Unit 8 - JFK / LBJ - New Frontier / Great Society / Cold War early 60s
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
1960 election
Dem JFK vs. Rep Nixon. JFK won because of the civil rights issue and his better TV appearance.

Great Debates
The Great Debates in 1960 between John F. Kennedy and Richard Nixon.

Kennedy Inaugural Address
In his inaugural address he called on Americans to "ask not what your country can do for you, ask what you can do for your country."

Lyndon B. Johnson (LBJ)
VP under JFK who was sworn in as president after JFK's assassination; Great Society and "war on poverty"

Fidel Castro (Cuba)
Cuban socialist leader who overthrew a dictator in 1959 and established a Marxist socialist state in Cuba (born in 1927)

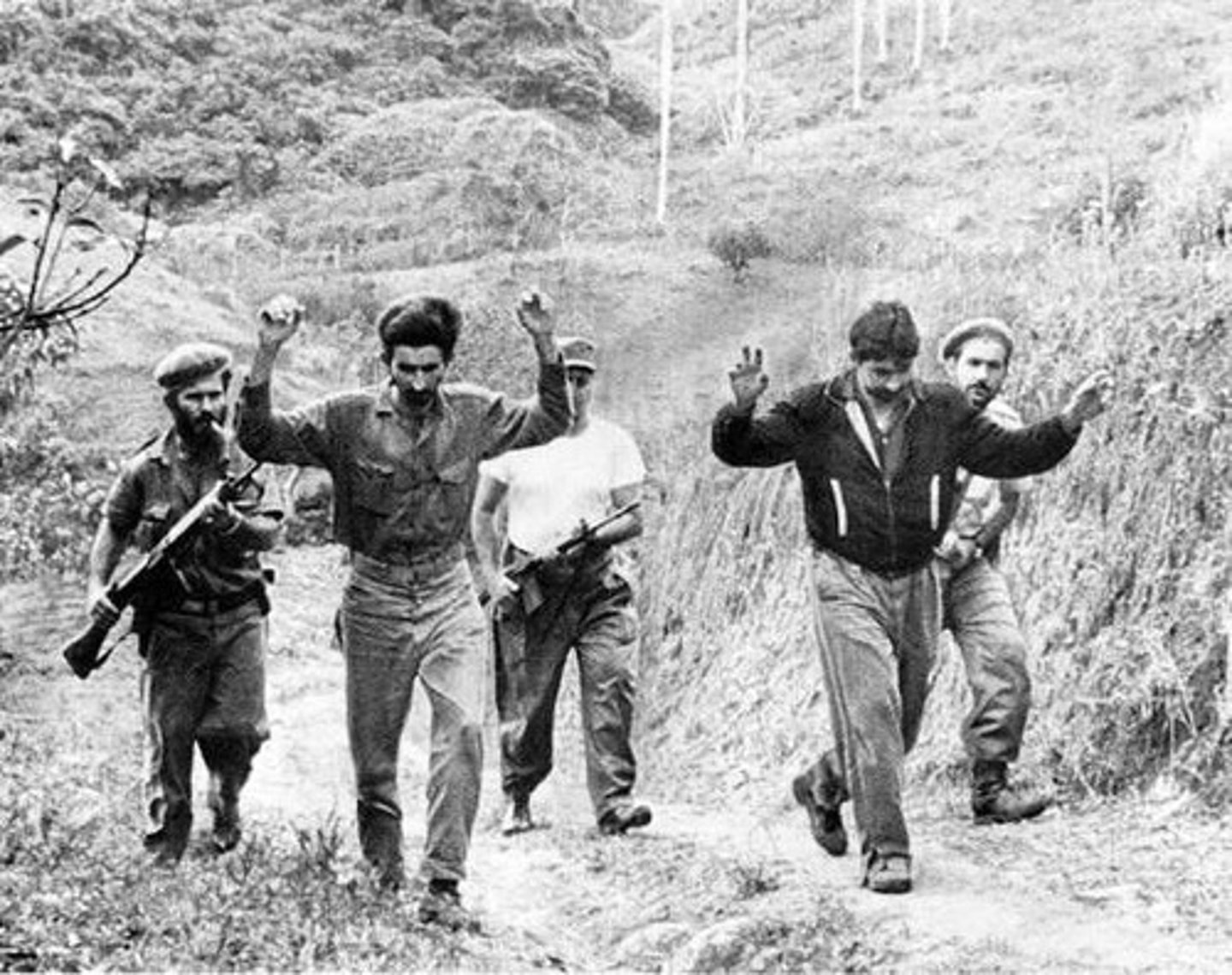
Bay of Pigs Invasion (1961)
An unsuccessful action by a CIA-trained force of Cuban exiles to invade southern Cuba, with support and encouragement from the U.S. government, in an attempt to overthrow the Cuban government of Fidel Castro.

