Mind brain and behavior EXAM 1
1/189
Earn XP
Description and Tags
signaling, somatosensory, neuroanatomy, and motor systems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
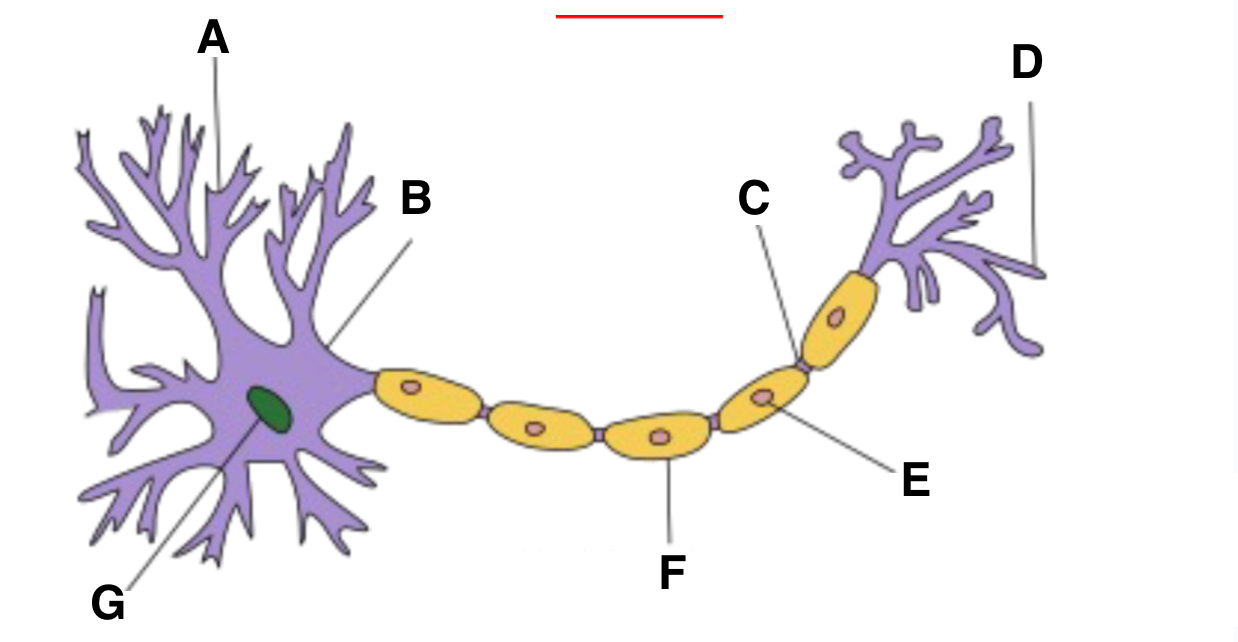
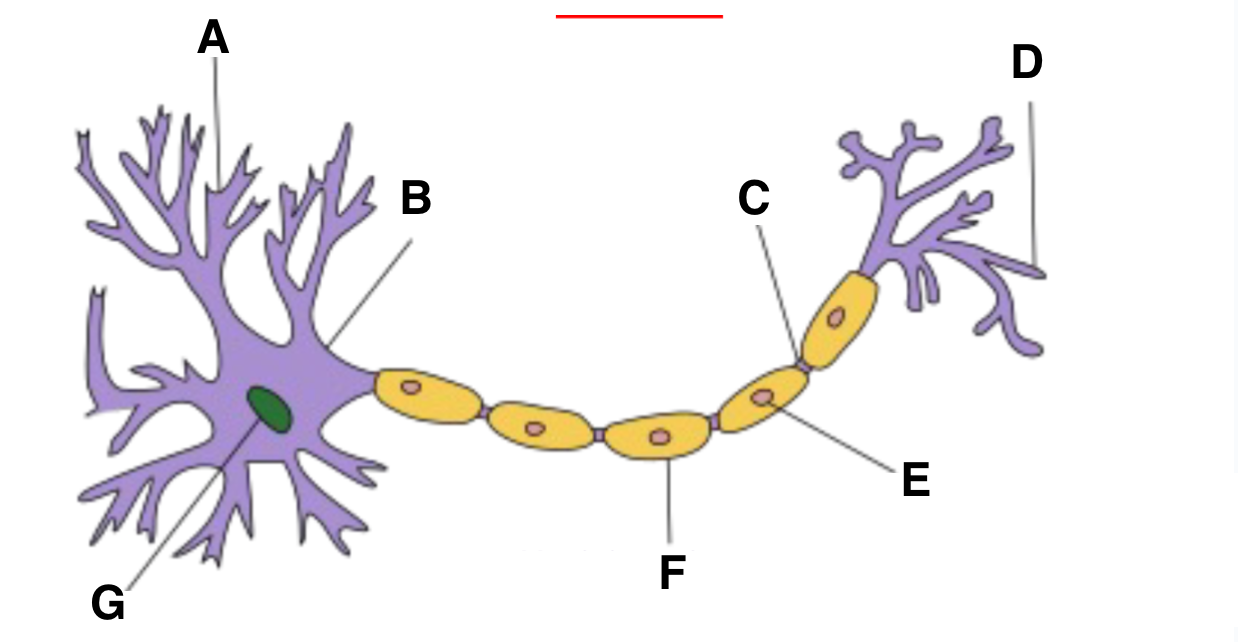
Dendrite
A?
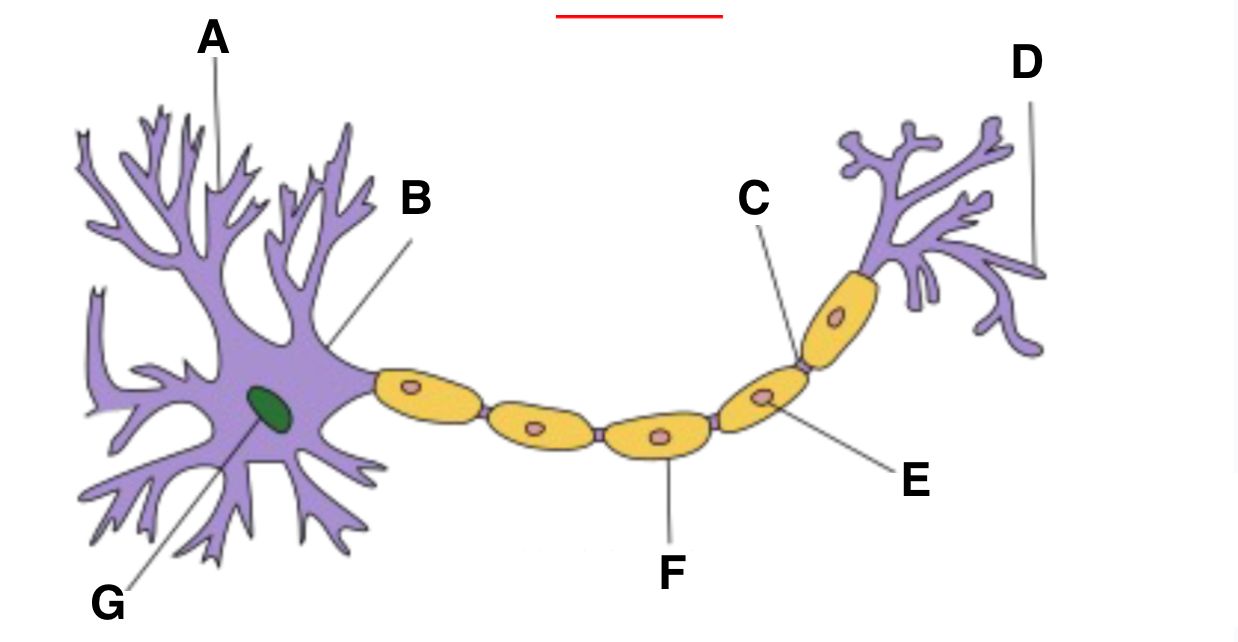
Axon hillock
B?
axon hillock
part of neuron where action potentials are initiated, integrates signals received from the dendrites before transmitting down axon
graded potentials (IPSP and EPSP)
excitatory (depolarizing, making the cell more positive) or inhibitory (hyperpolarizing, making the cell more negative), Influence whether an action potential will be triggered by summing together
node of ranvier
C?
