IB DT: Topic 3.2: Graphical modelling
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1-xkAJnuCsg52QYSRW9eyf9MzGEbsgOwPPorZJ2x99RU/present?slide=id.g2a097a0d7f5_0_344
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What are graphical models used for?
To simplify data and present it in such a way that understanding of what is being presented aids further development or discussion.
A tool to explore creative solutions and refine ideas from the technically impossible to the technically possible, widening the constraints of what is feasible
What is a formal drawing technique?
A type of drawing technique that has fixed rules, the most widely used being isometric projection and perspective drawing
What is a graphical model?
A visualisation of an idea, often created on paper or through software, in 2D or 3D
What is a part drawing?
Orthographic drawings of the components of an assembly containing details just about that component
What is a perspective drawing?
A set of formal drawing techniques that depict an object getting smaller and closer the further away they are. One point, two point, three point.
What is a projection drawing?
Systems of drawings that are accurately drawn, the two main types are isometric projection (formal drawing technique) and orthographic projection (working drawing technique).
What is a scale drawing?
Drawings that are bigger or smaller than the real product, but exactly in proportion with the product.
What is a sketch?
Rough drawings of ideas used to convey or refine the idea
What is a working drawing?
Drawings that are used to guide the production of a product, most commonly orthographic, section drawings, part drawings, assembly drawings and plan drawings
When is sketching used, as opposed to formal drawing?
Sketches are used in idea generation, and formal drawing is used in idea presentation. Sketching is used in the early stages of the design process, allow the designer to quickly jot down ideas that may influence the final design.
What are the different contexts where 2D and 3D sketches are useful?
2D sketches are able to isolate and detail structural features, 3D sketches provide designers with a sense of form, proportion and aesthetics to communicate with members of their team and the potential audience.
What are annotations for?
They accompany 2D and 3D drawings to improve the communication of information. They also help with the creative process documenting fleeting thoughts before they are forgotten.
What are the different ways designers can use annotations?
Identify problems for future resolution
Clarify obscure or difficult to sketch concepts
Note a range of related thematic variations or alternatives
Record thoughts about particular features
What do designers use models for?
As representations of reality and representing selected features of design. Useful throughout the design process from conceptual thinking to final development.
What is computer aided design (CAD)?
The use of a wide range of computer based tools that assist engineers, architects and product designers in developing realistic 3D rendered visuals of their ideas.
What are the benefits of virtual modelling?
Easy to change or edit and this enables designers to provide a number of variations of their ideas. The visualisations can be rotated so that different views of the idea can be seen, and then shared electronically.
What is the benefit of a perspective drawing?
It realistically represents an object by utilising foreshortening and vanishing points.
What are the three types of perspective and what are the differences between them?
One-point perspective: one vanishing point - buildings, roads, railway tracks
Two-point perspective: two vanishing points - the horizon is at eye level
Three-point perspective: adds a third point which creates an extra element of reality to the communicative impact of the object
What does an isometric drawing depict?
Depicts the proposed solution in 3D showing shape and form. Often formal drawings that show the proposed shape and form of the idea.
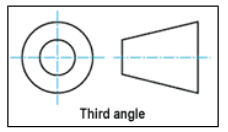
What is an orthographic projection?
A way of drawing an object from different directions/views. Usually a front, side and top are drawn so that a person looking at the drawing can see all the important sides. Useful to manufacturers as it shows precise details and dimensions. The dominant layout is 3rd angle projection.
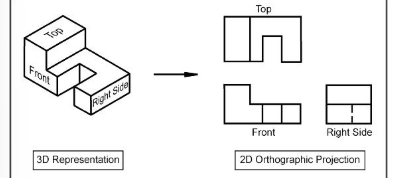
How is an orthographic drawing a working drawing?
Shows details and dimensions and can be used as a production drawing. Used to communicate design detail from designer to manufacturer. Produced at the final solution stage are used as working drawings in the realisation stage.
What is a section view?
A view used on a drawing to show an area or hidden part of an object by cutting away or removing some of that object. The cut line is called a cutting plane, and can be done in several ways.
What is a parts drawing and what is it used for?
Orthographic drawings of the components of an assembly containing details just about that component. Provides the information to assemble a product in a similar way that an assembly drawing does with the additional benefit of having a list of parts (LOP) or bill of materials (BOM).
What does a parts list provide?
Detailed information about parts, material and the quantity required to assemble the product successfully. Can either be specific to engineers, or designed for consumers (flat pack furniture).
What is an assembly drawing (fitted and exploded)?
Shows how parts of a product fit together
A fitted assembly drawing shows the parts put together (2D or 3D)
An exploded assembly drawing that shows the parts separated, but in the correct relationship for fitting together (3D)
What are the advantages and disadvantages of sketching?
Pros: ideas can be communicated v quickly, no formality or equipment necessary
Cons: can’t use the drawing for manufacture
What are the advantages and disadvantages of formal drawings?
Pros: shows detailed sizes of the concept, can be used in manufacturing, accurate, different views shown
Cons: time consuming , high level of skill needed, specialist equipment needed
What is an algorithm?
A self-contained step-by-step set of operations to be performed.