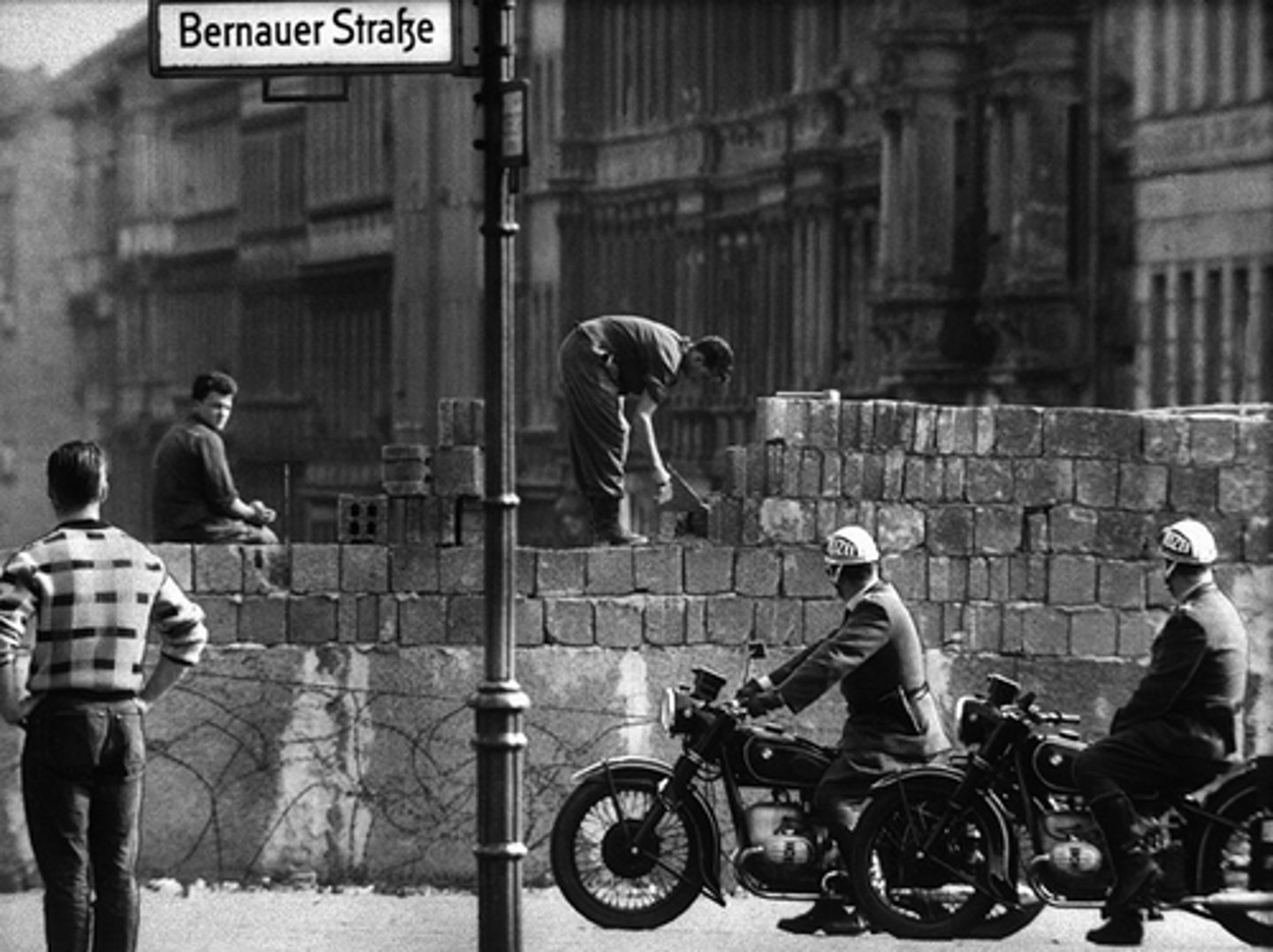
Berlin Crisis of 1961
EISENHOWER & KENNEDY 1961 Following the Soviet occupation of the Eastern Bloc, the people within the occupied areas aspired for independence and soviet withdrawal. However, this did not happen and in turn there was a mass resurgence in the evacuation of laborers and people from the Communist dominated region. In order to restrict emigration the Soviet Union built the Berlin Wall.

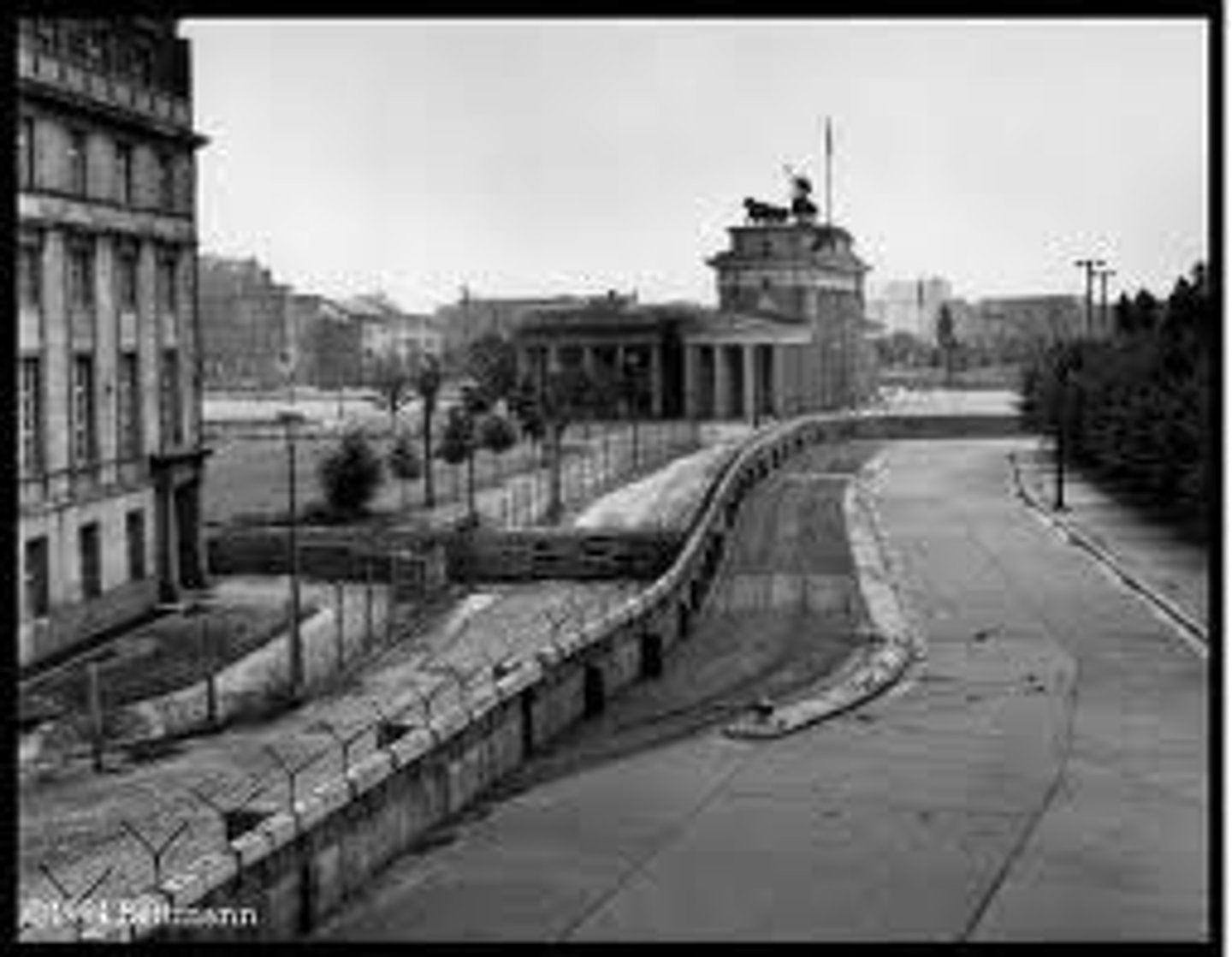
Berlin Wall (1961)
The Soviet Union, under Nikita Khrushchev, erected a wall between East and West Berlin to keep people from fleeing from the East, afterwards Kennedy asked for an increase in defense funds to counter Soviet aggression.