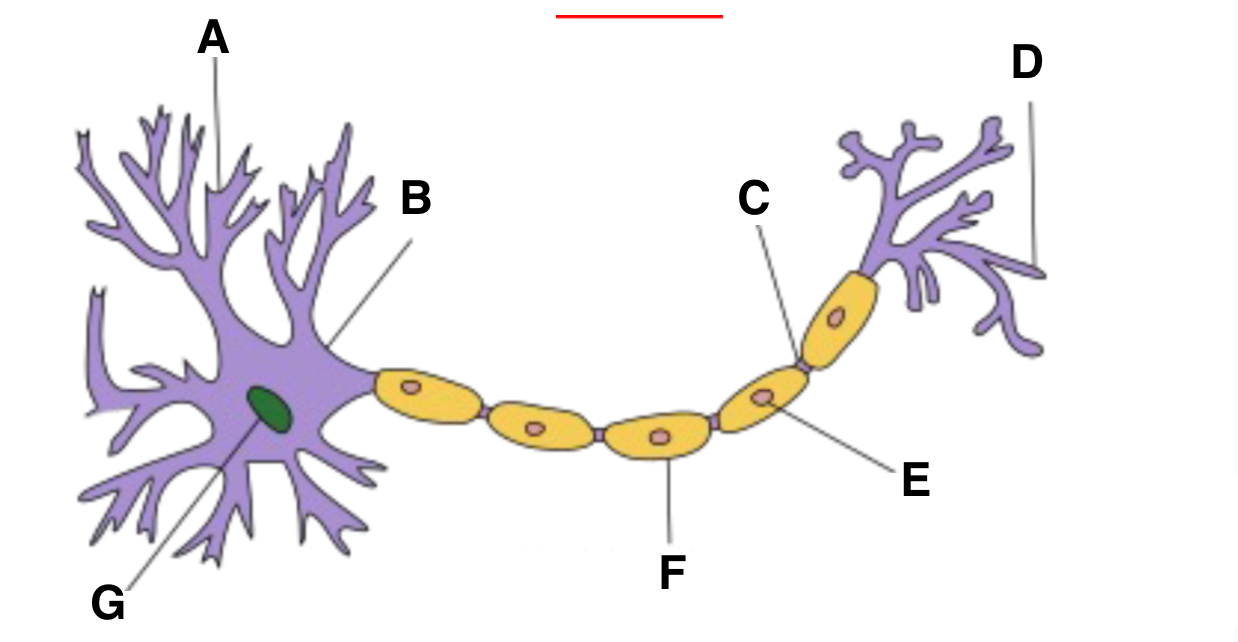
Axon terminal
D?
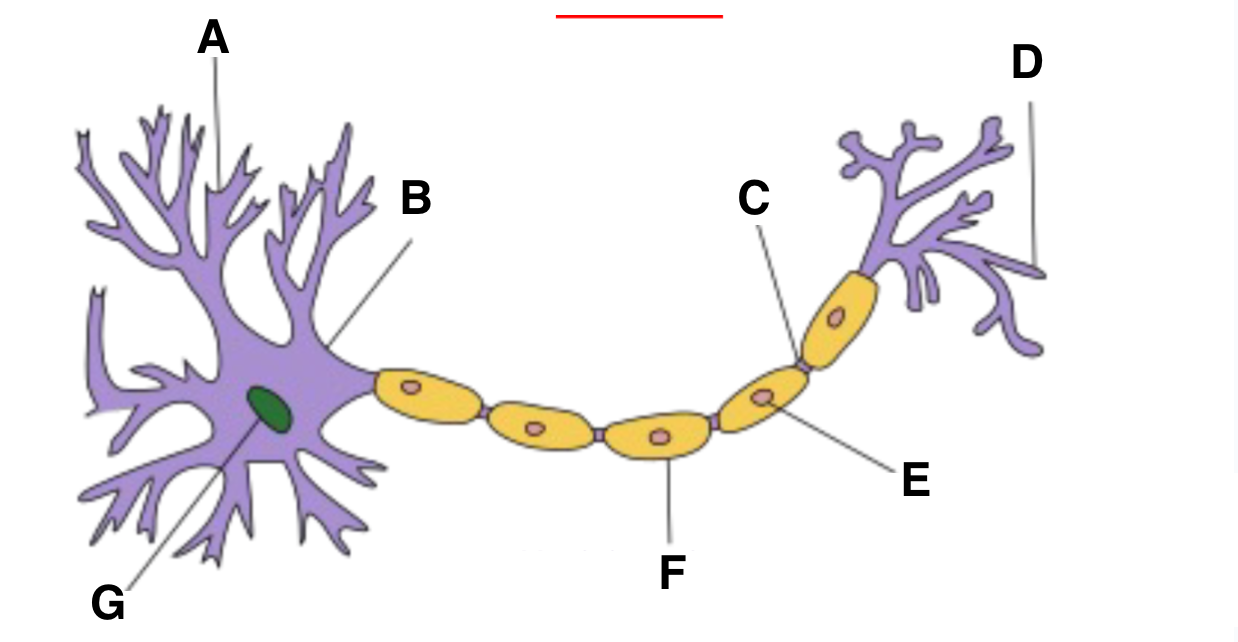
