CCBC BIOL 109 LECTURE EXAM 1
1/148
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of practice flashcards covering BIOL 109 Chapters 1-6, including basic concepts of anatomy, physiology, chemistry, cell biology, tissues, integumentary and skeletal systems.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
What is Biology and which two branches are its main subdivisions?
Biology is the study of life; anatomy and physiology are its main branches.
Name the five basic life functions shared by all living organisms.
Responsiveness, Growth, Reproduction, Movement, Metabolism.
What is Responsiveness in living organisms?
The ability to sense and respond to changes in the environment.
Give an example of Responsiveness.
Responding to changing blood glucose levels or moving a hand away from a hot stove.
What is Growth in biological terms?
An increase in size and often the number of cells.
Give an example of Growth.
An enlarged muscle or skin that is thicker in an adult versus a child.
What is Reproduction?
The production of offspring of the same kind.
What is Movement in living systems?
Movement of the organism or movement of substances/cell components within the body.
Define Metabolism.
All chemical processes that occur in the body, including building and breaking down substances for structure, physiology, or energy.
What is Gross (macroscopic) anatomy?
The study of body structures visible to the naked eye.
What is Systemic Anatomy?
Study of one organ system at a time (e.g., cardiovascular system).
What is Regional Anatomy?
Study of superficial and internal structures in a specific region of the body.
What is Surface Anatomy?
Study of the general form and superficial markings; used in physical examination.
What is Microscopic Anatomy?
Study of structures too small to be seen with the naked eye; includes cytology and histology.
What does Physiology study?
The life processes of the body and how it functions; includes cell and systemic physiology and pathology.
List the Levels of Structural Organization from simplest to most complex.
Chemical level, Cellular level, Tissue level, Organ level, Organ system level, Organism level.
What are the four tissue types?
Connective, Epithelial, Muscle, Nervous.
Define Homeostasis.
Existence of a stable internal environment within the body.
What are the three components of a homeostatic regulatory circuit?
Receptor (sensor), Control center, and Effector.
What is a Negative Feedback Loop?
A corrective response that opposes or reverses the original change, restoring stability.
What is a Positive Feedback Loop?
A response that reinforces the original change (e.g., blood clotting, labor contractions).
Describe the Anatomical Position.
Body erect, feet flat on the floor, face forward, upper limbs at the sides, palms facing forward; left/right orientation is reversed for the observer.
What do Supine and Prone mean?
Supine: laying face up. Prone: laying face down.
What are Abdominopelvic Quadrants?
Right Upper (RUQ), Right Lower (RLQ), Left Upper (LUQ), Left Lower (LLQ); used to describe organ location and pain.
What are the Abdominopelvic Regions?
Nine-region scheme: right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac; right lumbar, umbilical, left lumbar; right iliac, hypogastric, left iliac.
Name 2 directional terms that describe position.
Anterior (toward the front), Posterior (toward the back).
What are the three body planes?
Sagittal (vertical, divides right/left), Frontal/Coronal (vertical, anterior/posterior), Transverse (horizontal, superior/inferior).
What is the thoracic cavity and its internal cavities?
Contains two pleural cavities (around each lung) and the pericardial cavity; Mediastinum lies between the pleural cavities and contains the pericardial cavity.
What is the abdominopelvic cavity composed of?
Abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity; separated from the thoracic cavity by the diaphragm.
What are serous membranes and their layers?
Thin, double-layered membranes that line closed body cavities; layers are visceral (inner) and parietal (outer) with serous fluid between.
Name the serous membranes of the thoracic and abdominal cavities.
Pleura (around the lungs), Pericardium (around the heart), Peritoneum (around abdominal organs).
What is the basement membrane?
Connection between epithelium and underlying connective tissue; provides nutrients to avascular epithelia.
What are the three main shapes of epithelial cells?
Squamous (flat), Cuboidal (cube-shaped), Columnar (taller than wide).
Differentiate simple and stratified epithelium.
Simple epithelium has one single layer of cells, which makes it good for absorption, filtration, and diffusion.
Stratified epithelium has multiple layers of cells, which makes it better for protection against friction, chemicals, and pathogens.
What are glandular epithelia?
