Lecture 1 (in progress)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
*List the important properties of DNA (5)
Stores information compactly
Must be copied precisely
Information must be accessible to be copied into RNA
Must be stable (DNA in daughter cells must be identical to DNA in parental cells)
Must go through change mutagenesis at a low rate
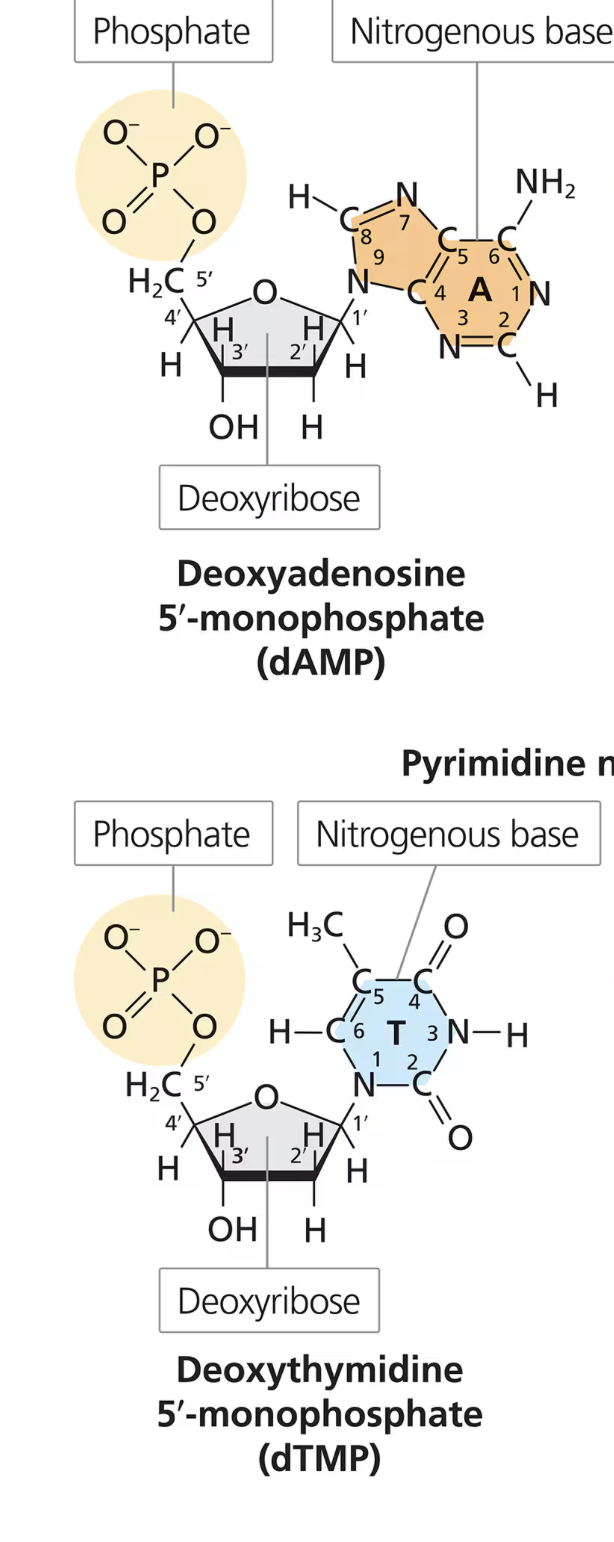
*What are the 3 parts of a DNA nucleotide? + draw the DNA nucleotide + draw the different carbons and what parts they’re attached to + which bonds?