schwann cell
E?
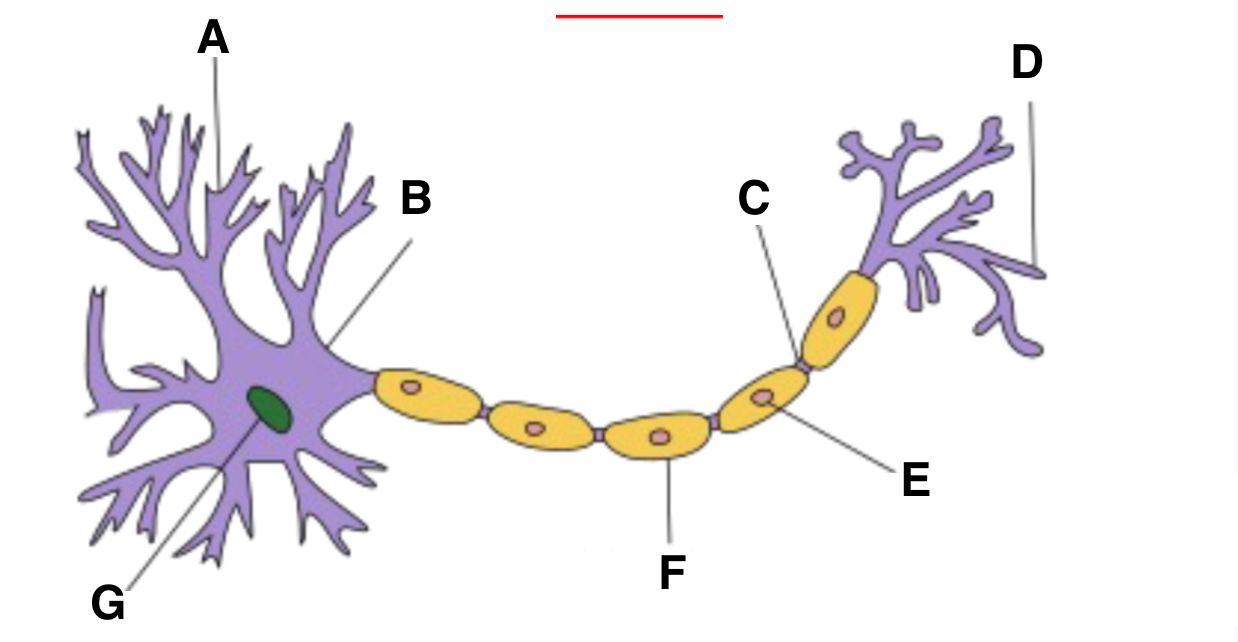
myelin sheath
F?