Epithelium that produces secretions; includes endocrine (hormones) and exocrine (ducts) glands.
What are the main components of connective tissue?
Extracellular protein fibers (collagen, elastic, reticular), viscous ground substance, and cells (e.g., macrophages, fibroblasts, adipocytes).
Name the five major types of connective tissue.
Areolar, Adipose, Dense (regular and irregular), Cartilage, Bone.
What are the three types of cartilage?
Hyaline, Elastic, Fibrocartilage.
What are the bone classifications by shape?
Long bones, Short bones, Flat bones, Irregular bones.
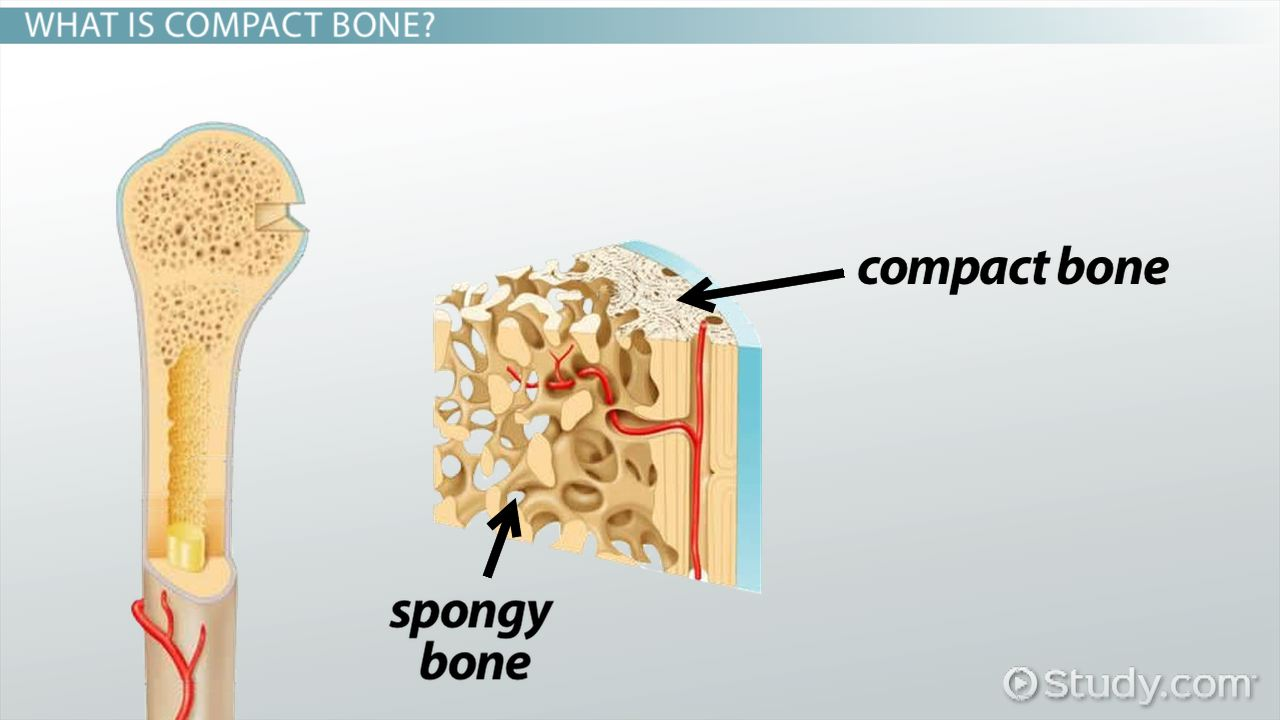
What is the difference between compact and spongy bone?
Compact: in concentric layers; spongy, porous finger network arrangment
What is an osteon?
The structural unit of compact bone, consisting of a central canal, concentric lamellae, and osteocytes in lacunae.
What is the periosteum and endosteum?
Periosteum: outer covering of bone. Endosteum: lining of marrow cavity and inner bone surfaces.
What are the two ossification processes?
Intramembranous ossification (flat bones from connective tissue membranes) and Endochondral ossification (most bones from hyaline cartilage).
What is an epiphyseal plate?
Hyaline cartilage plate between diaphysis and epiphysis responsible for lengthwise bone growth in youth.
