Lecture 3: Biological Bases of Behaviour: The Nervous & Endocrine Systems and the Developing Brain
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Module 1: Biological Foundations of BHD Lecture 3: The Nervous & Endocrine Systems and the Developing Brain - Tutorial 1 - Required Readings from Psychology textbook
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Biopsychosocial lifespan model
Considers the whole person (biological, psychological and social)
Lifespan model
Early experiences can shape the brain that can impact people throughout the rest of their lives
Frontal lobe and prefrontal lobe
Governs executive functions - organising, planning, attentional control. Regulates behaviour.
The two subgroups of the Peripheral Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System and Autonomic Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System
Carries messages from CNS to muscles throughout the body, controlling and coordinating voluntary movement
Autonomic Nervous System
Controlling the involuntary actions of our internal organs and glands, which (along with the limbic system) participates in emotion regulation
Subgroups of Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic Nervous System and Parasympathetic Nervous System
Sympathetic Nervous System
Division of the autonomic nervous system engaged during a crisis or after actions requiring fight or flight (emergency situations)
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Division of the autonomic nervous system that controls rest and digestion (everyday situations)
Function of frontal lobe and pre-frontal cortex
Higher cerebral functions, abstract thought, planning, decision making.
Function of Hippocampus
New learning and formation of memory
The Hippocampus and depression
Smaller in depression - more depression related to smaller hippocampus
Function of Amygdala
Emotion centre of the brain; processes feeling. Plays key roles in fear (fear conditioning - predicting when something scary is about to happen)
The Amygdala and depression
Higher activity with depression
Function of Hypothalamus
Regulates motivated behaviour (heart rate, temperature, thirst, sexual motivation)
Hypothalamus and depression
Key in stress response system (HPA axis) and triggers stress response
Function of Thalamus
Major relay system of the brain: Sends signals to other parts of the brain to interpret information
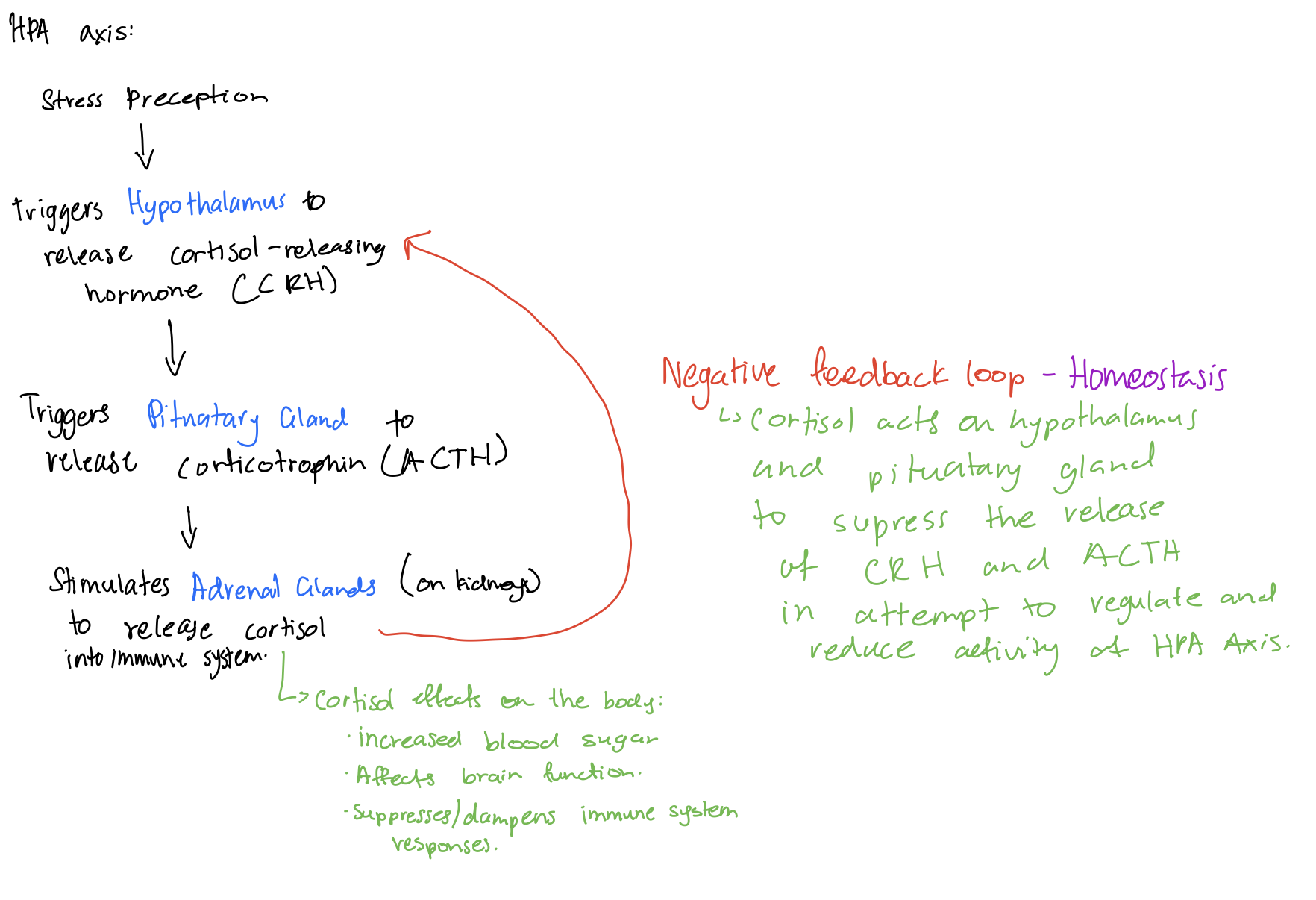
Stress response system (HPA axis)
Stress perception triggers hypothalamus to release cortisol releasing hormone (CRH). This triggers the pituitary gland to release corticotropin (ACTH), which stimulates the adrenal glands (located on the kidney) to release cortisol and other hormones into the immune system to prepare the body to deal with the stressor.
