Art History: Survey of Indian Art and Architecture P1
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
anthropomorphic
depiction of human-like figure.
solid lost wax casting
figure sculpted, covered in clay with hollow channels, wax melted out, molten bronze poured in, clay mold broken. broken mold = one of a kind.
torsion
the action/state of twisting/being twisted. adds dimensionality around ENTIRE figure.
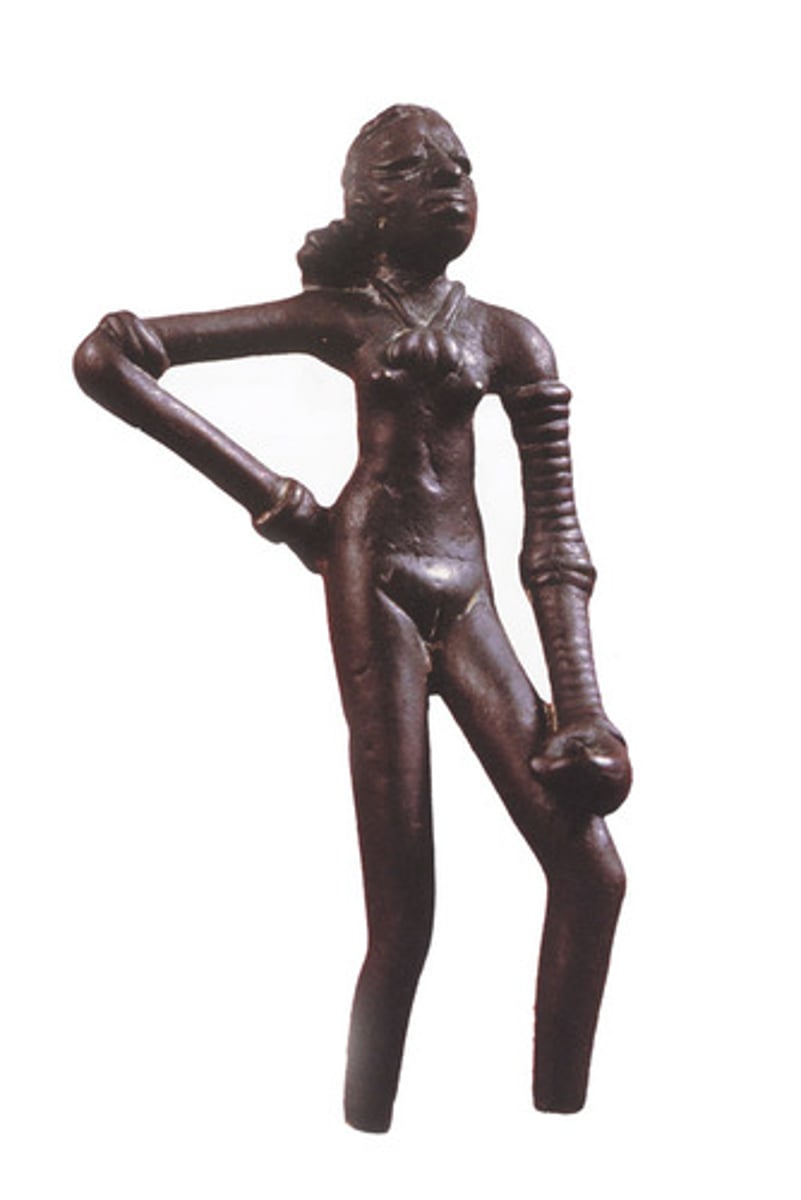

prana
vital breath. represented in the gut; "full of air."
Shramana
"one who labors or toils." 3 Indic traditions: Ajivika, Jainism, Buddhism. Do not accept authority of Vedas.
ahimsa
non-harm. respect for all beings, avoiding physical/mental violence.
Tirthankara (Jinas)
"ford-maker," enlightened human who crosses bridge of samsara, victorious. 24 in Jainism. not gods.
Bitumen
natural, sticky substance. used to waterproof, like a sealant; asphalt.
fetish
small, handmade object imbued with supernatural powers; transportable.