What is appositional growth?
Growth in bone diameter via osteoblast activity at the periosteum.
Which hormones regulate bone growth and mineral balance?
Growth hormone, thyroid hormone, sex hormones (testosterone and estrogen); Parathyroid hormone (PTH) and Calcitonin regulate blood Ca2+.
Describe the stages of fracture repair.
Hematoma formation → Callus formation → Hard (bony) callus formation via ossification → Remodeling of bone to restore original structure.
What is osteopenia vs osteoporosis?
Osteopenia: thinning of bone; osteoporosis: significant bone mass loss with fracture risk.
What are the major skin layers and their functions in the integumentary system?
Epidermis (protective, avascular) and Dermis (vascular, supports). Hypodermis (not part of skin) stores fat.
Name the major epidermal cell types.
Keratinocytes, Melanocytes, Dendritic (Langerhans) cells, Merkel (tactile) cells.
List the epidermal strata from deep to superficial.
Stratum basale, Stratum spinosum, Stratum granulosum, Stratum lucidum (thick skin only), Stratum corneum.
What is the function of the dermal papillae and Meissner corpuscles?
Dermal papillae increase surface area and contribute to fingerprints; Meissner corpuscles detect light touch.
What distinguishes thick skin from thin skin?
Thick skin has all five epidermal layers and no hair; thin skin has four layers and usually includes hair.
What is the hypodermis and its role?
Subcutaneous layer; not part of the skin; stores fat, insulates, provides blood vessels and nerves; common site for injections.
What pigments contribute to skin color?
Melanin (produced by melanocytes), carotene; dermal circulation (hemoglobin) also affects color.
What are hair structures and functions?
Hair shaft, hair root; hair papilla; matrix; arrector pili; functions include protection and signaling maturity.
What are sebaceous glands and their function?
Sebaceous glands produce sebum (oil) to lubricate skin and hair; ducts usually connect to hair follicles.
What are the major types of sweat glands and their characteristics?
Eccrine (merocrine): widespread; secrete watery sweat for thermoregulation. Apocrine: active at puberty;secrete thicker fluid in armpits and groin; modified glands include mammary and ceruminous.
What are nails composed of and their parts?
Nails are made of hard keratin; parts include nail body, nail bed, nail root, lunula, and eponychium (cuticle).
What are the three classes of burns?
First-degree: epidermis only; Second-degree: epidermis and part of dermis; Third-degree: through all skin layers and possibly deeper tissues.
What are the basic components of the skeletal system?
Bones, cartilage, ligaments; functions include protection, support, mineral storage, hematopoiesis, and movement.
How are bones classified by shape and give examples?
Long bones (arm, leg), Short bones (carpal, tarsal), Flat bones (skull, sternum), Irregular bones (vertebrae, facial bones).
Describe the diaphysis of a long bone.
The shaft; thick compact bone wall; contains the marrow cavity.
What is the epiphysis of a long bone?
The expanded ends of the bone; filled with spongy bone and articular cartilage at joints.
What is the role of articular cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage that covers epiphyses; reduces friction in joints; avascular.
What is the bone’s marrow cavity and its two types of marrow?
Marrow cavity within the diaphysis; Red marrow produces blood cells; Yellow marrow stores fat.
What is the periosteum’s role in bone?
Connective tissue layer that covers outer bone surface; involved in growth, repair, and attachment of ligaments/tendons.
What is endosteum?
Connective tissue lining the marrow cavity and inner surfaces of bone; active in growth and remodeling.
What are the two ossification methods and what bones they form?
Intramembranous ossification forms flat bones (skull, mandible, clavicles) from membranes. Endochondral ossification forms most other bones from hyaline cartilage.
Explain endochondral ossification steps.
Cartilage model enlarges, chondrocytes die creating cavities; perichondrium becomes periosteum and osteoblasts form bone around diaphysis; vessels invade creating primary ossification center; bone spreads toward ends; secondary centers form later in epiphyses.
What is the epiphyseal plate and epiphyseal line?
Epiphyseal plate is the growth plate in children; epiphyseal line is its former location in adults after growth ends.
What factors affect bone growth?
Nutrition (calcium, phosphate, vitamins D3, C; protein), and hormones (growth hormone, thyroid hormone, sex hormones).