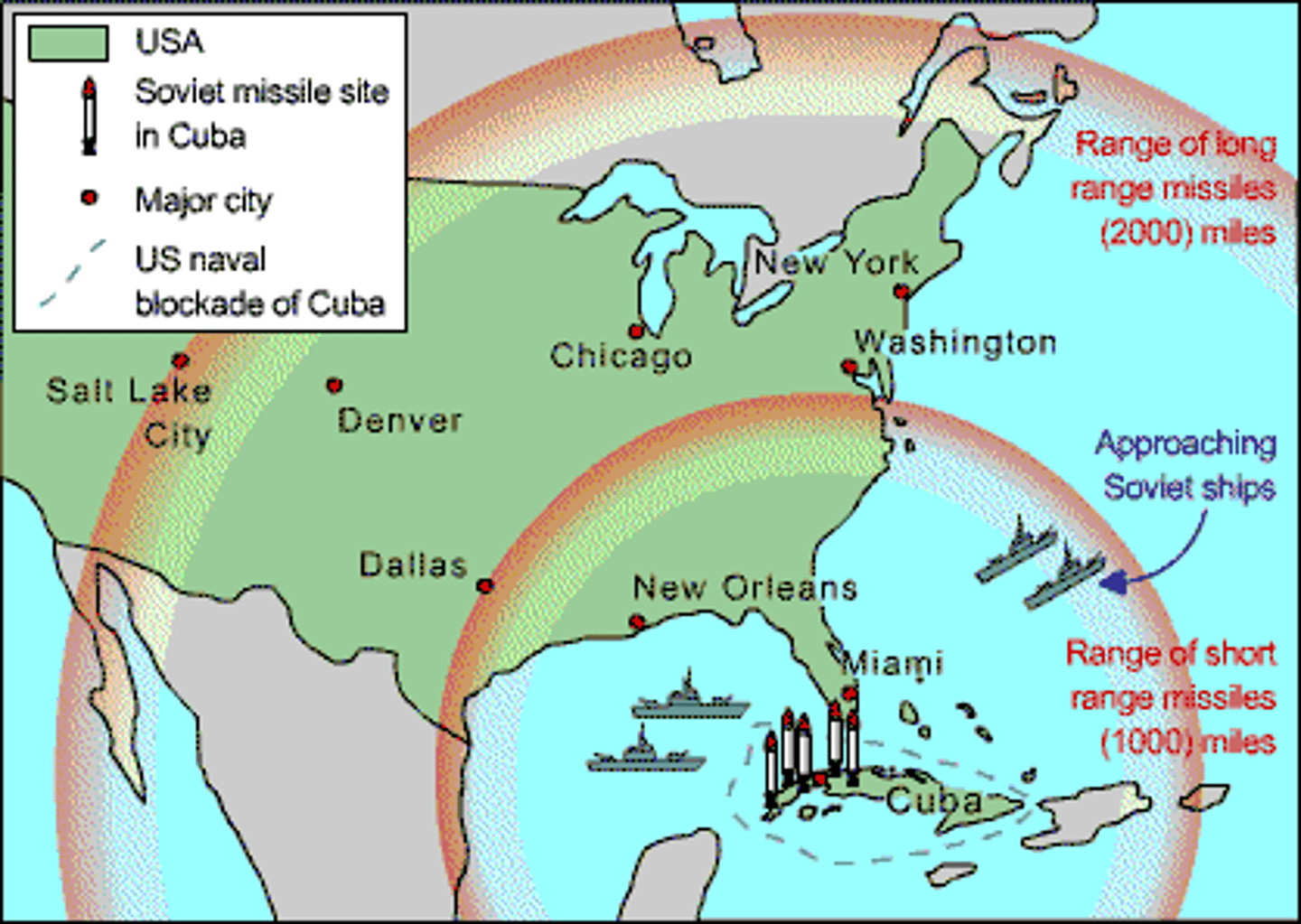
Cuban Missile Crisis (1962)
A confrontation among the Soviet Union, Cuba and the United States in October 1962, during the Cold War.
Brinkmanship
A policy of threatening to go to war in response to any enemy aggression.
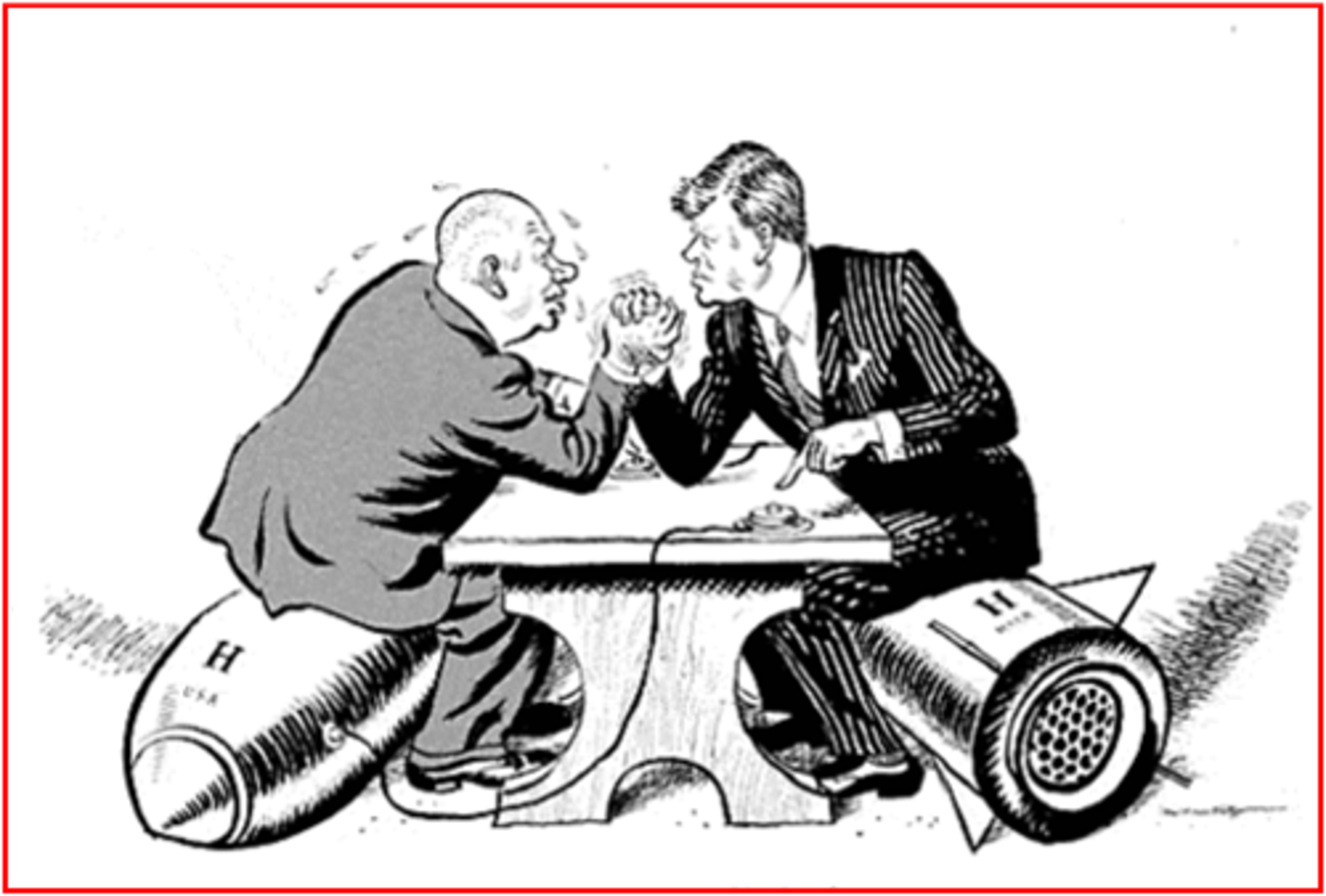
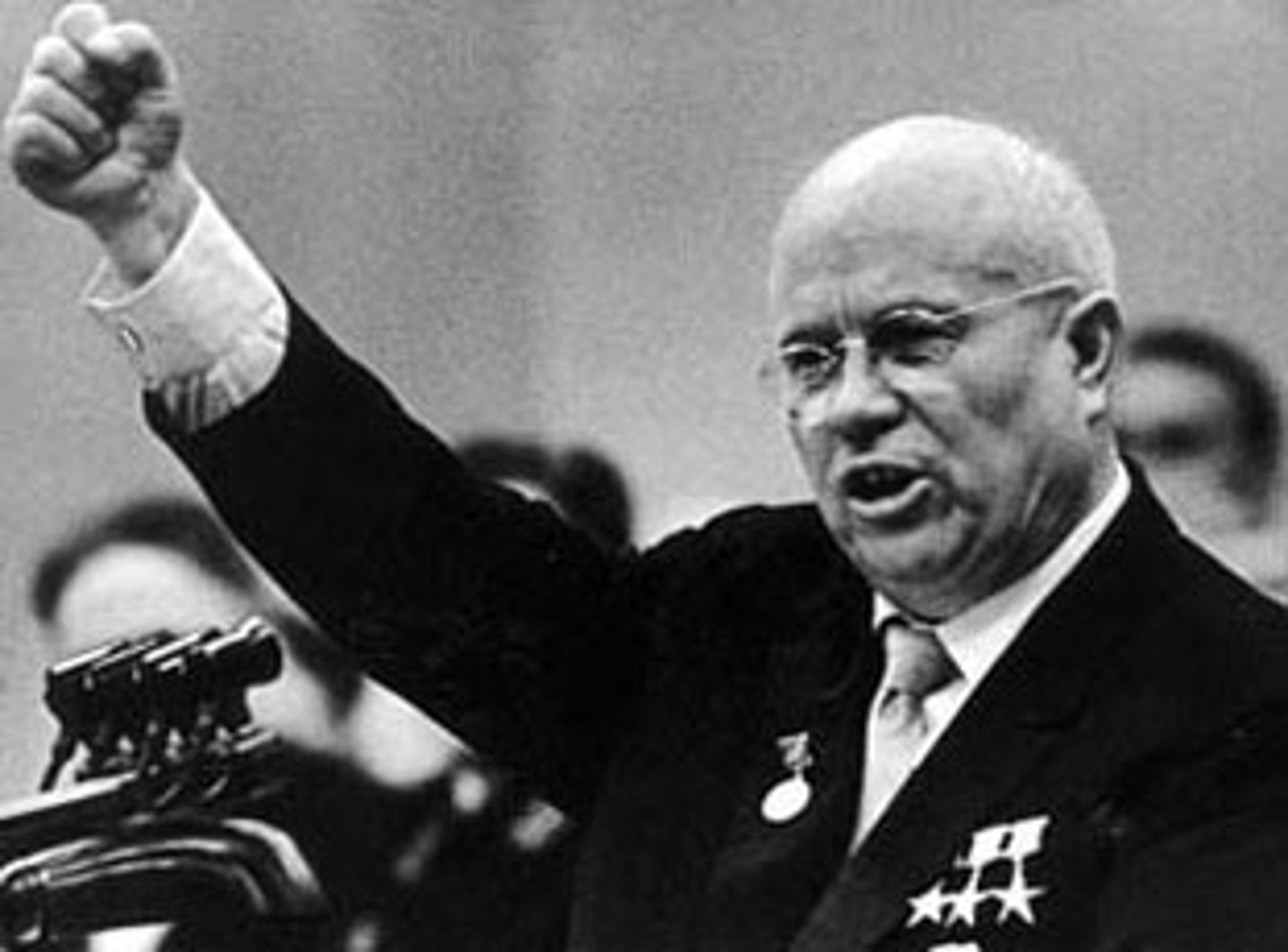
Khrushchev, Nikita
Leader of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964.