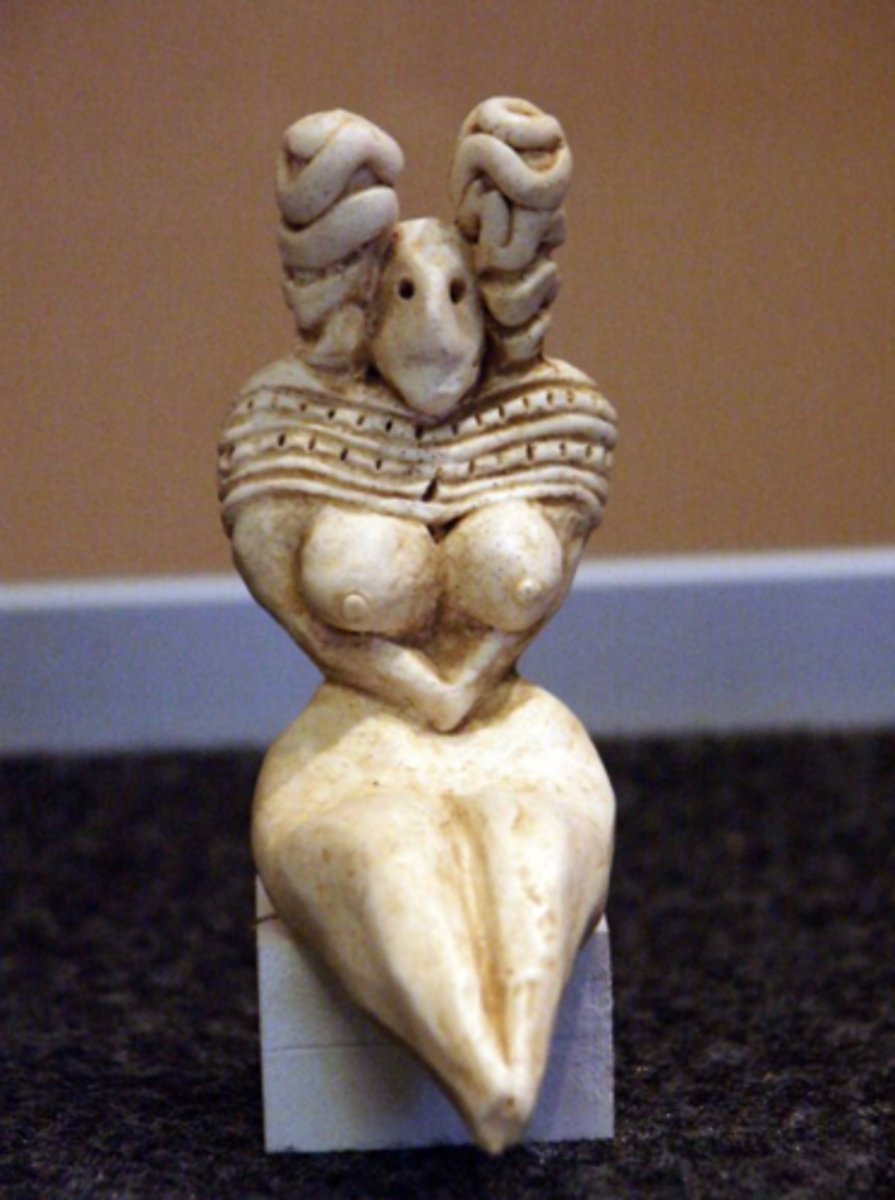

zoomorphic
depiction of animal-like figure.
Digambara
"sky-clad," male monastic order that shuns all property and wears no clothes. Jainism.
Shvetambara
"white-clad," monastic order (monks AND nuns) that wear minimal white clothing for modesty. Jainism.
Vedas
"knowledge," sacred texts of Vedic people.
Unpanishad
"to sit near," a series of texts that reinterpret/reevaluate the Vedas. Led to Shramana.
Trimurti
"3 embodiments," Bramha, Vishnu, and Shiva. Hinduism.
mudra
any symbolic/ritual gesture (usually made with hands and fingers) used to indicate a specific meaning.
itihasa
"histories." Includes the Mahabharata, the
Ramayana, and the Puranas. Believed to at least be based on actual historical events.
avatara
anthropomorphic/zoomorphic incarnation/manifestation of a diety on earth. in Hindu, most associated with Vishnu.
puranas
"of the ancient," a vast series of texts covering numerous topics. composed as early as 4th cen. CE, but origins are much older.
vahana
a vehicle/conveyance used to carry/transport a god. often the form of an animal (ex: Shiva=bull, Zeus=eagle).
