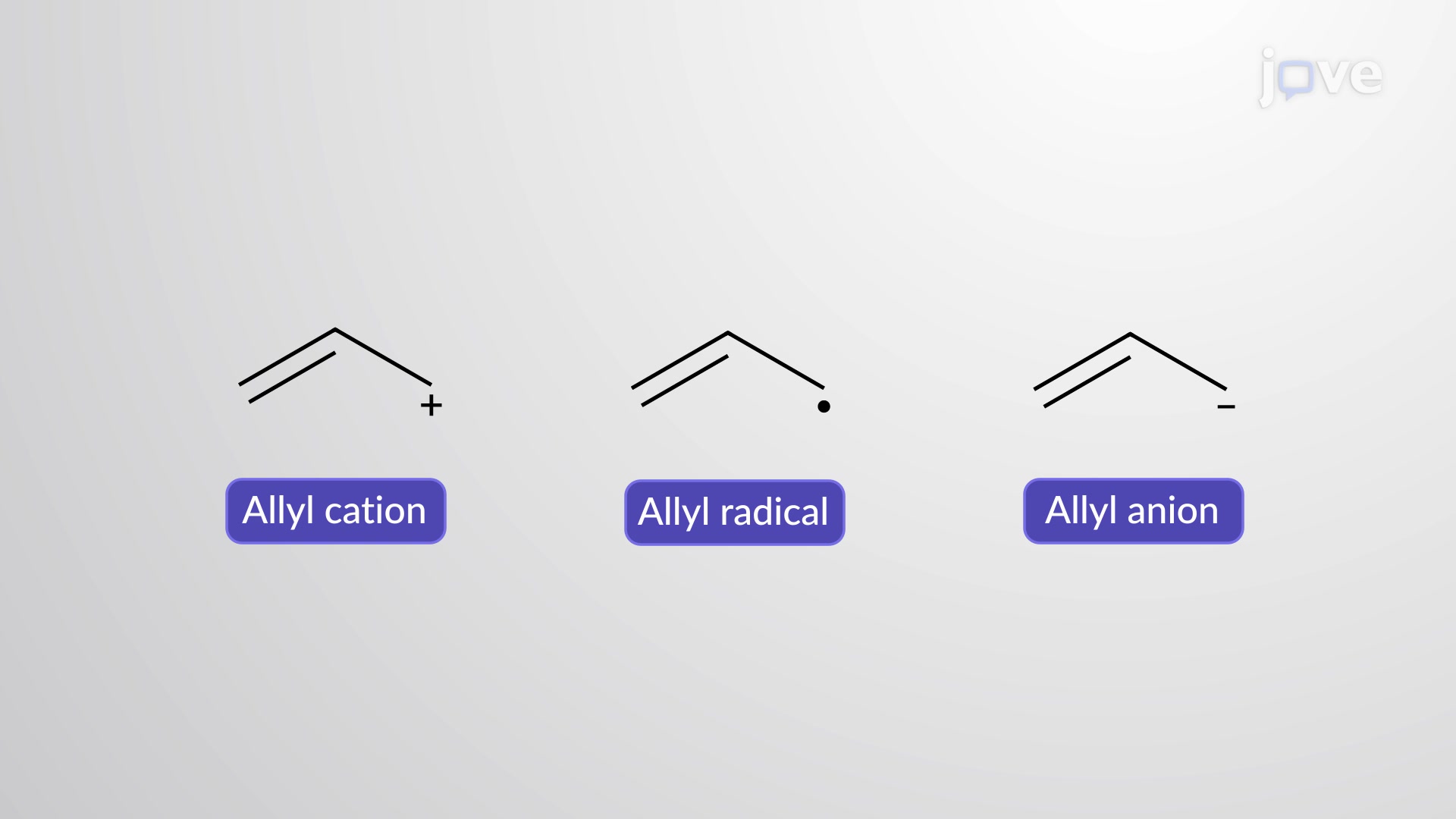
Radical stability order (unstable to stable)
primary, secondary, tertiary, allylic
What is the most stable radical?
An allylic radical, has resonance
What does allylic mean?
carbon that is adjacent to a double bond
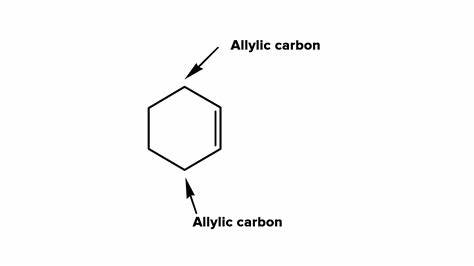
What is an allylic radical?
A carbon adjacent to a double bond with a radical attached
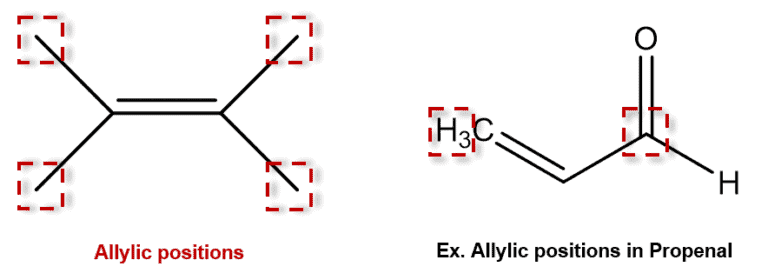
Why is the trend this way?
More carbons = more places to SHARE the electron density, making the molecule more stable
What happens when you stabilize a radical?
It becomes less reactive.
Why are primary radicals less stable than secondary radicals and so on?
When we talk about R groups (like alkyl groups), we mean groups that contain carbon-hydrogen bonds (such as methyl, ethyl, etc.). These groups are electron-donating, meaning they push electrons towards the radical site. This helps to stabilize the unpaired electron because the electron density around the radical increases, making it less reactive.
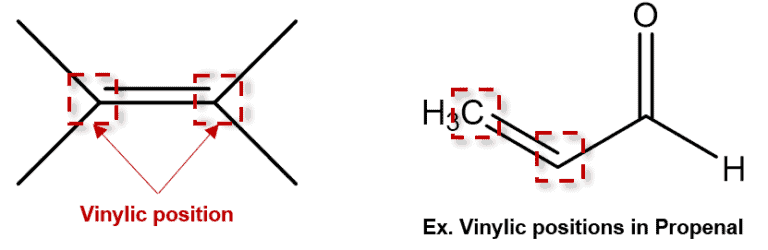
What does vinylic mean?
carbons in the double bond
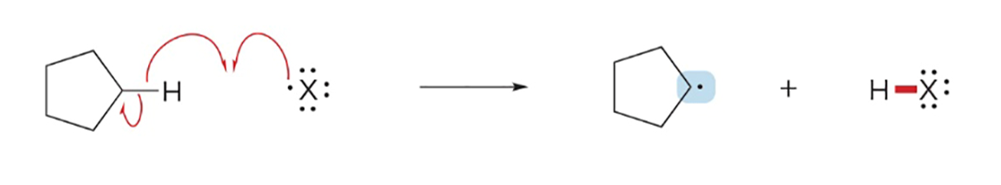
Reactions with sigma bonds form?
H-X and a carbon radical
Reactions with pi bonds form?
C-X and a carbon radical (now connected as one molecule!)