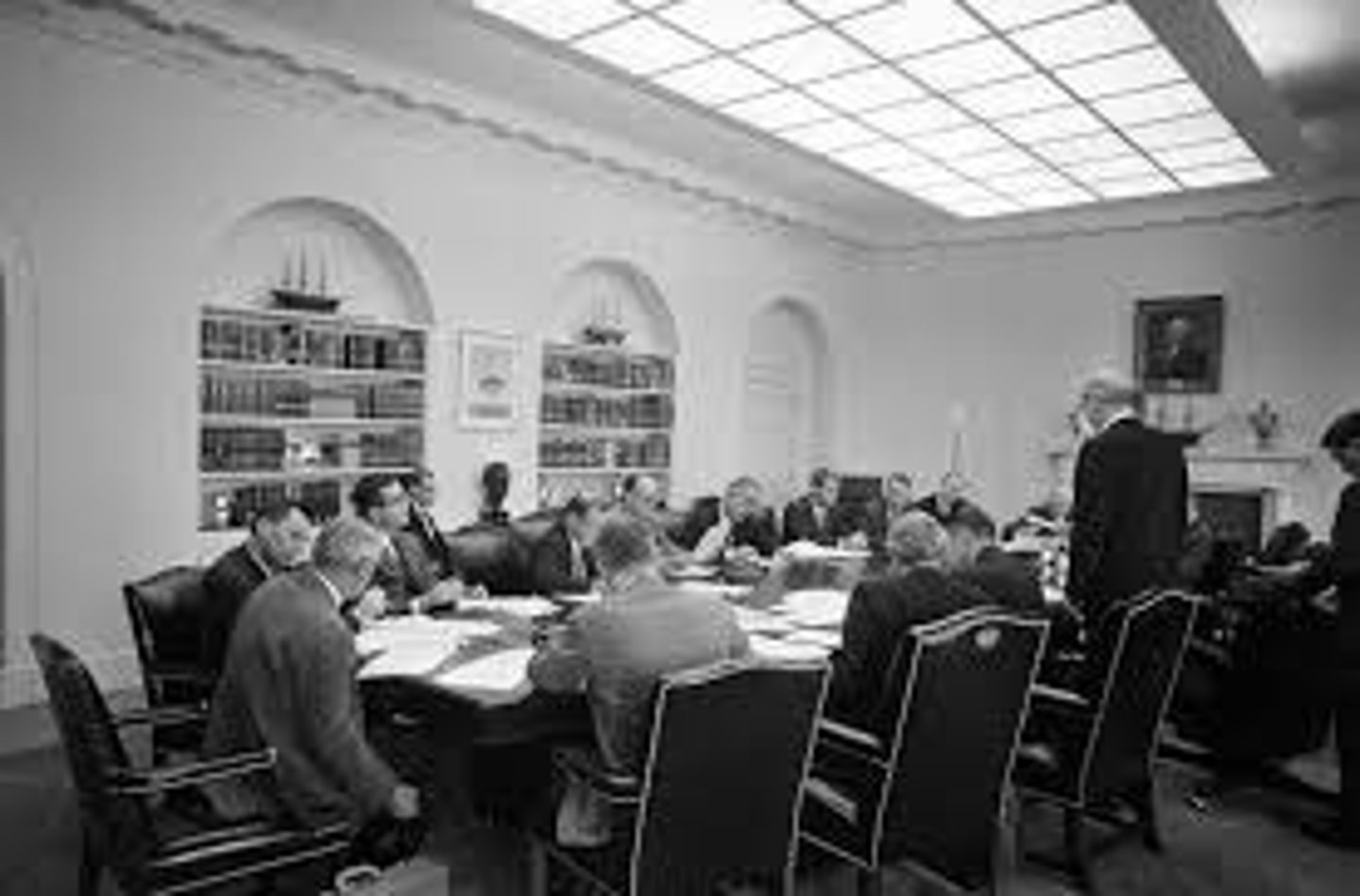
EX-COMM
Secret group that advised JFK during Cuban missile crisis.