Mauryan polish
mirror-like finish applied to sandstone/granite monuments during the Mauryan period. acts as protective seal. stayed in practice several centuries after the collapse of the Mauryan Empire.
dharmachakra
"Wheel of the Dharma." Dharma=universal "law/practice." describes the teachings of Buddha, represented by a spoked wheel.
chaitya arch (chandrashala)
"moon house," or horse-shoe shaped arches often on faccades of Buddhist Chaityas (shrine halls). Represent a transistion between wooden and stone architecture (ex: the lattice).
stupa
a rounded mound structure that contains relics, a type of chaitya. can be miniature or monumental form.
chaitya hall
a hall that contains a chaitya, a type of shrine hall.
vihara
a monastery. either free-standing (structural) or rock-cut (monolithic).
chhatri
a parasol/umbrella, sometimes multi-tiered. ancient Indic tradition of royalty, protection, and honor. placed atop stupa, acts as sacred/divine lightning rod.
pradakshina patha
a walkway that surrounds an image/shrine/building to be used for circumambulation (walking all the way around someone/thing). Indic tradition, clockwise=veneration/reverence.
darshana
auspicious Indic tradition of reciprocal sight. looking at a sacred object/person, and in turn having their energy reabsorbed back into the viewer; to see and be seen.
vajrasana
"the lightning seat," or "adamantine (diamond) throne." seat of enlightenment under Bodhi tree.
vaksha
