Unit 3
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
The original schools
Conflict, Functionalism, symbolic interaction
Views the original schools omitted
race and feminism
What is research?
An attempt to develop knowledge based on :empirical’ evidence from the real world.
Why do research?
Babbie: the importance of social research
What assertions about research are made by Babbie and Best?
Babbie: The Importance of Social Research→ Research helps us confirm or deny whether something is true or not that people state
Best: Damn Lies & Statistics→ when you see statistics, it can be easily fabricated or bad, don’t just assume its true.
What is the difference between positivism and verstehen as approaches to research?
Positivism emphasizes ‘objective’ (facts and verifiable data); uncovering research, whereas Verstehen emphasizes ‘subjective’ (personal opinions, feelings, perspectives); understanding the experience of the participants.
Important dates in the history of sociological research:
1850: Martinuea; descriptive (‘empiracally grounded, narratively vivid’ description of the principles governing social life)
1900: quantitiative: durkheim, Du Bois
1930: Chicago, Participant/observer
1950: statistics
1975: combinations and secondary analyses
What is the key difference between quantitative and qualitative?
Quantitative research: numerical, counting things, about a broader thing (survey)
Qualitative research: deeper understanding about a narrower thing (ethnography)
Survey
Survey: Quality depends on having the right people, right questions, experiments. (utilizes surveys and has a focus group)
steps:
define research question
literature search
(focus group)
compose, pilot and revise questionnaire
collect and analyze data
draw conflusions and write.
treated ‘real’ like an experiment, lab/field experiments, problems
ethnography
Ethnography:
steps: Choose topic and join group.
stage 1: keep your mouth shut
stage 2: penetrate to a true understanding
stage 3: withdraw and write
example: life history/oral history, case study
What does survey and ethnography each do best?
Survey can describe/explain:
what they do well (size)
what they do poorly (depth)
Ethnography can:
offer in-depth, qualitative insights into social groups and cultures through direct observation and immersion, allowing for a nuanced understanding of lived experiences and social dynamics
however its limits: hard to repeat precisely, may not be representative, researcher’s focus is selective, researcher may ‘go native’
Four examples of where and why sociological research is used
Where:
public sector (government)
to understand social problems and formulate policy
private sector (business)
to understand groups for better marketing and public relations
education sector (research U’s)
to advance knowledge
Nonprofict sectors (Ngos)
to improve society
Activism
An action (An intentional effort to create change) Marx called this praxis.
What is the relationship of activism to theory and research?
Activism connects theory and research by applying theoretical insights to real-world issues, using research to inform actions and advocating for change based on empirical findings.
Marx’s word for action in the world
Praxis
Categories of physical world activism
there are many but some include:
conciousness raising
community building
lobbying
media activism
propaganda
economic activism (boycott, divestment)
protest
strike action
non-violent confrontion
violent confrontation
revolution
Key thing about al of these: ITS AN ACTION!! PHYSICAL ACTION
Three levels of Milbrath’s hierarchy and online activities: digital spectator
digital spectator activities
clictivism (endorses by liking, upvoting, or following. Individual is remote, detached, does not have original voice, requires few resources.) Large volume of ‘clicks’ can add legitimacy to a cause.
metavoicing (echo chamber) sharing, retweeting, reposting. individual adds their voice enhancing/detracting from the original message. impact based on size of individuals social network and their status as an influencer.
Assertion (content creation) video, audio, image, text. Low resuorces, but more skill. Social movement organization often rely on top down messaging and under employ this grassroots method. The risk: individual content creators could go off message.