Blockade
an act or means of sealing off a place to prevent goods or people from entering or leaving.
Peace Corps
Federal program established to send volunteers to help developing nations

Alliance for Progress (1961)
a series of cooperative aid projects with Latin American governments (Kennedy's plan to improve relations between the US and Latin America); called for a 10-year $20 billion donation to establish good schools, housing, health care, and land distribution; Good effect on Chile, Columbia, Venezuela, and the Central American republics (prevented Communism); Other countries just used the $ to keep the rulers in power

Flexible Response
the buildup of conventional troops and weapons to allow a nation to fight a limited war without using nuclear weapons

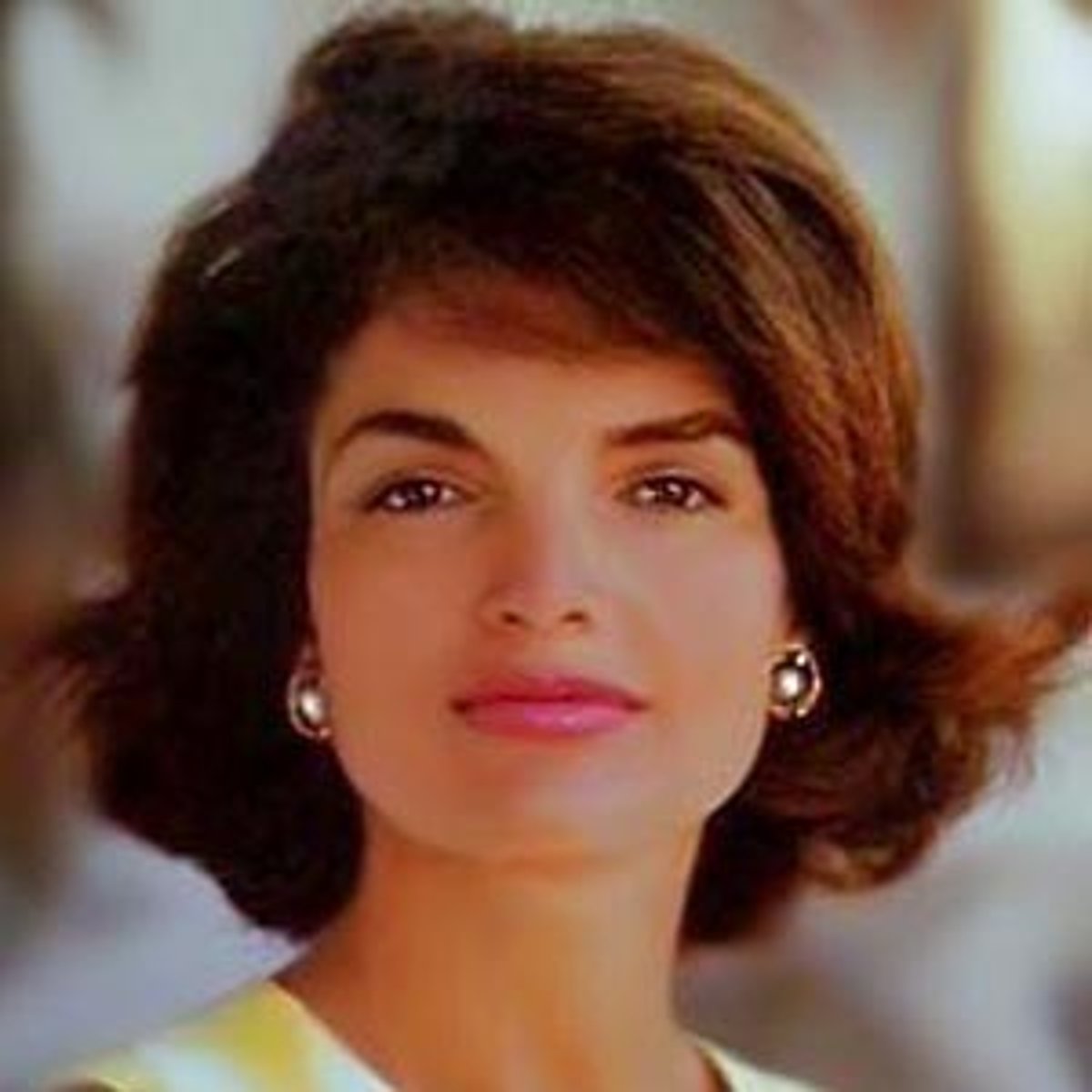
Jacqueline Kennedy
American first lady and wife of president Kennedy; she was known for her style and social grace; was used to create a favorable public opinion about his presidency.