male nature spirit (fem=yakshi). minor wealth deities/guardians of secret treasures, associated with natural features. Trace back to indigenous tradition.
Vedika
railing enclosing chaitya/stupa. stone modeled after wood.
torana
an arch/portal/gateway. comparable to Japanese torii gates.
jataka
"birth story," the narratives that detail the previous lives of Shakyamuni Buddha.
iconographic program
the intentional choice and placement of specific images within a composition, either according to canonical written rules or creative liberty.
dvarapala
door guardians; celestial beings or human figures that guard the entrances of shrines/chaityas/temples.
maithuna figures
male AND female couples that represent fertility,
abundance, and auspiciousness.
Mount Meru (Sumeru)
the celestial mountain at the center of the
Buddhist cosmos, comparable to Mount Olympus. Also in Jainism and Hinduism, but role/significance differs.
trikaya system
"Three bodies." a doctrine concerning the threefold nature of Buddha-hood. primarily upheld in Mahayana and Vajrayana (tantric or esoteric) Buddhism.
abhayamudra
gesture of "do not fear." hand up, facing out, open-palmed.
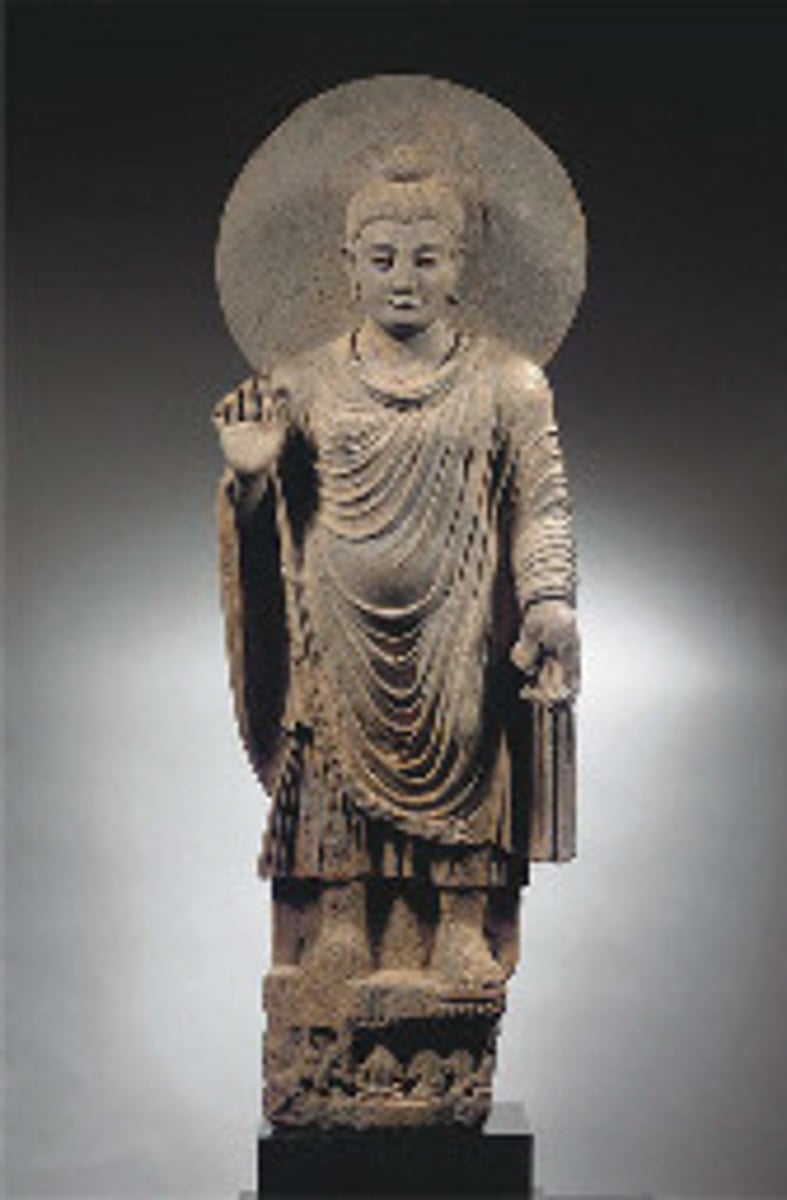

dharmachakra mudra
gesture of turning the Wheel of Dharma in motion. signifies the act of teaching buddhist principles.
dashavatara
the 10 major incarnations of Vishnu
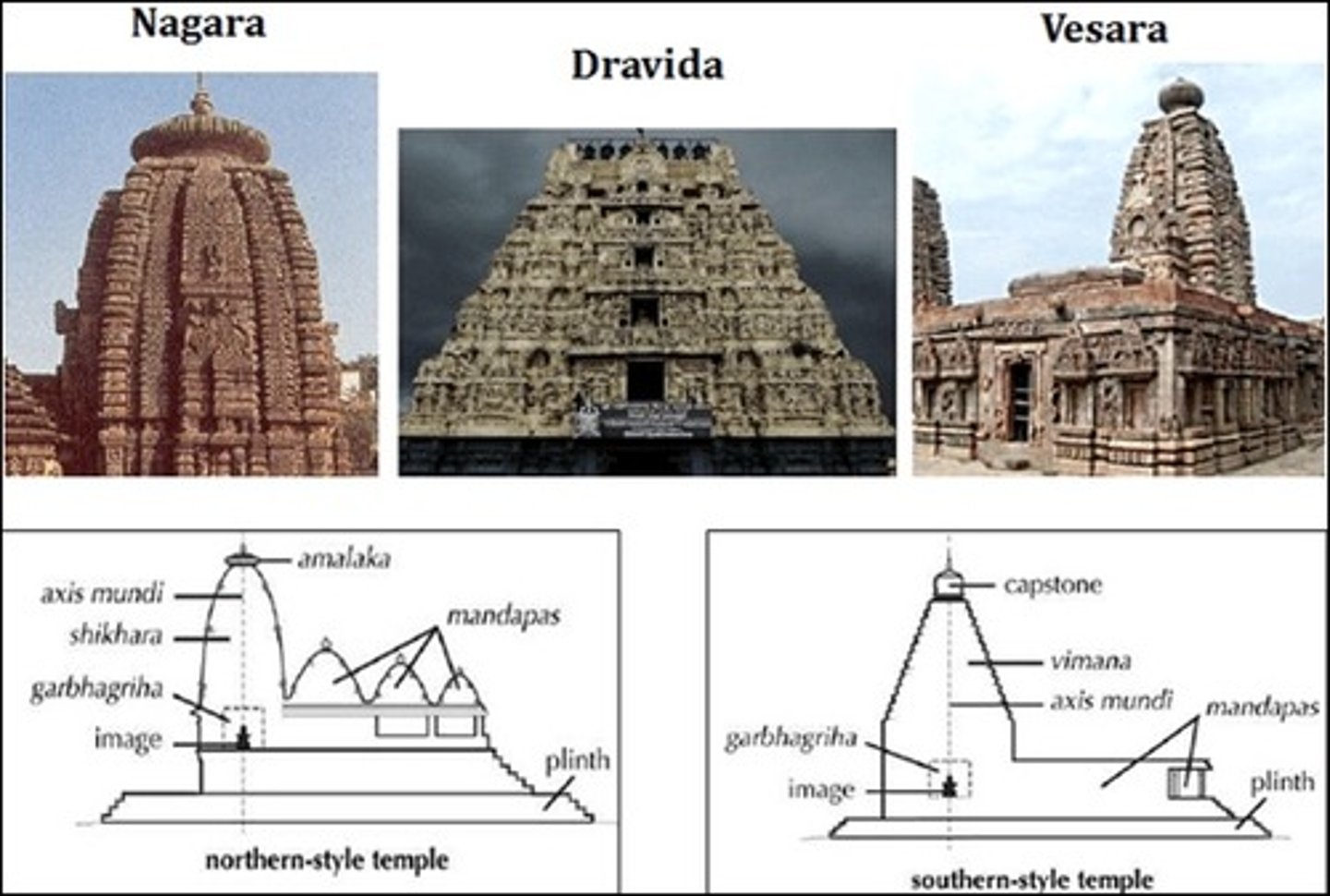
nagara
the northern style of temples, typified by the inclusion of a shikara.