Characteristics of Depression
Weight loss/gain (changes in appetite)
Sleep disturbances
Loss of pleasure in things they previously enjoyed
Problems thinking, concentrating
Isolation, withdrawl from friends & activites
Feelings of helplessness & hopelessness
Depression and GBD (noncommunicable diseases)
Depression ranks 2nd in the Global Burden of Non-communicable diseases and is the leading risk factor for suicide
Neurotransmitters associated with depression
Serotonin, Dopamine, Norepinephrine (adrenaline), Acetylcholine, Glutamate, GABA
What is dopamine associated with?
Reward and pleasure
What is Acetylcholine associated with?
Memory, learning, recall
What is Glutamate involved with?
Bipolar disorder
Serotonin levels in people with depression
Lower levels of serotonin in people with depression
What does GABA do?
Reduces anxiety
The hormones associated with depression
Cortisol, Estrogen and testosterone
Cortisol in depression
Is higher
Estrogen and testosterone in depression
Is lower
Brain development at 6 months
Neurons start to connect with other neurons around them
Brain development at 2 years
Many more connections between neurons - connectivity is important in the brain
Sequence of brain development
Primitive areas, Cortical areas and Prefrontal cortex
Brain development of Primitive areas
Limbic system develops over the first three years (emotional development) - baby develops a sleep cycle
Brain development of Cortical areas
The development of thinking and cognitive processes
Brain development of the Prefrontal cortex
Controls executive functions - develops middle childhood into adulthood (mid 20’s)
The optimal environment for a baby and why
A warm and responsive caregiving relationship - environment must be nurturing and responsive during this time to optimise positive development it is a sensitive time period where the brain is vulnerable
Positive or normal stress
Moderate, short-lived stress responses are normal part of life & learning to adjust to this kind of stress is adaptive
Tolerable stress
Serious illness, frightening accident, parental separation - tolerable if there is parental support that creates a safe environment. (e.g. a parent is hospitalised - child is away from parent for a period of time)
Toxic stress
Strong, frequent or prolonged activation of the body’s stress management system - stressors are chronic, uncontrollable & are experienced without the support of a caring adult.
When does toxic stress usually occur?
When in a harsh environment - maltreatment and neglect of children. The absence of the warm, responsive caregiving relationship
What does prolonged periods of stress mean in children? (constant activation)
Toxic stress resulting in a stress response system set permanently on high alert
Features of Occasional Inattention
Intermittent, diminished attention in an otherwise responsive environment
Effects of Occasional Inattention
Can be growth promoting under caring, supportive environments
Features of Chronic (ongoing) Under-stimulation
Ongoing, diminished level of child-focused responsiveness & developmental enrichment
Effects of Chronic (ongoing) Under-stimulation
Often leads to developmental delays and may be caused by a variety of factors
Child stress scenario in a caring household
When a child is stressed, the HPA axis (stress response system) activates - then a caring caregiver calms them down and relieves their stress and the body quickly returns to normal.
Child stress scenario in a toxic/neglected household
No caring adult present to act as a buffer against stress so the stress response stays activated
Example of child stress in a neglected household
The extended period of time away from parents can trigger the stress response system
Clinical presentations of toxic stress
Hyperactivity - problems regulating activity level/behaviour
Child appears withdrawn
Hyper vigilance (stress response system becomes easily triggered)
Child presented with learning problems
What does contuinous exposure to cortisol due to high stress levels mean?
The functions of other organs of the body will be affected. High stress levels —> physical problems
Adrenaline
Mobilises energy stores and alters blood flow, thereby allowing the body to deal with a range of stresses
Cortisol
Mobilises energy stores, suppresses immune responses
What has sustained levels of cortisol shown?
To damage the hippocampus, leading to impairments to regulate certain stress response
What is the leading cause of death for males in NZ?
Ischemic heart disease
Behavioural patterns contribution (%) to premature deaths
Contribute 40% to premature death
Genetic predisposition contribution to premature deaths
Contributes 30% to premature death
Social circumstances contribution to premature deaths
Contributes 15% to premature death
Health care contribution to premature death
Contributes 10% to premature death
Environmental exposure contribution to premature death
Contributes 5% to premature death
Tolerance
Reduction in the effect of a drug as a result of repeated use, requiring users to consume greater quantities to achieve the same effect
Withdrawal
Unpleasant effects of reducing or stopping consumption of a drug that users had consumed a lot of
Physical dependence
Dependence on a drug that occurs when people continue to take it to avoid withdrawal symptoms
Psychological dependence
Non-physiological (body) dependence on a drug that occurs when continued use of the drug is motivated by intense cravings
Hypnotic
Drug that exerts a sleep-inducing effect
What drug is categorised as a depressant?
Alcohol (and sedative hypnotics)
Stimulant
Drugs that increase activity in the central nervous system (CNS) including heart rate, respiration, and blood pressure.
What neurotransmitters does cocaine increase the activity of?
Dopamine
Narcotic
Drug that relives pain and induces sleep (e.g. opioid drugs such as heroin, morphine, and codeine)
Hallucinogenic
Causing dramatic alternations of perception, mood, and thought (e.g. marijuana)
Psychoactive drugs
Substance that contains chemicals similar to those found naturally in our brains that alter consciousness by changing chemical processes in neurons.
Pituitary Gland
Referred to as the "master gland" because it produces and releases hormones that regulate the activity of other endocrine glands in the body
Endorphins are the neurotransmitters that..
act as natural painkillers