New Frontier
The campaign program advocated by JFK in the 1960 election. He promised to revitalize the stagnant economy and enact reform legislation in education, health care, and civil rights.

Space Race
A competition of space exploration between the United States and Soviet Union.
Earl Warren
Chief Justice during the 1950's and 1960's who used a loose interpretation to expand rights for both African-Americans and those accused of crimes.
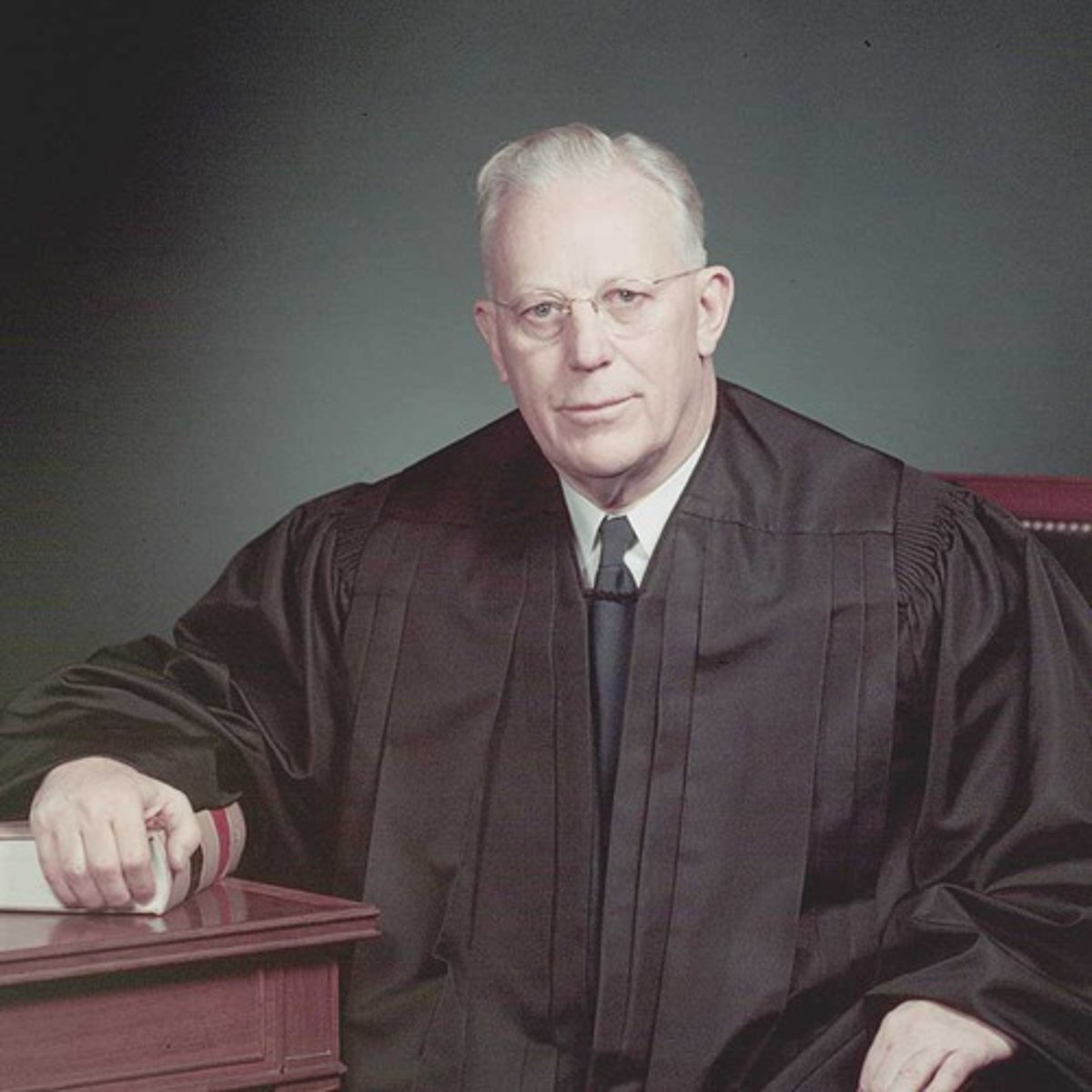

Warren Court
the chief justice that overturned Plessy v. Ferguson in Brown v. Board of Education (1954); he was the first justice to help the civil rights movement, judicial activism

rights of the accused
The protections that the Constitution guarantees to citizens who are accused of crimes.