shikara
a four-sided sloping tower on nargara temples.
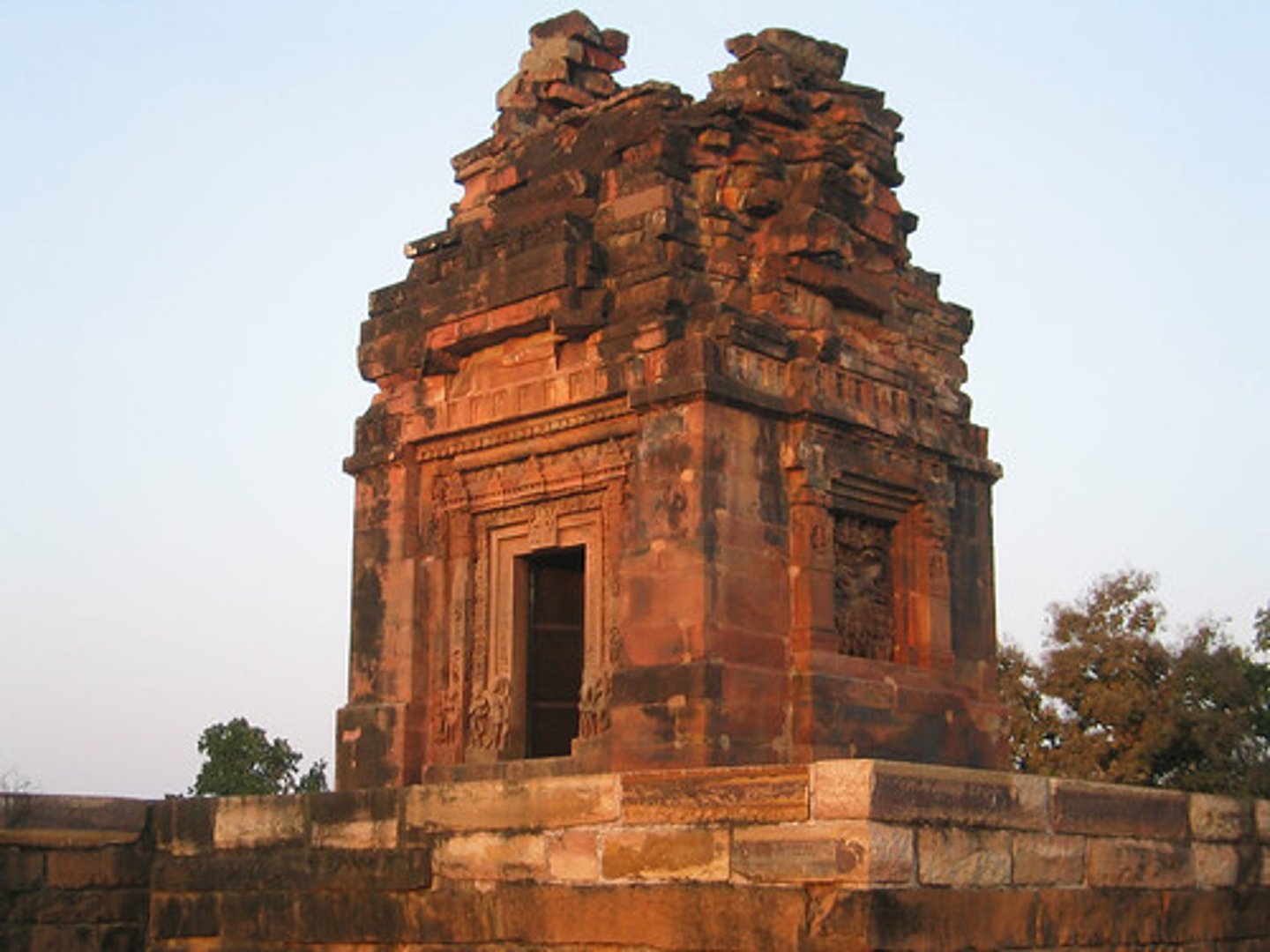

bhakti
selfless, devotion. a philosophical concept that became a core aspect of classical and later hinduism.
