✅️⭐️8 - Pelvic Muscles & Joints I
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
sacroiliac joint
Which joint is associated with the following?
-Transmit the weight of the trunk to the pelvic limbs when standing
-Drive the force of the limbs to the trunk in progression
synovial; fibrous
The sacroiliac joint is created through the combination of a _____ joint with an adjacent region of extensive _____ union
synchondroses
The sacroiliac joint is a cartilaginous joint, labeled as cartilaginous _____
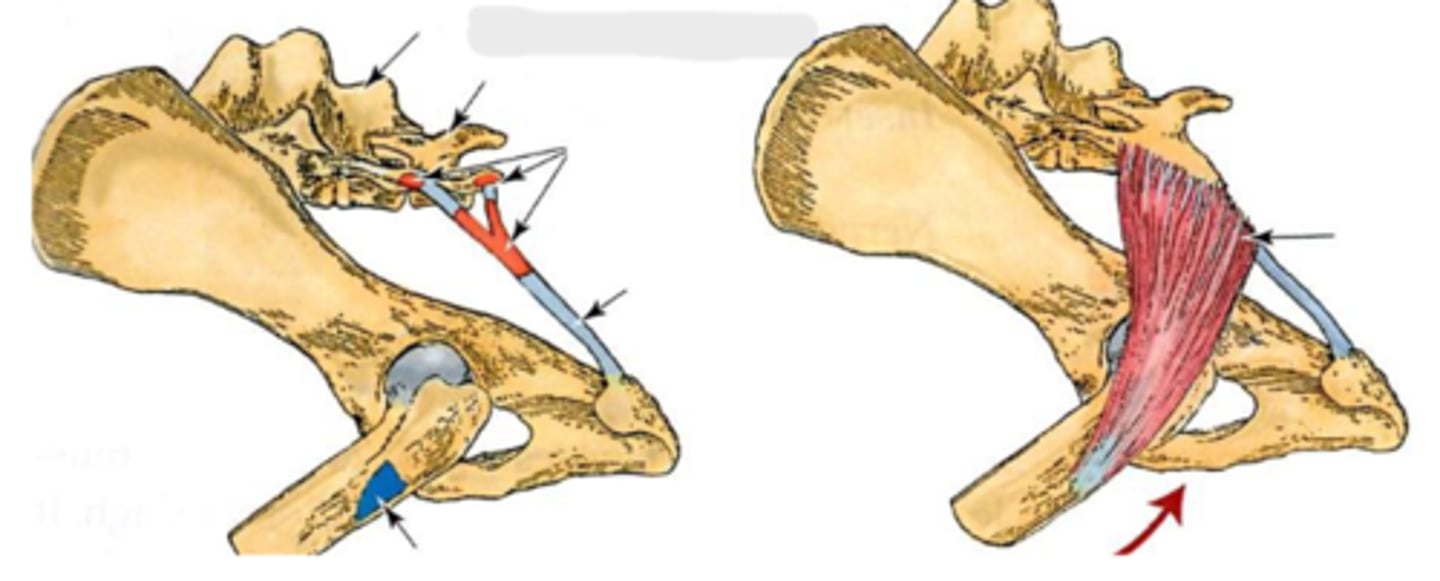
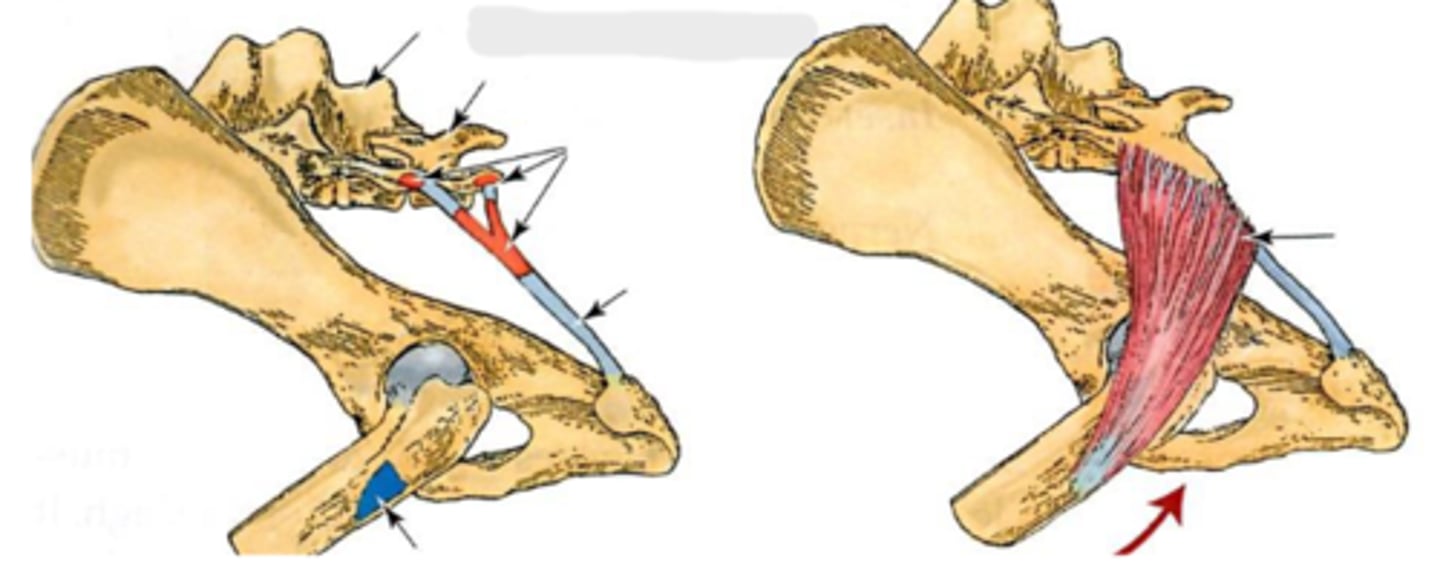
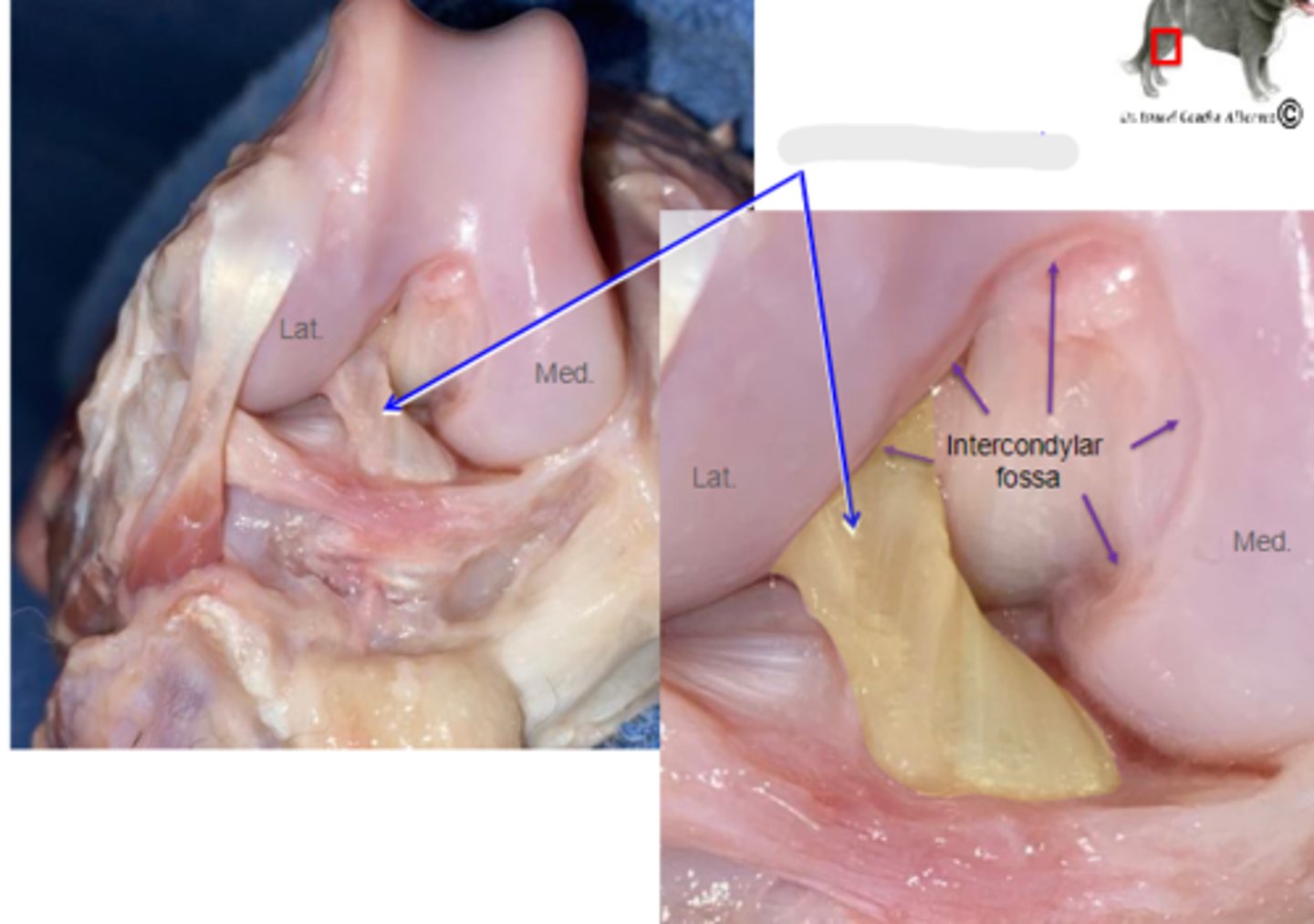
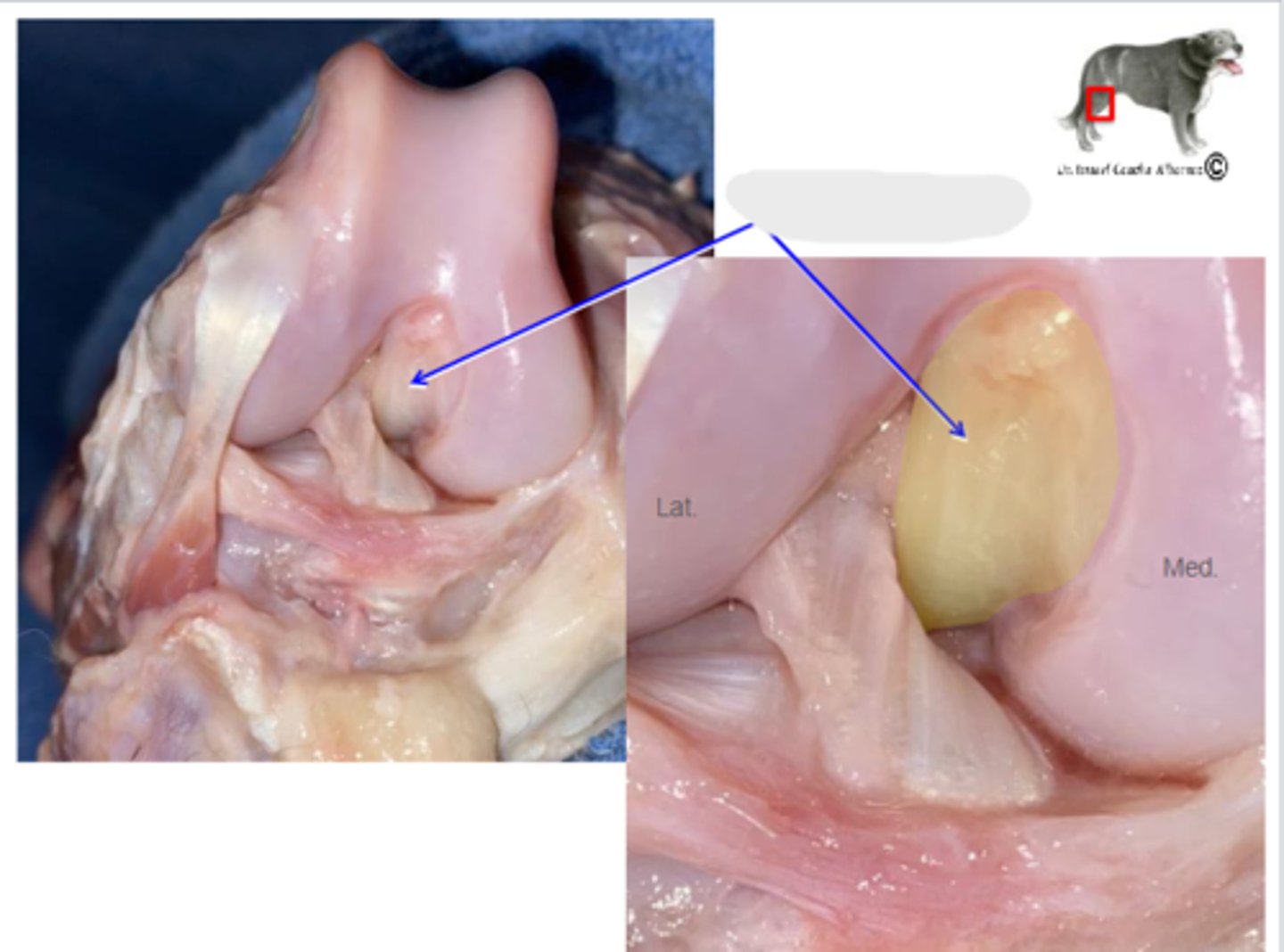
dorsal & ventral sacroiliac ligaments
What is the blue arrow pointing to?
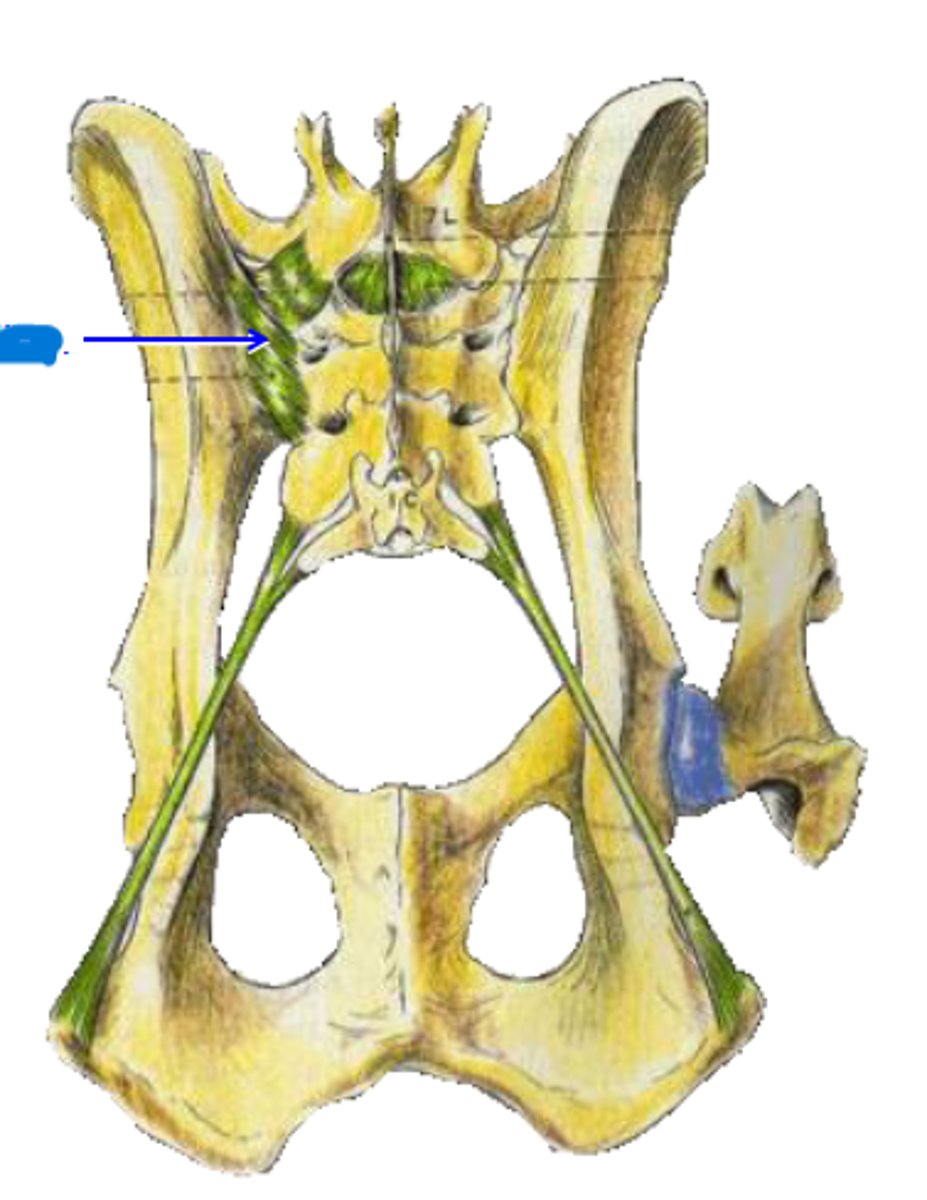
sacrotuberous ligaments
What are the blue arrows pointing to?
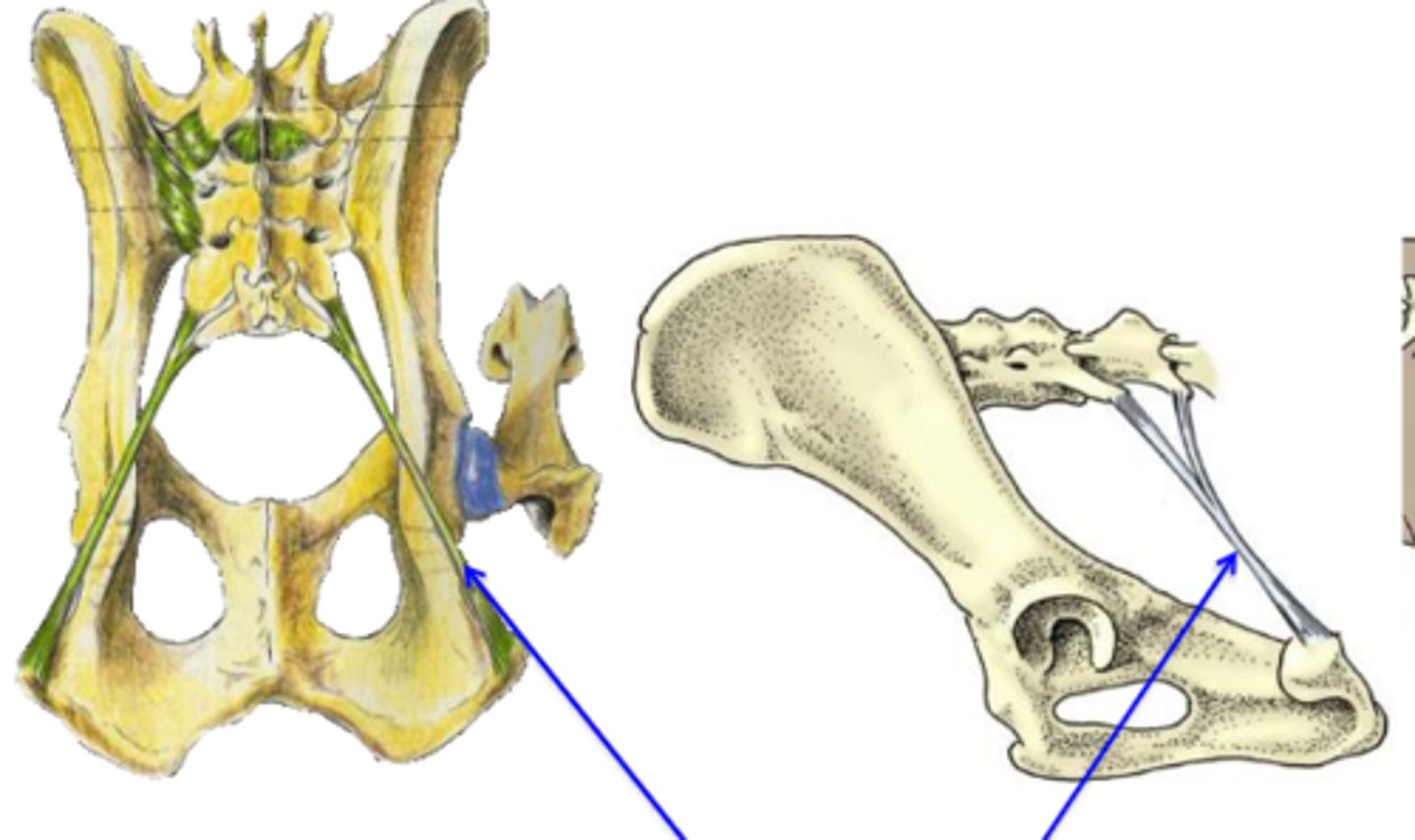
reviewed
Review
coxae (hip) joint
Spheroidal joint formed between the lunate
surface of the acetabulum and the head of
the femur
ligament of the head of femur
What is 1?
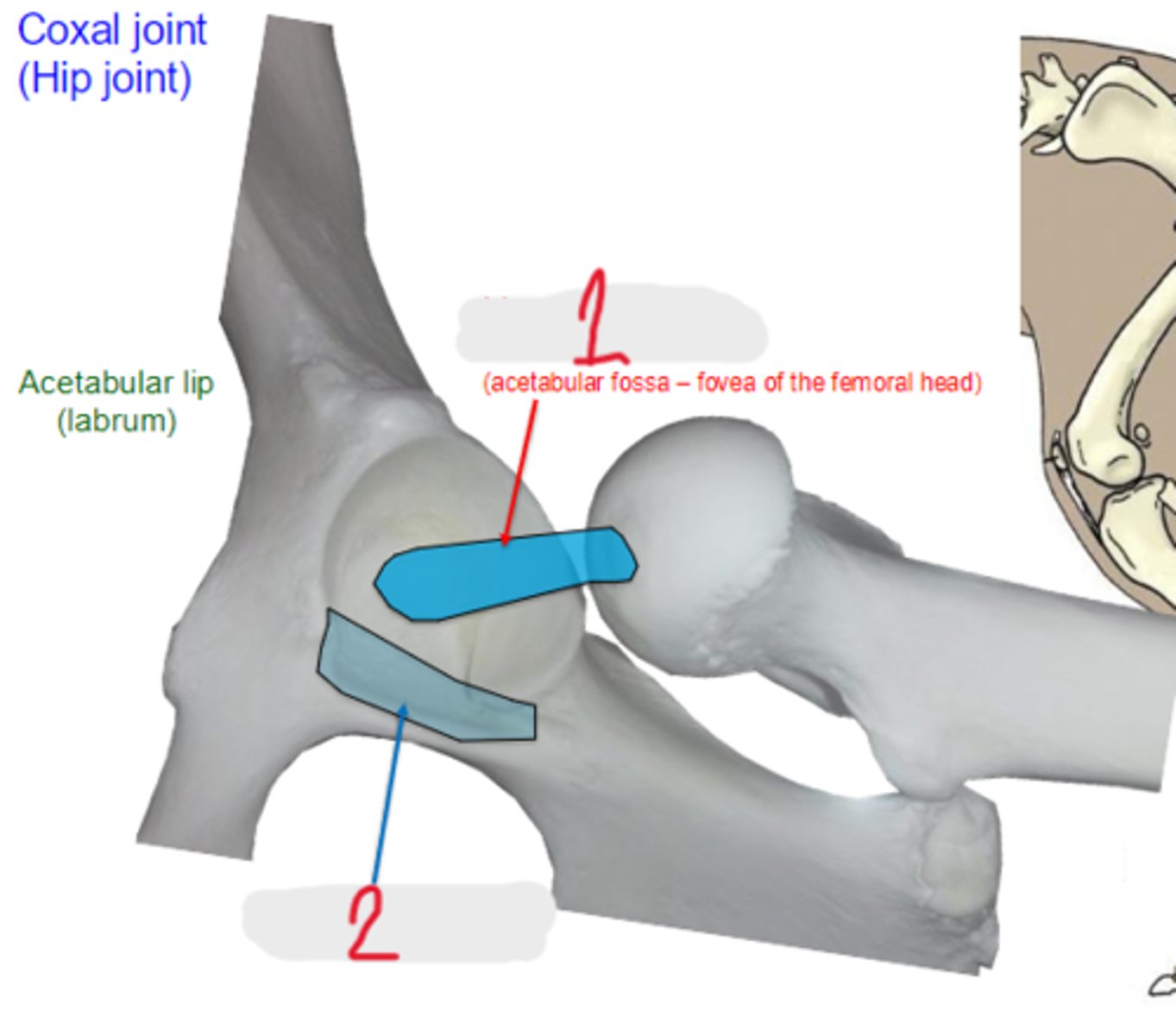
transverse acetabular ligament
What is 2?
