Seed Plants
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Sporophyte
phase is dominant in seed plants and seedless plants
Heterospory
in seed plants and seedless plants
Gametophyte
reduced to microscopic structure inside sporophyte in seed plants
Pollen and Seeds
adaptations for true terrestrial living (not water dependent)
Female gametophyte and sporophyte
always haploid
Seed coat
protection around the plants embryo
Pollen
male gametophyte (microscopic)
Gymnosperms
“naked seed”- conifers, cycads, ginkgophytes
Angiosperms
“seed in vessel”- flowering plants, fertilization and embryo development occur inside the plant
Monoecious
“one home”- male and female cones on the same plant (in gymnosperms)
Tracheid
xylem has more lignin cells to transport water and minerals
Conifers
dominant phylum of gymnosperms, leaf shaped like needle (pine trees)
Conifer
a sporophyte and monoecious with heterosporous
Microsporangia
are located on male pollen cones
Produce female megaspores
Megasporangia
Produce male microspores and contain microsporocytes
Microsporangia
Microsporocyte cells
diploid and produces haploid microspores via meiosis
2 celled male gametophyte (pollen) through mitosis
Microspores produce
contains two haploid cells produced by mitosis
Pollen Grain
Megasporangia
located on female ovulate cones
diploid cells in the microsporangium which produces megaspores (4 haploid cells via meiosis)
Megasporocytes are
Female Gametophyte
produces archegonium which makes haploid egg by mitosis
Sepals
photosynthetic (D)
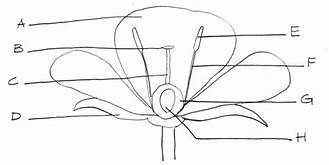
Stigma
part of carpel (female flower) (B)
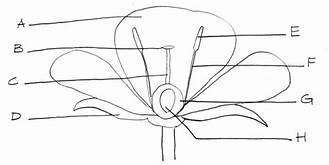
Style
part of the carpel, female flower (C)
Ovary
part of the carpel, female flower (H)
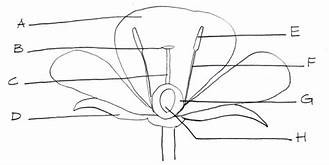
Anther
part of the stamen, male flower (E)
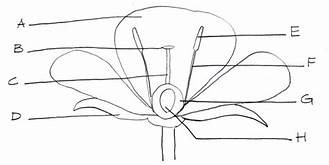
Filament
part of stamen, male flower (F)
Perfect flower
is monoecious with carpels and stamen
Gynoecium
female flower which will produce eggs (also called carpel of pistil)
pollen is deposited
stigma is where
Androecium
the male flower which will produce male gametophyte-sperm
megasporangia
Ovule contains
microspores, microsporangia
Anther contains
Pollen (mitosis)
male gametophyte
two haploid cells surrounded by sporopollenin
Pollen have
tube cell and generative cell
Pollens two cells are called
Female Gametophyte
divides three times via mitosis to make eight nuclei
Polar nuclei
contains two nuclei- will become endosperm
Mature embryo sac
1 egg, 2 synergids, 3 antipodal cells that degenerate, and a central cell with polar nuclei
Double Fertilization
1 sperm and egg fuse to form diploid zygote, 1 sperm fuses with the polar nuclei cell to form a triploid cell that will become the endosperm
Cotyledon
leaf like structure in embryo
Pollination
transfer of pollen from male to female
Fertilization
male sperm fusing with female egg
Self- pollination
transfer of pollen from male to female on same plant
Cross pollination
transfer of pollen from male of one plant to female of a different plant
Monocots
one cotyledon, petals in symmetry of 3 or 6, leaf venation is parallel, multiple roots
Eudicots
two cotyledons, symmetry of 4 or 5, lead venation is networked, on main root