fresco-secco
technique of painting on dry plaster.
mandapa
a pavilion/porch-like structure supported by columns. passed through in order to enter the temple, can be attached or separate from the temple.
vimana
southern-style, dravida temples. the tower placed above the Garbha-griha. straightlined, unlike curved slope of northern style shikharas. strong, horizontal steps.
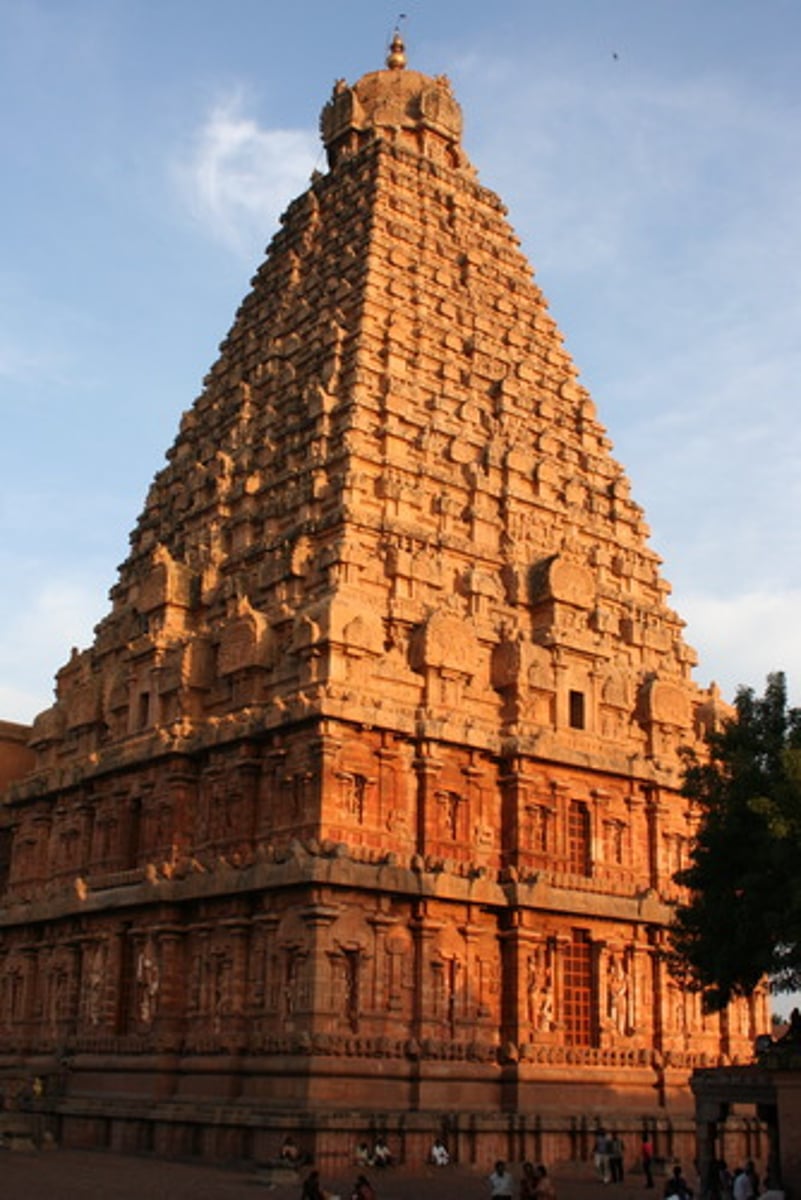

dravida
southern style of Indian temples. features a vimana and flat-roofed mandapa (northern style=domed/pyramid roofs).