Deoxyribose sugar - A 5-carbon sugar (5 sides)
1’ carbon:
Oxygen connects the 1’ carbon to the 4’ carbon
nucleotide base is attached to the 1’ carbon VIA covalent bond
2’ carbon:
Hydrogen at 2’ carbon (which is why it’s called a DEOXyribose, without oxygen)
3’ carbon:
OH (hydroxyl) group attached to 3’ carbon
OH has phosphodiester bond with the next nucleotide
5’ carbon:
projects outward from the 4’ carbon
a phosphate is attached to the 5’ carbon
One nitrogenous base (A C T G)
Up to 3 phosphate groups
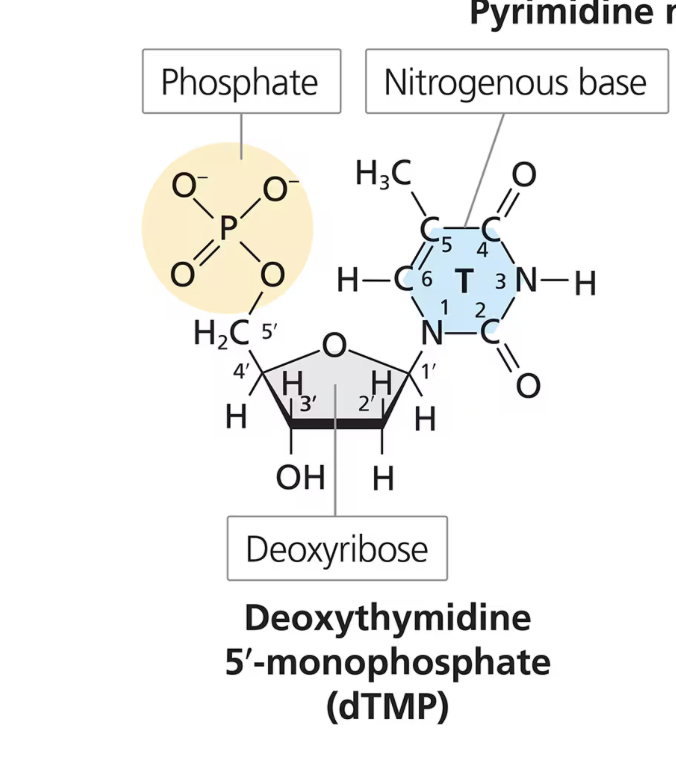
monophosphate
DNA nucleotide form when it is in a nucleotide chain
Triphosphate
DNA nucleotide that is free and not in a nucleotide chain
2 structures of nitrogenous bases
Pyriminidnes - single-ringed, C T
Purines - double-ringed, A G
dNMPs
Monophosphate forms of deoxynucleotides (DNA nucleotides)
N→ any of the four nucleotide bases (for example, Adenine base would be called dAMP, Guanine dGMP, etc…)
*WHEN DNA HAS 1 PHOSPHATE
dNTPs
Triphosphate forms of deoxynucleotides (DNA nucleotides)
N→ any of the four nucleotide bases (for example, Adenine base would be called dAMP, Guanine dGMP, etc…)
*WHEN DNA HAS 3 PHOSPHATES
NTP
When RNA has 3 phosphates
Draw a purine vs a pyrimidine nucleotide
MAIN IDEA: purine has 2 rings, pyrimidine has 1 ring
What bonds hold nitrogenous bases together?
Hydrogen bonds (they act like velcro)
How many hydrogen bonds hold A and T together?
2 hydrogen bonds
How many hydrogen bonds hold G and C together?
3 hydrogen bonds
What is the direction for template vs. new DNA strands?
Template strand runs from 3’ → 5’
New strand is synthesized from 5’ → 3’
this is so that the hydrogen bonds are stable between nitrogenous bases
DNA polymerase
enzyme that adds new nucleotides to the growing DNA strand
Explain the steps for DNA strand elongation
DNA polymerase forms a phosphodiester bond with the 3’ OH of one nucleotide and the 5’ triphosphate group of the incoming nucleotide
When this bond is formed, 2 out of 3 of the phosphates are removed from the incoming nucleotide
This extends the DNA strand
Why is DNA antiparallel?
So the hydrogen bonds between nucleotide bases are STABLE
Semiconservative DNA replication
if you replicate a DNA strand, one side of the replicated strand would be new, while the other side of the replicated strand would be old
conservative DNA replication
if you replicate a DNA strand, both sides of the replicated DNA would be new
dispersive DNA replication
if you replicate a DNA strand, new and old DNA will be dispersed together on both sides
PCR
DNA replication that takes place in a test tube
PCR steps
Denaturation (mixture is heated to 95 degrees celsius → DNA denatures from double-stranded to single stranded) → (breaks hydrogen bonds)
Primer annealing (temperature is lowered to 45-68 deg celsius → lets primers attach to the DNA strands)
Primer extension (temperature is raised to 72 degrees celsius,