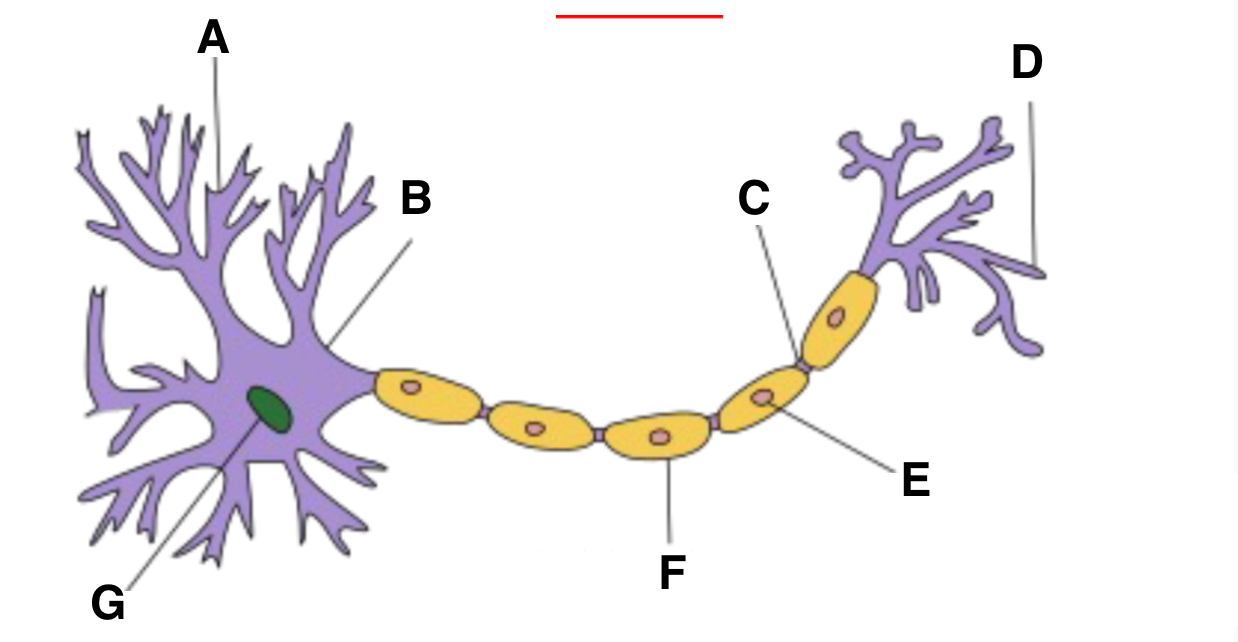
nucleas (within soma)
G?
3 Na out, 2 K in
how does the Na-K pump maintain a neurons resting membrane potential
action potential
ALL or NONE depolarization and repolarization of neuronal membrane that carries an electrical signal along the axon
potential sum (EPSP>IPSP) reaches threshold
how is an action potential generated?
Ca, K, and Na
Important electrolytes involved in action potential generation and transmission
during depolarization, initiates action potential
when is there an INFLUX (entry) of Na during AP generation
after the peak, returns to resting potential
when is the an EFFLUX (exit) of K during AP generation
Synapse
interface/structure permitting a neuron to pass a chemical or electrical signal from one neuron to the next
synaptic cleft (chemical)
MOST COMMON SYNAPSE, small gap between the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons where neurotransmitters are released and received
gap juction (electrical)
a specialized connection that allows direct electrical communication between cells, facilitating rapid signal transmission
Ca
electrolytle required for stored neurotransmitters to be RELEASED from AXON TERMINAL into a synapse
presynaptic axon terminal
where are neurotransmittors released from?
frequency (number of APs)
What property of an action potential CHANGES in response to stimulus? (ie. amplitude or frequency? )
increases frequency
How would a high-intensity stimulus impact an action potential?
Refractory period
What property of voltage-gated ion channels allows for the unidirectional transmission of an electrical impulse down an axon?
EPSP (excitatory post-synaptic potential)
promotes neuron firing, causes depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane by allowing positively charged ions (such as Na⁺ and Ca²⁺) to enter the cell
IPSP (inhibitory post-synaptic potential)
inhibit neuron firing, causes hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane by allowing either positive ions (K⁺) to leave or negative ions (Cl⁻) to enter the cell
myelinatiom
significantly INCREASES speed of signal transmission down an axon by insulating the axon membrane and enabling a process called saltatory conduction
Nodes of Ranvier
gaps in the myelin sheath that facilitate rapid signal conduction along the axon by allowing ions to flow in and out of the neuron.