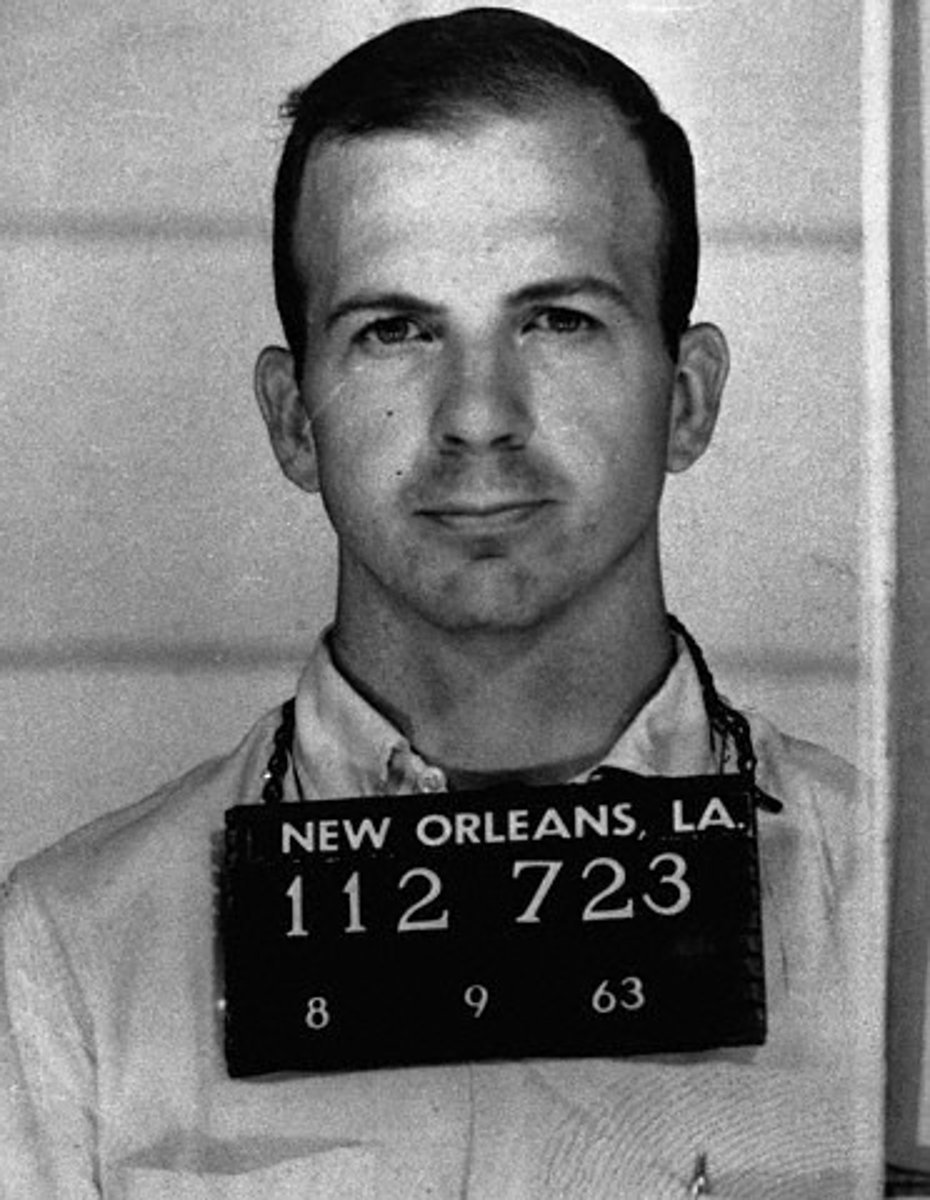
Lee Harvey Oswald
On November 22, 1963, he assassinated President Kennedy who was riding downtown Dallas, Texas. Oswald was later shot in front of television cameras by Jack Ruby.

Kennedy Assassination (1963)
On November 22nd of 1963, while riding in an open limousine through Dallas, Texas, President John F. Kennedy was assassinated by a concealed rifleman; perhaps ironically, the alleged assassin of President Kennedy was himself assassinated a few days later in front of television cameras.
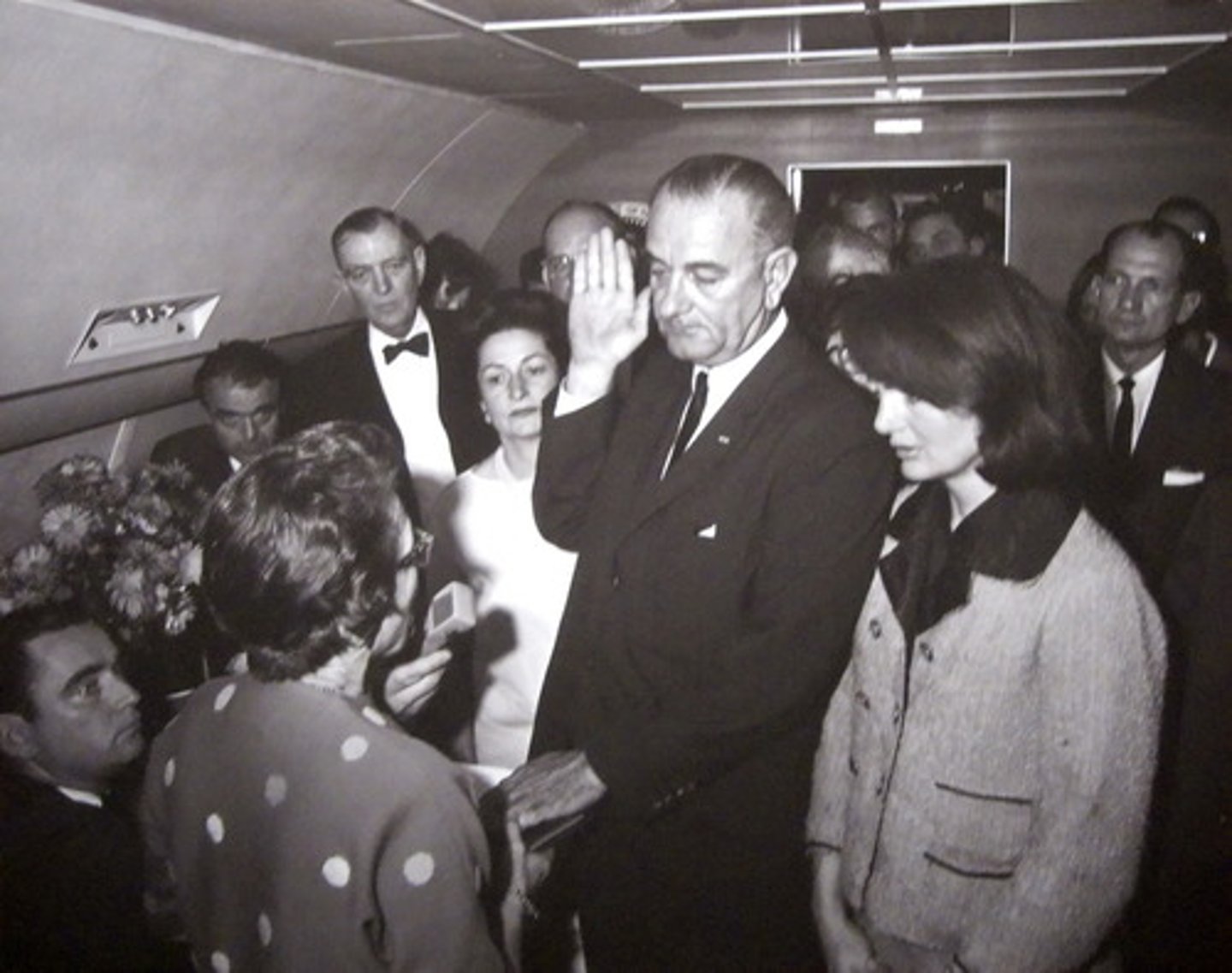