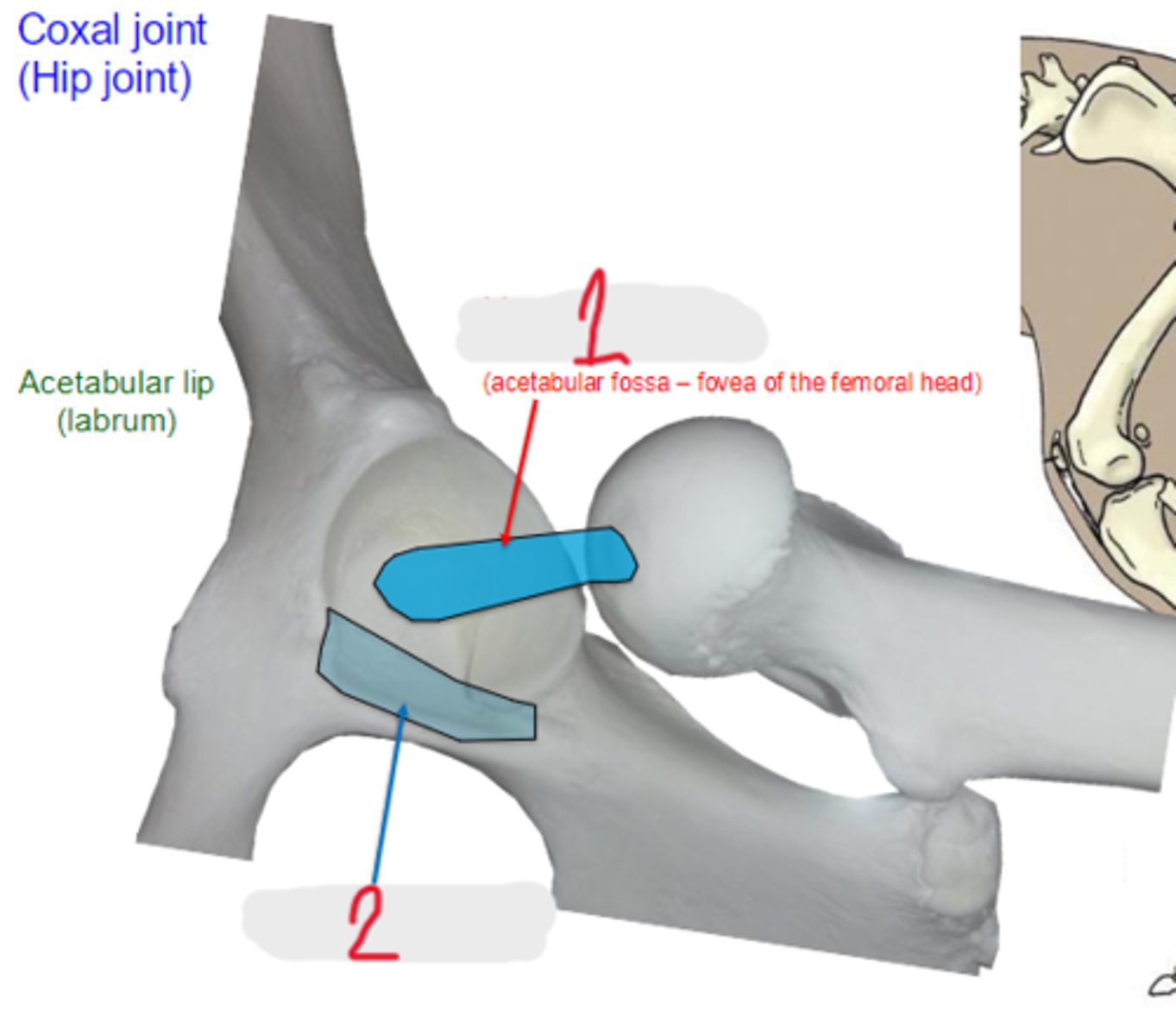
1. gluteal group
2. deep group
3. caudal group
4. medial group
What are the muscles groups that act primarily on the hip joint?
1. extensor group
2. flexor group
What are the muscle groups that act primarily on the stifle joint?
1. craniolateral group: flexor of tarsal joint & extensors of the digits
2. caudal group: extensors of tarsal joint & flexor of the digits
What are the muscle groups that act primarily on the tarsal and digital joints?
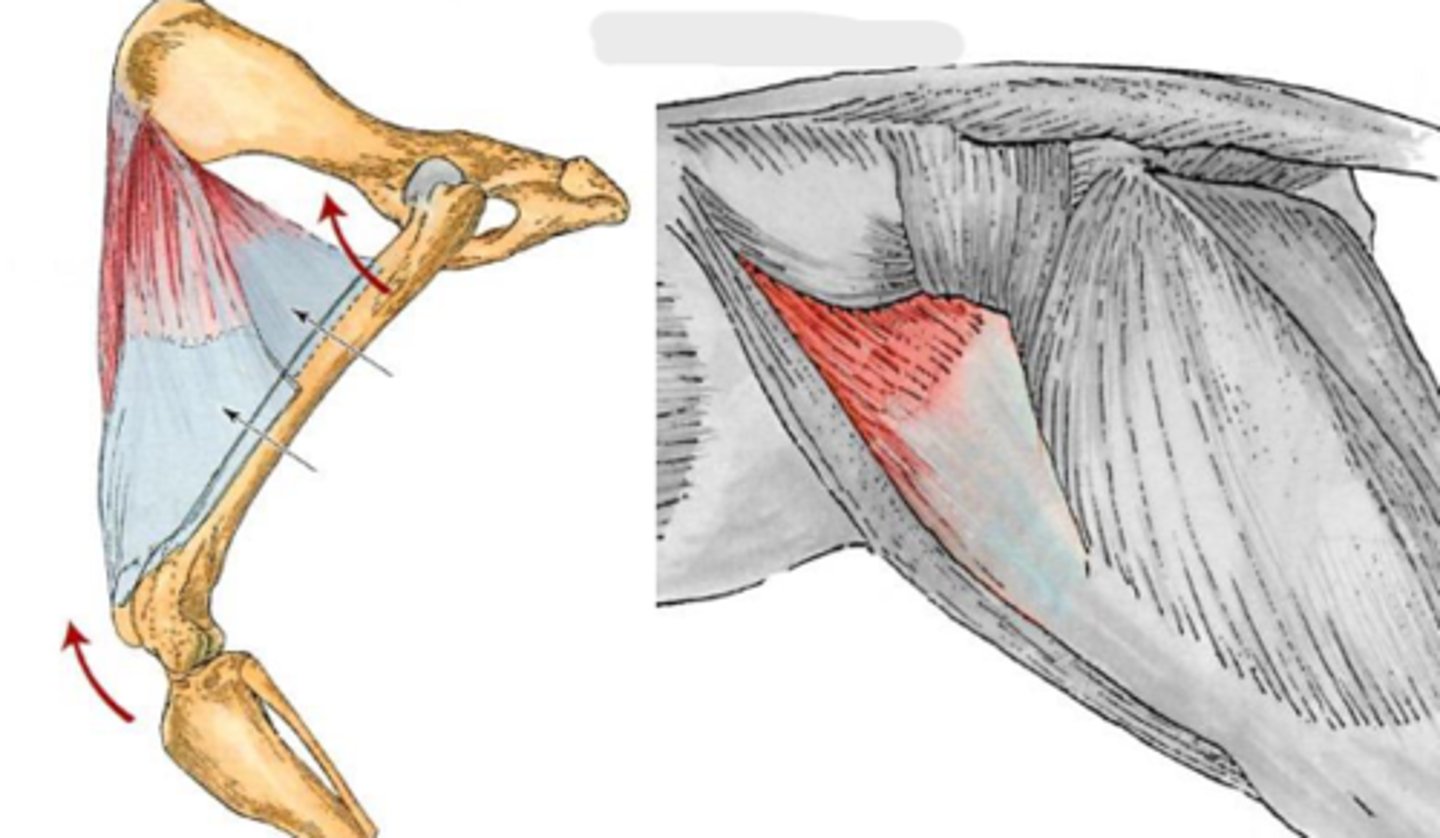
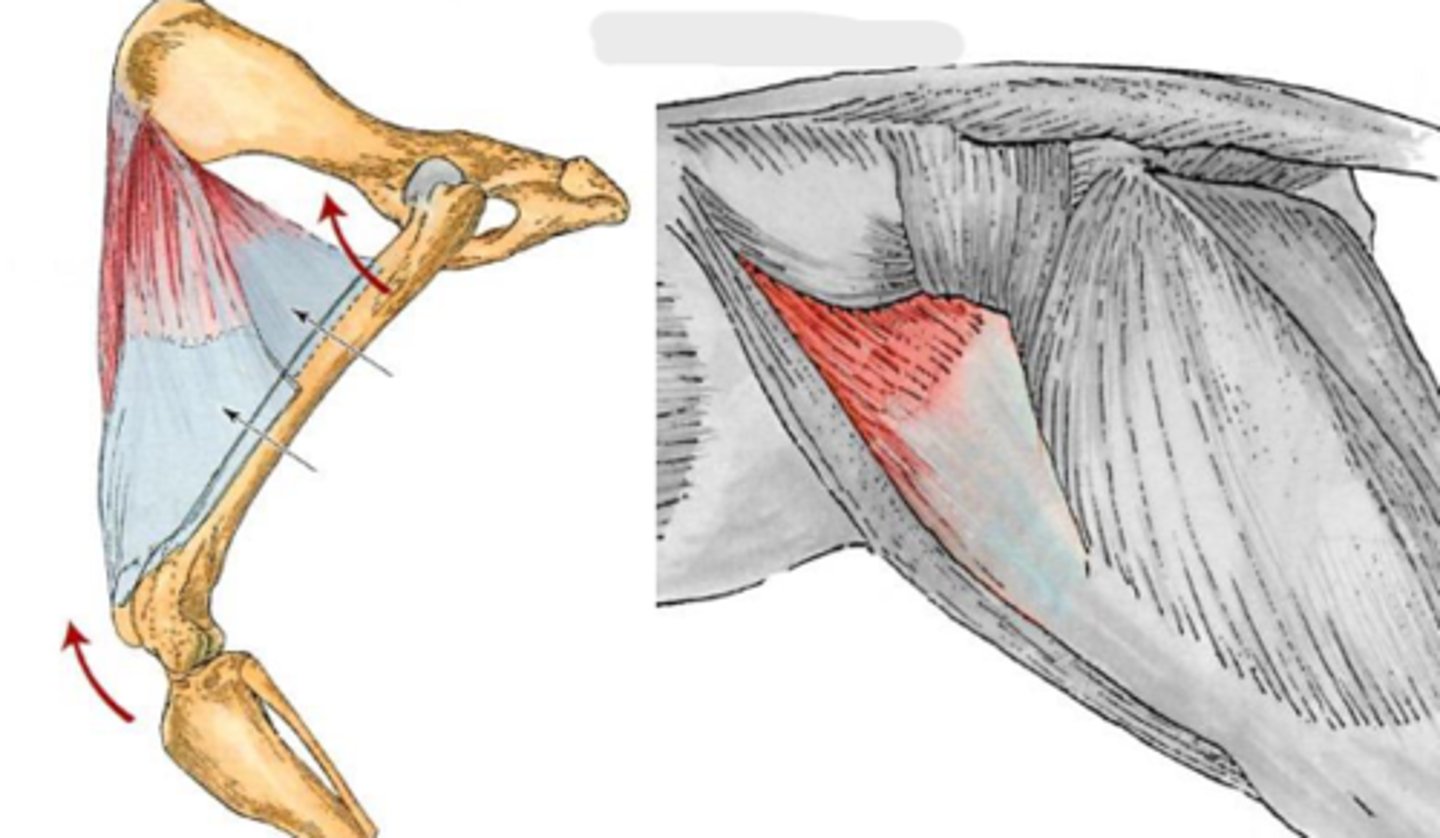
tensor fascia lata
What is this muscle, acting on the hip joint?
tuber coxae
Origin of the tensor fascia lata
fascia lata
Insertion of tensor fascia lata
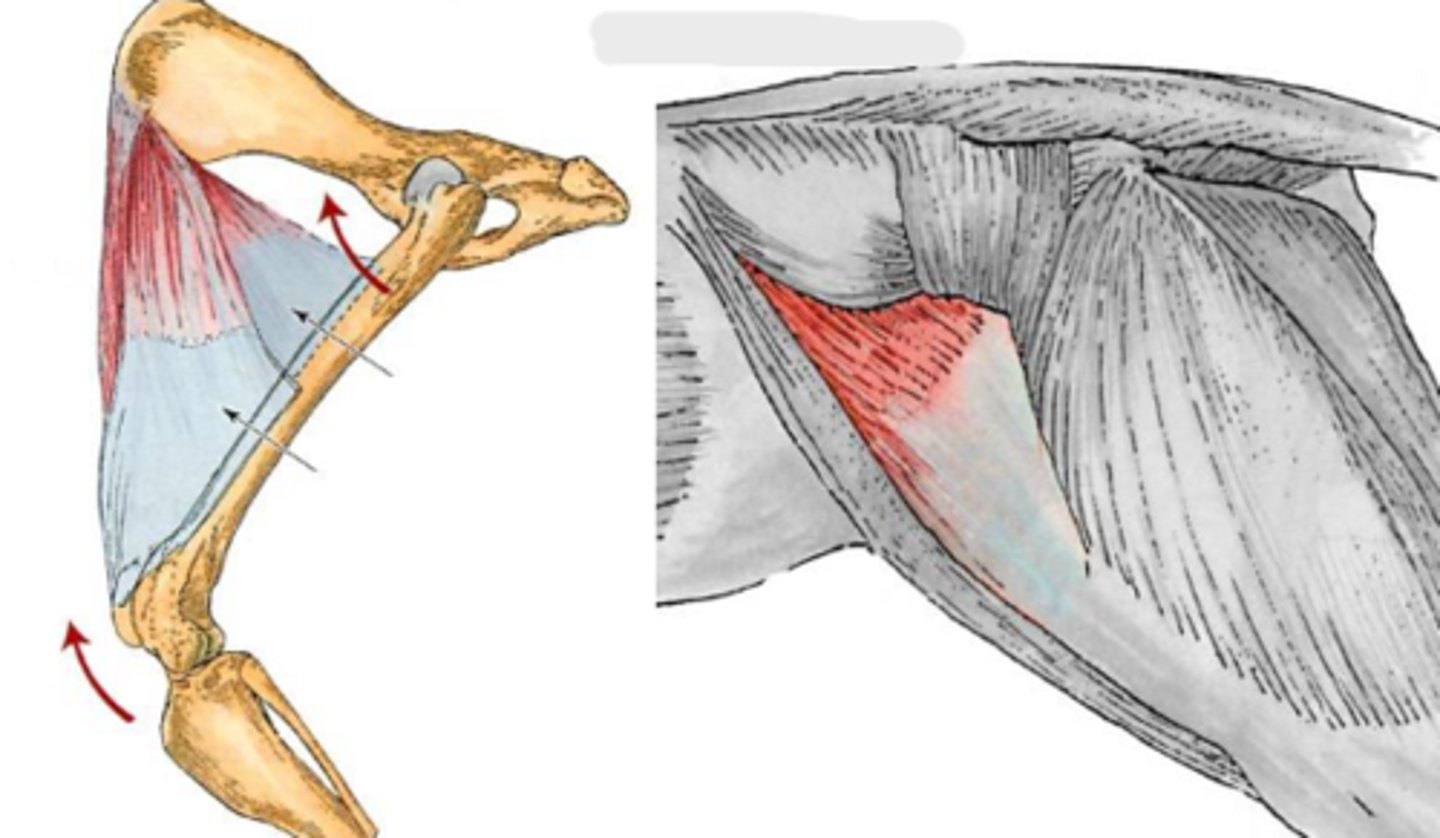
tense the fascia lata, flex the coxal joint and extend the genual joint
Action of tensor fascia lata
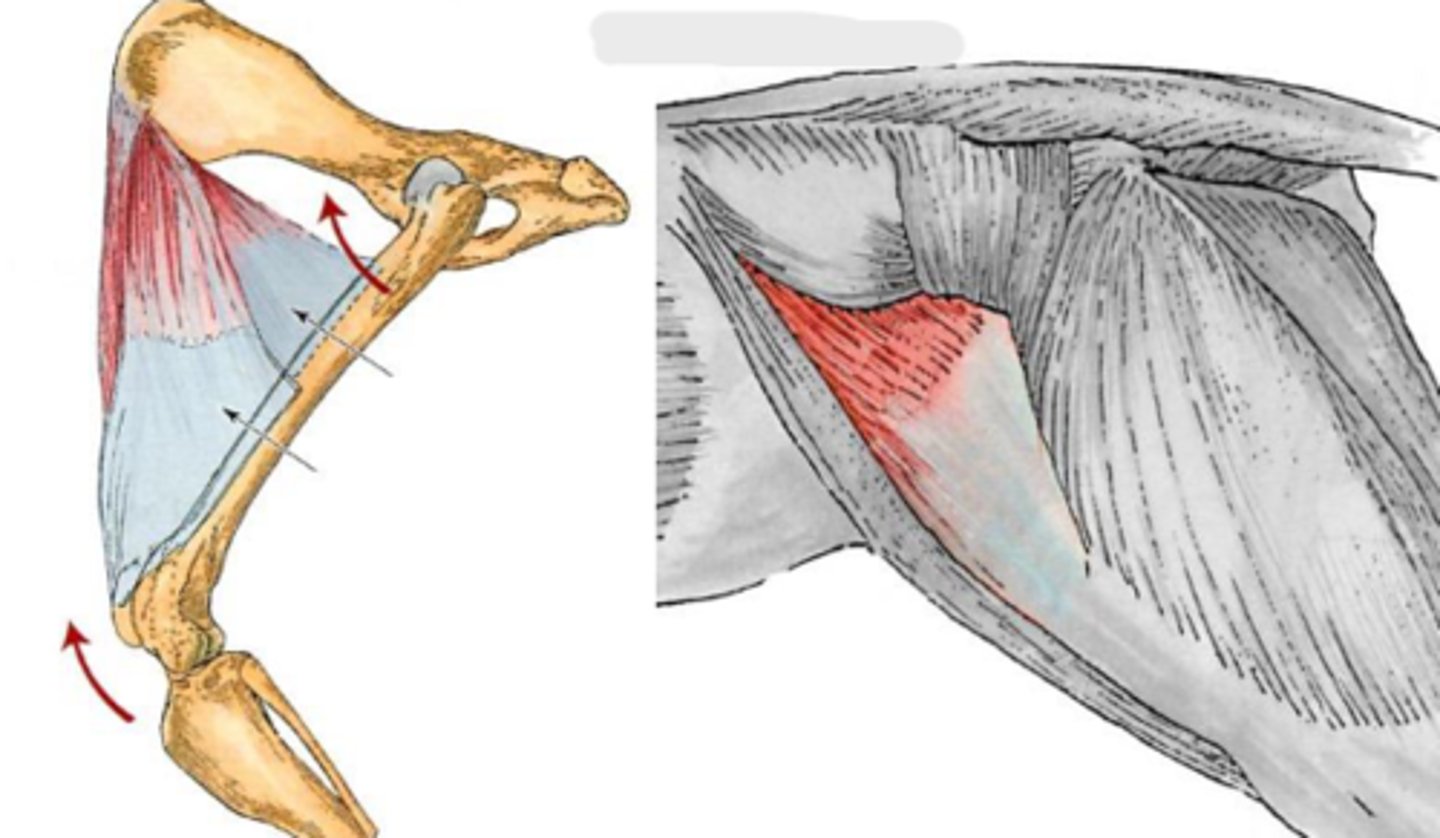
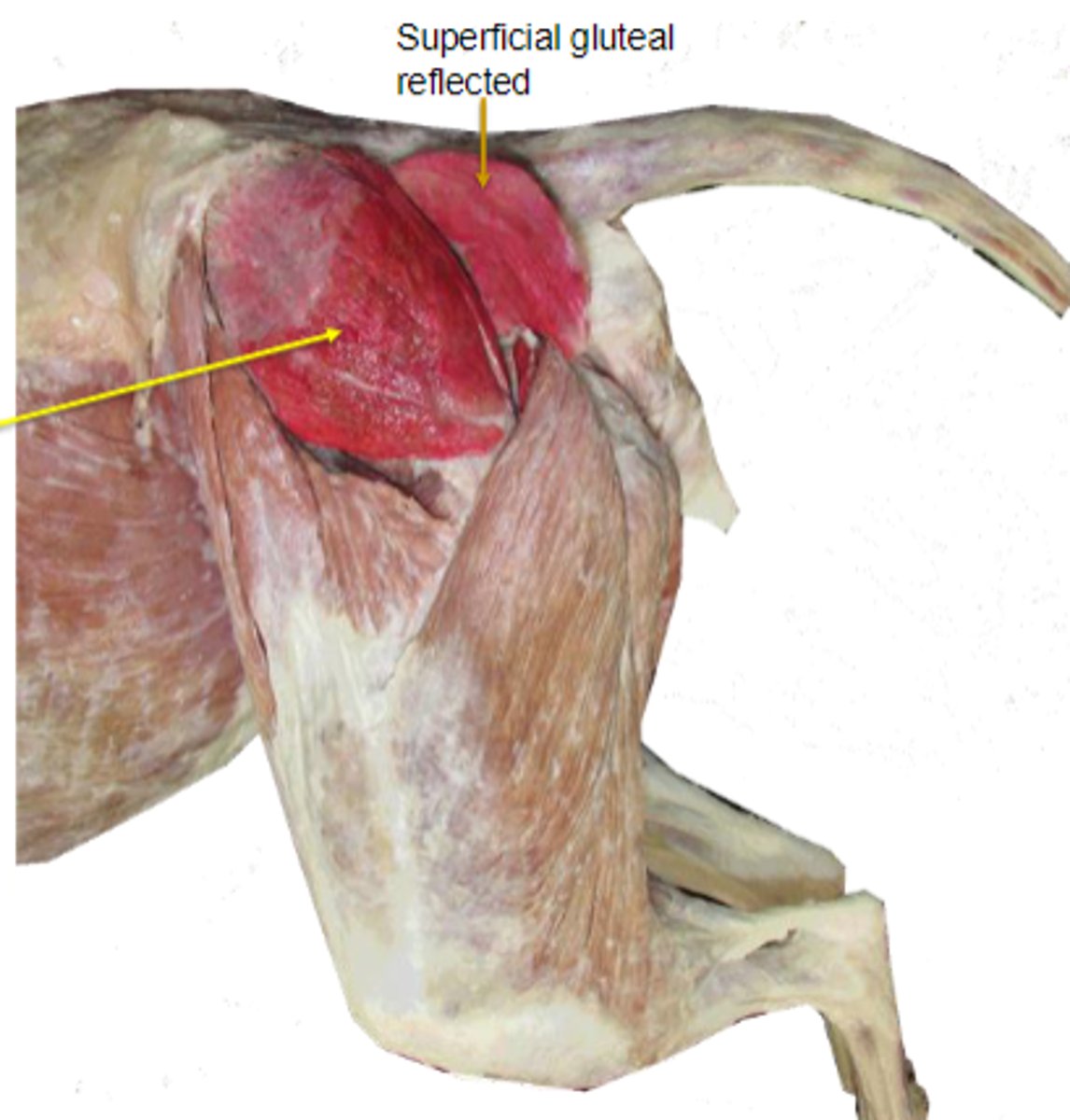
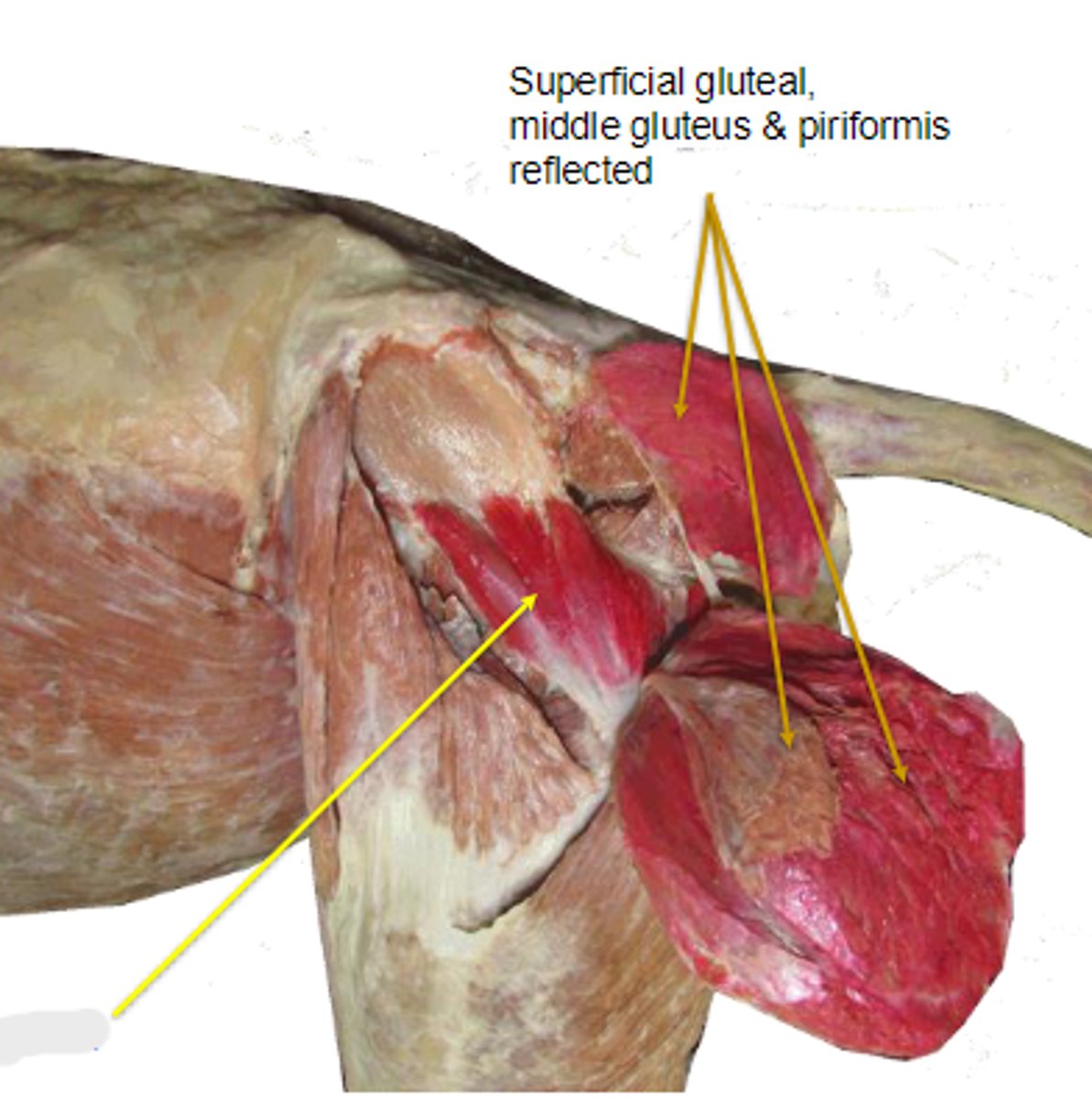
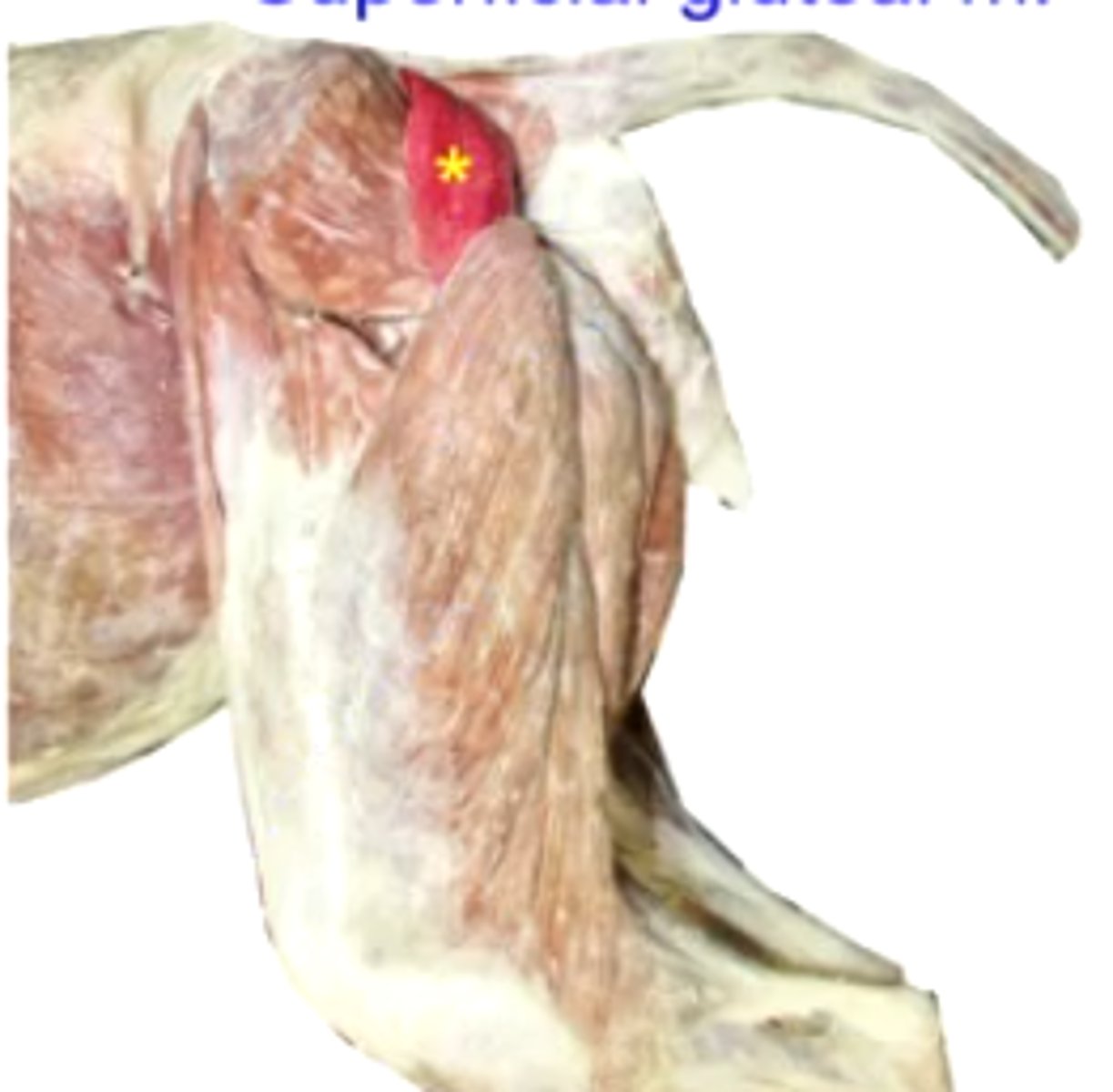
superficial gluteal
What muscle is this, acting on the hip joint?