What is calcium homeostasis and which hormones regulate it?
Calcium homeostasis is the balance of blood calcium levels, regulated mainly by parathyroid hormone (raises calcium), calcitriol/vitamin D (increases absorption), and calcitonin (lowers calcium).
What is the process of bone remodeling?
Osteoclasts remove old bone; osteoblasts lay down new bone; responds to stress and calcium needs.
What is hematopoiesis and where does it occur in bones?
Blood cell formation; occurs in red bone marrow within certain bones.
Which cell types are involved in bone maintenance and remodeling?
Osteocytes (maintain bone), Osteoblasts (form bone), Osteoclasts (resorb bone).
What are the two major components of the bone matrix?
Approximately 35% collagen (organic) and 65% mineral (calcium phosphate crystals).
What roles do osteocytes play?
Maintain bone and participate in repair; some can remodel bone and respond to stress.
What structures make up compact bone’s basic unit?
it’s the osteon (Haversian system), which is made up of concentric rings of bone called lamellae, with osteocytes in spaces called lacunae, connected by canaliculi, all surrounding a central (Haversian) canal that contains blood vessels and nerves.
What is the difference between compact and spongy bone in terms of organization?
Compact bone is dense and forms the hard outer layer; spongy bone has trabeculae and houses bone marrow within spaces.
What are the layers of the epidermis in order, and what is a key mnemonic for remembering them?
Basale, Spinosum, Granulosum, Lucidum (thick skin only), Corneum; mnemonic: Brilliant S tudying G ives L oads of C onfidence.
Which epidermal layer is the deepest and houses mitotic activity?
Stratum basale (germinativum).
What are the functions of the integumentary system?
Protection, thermoregulation, vitamin D3 synthesis, storage of lipids, sensory reception, excretion and secretion.
Which skin cells produce melanin and what is its function?
Melanocytes in the stratum basale; melanin protects underlying tissue from UV radiation and determines skin color.
What defines thick skin vs thin skin?
Thick skin has all five epidermal layers and no hair; thin skin has four layers and usually has hair.
Name the major hair structures.
Hair shaft, hair root, hair papilla, matrix, arrector pili muscles.
What is the function of arrector pili muscles?
Smooth muscles that contract to make hair stand upright (goose bumps) in response to cold or fear.
What glands are associated with hair and skin, and what do they secrete?
Sebaceous glands secrete sebum; sweat glands (eccrine and apocrine) secrete sweat; modified glands include mammary glands and ceruminous glands.
What are nails composed of and their key parts?
Nails are made of keratin; nail body, nail bed, nail root, lunula, and eponychium (cuticle).
What are the three classes of burns and their effects?
First-degree: epidermis only; Second-degree: epidermis and part of dermis; Third-degree: all layers and possibly deeper tissues.
What are the major structural components of the skeletal system that protect organs?
Bones protect delicate organs such as the cranium (brain), thoracic cage (heart and lungs), and vertebral column.
Differentiate osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts.
Osteoblasts form new bone matrix; osteocytes maintain bone; osteoclasts resorb bone.
What is the role of the periosteum and endosteum in bone growth and repair?
Periosteum supplies a surface for attachment and provides blood supply; endosteum lines marrow cavities and is active in growth and remodeling.
What tissue types form the four major tissue categories?
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nervous tissues.
What is the difference between a molecule and a compound?
A molecule is two or more atoms bonded together; a compound is a molecule composed of two or more different kinds of atoms.
What are the three main types of chemical bonds?
Ionic bonds (transfer of electrons), Covalent bonds (sharing electrons; nonpolar and polar), Hydrogen bonds (weak attractions between molecules).
Define the octet rule.
Outer electron shell is full with 8 electrons; atoms with incomplete outer shells are reactive; inert gases have full outer shells.
What makes water a universal solvent?
Water’s polarity enables it to dissolve many solutes, forming aqueous solutions.
What is osmosis?
Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane toward higher solute concentration.
Differentiate hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic solutions.
Hypotonic: lower solute concentration than the cell; cell may swell. Isotonic: equal solute concentration; no net water movement. Hypertonic: higher solute concentration; cell may shrink.