Saltatory conduction
action potentials jumping between the gaps (Nodes of Ranvier) in myelinated axons, INCREASES speed of signal transmission along the neuron.
Dopamine
neurotransmitter for MOVEMENT and REWARD
Glutamate
Main EXCITATORY neurotransmitter in the brain
Serotonin
neurotransmitter for MOOD
Acetylcholine
neurotransmittor in NEUROMUSCULAR junction and Autonomic nervous system, particularly parasympathetic
GABA
Main INHIBITORY neurotransmitter in the brain
Norepinephrine
neurotransmitter for AROUSAL and ALERTNESS, Sympathetic nervous system
Melatonin
neurotransmitter for CIRCADIAN RHYTHM
Oxytocin
neurrotransmitter involved in Childbirth, Breastfeeding, and Bonding
Absolute refractory period
Na+ channels are inactivated, subsequent AP is NOT possible
Relative refractory period
residual Na+ channel inactivation makes it harder to generate AP, but possible
thalamus
part of the brain that serves as a relay station for sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex.
corpus callosum
a band of nerve fibers that CONNECTS the LEFT AND RIGHT cerebral hemispheres, facilitating interhemispheric communication.
central sulcus
a prominent groove that SEPARATES FRONTAL lobe from PARIETAL lobe
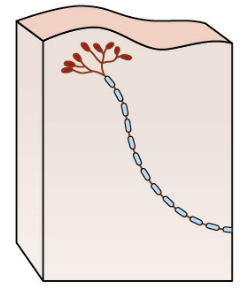
1st order neuron (SENSORY tract)
FIRST SENSORY NEURON to get the SIGNAL that something happened
2nd order neuron
SENSORY neuron that goes up to the THALAMUS
3rd order neuron
SENSORY neuron that goes from THALAMUS TO CORTEX
upper motor neuron
cells in the CNS where MOTOR impulse ORIGINATES
lower motor neuron
cells in the PNS synapsing on the MUSCLE itself
decussation
the crossing of nerve fibers from one side (ipsilateral) of the brain or spinal cord to the other (contralateral)
ipsilateral
referring to the SAME SIDE of the body as another structure or location
contralateral
referring to the OPPOSITE SIDE of the body compared to another structure or location
acetylcholine
neurotransmitter primarily used in the PARASYMPATHETIC nervous system (rest and digest)
norepinephrine
neurotransmitter primarily used in the SYMAPATHETIC nervous system (fight or flight)
nucleus/ganglion
clusters of neuronal soma (cell bodies) in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and central nervous system (CNS)
Adult nerve cells do not divide
why is recovery for a nervous system injury/trauma often difficult or incomplete?
neural plasticity
capacity of the nervous system to change and adapt in response to experience, learning, or injury
long term potentiation (LTP)
patterns of recent synaptic activity that produce lasting INCREASE in signal transmission (SYNAPTIC STRENGTH)
synaptogenesis
the process of forming new synapses between neurons, critical for neural development and plasticity
long term potentiation (LTP)
major mechanism of learning and memory by strengthening the connections between neurons
increased excitatory post-synaptic receptor density
What is the result of long term potentiation (LTP)?
long term potentiation (LTP) and synaptogenesis
What are 2 main cellular mechanisms underlying neural plasticity?
increased post-synaptic receptor density (# of receptors)
How does long-term potentiation (LTP) increase synaptic efficacy (effectiveness)?
use-dependent plasticity/ motor learning
A professional violinist has increased grey matter density in the sensorimotor cortex controlling their left hand. This is an example of _________.
motor learning
increases the number of synapses in motor cortex through practice and experience
gray matter
matter composed primarily of neuronal cell bodies; it plays a key role in processing and transmitting information.
white matter
matter with axons with glial sheath (myelin) that facilitate communication between different brain regions.