sacrum & 1st caudal vertebra
Origin of superficial gluteal
third trochanter
Insertion of superficial gluteal
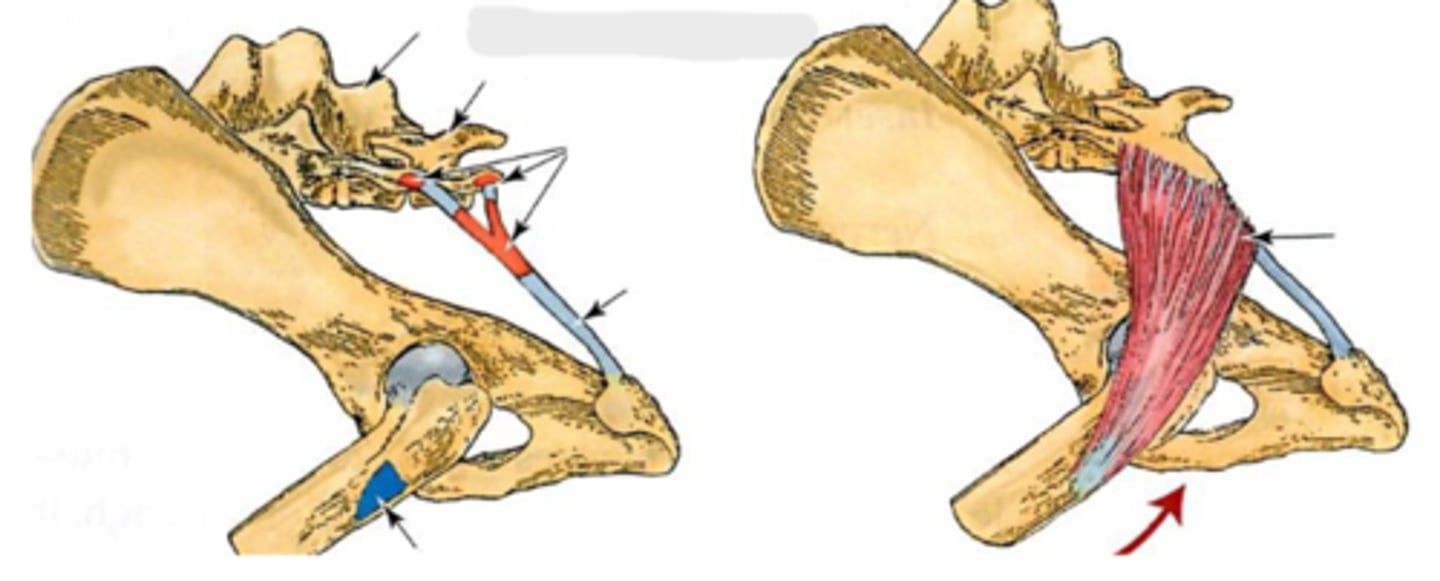
extend the coxal joint; abduct the
pelvic limb.
Action of superficial gluteal
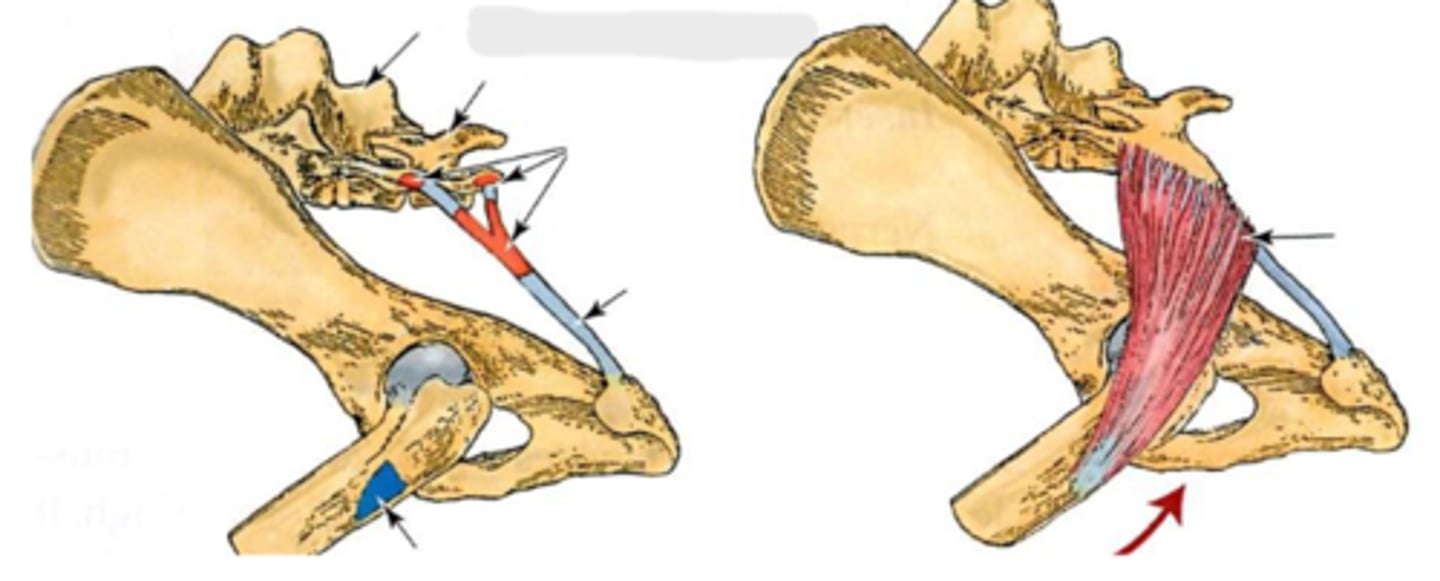
superficial gluteal
What muscle is shown?
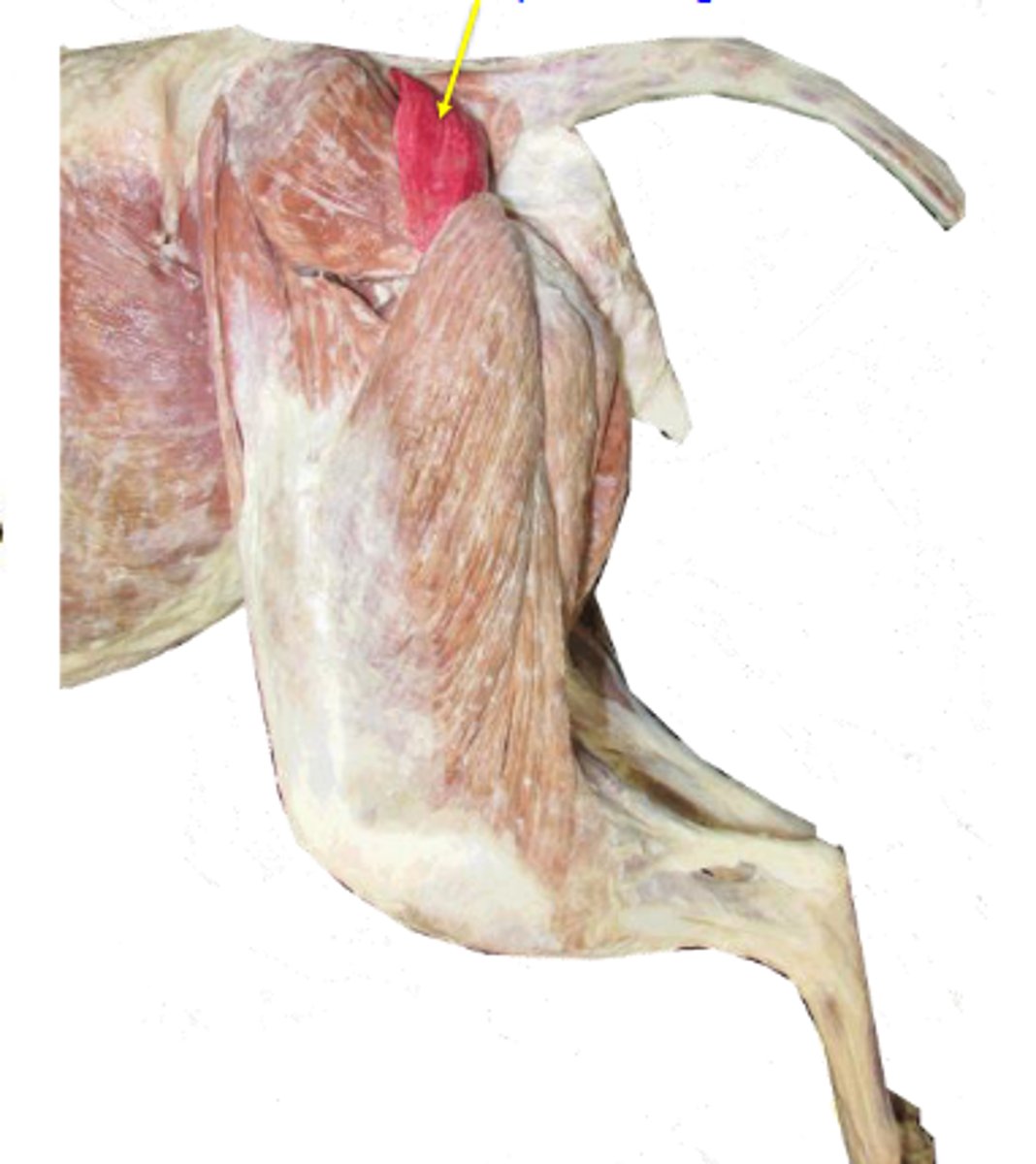
middle gluteal
What muscle is this, acting on the hip joint?
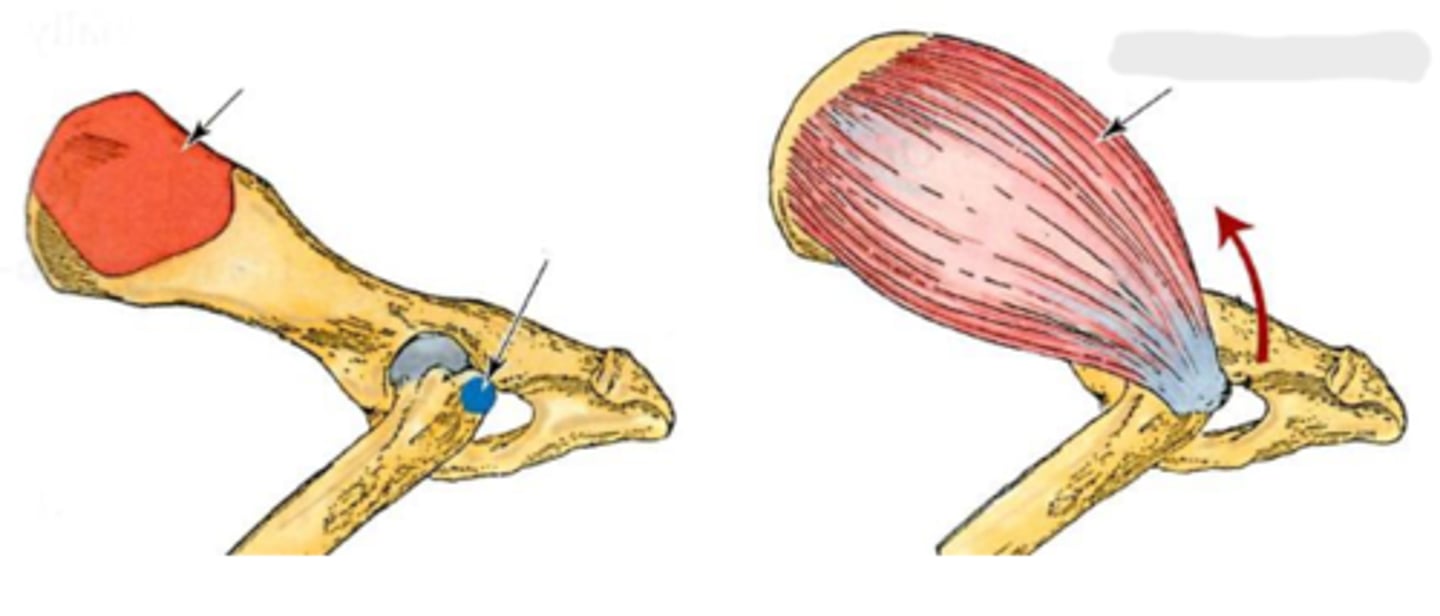
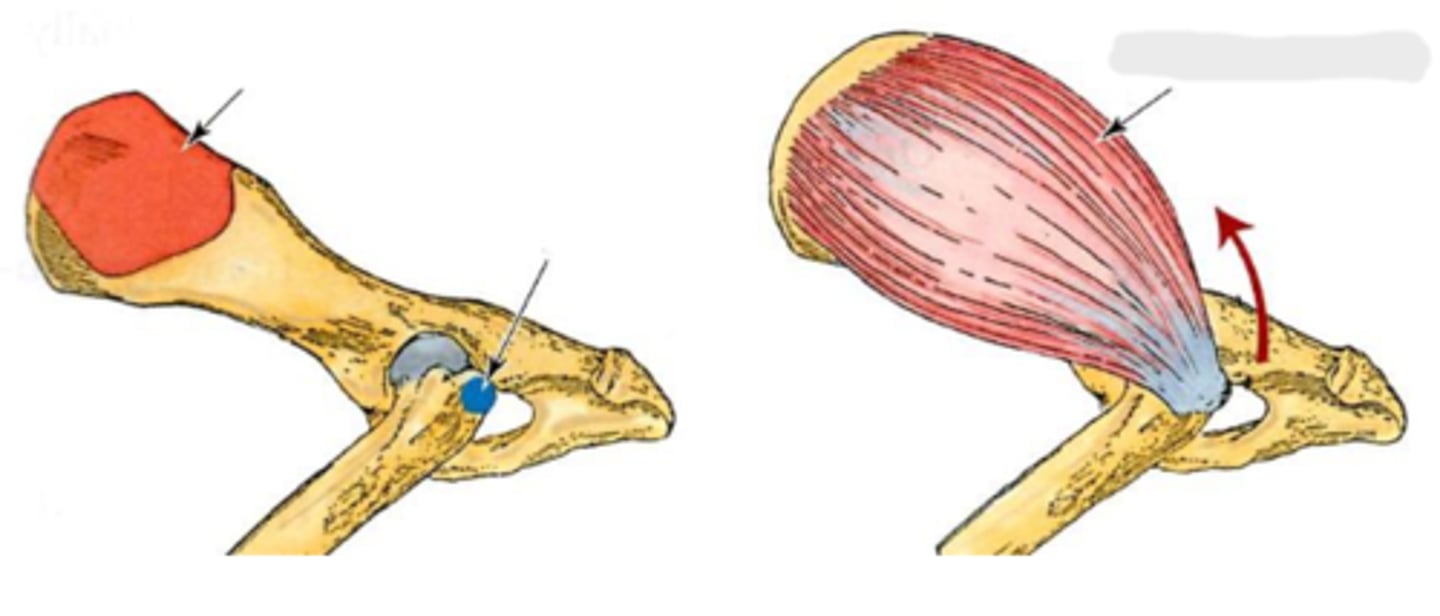
gluteal surface of the ilium
Origin of middle gluteal
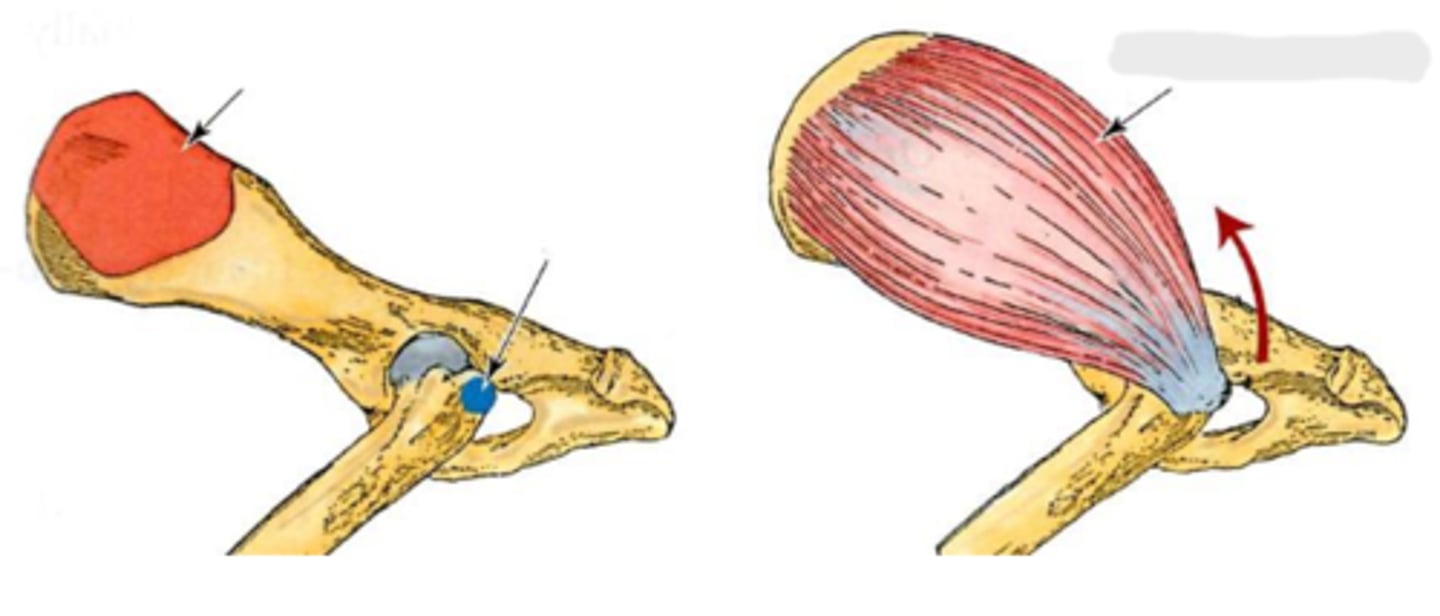
greater trochanter
Insertion of middle gluteal
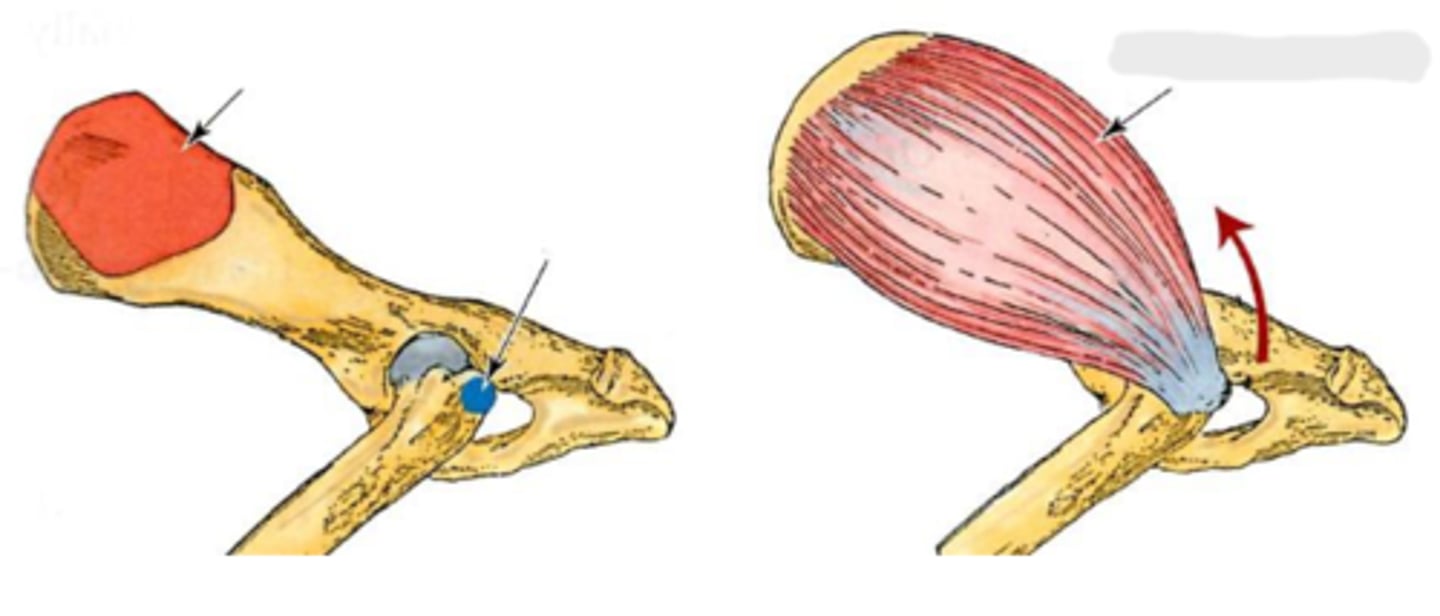
extend the coxal joint; abduct and rotate the pelvic limb medially
Action of middle gluteal
middle gluteal
What muscle is shown?
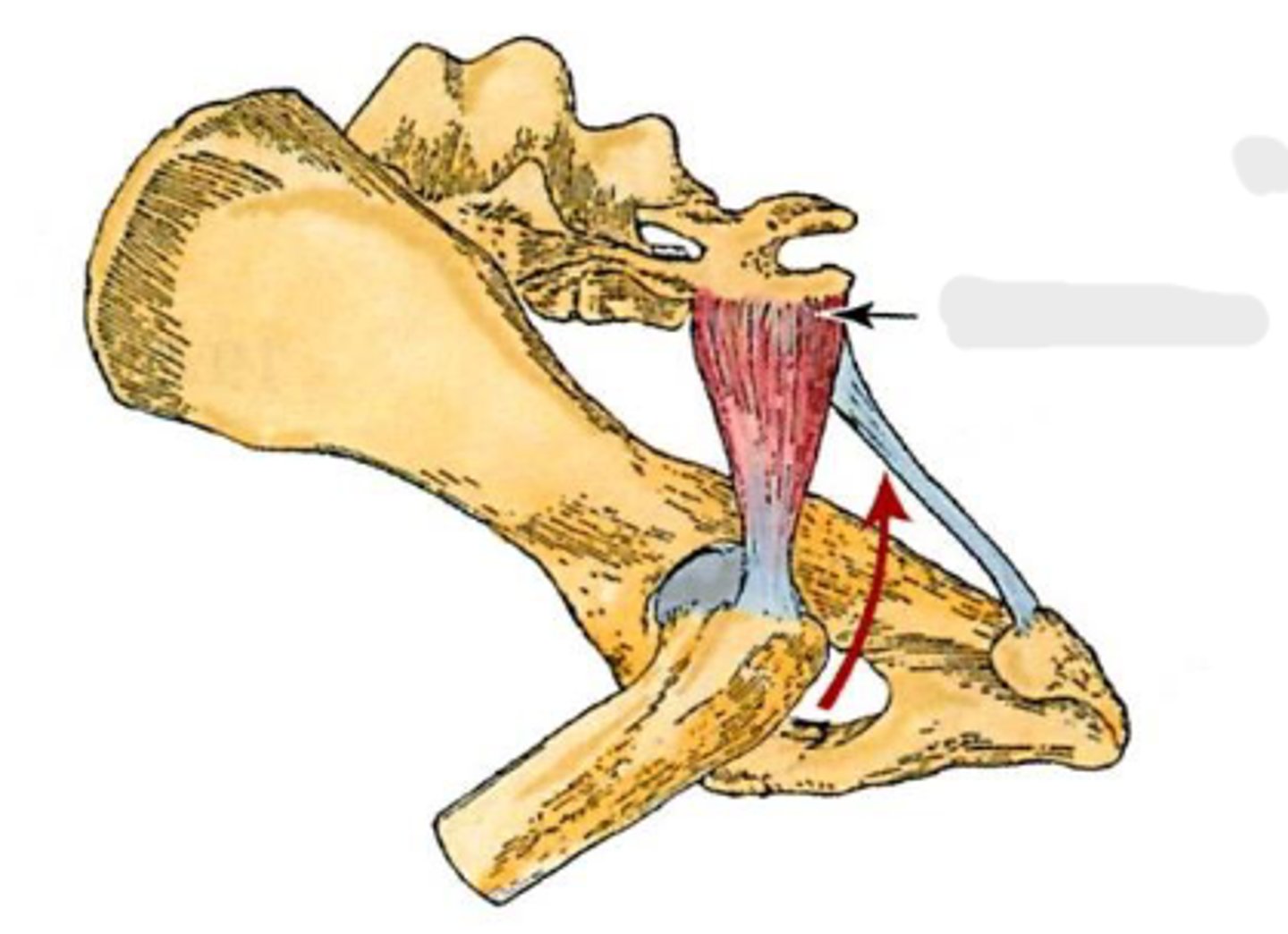
piriformis
What muscle is this, acting on the hip joint?