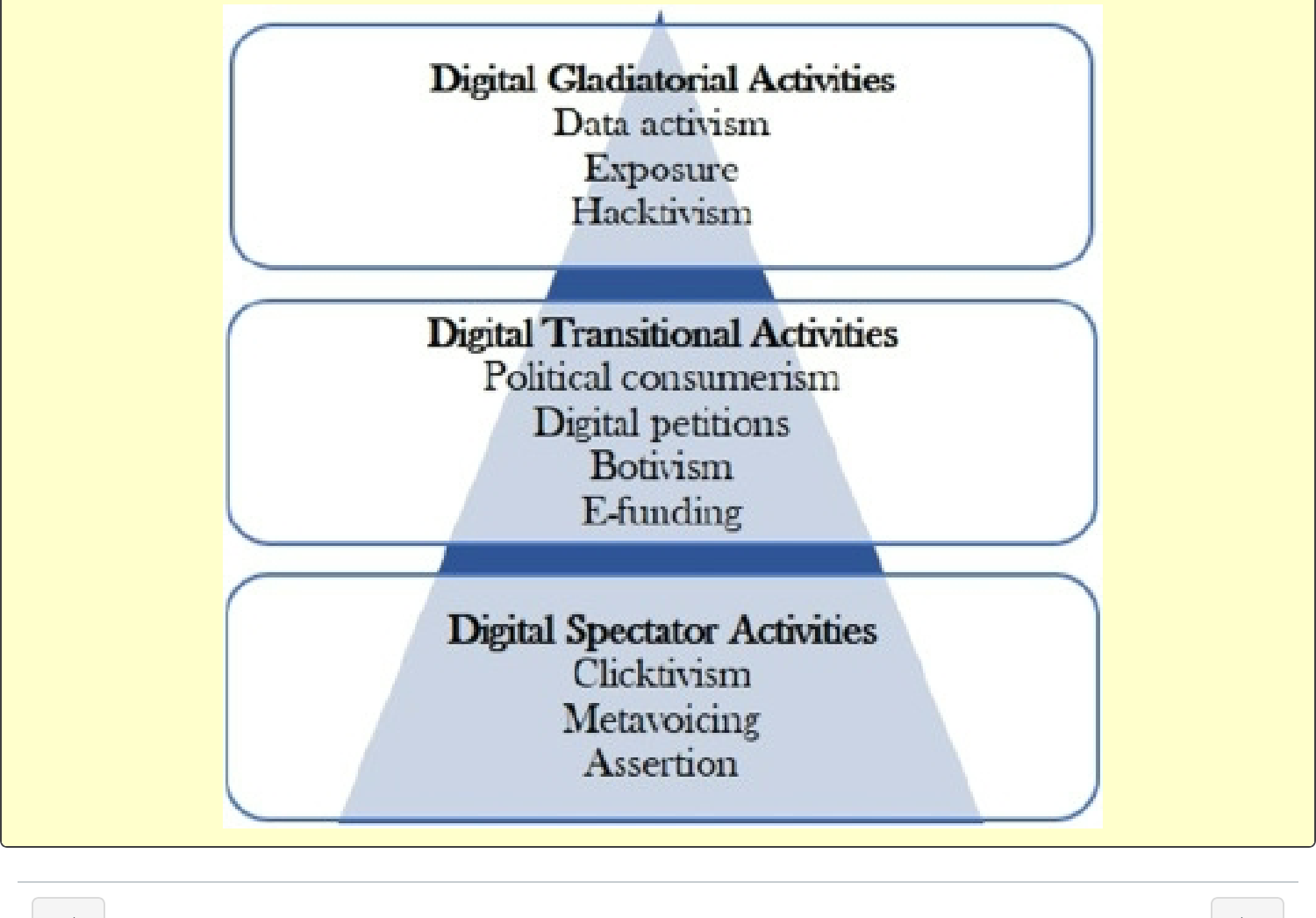
Milbrauth’s hierarchy and online activities: digital transitional
Digital petitions: Government sponsored (we the people) a response is guaranteed if a minimum number of citizens sign. Effort is for the creator and implementer of the petition not the signers. Government response is at least another ‘promotional’ effort.
Botivism: ‘bot’ + ‘activism’. applications. that prod action, ask for money, share information, even respond to trolling. medium resources, much less effort than human counterparts. Big effect for limited investment
E Funding: Providing revenue for a cause. Donation buttons and online auctions, to hacking accounts and ransomware. Impersonal, individ. contributions are selfdom very impactful. Cryptocurrency activities have high potential.
Milbrauth’s hierarchy and online activities: digital gladitorial
data activis: volunteers rescue, preserve, and disseminate open data when governments refuse to share data or remove it. Requires, time, skills. Not advocating a particular position, working for freedom/preservation of information.
Exposure: Unauthorized leaking or distribution of confidential info. Done by those with or without legitimate access. May or may not be politically motivated. High effort high risk.
Hactivism: hacking to achieve social or political goals. exposes information, destroys data, or disrupts operations. may target gov, organizations, or individuals. Requires high skill level, high risk. Impact can be very high.
definition of social movement:
an organized group that acts with continuity and coordination to promote or resist change in society. (social movements are the most organized form of colective behavior)
aberle’s types of social movements:
alternative: change one behavior
Redemptive: personal transformation movements (hippie, religious movements)
reform: Social change movements (civil rights movements, environmental)
revolutionary: completely change society (reactionary movements ex aryan nation)
Michigan theorist famous for early social movement theory (resource mobilization)
mayer zald
key social movement theories: What is Kornhouser’s mass society theory?
sense of being detached from personal social groups makes non elite individuals feel alienated, so they are more likely to take etreme action against elites.
key social movement theories: What is Mertons relative deprivation theory?
