Quantum Numbers and Orbitals
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
1
New cards
Quantum Number
these numbers define the orbitals and electrons within these numbers mathematically; describe shape, size, energy, etc.
2
New cards
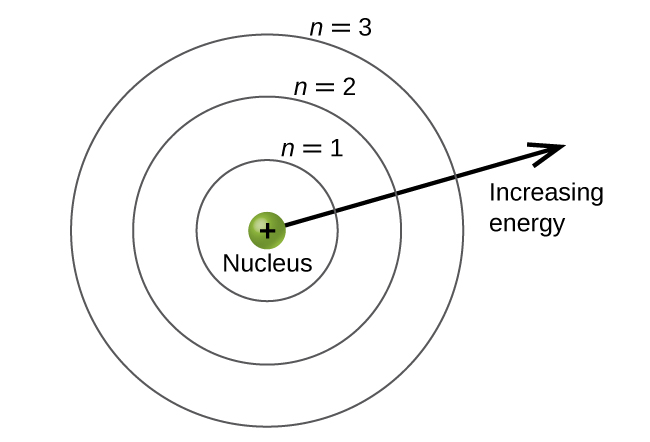
n, The Principal Quantum Number
a positive integer describing relative size and energy of an atomic orbital; if n increases, size and energy increases
3
New cards
Orbital
a 3D region where the probability of finding an electron is the highest
4
New cards
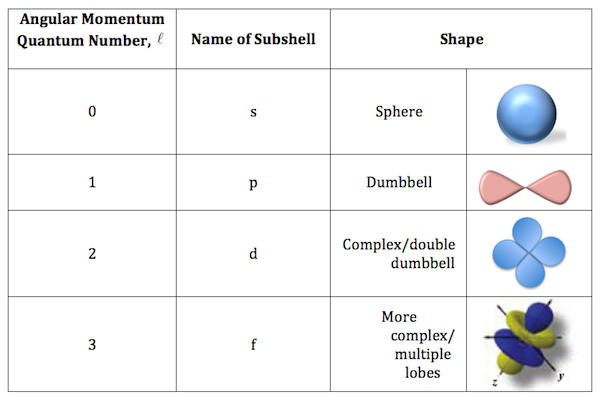
l, The Angular Momentum Number
defines orbitals shape, ranges from 0 to n-1
5
New cards
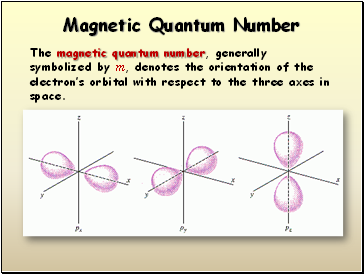
Ml, The Magnetic Quantum Number
describes the orientation of the orbital in space; ranges from -l to l
6
New cards
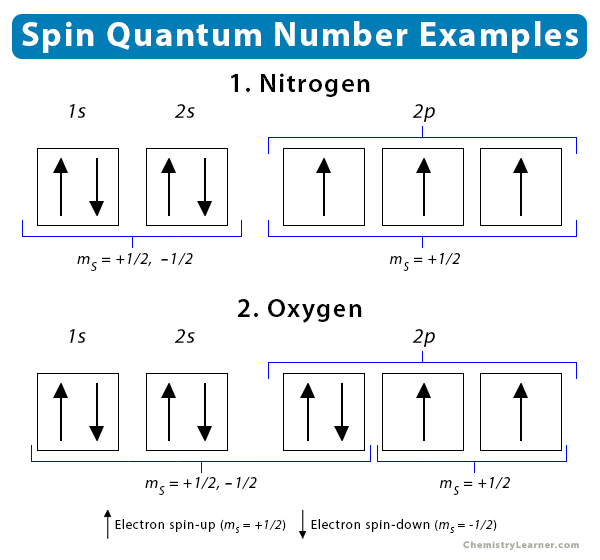
Ms, The Spin Quantum Number
an integer describing the spin of electrons in the orbital, (-1/2 or +1/2 only). Each orbital can hold 2 electrons, one +1/2, and one -1/2.