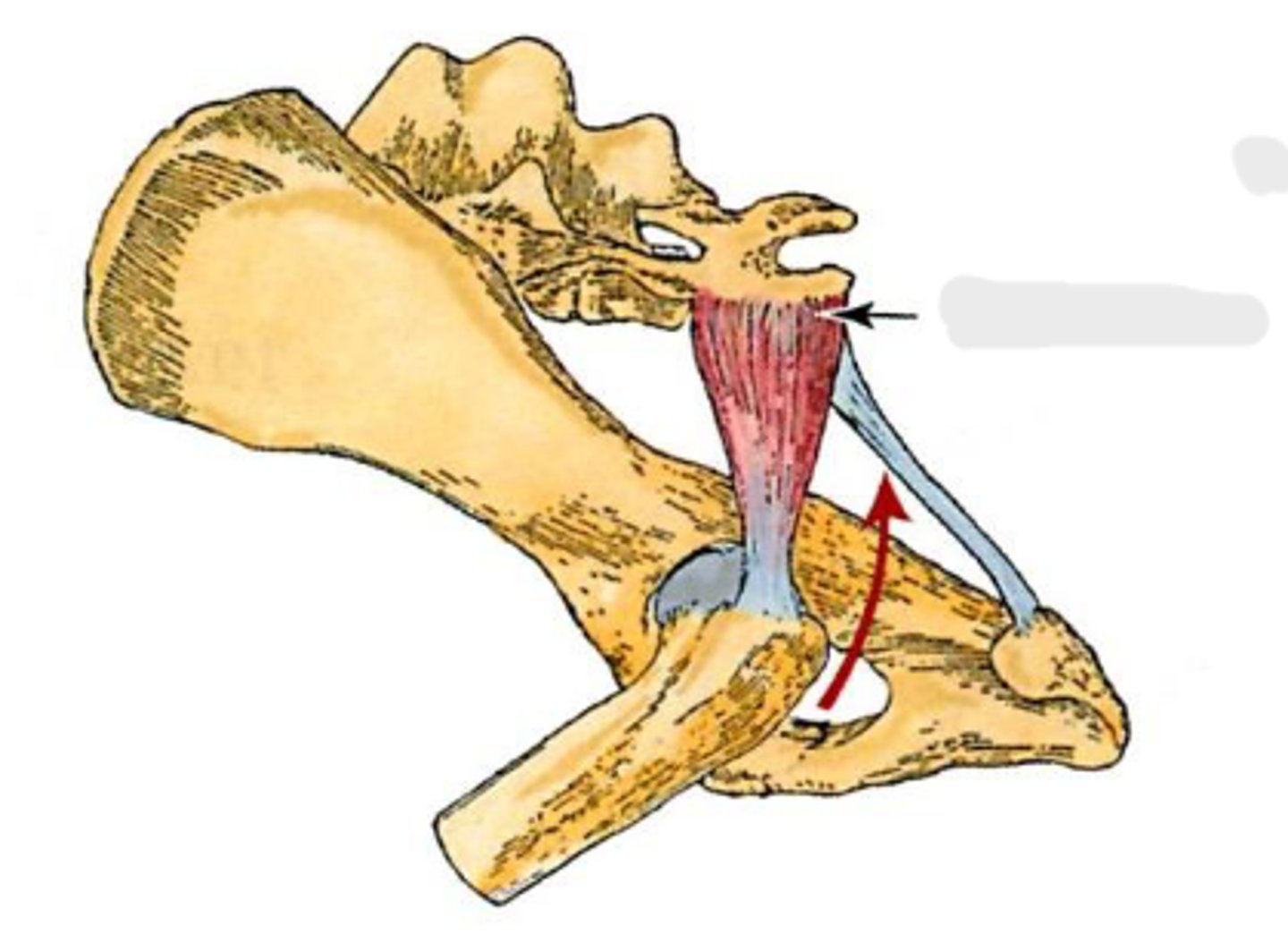
sacrum and 1st caudal vertebra
Origin of piriformis
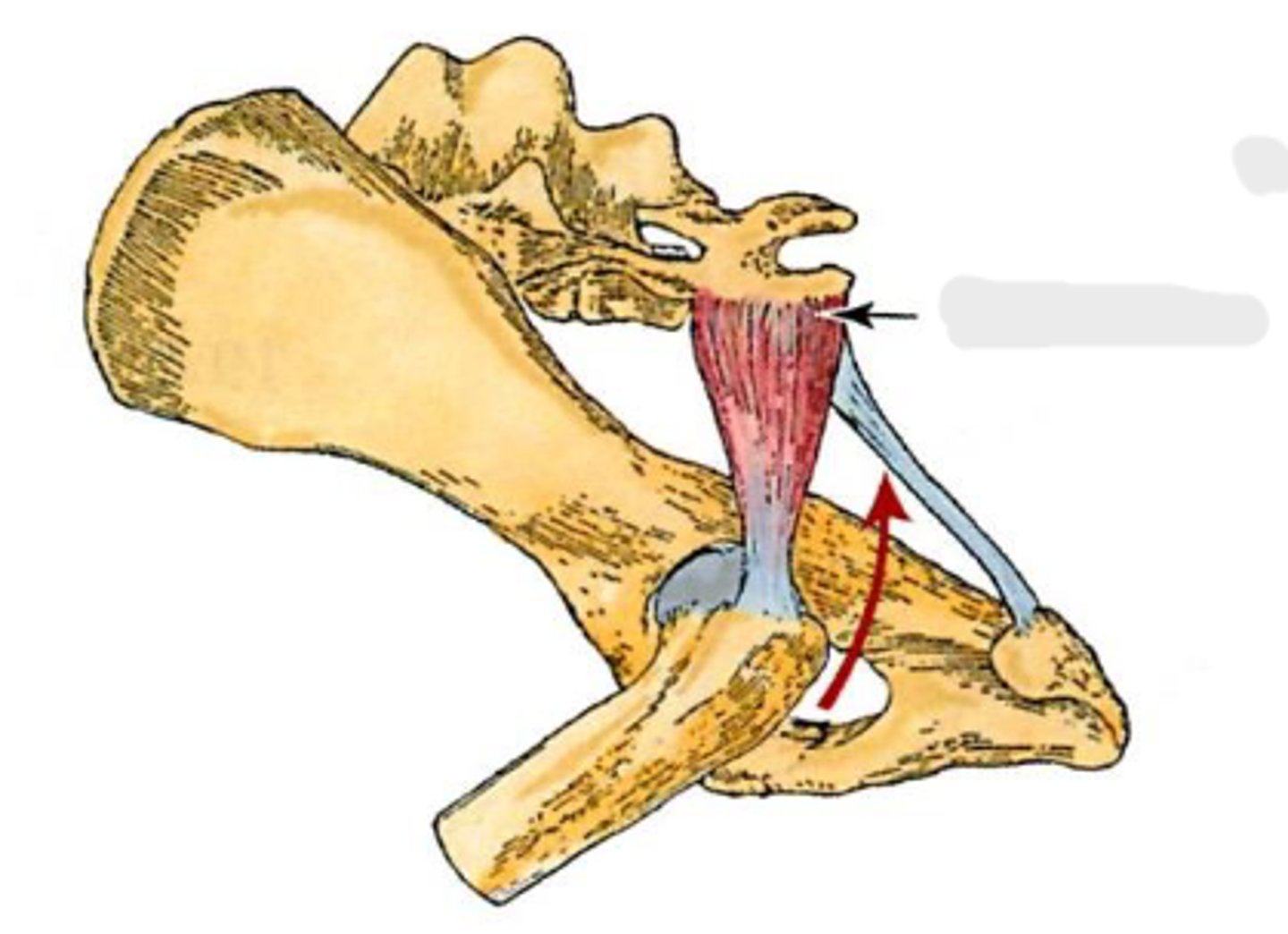
greater trochanter
Insertion of piriformis
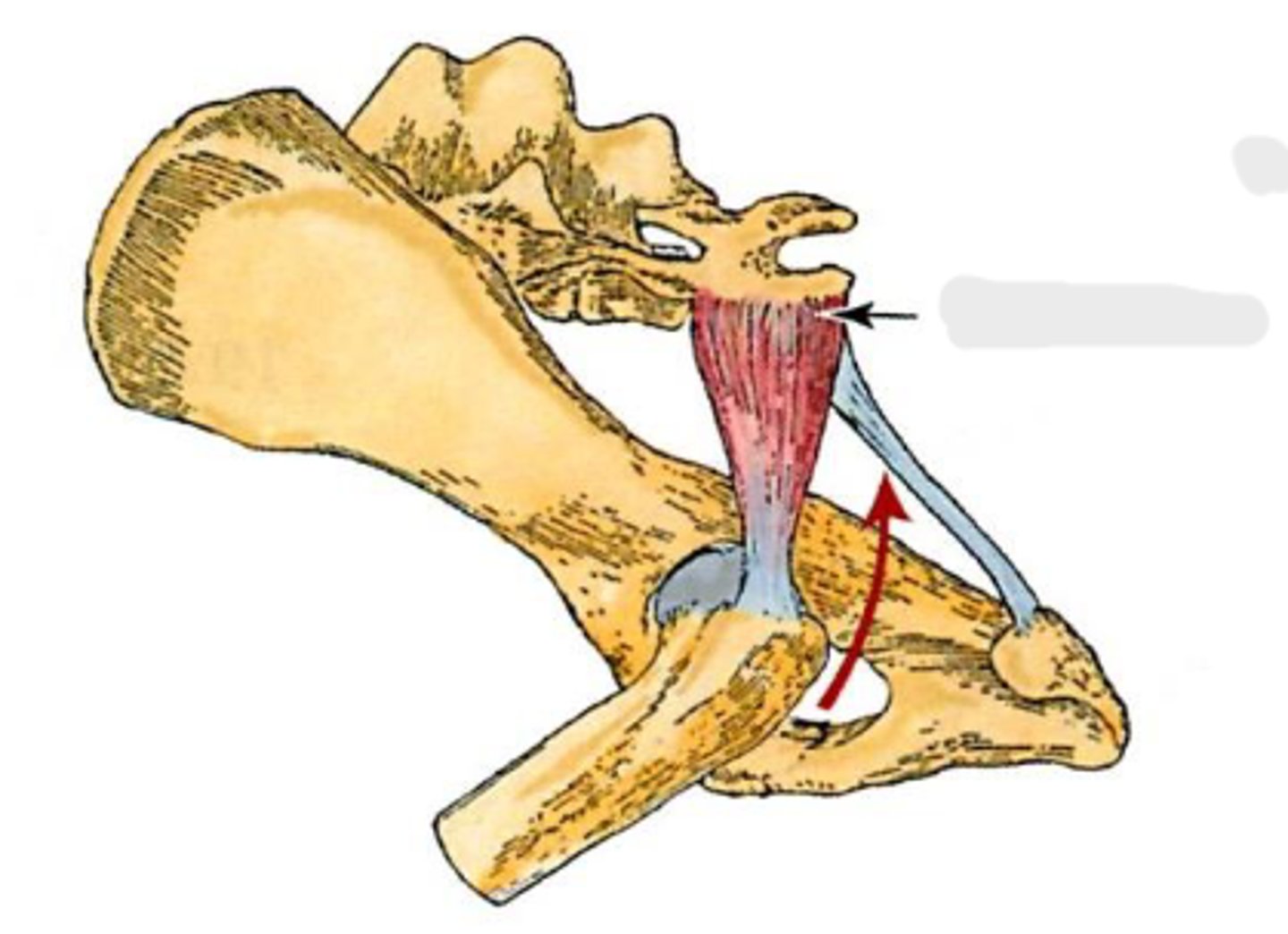
extend the coxal joint
Action of piriformis
deep gluteal
What muscle is this, acting on the hip joint?
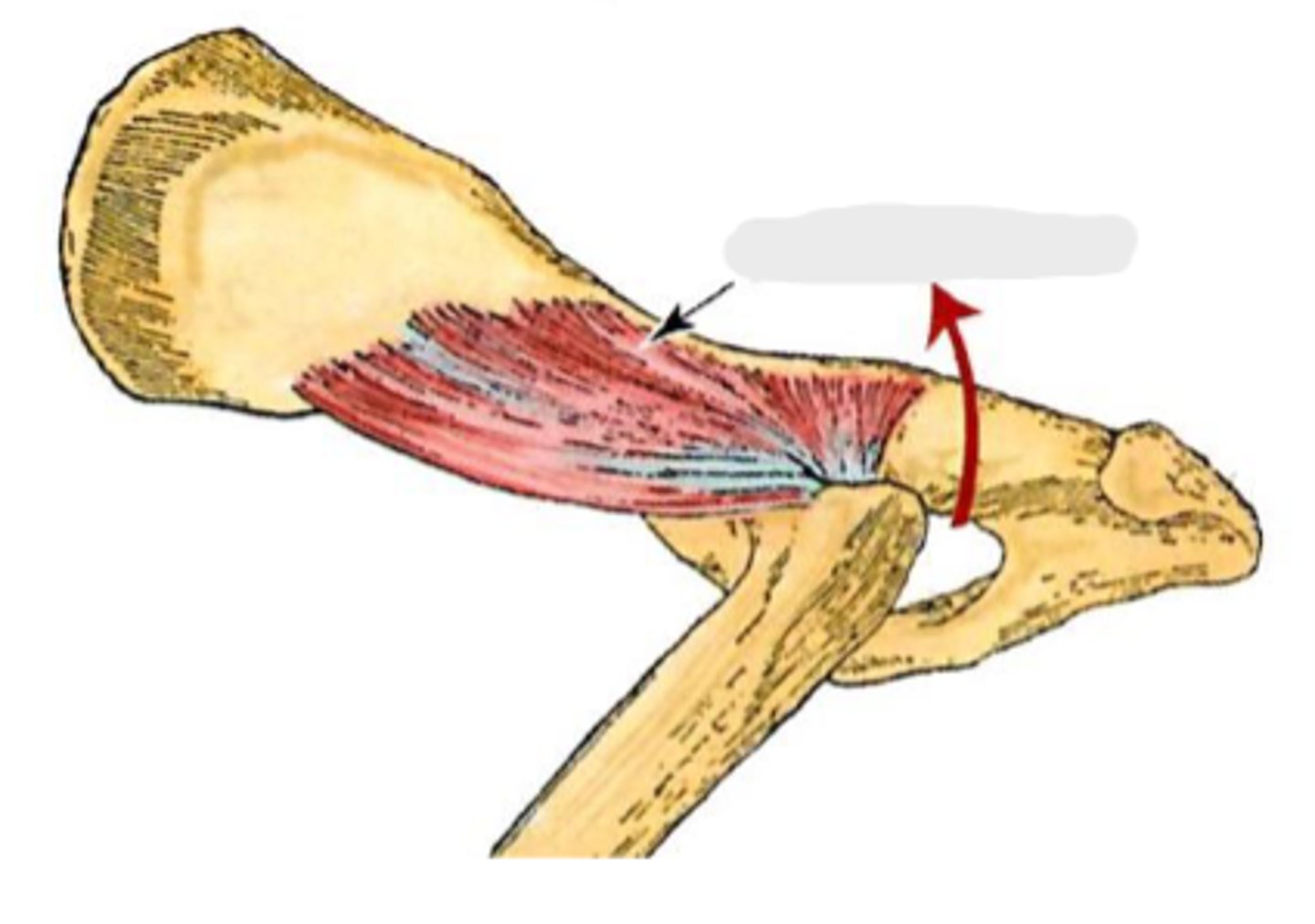
body of ilium and ischiatic spine
Origin of deep gluteal
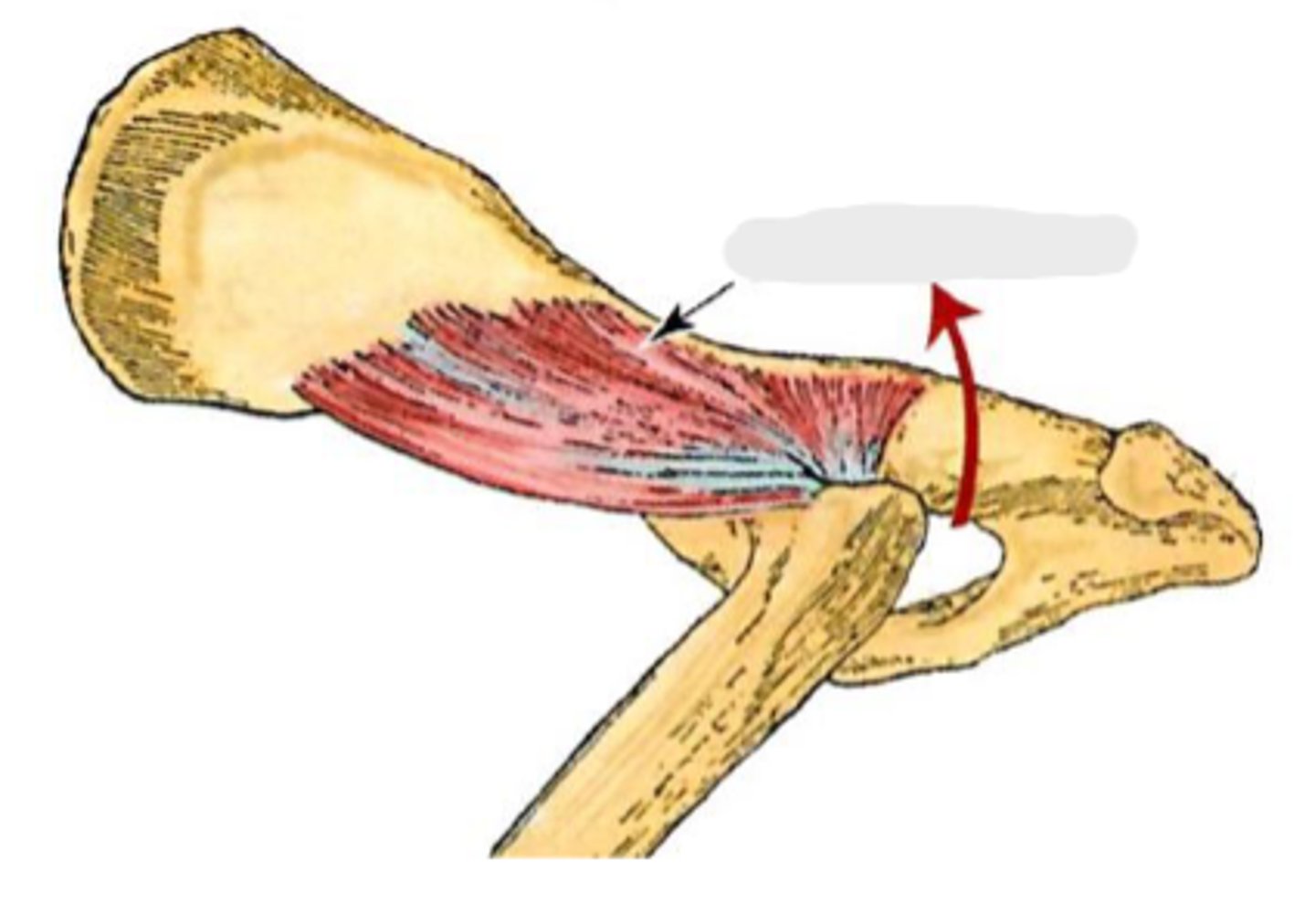
greater trochanter
Insertion of deep gluteal
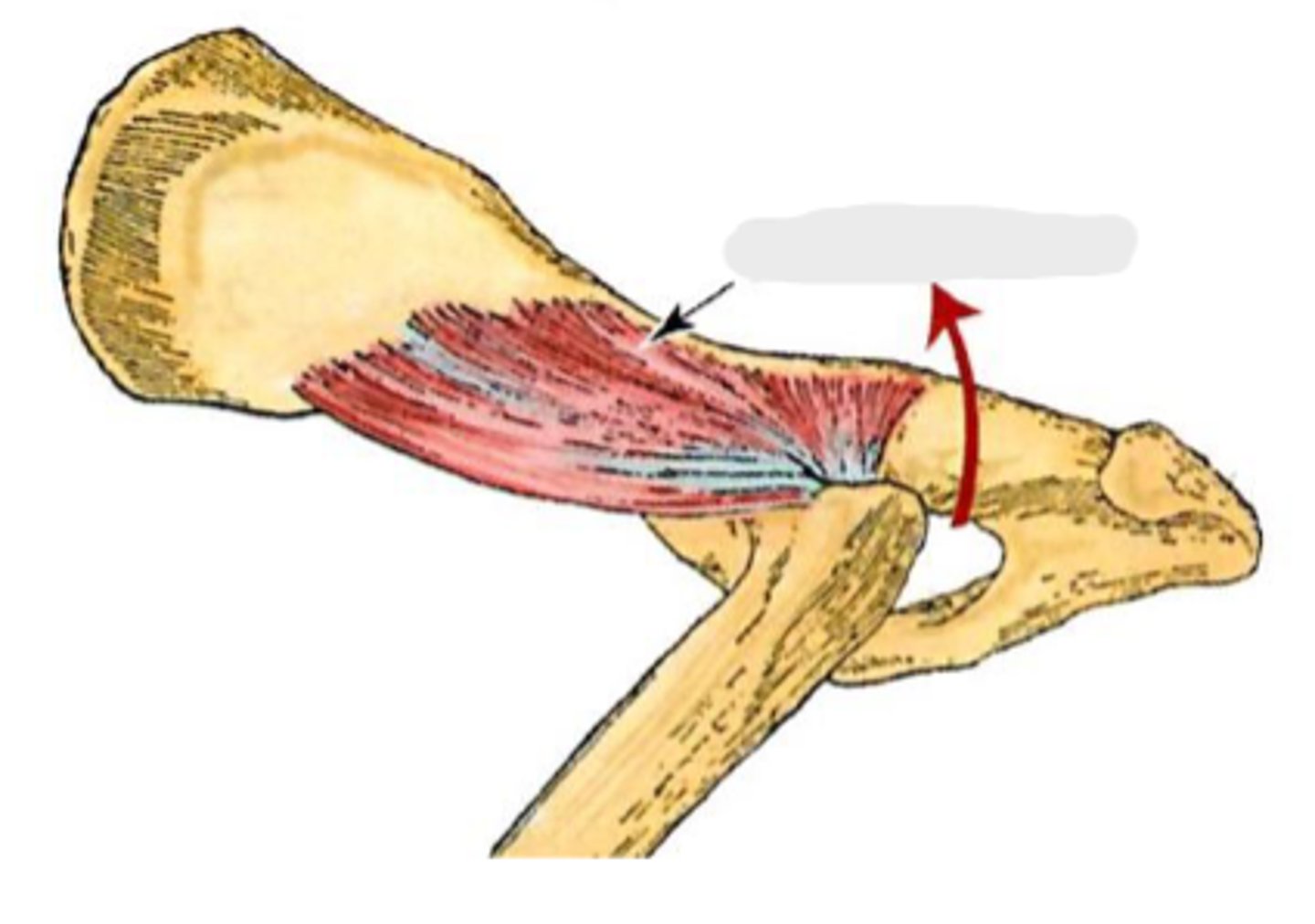
extend the coxal joint; abduct and rotate the pelvic limb medially
Action of deep gluteal
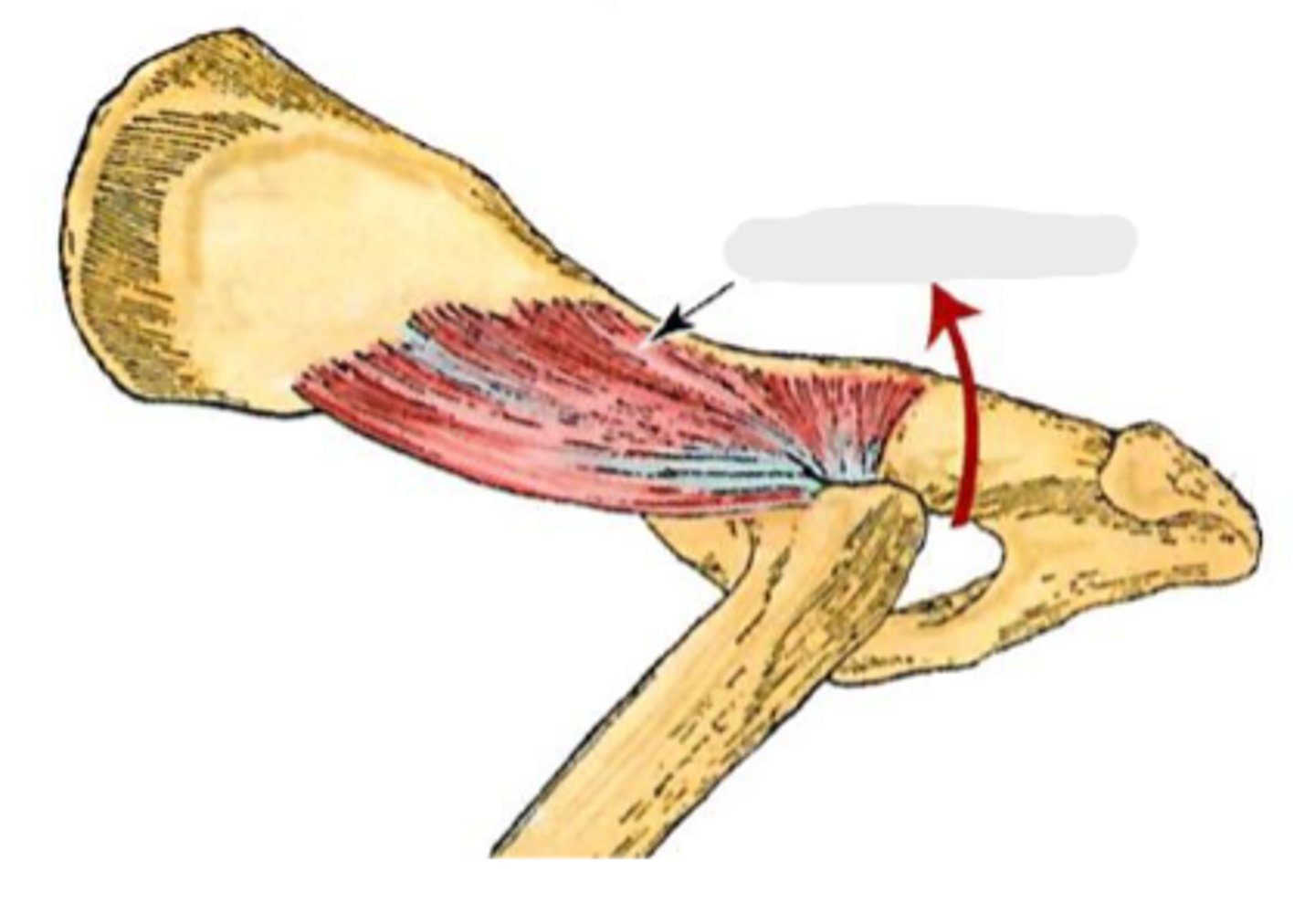
deep gluteal
What muscle is shown?
external obturator
What muscle is this, acting on the hip joint?