Warren Commission
Commission made by LBJ after killing of John F. Kennedy. (Point is to investigate if someone paid for the assasination of Kennedy.) Conclusion is that Oswald killed Kennedy on his own. Commissioner is Chief Justice Warren.

Kennedy Legacy
The argument over JFK's legacy, as a man and as a president, continues unabated. After JFK's death, Jackie and JFK's aides helped mythologize his presidency as a golden age, a second

Johnson Treatment
LBJ's tactic of "negotiation" with members of congress. He used his size and abrupt manner to manipulate them

War on Poverty
President Lyndon B. Johnson's program in the 1960's to provide greater social services for the poor and elderly

The Great Society, 1964-65
LBJ & Democratic social reforms that sought the elimination of poverty and racial injustice. New major spending programs that addressed education, medical care, urban problems, and transportation were launched during this period. The Great Society in scope and sweep resembled the New Deal domestic agenda of FDR. Most important: Medicare (health care for those over 65), Medicaid (health care for poor, disabled)

Job Corps
program under President Johnson that offered work-training programs for unemployed youth

1964 election
LBJ ran against Barry Goldwater, LBJ won in a landslide victory
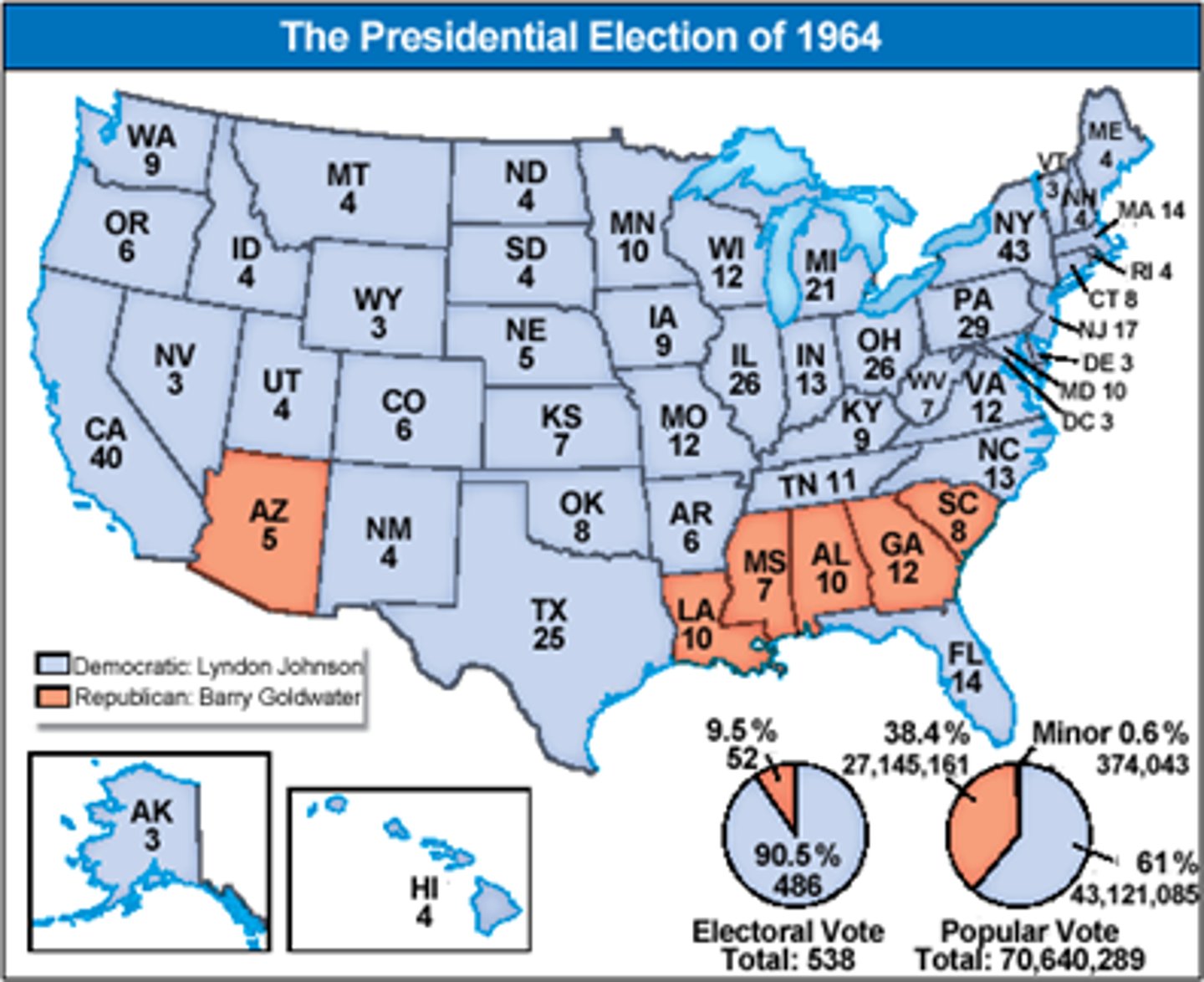
Barry Goldwater
1964; Republican contender against LBJ for presidency; platform included lessening federal involvement, therefore opposing Civil Rights Act of 1964; lost by largest margin in history

Medicaid
A federal and state assistance program that pays for health care services for people who cannot afford them.

Medicare
A federal program of health insurance for persons 65 years of age and older