transmitter release
proportional to the FREQUENCY of action potentials
A-delta (type III)
nerve fibers that sense FAST, SHARP PAIN and COLD
C-fiber (type IV)
nerve fibers that sense SLOW, DULL PAN, and WARM
mechanoreceptors
specialized structures at terminals of sensory nerves that detect stimuli such as touch, pressure, and vibration.
merkels disks
superficial nonencapsulated mechanoreceptors
meissner corpuscle
superficial ENCAPSULATED mechanoreceptors in fingertips, palm, feet and lips
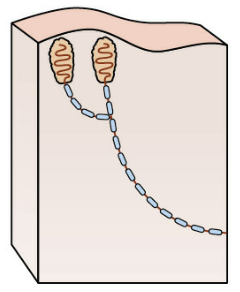
ruffini endings
deep mechanoreceptos in skin and joint ligaments
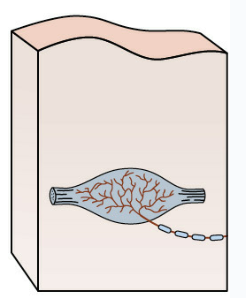
pacinian corpuscules
subcutaneous nechanoreceptors in connective tissue of skin, periosteum, and joint capsule
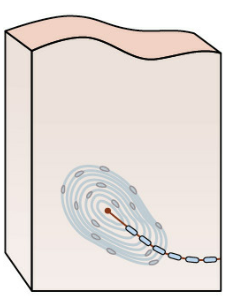
meissner and pacician corpuscles (rapidly adapting)
mechanoreceptors with QUICK response, detect MOTION and VIBRATION
merkels disks and ruffini endings (slowly adapting)
mechanoreceptors with SUSTAINED response, detect STEADY presence and INTENCITY of stimulus
merkel disk
mechanoreceptor that senses object FORM and TEXTURE
meissner corpuscle
mechanoreceptor that senses OBJECT MOTION
ruffini ending
mechanoreceptor that senses joint conformation, posture, and stereognosis
pacinian corpuscle
mechanoreceptor that senses OBJECT VIBRATION
fingertips
which body part has the highest TACTILE SENSITIVITY
proprioception
the body's ability to SENSE position, movement, and equilibrium through sensory feedback from MUSCLES, TENDONS and JOINTS
periodontal ligament receptors
after tooth extraction or tooth loss, information on the load exerted on a tooth is no longer available due to the abscnce of which receptor?
nociceptor
a type of sensory receptor responsible for detecting PAIN or harmful stimuli in the body
myelinated a-delta and unmyelinated C fibers
nerve fibers that transmit BURING PAIN caused by HIGH TEMP
motor cortex
which structure is prrimarily involved in generating fine motor contrrol of fingers?
false
T/F tongue or jaw tremor found in parkinsons is a dysfunction affecting the direct pathway
DCML and ALS
two main ascending SOMATOSENSORY pathways
dorsal column medial lemniscal system (DCML)
responsible for discriminitive/FINE touch, conscious proprioception, and steriogenesis (identify object by touch alone)
anterolateral system (ALS)
A major ascending somatosensory pathway responsible for transmitting PAIN, temperature, and CRUDE touch sensations to the brain.
medial lemniscus (lower medulla)
where is the decussation of the DCML pathway?
spinal cord
where is the decussation of the ALS pathway?
spinal cord (dorsal root ganglion)
location of 1st order neuron in DCML pathway
spinal cord
location of 1st order neuron in ALS pathway
medulla
location of 2nd order neuron in DCML pathway
spinal cord
location of 2nd order neuron in ALS pathway
thalamus
location of 3rd order neuron in DCML pathway
thalamus
location of 3rd order neuron in ALS pathway
ipsilateral (same) (DCML has not decussated yet)
An injury at the level of the SPINAL CORD would result in LOSS of FINE TOUCH and PROPRIOCEPTION (DCML) on the _______ side as the injury
contralateral (opposite)
An injury at the level of the SPINAL CORD would result in LOSS of PAIN and TEMPERATURE sensation (ALS) on the _______ side as the injury
dental pulp and PDL
where are the sensory receptors for the teeth?
CN V (trigeminal)
Which nerve transmits oral sensation from teeth, tongue, and TMJ?