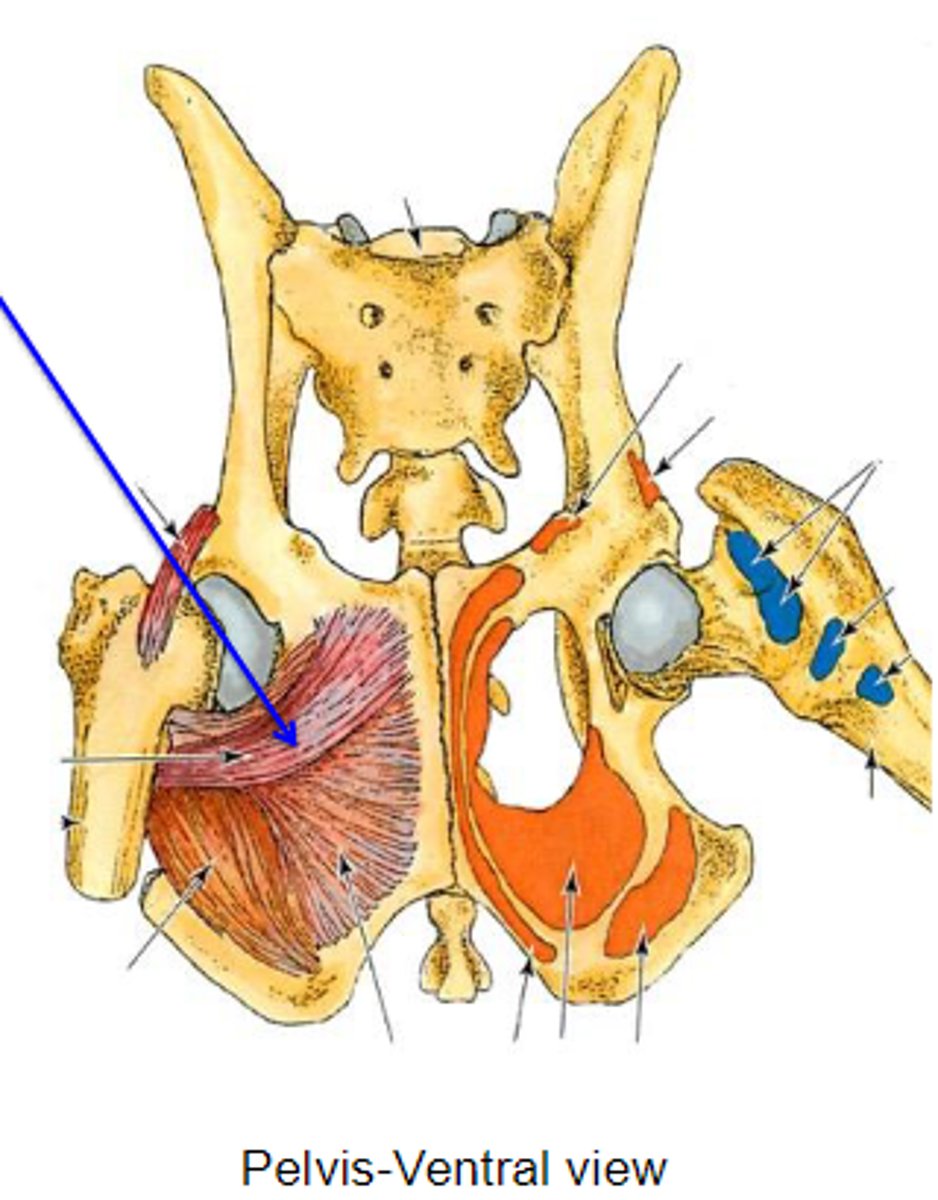
ventral aspect of os coxae around obturator foramen
Origin of external obturator
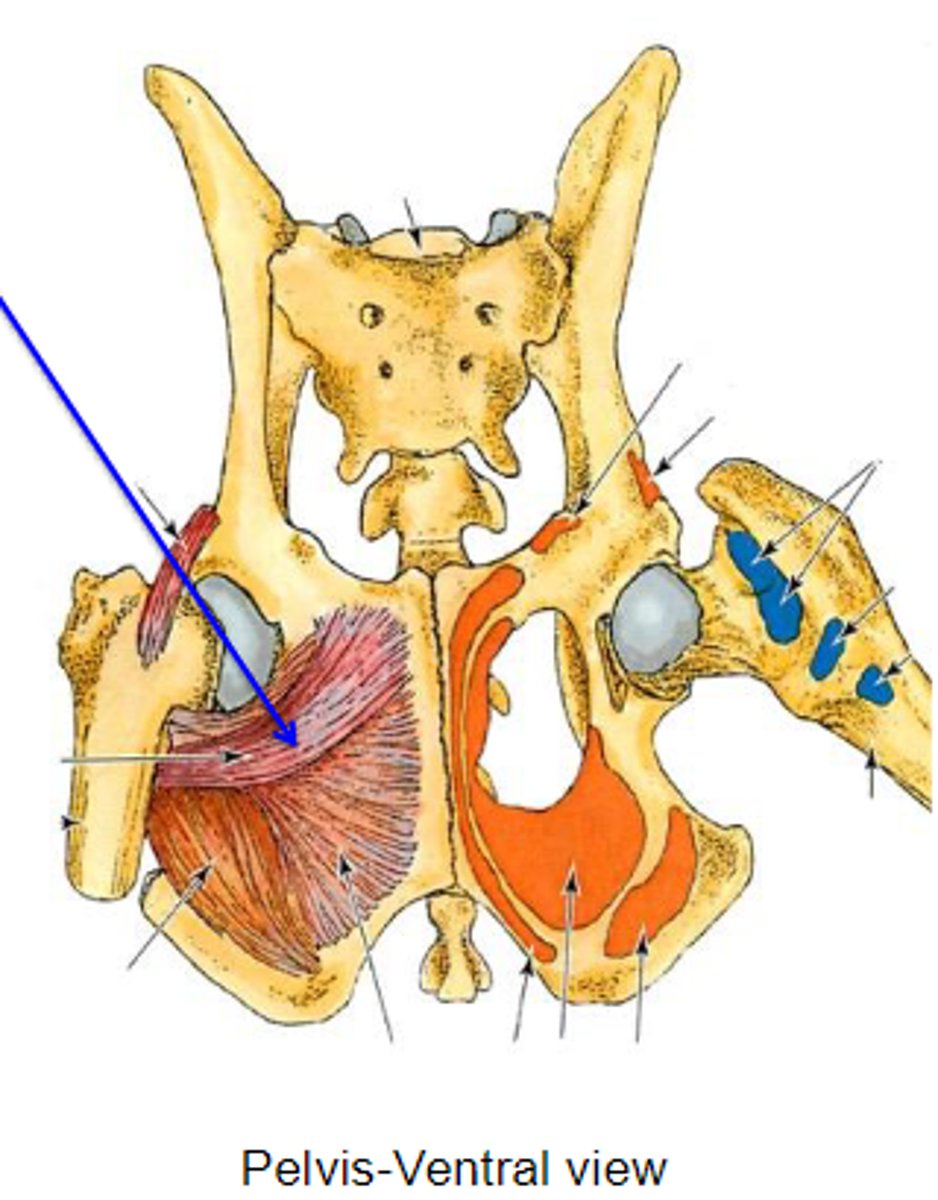
trochanteric fossa
Insertion of external obturator
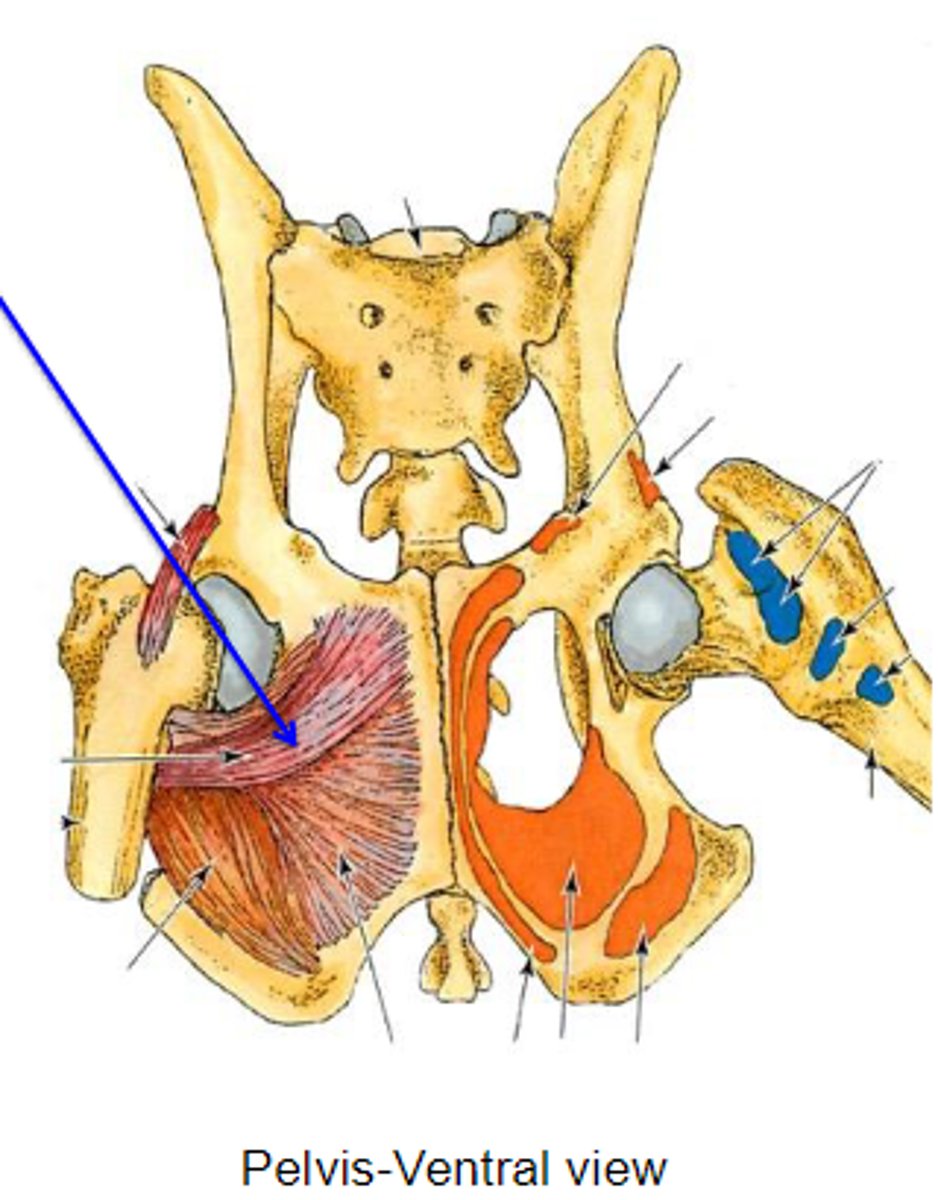
rotate the limb laterally at thecoxal joint
Action of external obturator
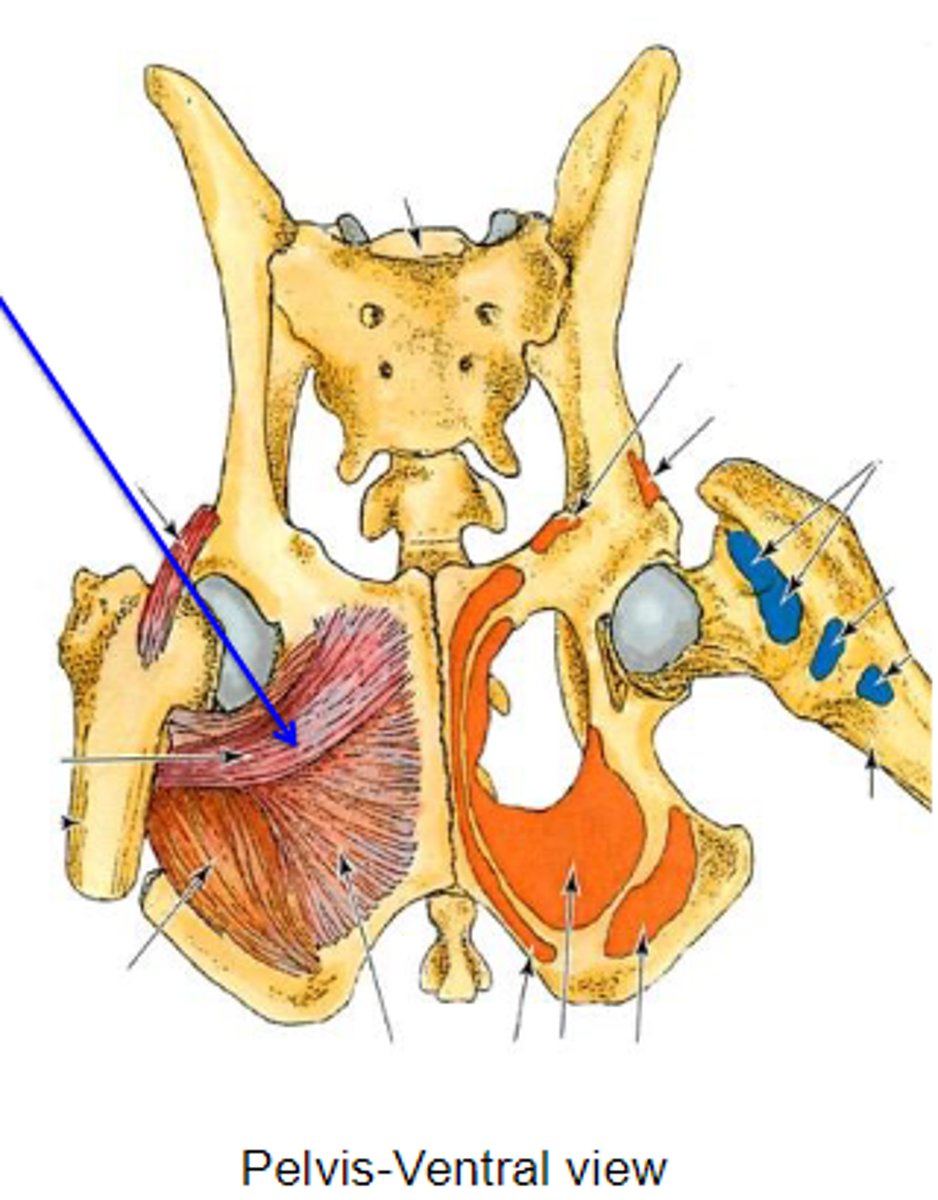
interna obturator
What muscle is shown, acting on the hip joint?
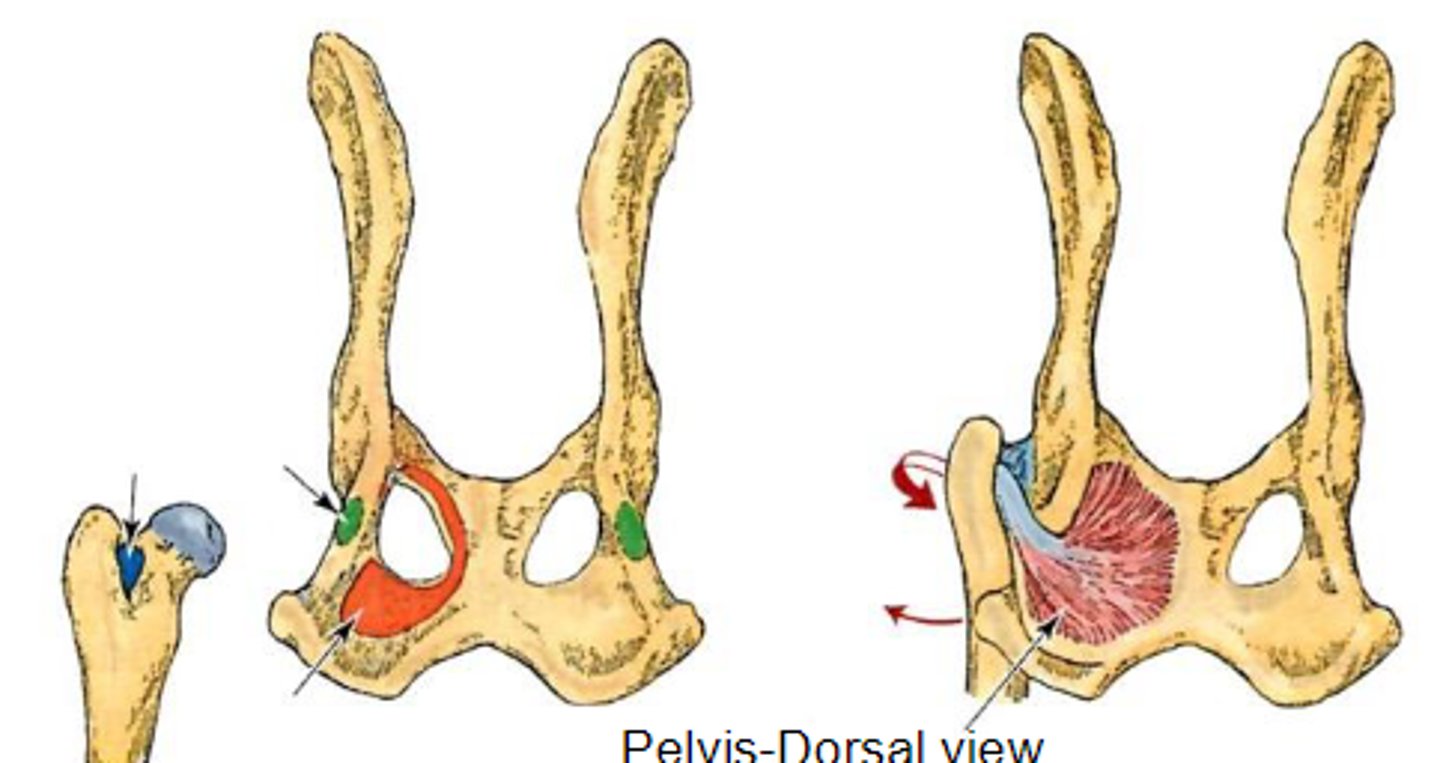
dorsal aspect of os coxae around obturator foramen
Origin on internal obturator
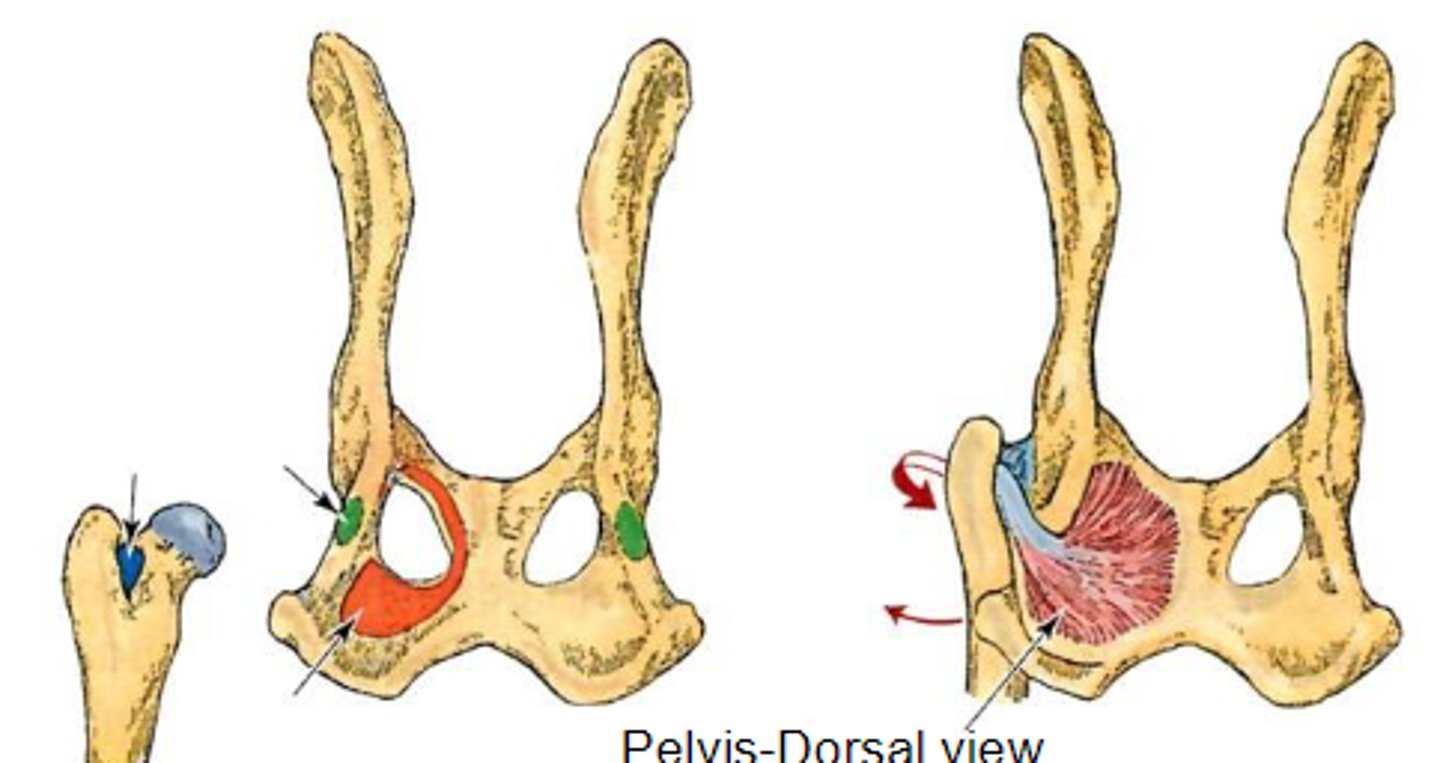
trochanteric fossa