7
New cards
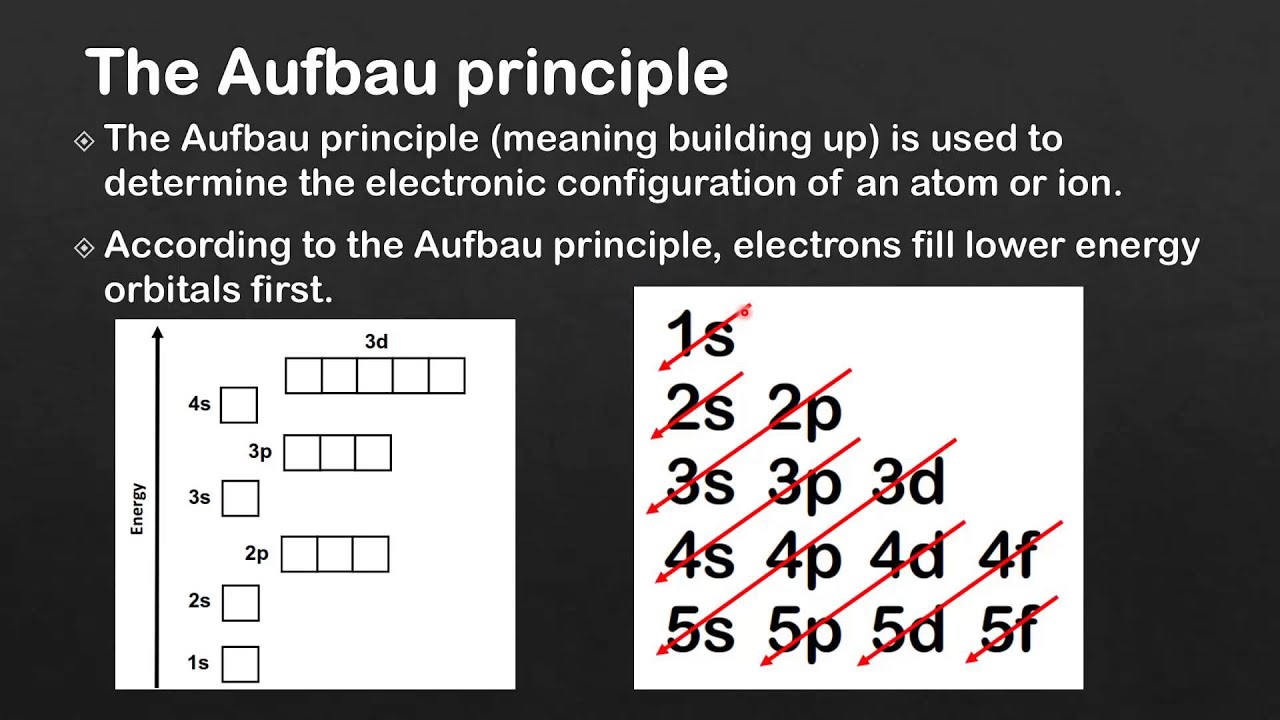
Aufbau Principle
add electrons to the lowest energy orbital first
8
New cards
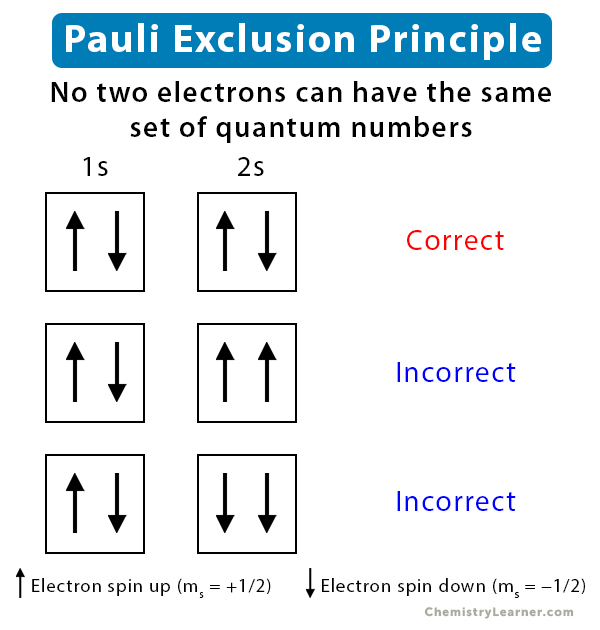
Pauli's Exclusion Principle
electrons in a given atom cannot share the same 4 quantum numbers.
9
New cards
Degenerate
if two orbitals have the same n+1 value, they have equal energy and are called degenerate.
10
New cards
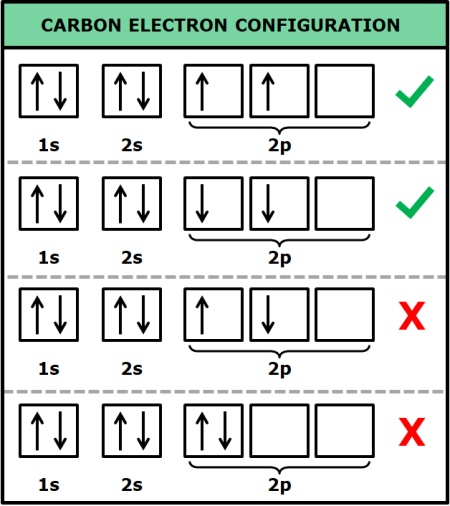
Hund's Rule
when filling degenerate orbitals, it's best to leave unpaired electrons
11
New cards
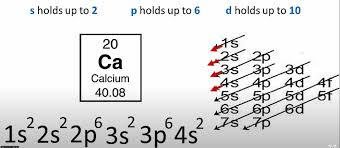
Electron Configuration
denotes number of electrons in each orbital
12
New cards
Orbital Diagrams
a box as the orbital, half-arrow as electron
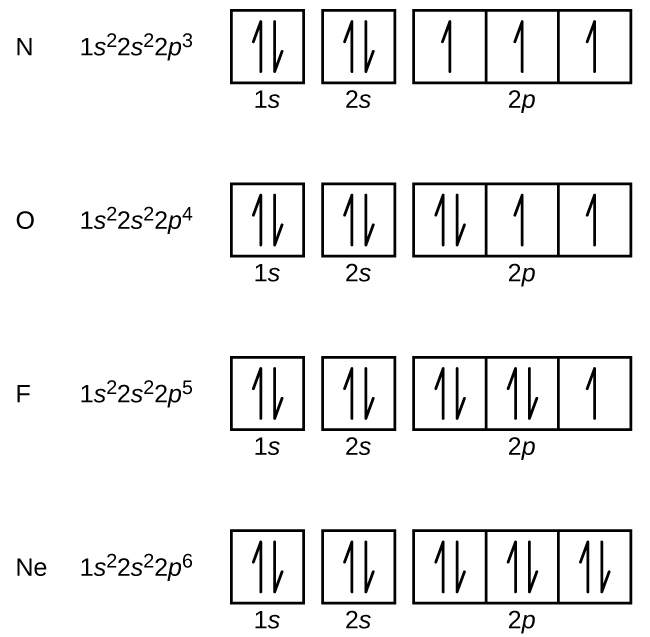
13
New cards
Condensed Electron Configuration

14
New cards
Core Electrons
electrons in the inner shells; not very reactive
15
New cards
Valence Electrons
electrons in outer shells; very reactive