Insertion of internal obturator
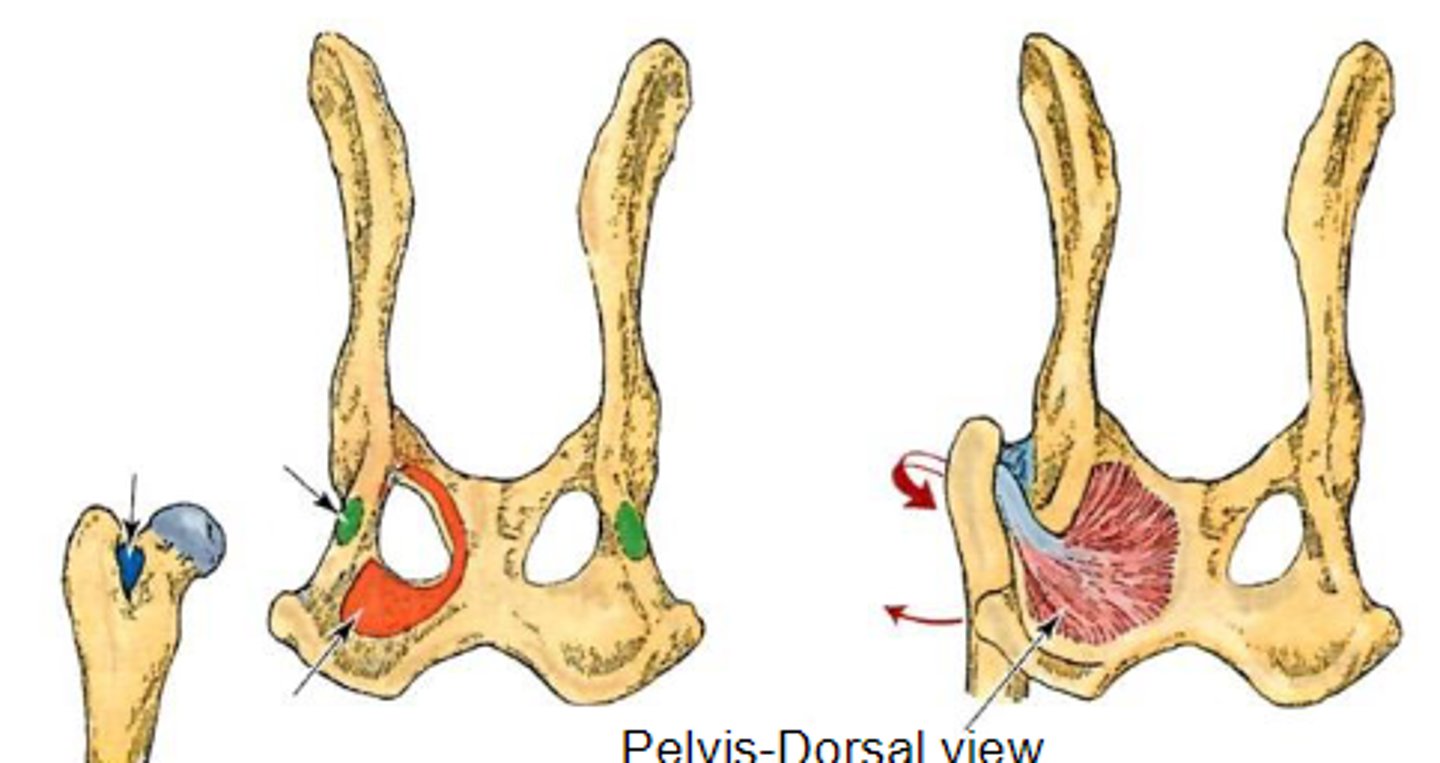
rotate the limb laterally at the coxal joint
Action of internal obturator
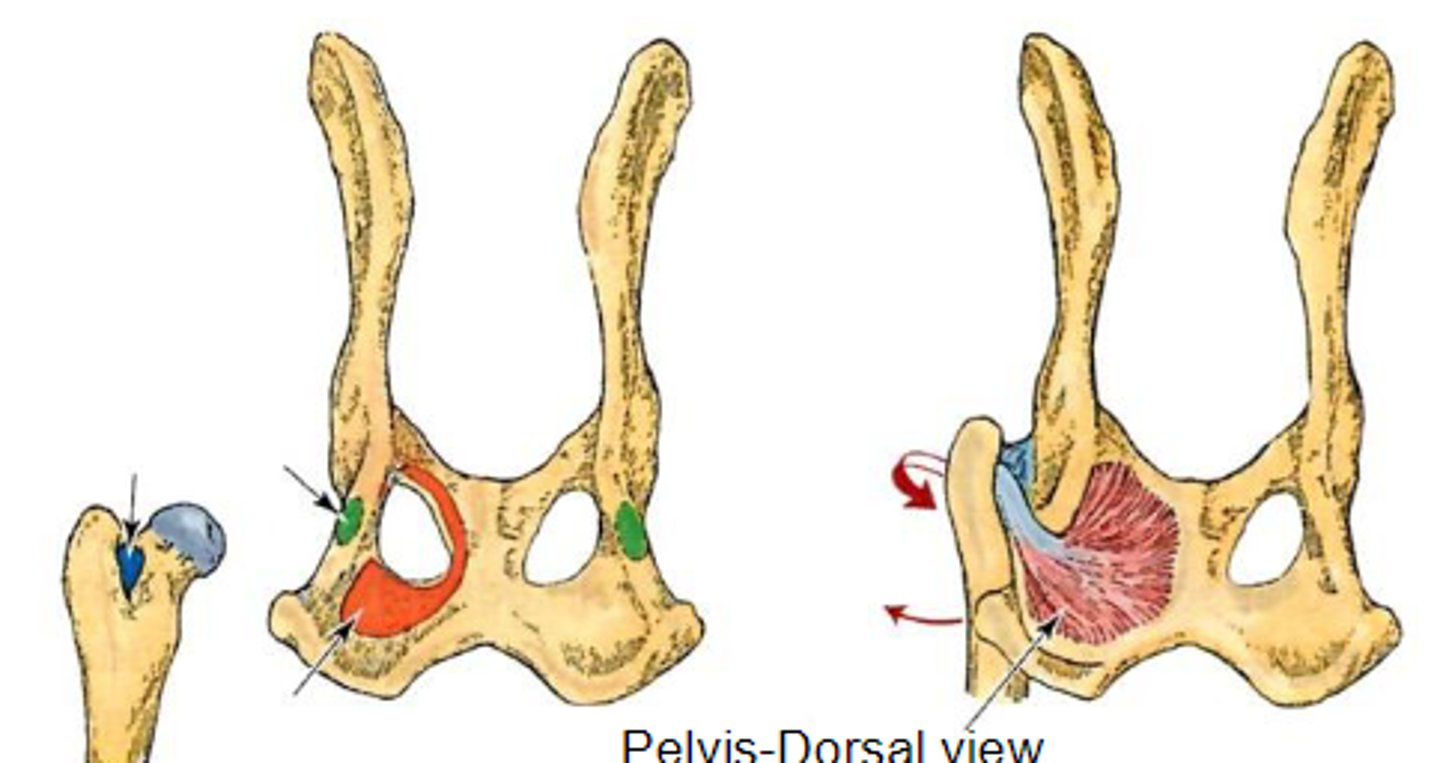
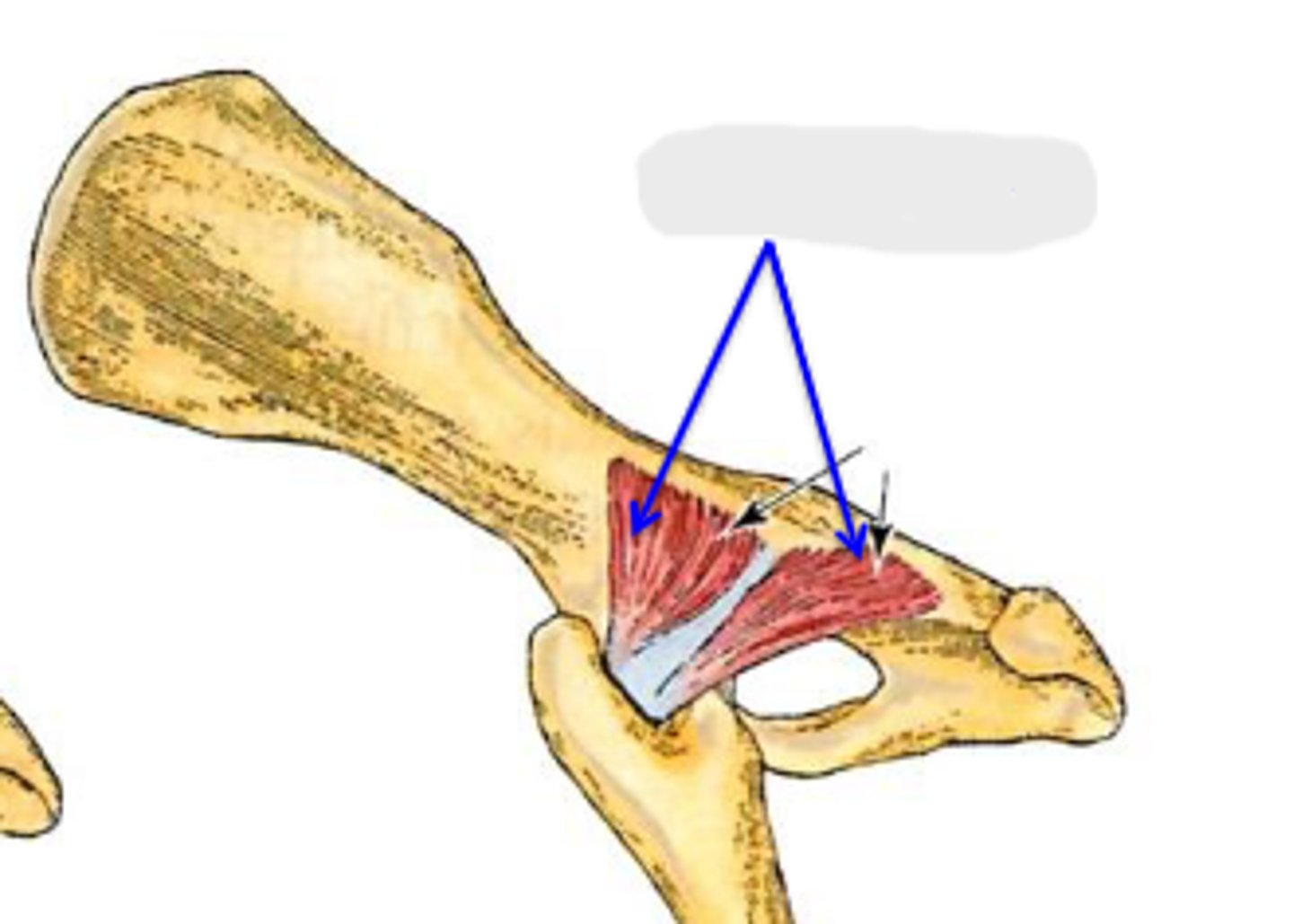
gemelli
What muscle is this, acting on the hip joint?
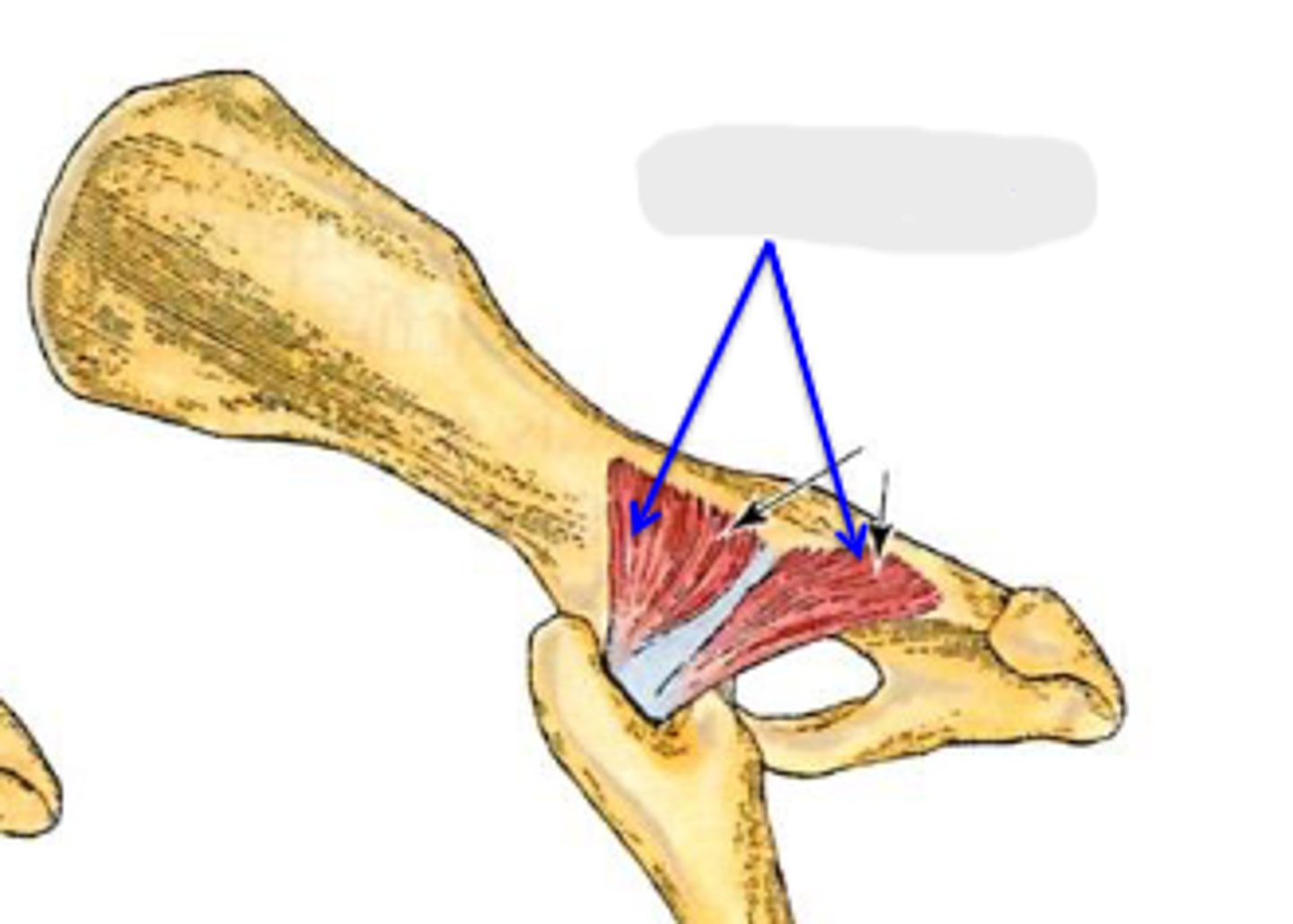
lateral aspect of ischium
Origin of gemelli
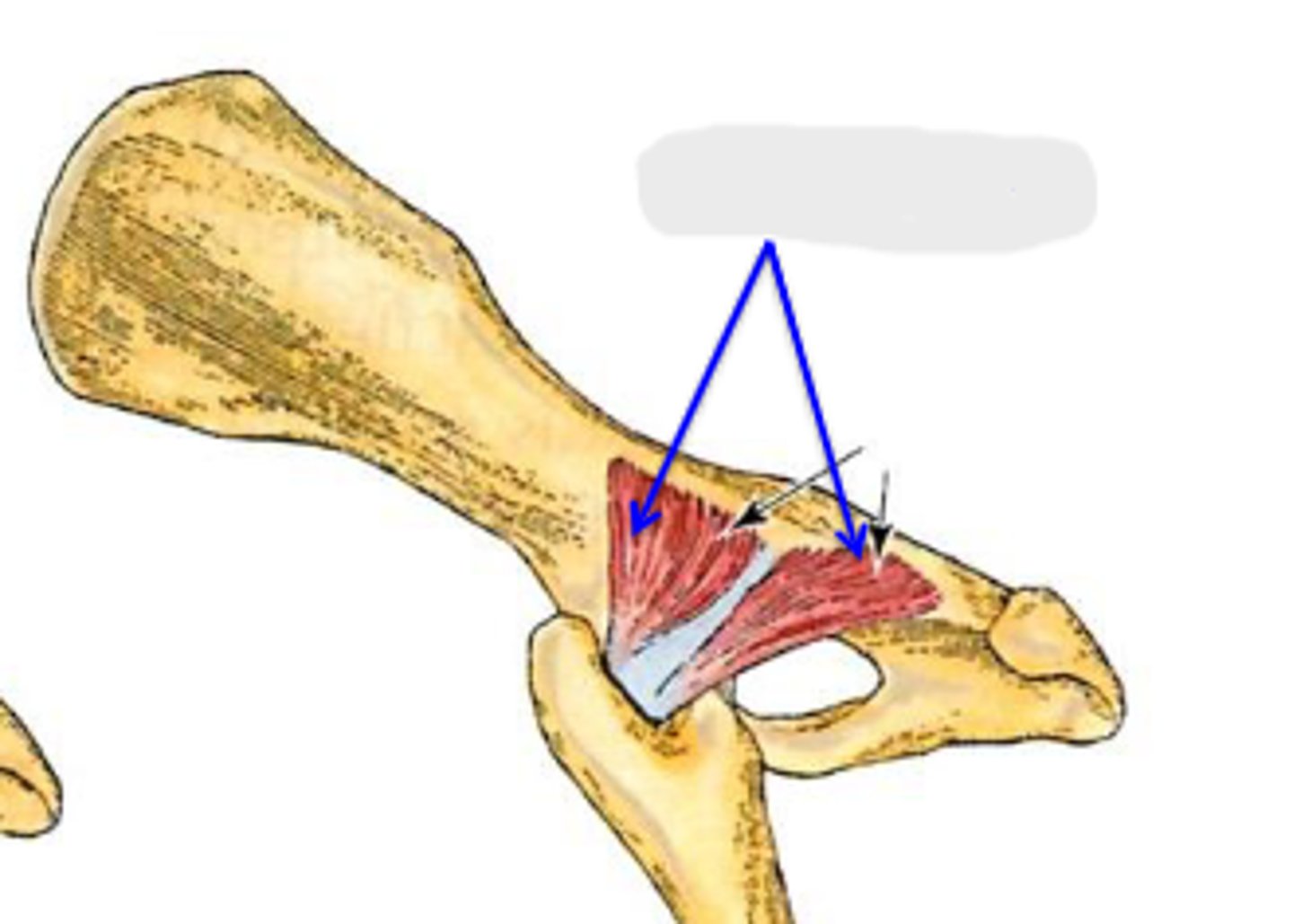
trochanteric fossa
Insertion of gemelli
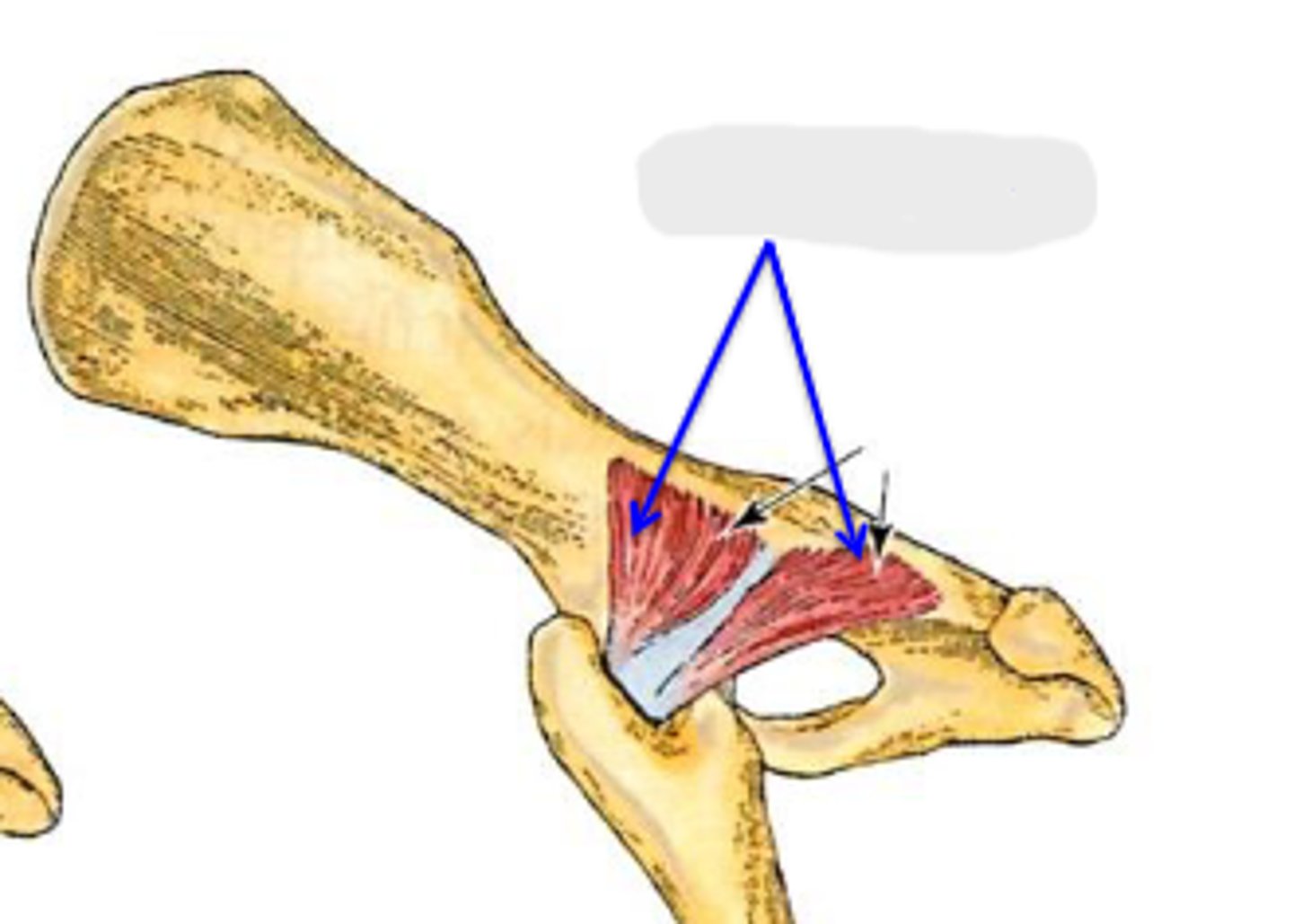
rotate the limb laterally at the coxal joint
Action of gemelli
quadratus femoris
What muscle is this, acting on the hip joint?
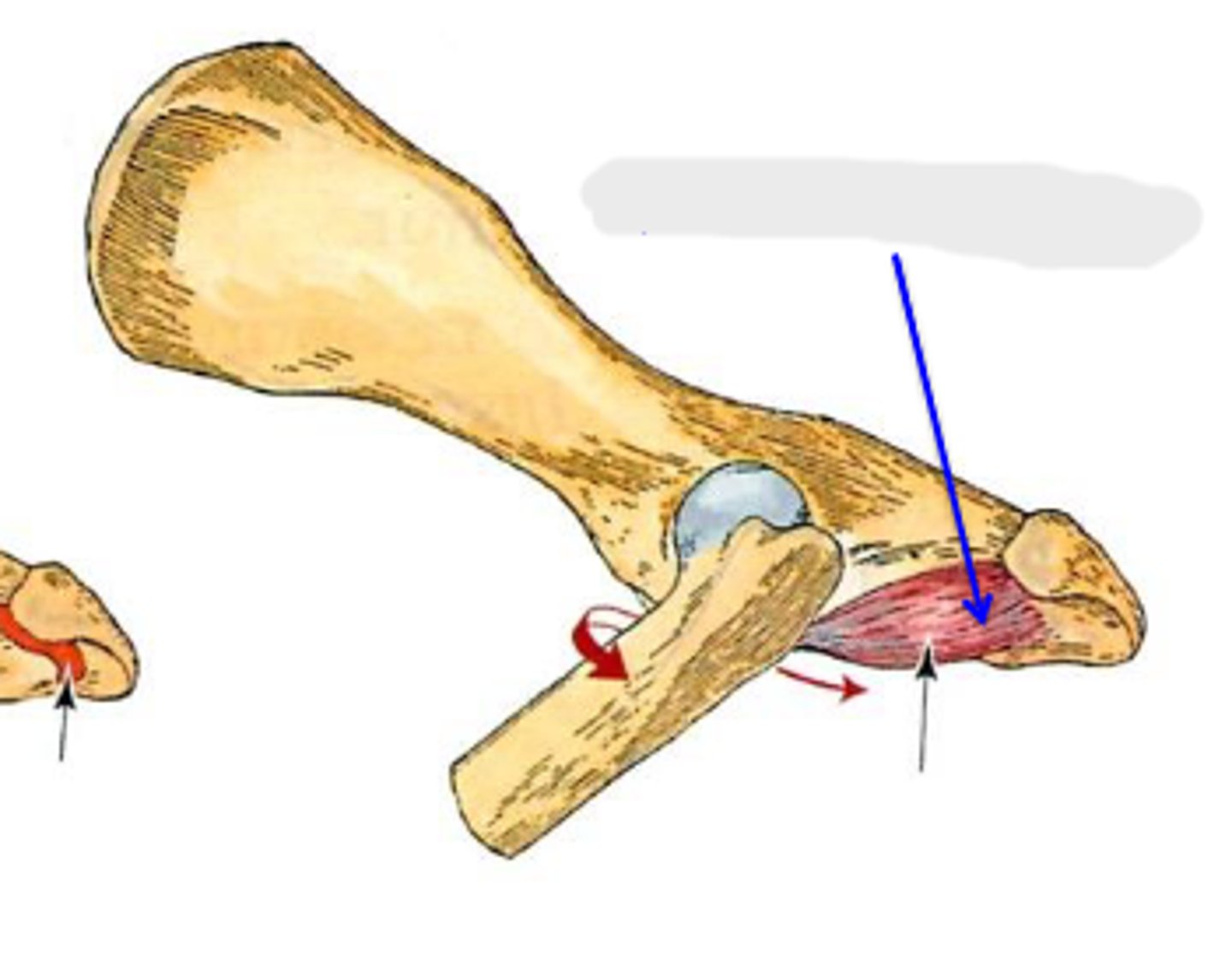
ventral aspect of ischium
Origin of quadratus femoris
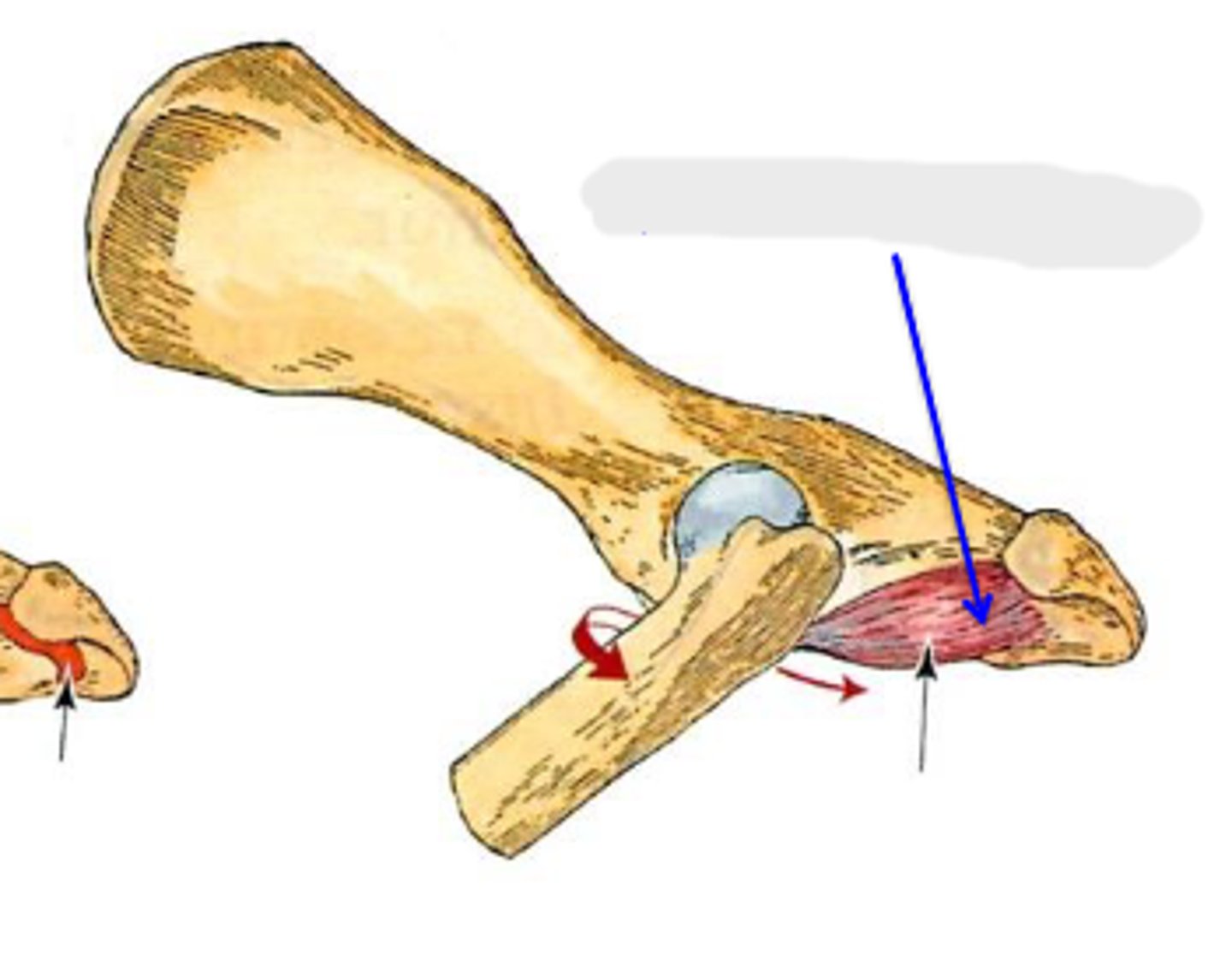
near the trochanteric fossa
Insertion of quadratus femoris
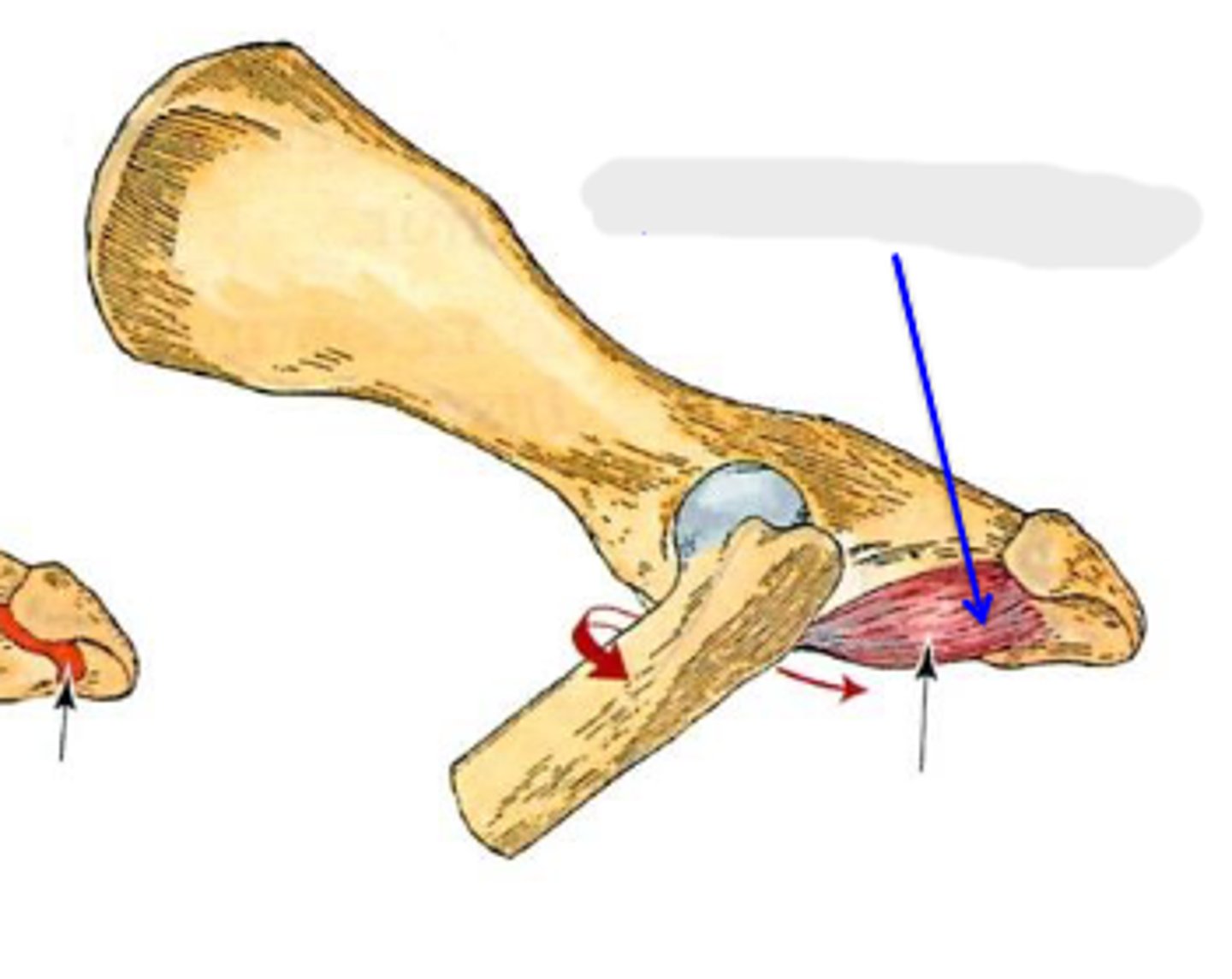
extend coxal joint; rotate the limb laterally at the coxal joint
Action of quadratus femoris
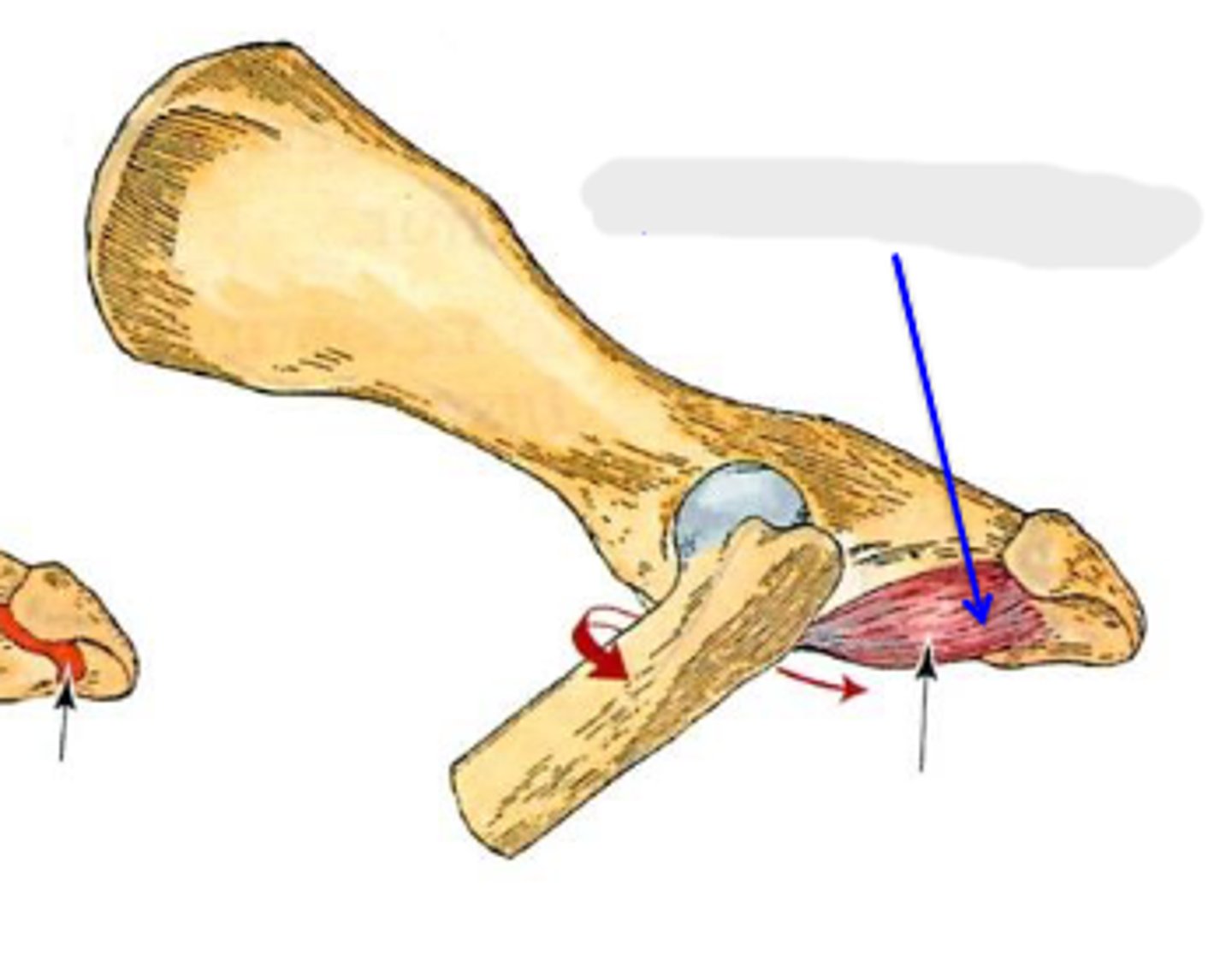
genual/stifle
This is the _____ joint

1. femoropatellar
2. femorotibial
3. proximal tibiofibular
The genual/stifle joint is comprised of what 3 joints?
hinge
The femoropatellar joint is a _____ joint
condylar
The femorotibial joint is a _____ joint
plane
The proximal tibiofibular joint is a _____ joint
reviewed
Review
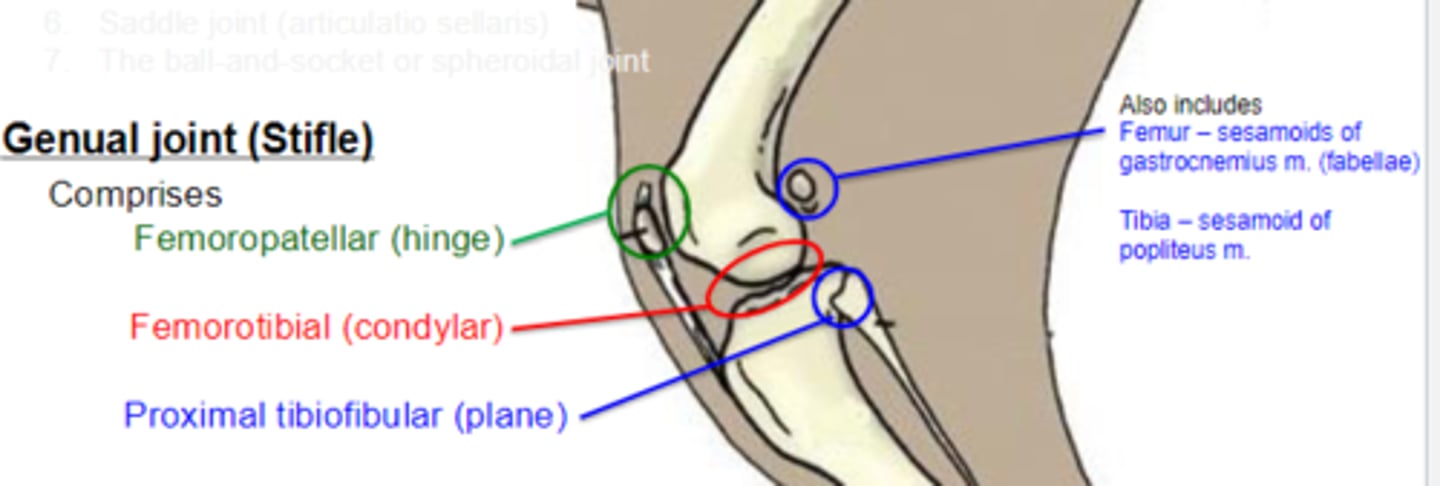
genual/stifle joint
What is the largest synovial joint in the body?
1. lateral collateral ligament
2. medial collateral ligament
3. cranial cruciate ligament
4. caudal cruciate ligament
The genual/stifle joint consists of what 4 main ligaments?
femoropatellar
The _____ joint is associated with the patellar ligament and lateral & medial ligaments
infrapatellar body fat
Fatty body located
between the patellar lig
and the joint capsule
femorotibial
The _____ joint is associated with the cranial cruciate ligament and caudal cruciate ligament
caudal cruciate
The _____ ligament prevents:
-caudal displacement of the tibia against the femur
-lateral rotation of the joint
cranial cruciate
The _____ ligament prevents:
-cranial displacement of the tibia against the femur
-hyperextension of the genual joint-medial rotation of the joint
parapatellar fibrocartilage
What is 1?
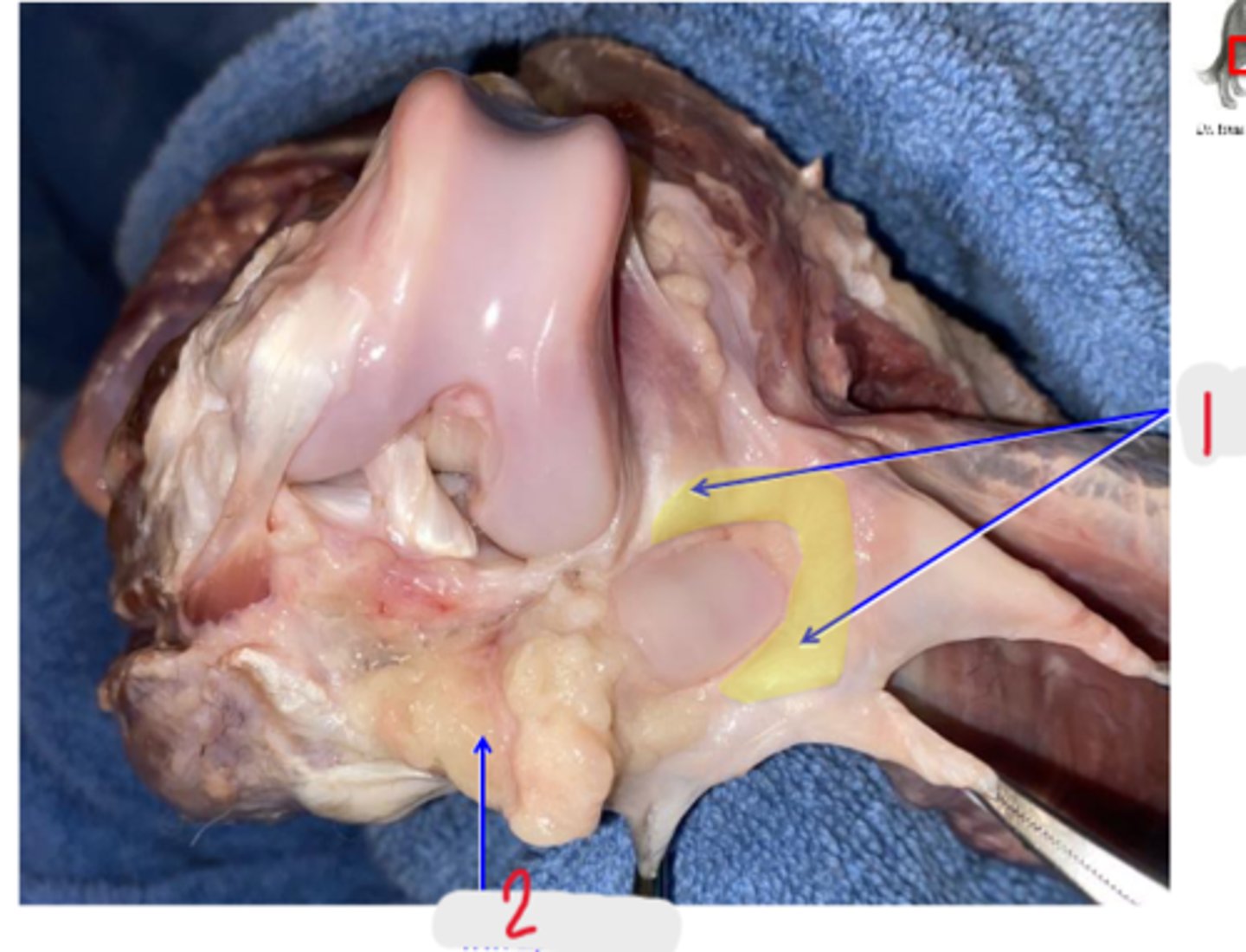
infrapatellar body fat
What is 2?
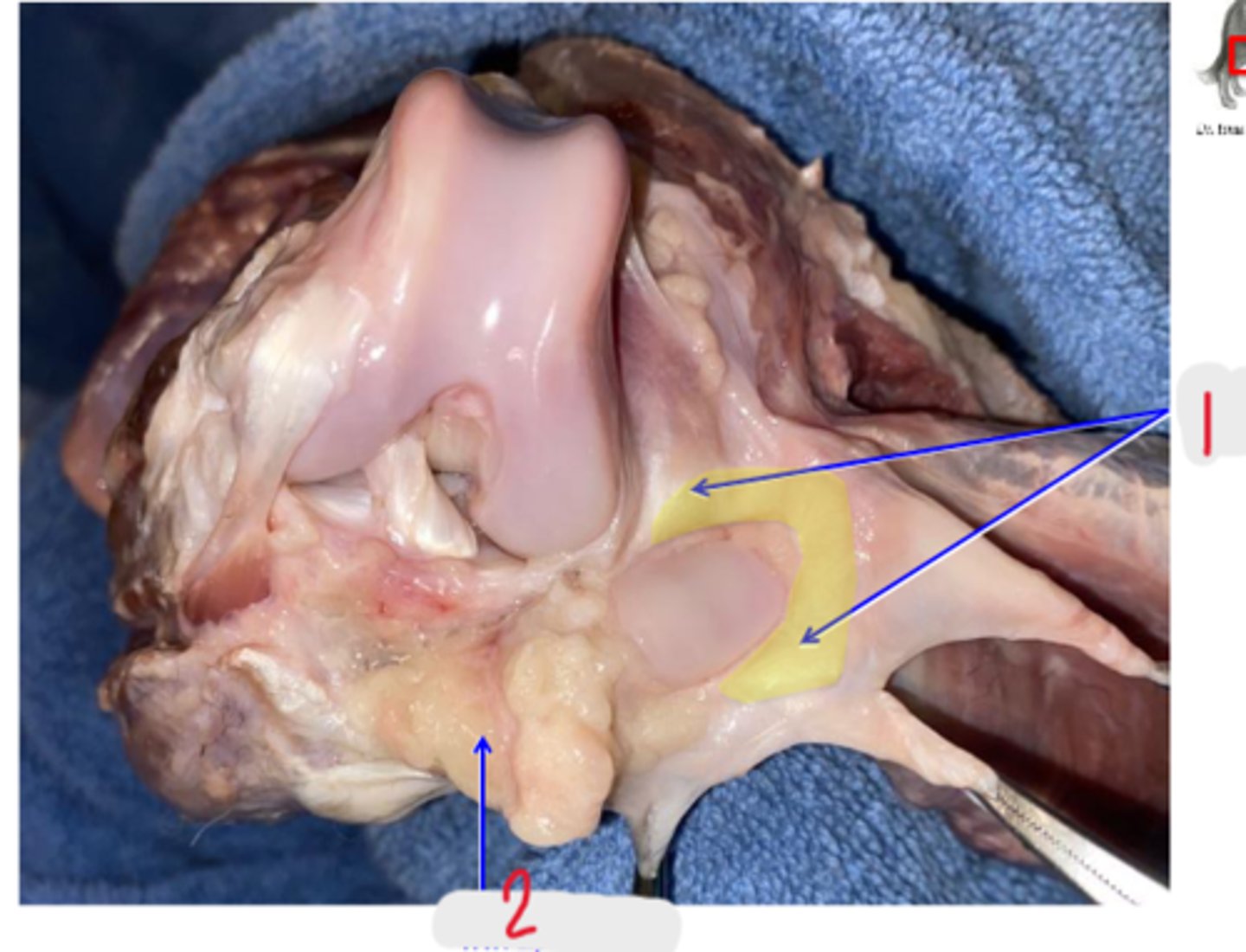
cranial cruciate ligament
What is shown?
caudal cruciate ligament
What is shown?
meniscus
The femorotibial joint consists of 2 _____, lateral and medial
drawer sign/test in stifle joint
What can we do determine if there is a rupture of the cranial cruciate ligament?
extracapsular
The collateral ligaments and popliteal tendon are _____ structures
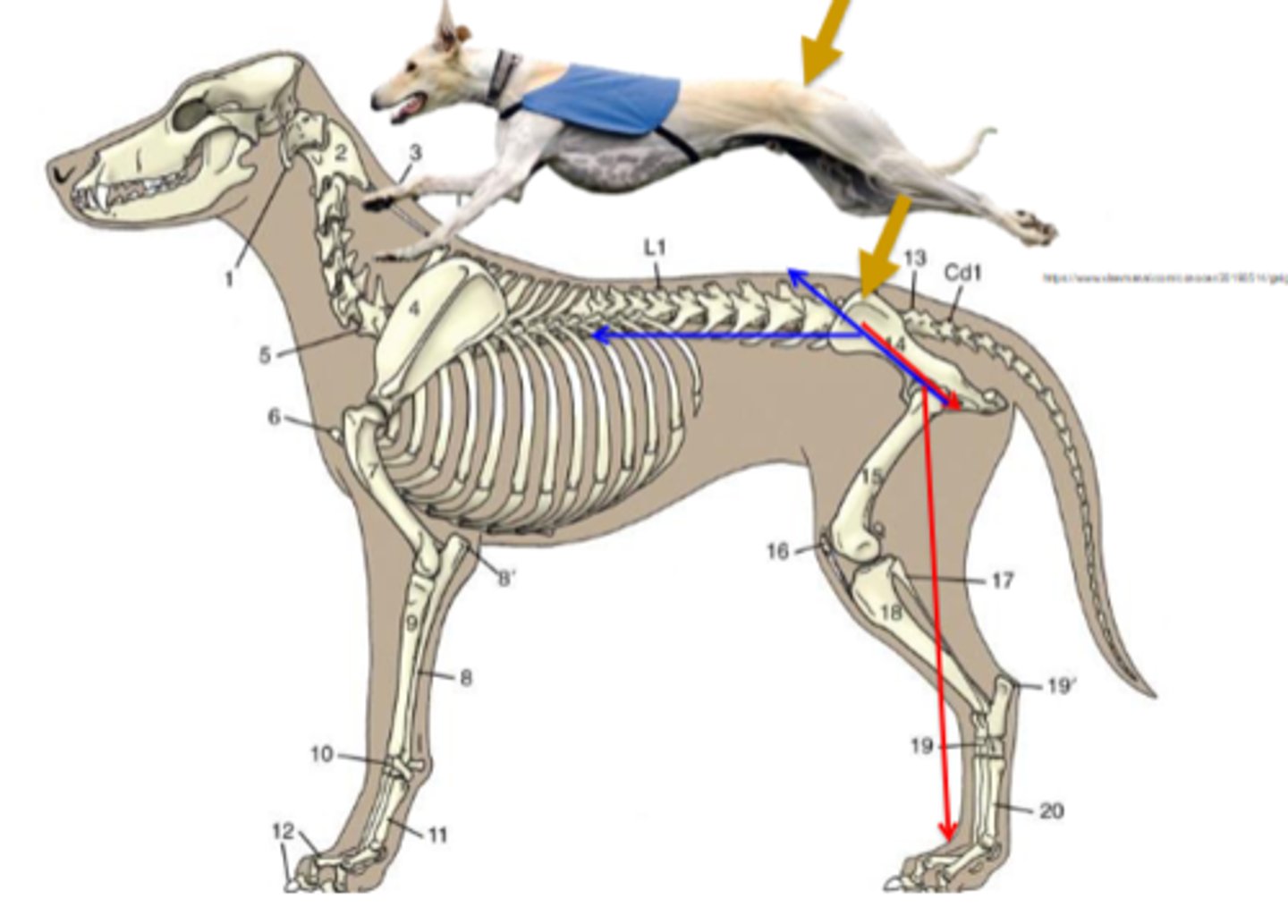
40
Only _____% of the weight of the body falls on the pelvic limb
synovial
Because the sacroiliac joint has a small _____ area, there is some mobility/flexibility
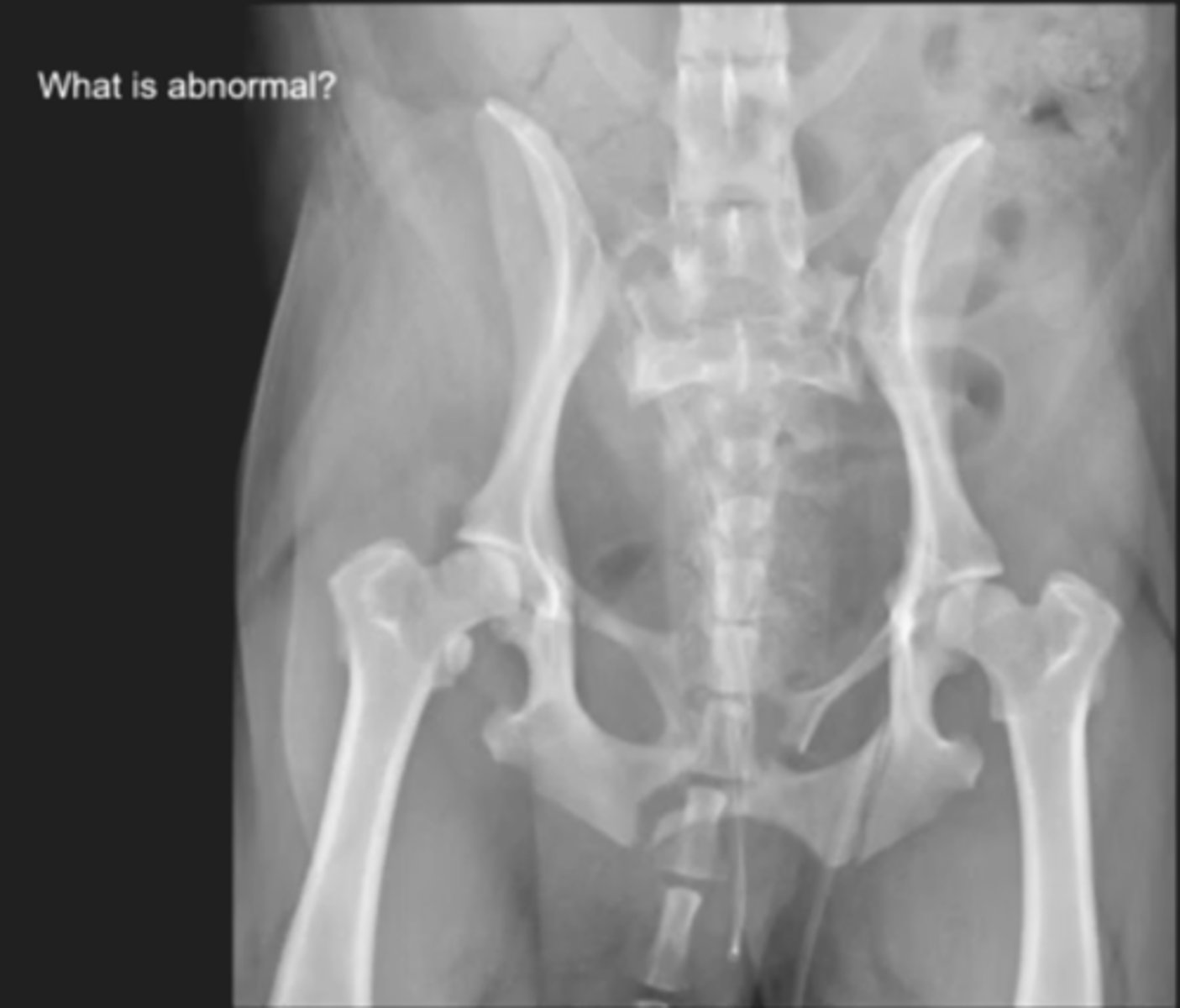
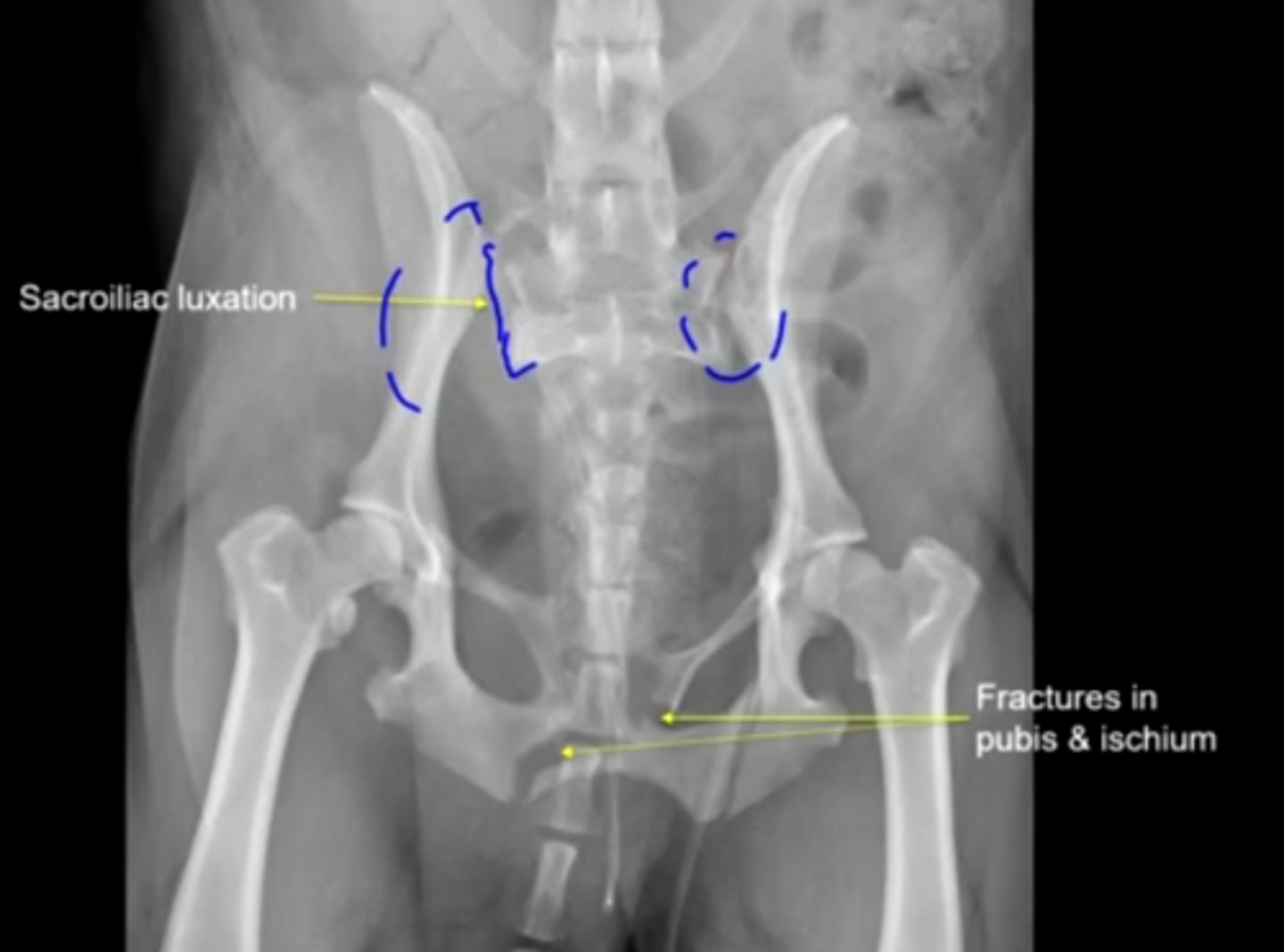
-fracture of the pubis & ischium
-sacroliliac luxation
What is abnormal here?
sacroiliac luxation - point where the pelvic limb transmits all the force toward the rest of the body
Which of these issues is more important? Why?
dorsal; plantar
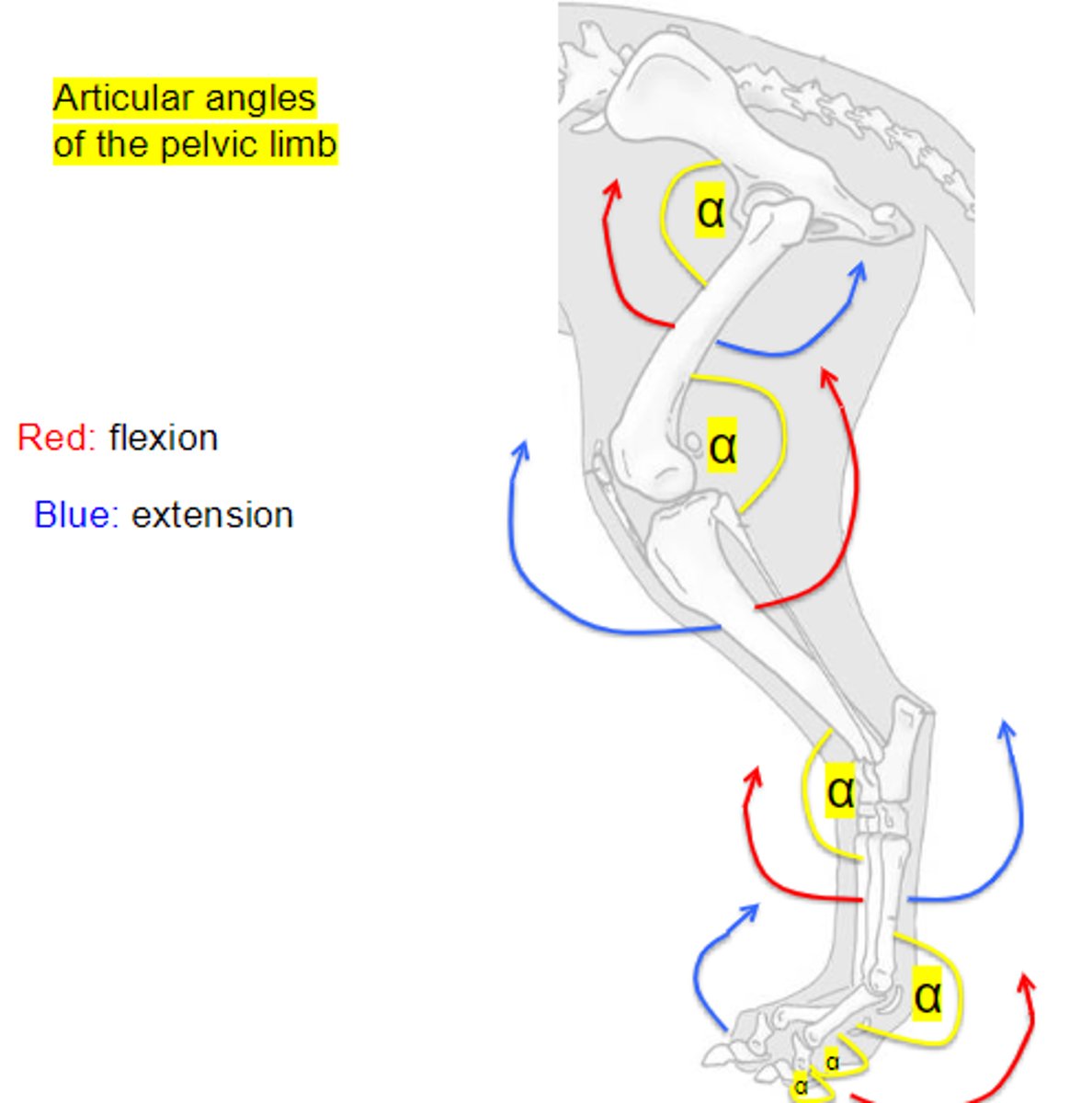
In the tarsus, the angle is _____ and in the digits, the angle are _____
extension of coxal joint
Name the movement & associated joint

coxal joint
What is the name of the hip joint?
tensor fascia lata
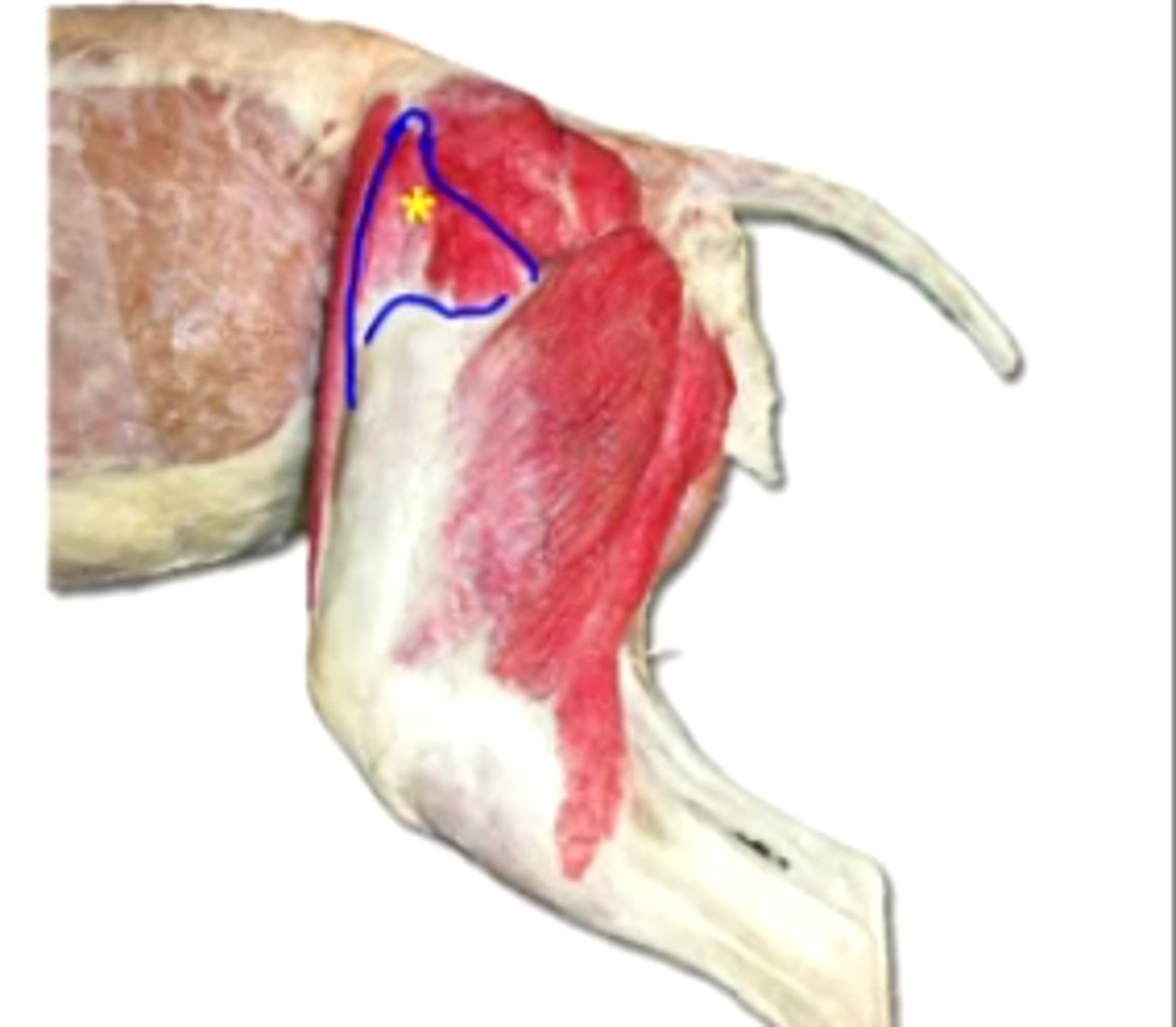
superficial gluteal
middle gluteal
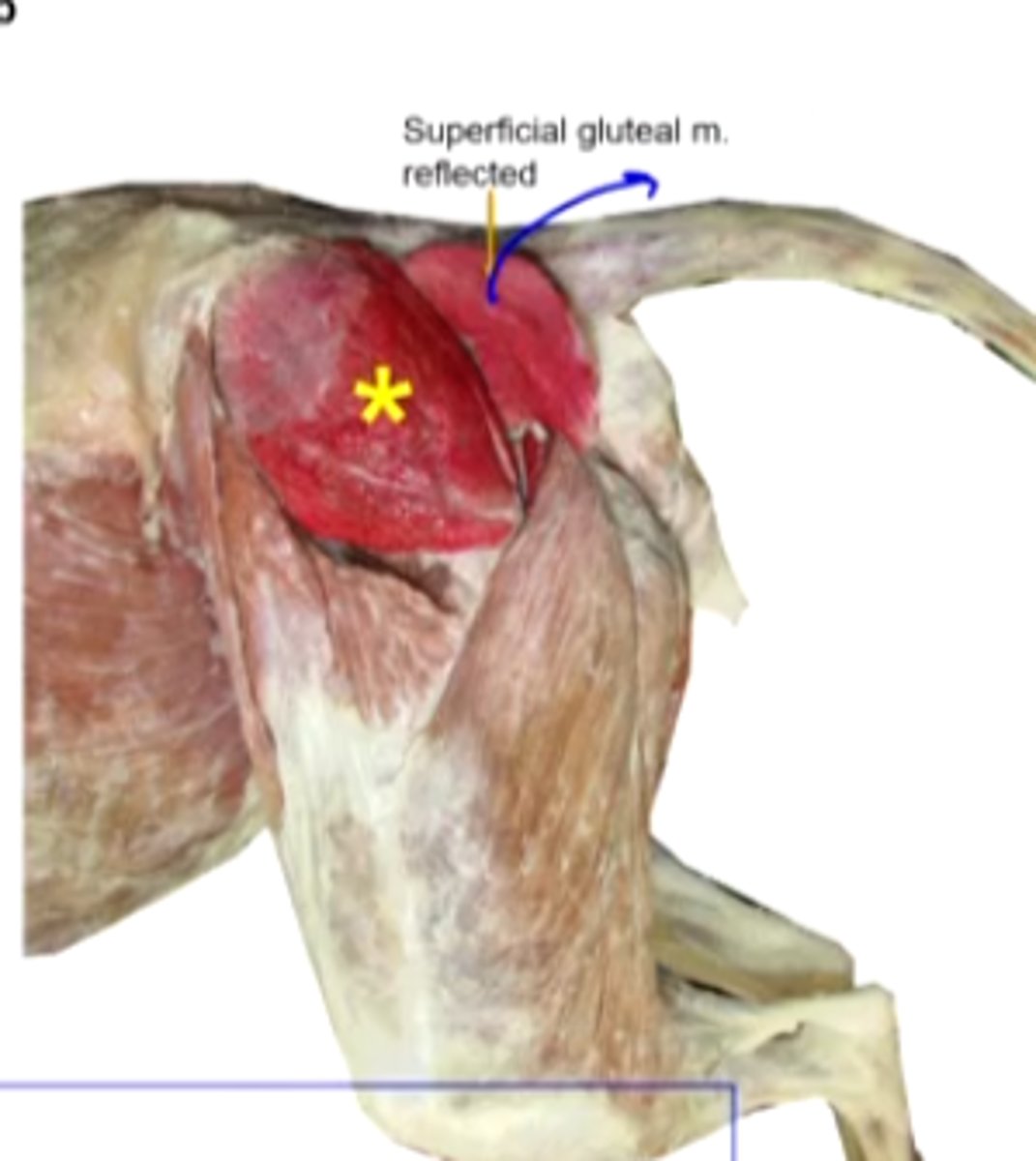
middle gluteal
Which gluteal muscle is the strongest?
extensor
The middle gluteal is a powerful [flexor/extensor] of the coxal joint
piriformis
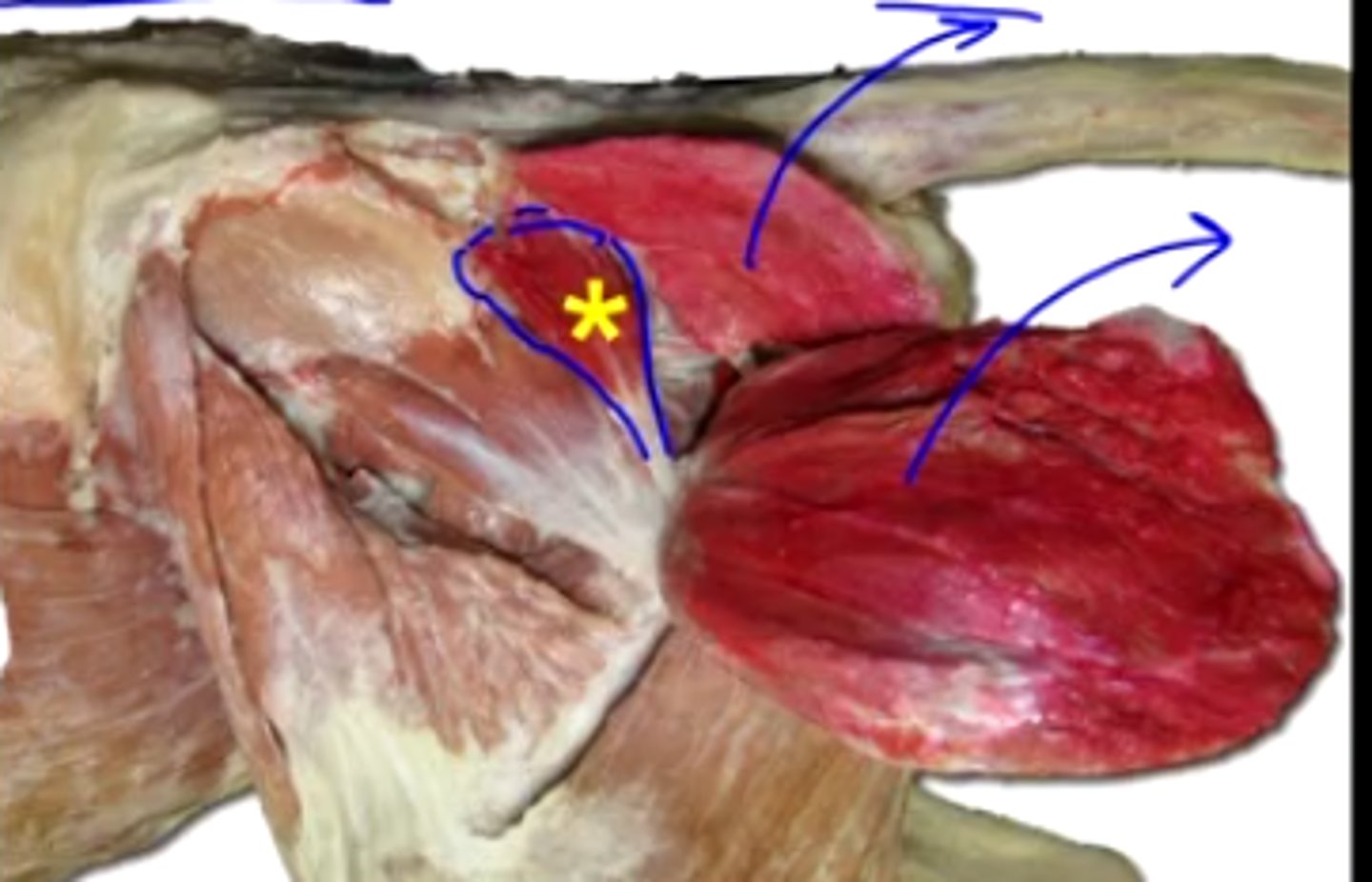
extensor
Piriformis is a(n) [extensor/flexor]
deep gluteal
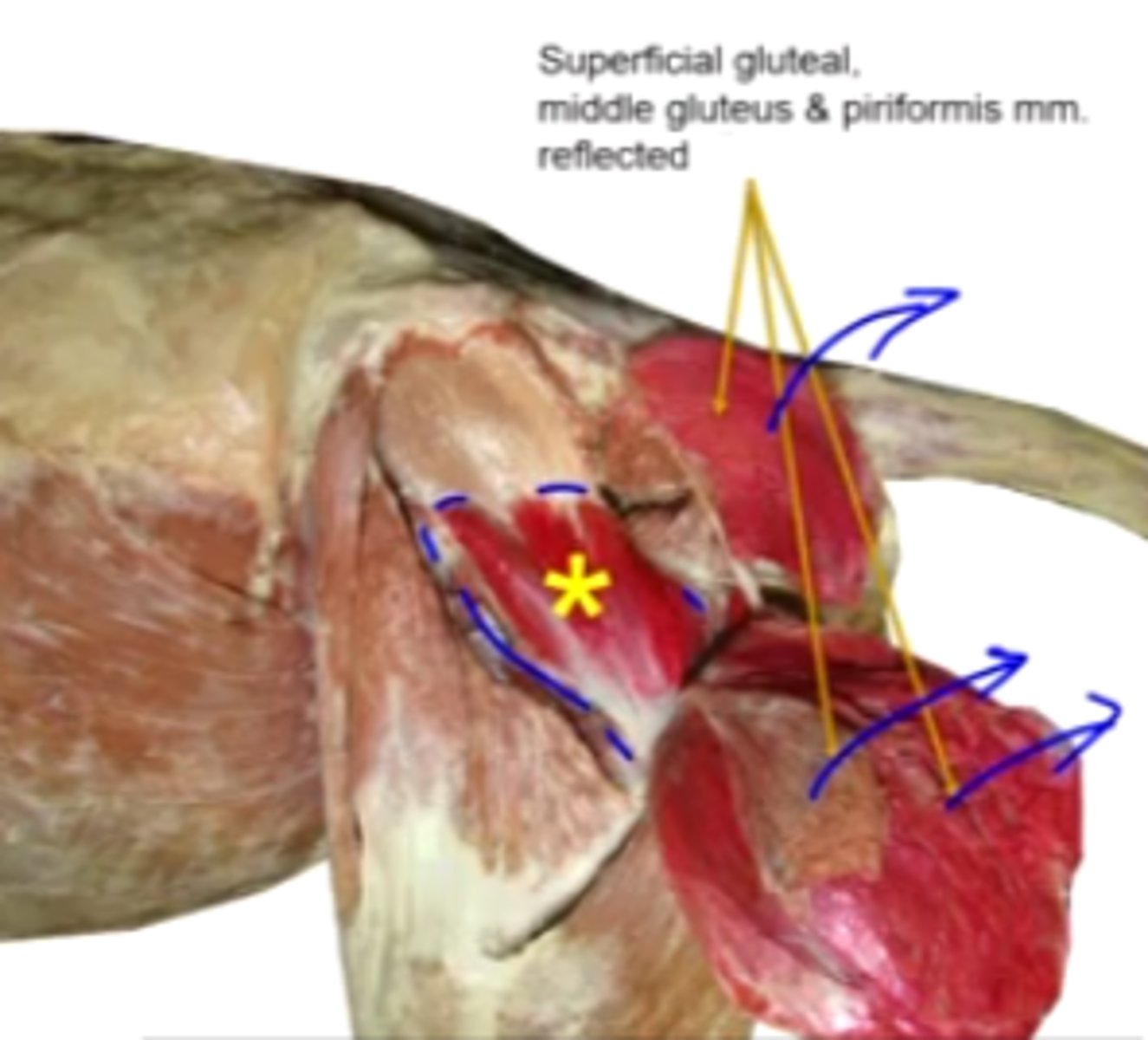
extensor
The deep gluteal is a [flexor/extensor]
genual/stifle joint
What is the name for the "knee" joint?
cranial
If the cruciate ligament is attached cranial in the tibia, it is the _____ cruciate ligament
caudal
If the cruciate ligament is attached caudal in the tibia, close to the popliteal area, is it the _____ cruciate ligament
hyaline
_____ cartilage covers the trochlea and condyles of the femur
fibro
_____ cartilage surrounds the patella
infrapatellar body fat
What serves as a cushion cranial to the genual joint, ventral to the patella?
for strength
Why are the striations of the cruciate ligament "twisted"?
laterally
The cranial cruciate ligament is normally facing [medially/laterally]
medially
The caudal cruciate ligament is normally facing [medially/laterally]
tibia
Are the menisci (mainly) attached to the tibia or the femur?
genual
The capsule in the _____ joint is the larger synovial capsule out of all other joints in the body