Asserts that people will organize or join social movements in order to obtyain things of which they feel they are being deprived of. ex. resources, rights, voice, status
key social movement theories: What is Zald’s resource mobilization theory?
explores how movements ‘gain momentum by successfully garering resources, competing with other movements, and mobilizing their available resources
key social movement theories: What is Opp’s rational choice theory?
asserts that people will make concious choices to organize and seek change that is in their own self interest
key social movement theories: What is Gamson’s new social movement theory?
stresses cultural factors rather than structural factors. a perspective that emphasizes the relationship between social movements and issues like politics, identity, culture, and social change (not economical based like other ones)
Addams and alinsky (time frame and location and key themes of each)
Jane addams: 1860-1935 (social change through service and reform)
founded hull house
founded chicago women’s school of sociology
became the most prominent woman in america
hands on activism
Alinsky:
social change through confrontation and conflict
generally considered the father of community organizing
organized neighborhoods for protest in 1930s, served as precursor of 1960s grassroot political movements. focused on community
Key differences in style/approach between alinski and addams
alinski believed in community gathering and rallying for protests, while addams preferred hands on, and created the hull house and a college
what sociologist/activist does Terry see as the balance between addams and alinski
Martin Luther King Jr. He believed in non violent confrontation
what is the key trend in the US economy over the past 30 years that stiglitz identifies and discusses?
For the past 30 years, we have been growing apart to worst level since the Great Depression
What is trickle down economic theory?
Investing in the upper class (ie the job creators) causes them to increase business and create jobs for those in the lower classes.
Does stiglitz agree or disafree with trickle down economic theory?
he disagrees and believes in trickle up (benefit the rich by investing in the middle and lower classes)
key ideas about us economic inequality in pew resaerch link
Over the past 50 years, the highest earning 20% of us hjouseholds have steadily brought in a larger share of the country’s total income
income inequality in the us is the highest of all the G7 nations
The black-white income gap in the us has persisted over time
over 61% of americans say there is too much economic inequality in the country today but views difder
the wealth gap between america’s richest and poorer families more than doubled
Middle-class incomes have grown at a slower rate than upper-tier incomes over the past five decades
what is the role of education in opportunity for americans?
Education DOES help to provide opportunity, but the rich get a better education. rich kids without degrees do better than poor kids with degrees
the Gini coefficient
most commonly used measure of inequality; higher than it used to be
Everyones income is
equal = 0. One person gets all the
money = 1.0
approximately what is the us coefficient in 2025?
0.41
what is a good/bad gini coefficient?
elow 0.3 is good; above
0.5 is bad
In analyzing group income differences, which is the most important
factor for women? For African Americans?
women: Industry and occupation
AA: Education and workforce experience
What is the effect of sexuality on pay (up, down, the same) for (1)
gay & bisexual women; (2) gay men; (3) transgender women (biologically male); (4)
transgender men (biologically female)
Gay/bi men: earn 10-32% less than straight men
Gay/bi women: earn the same as other women
Trans women: earnings fell by 30%
trans men: earnings rose slightly
How does Stiglitz blame US economic inequality on society’s (and
specifically the government’s) response to market- based
inequalities? (know examples 2,5,6,7
We have taken away power from the unions which protect workers
taxes are reduced for the rich
corporate taxes as a percentage of GDP have decreased
expenditure programs are decreasing
The CATEGORIES of action Stiglitz would take to reduce US
economic inequality (know I. A and B, IIA, and III A,C,D,E)
CURB EXCESSES AT THE TOP
Level the playing fieldTax reform
HELP THE REST
Help the restPOLITICAL REFORM
Campaign finance reform
Require voting
Make registration/voting easier
Reduce gerrymandering
1. Curb excess at the top
Ex- 2. Strengthen anti-monopoly laws3. Improve corporate governance (especially CEO power to grab money)4. Make bankruptcy law tougher on lenders, easier on borrowers5. End government give-aways6. End corporate welfare (tax code; loan breaks)7. Reduce ability to "buy justice" thru lawyers
II.-A. HELP THE REST (99%)1. Improve access to education2. Provide savings incentives (e.g. assistance in purchasing homes)3. Health care for all4. Strengthen other programs that help those out of work or in poverty (unemployment, food stamps, etc.)
III Political Reform: A. CAMPAIGN FINANCE REFORM
B. ACCESS TO LESS BIASED INFORMATION
C. REQUIRE VOTING
D.MAKE REGISTRATION/VOTING EASIER
E. REDUCE GERRYMANDERINGF. REFORM FILIBUSTER
What are the two scenarios that Stiglitz describes as the alternative
futures of the US
Reform- Moving closer to "Liberty and Justice for all." The 99% will realize they have been duped, OR
the 1% will realize that reform benefits them too.
Current Trend Worsens- Dual economy, possible popular violence
What are frequently used measures of health? How is the US
doing on these measures?
Amenable Mortality- US last among developed nations (except for cancer)
Life Expectancy at Birth- US: 81(M), 87 (F) - 37th overall
Other Measures - US: #26
Infant Mortality- US: 6.1/1000 (US near the bottom because of health system)
Heart disease- US: leading cause of death in the US
What are “Structural Inequities,”?
the systematic disadvantage of one social group over another
(therefore healthy inequities=systematic diff. in the oppurtunities groups have to achieve optimal health, leading to unfair and avoidable diff. in health outcomes)
what are “Social
Determinants of Health”?
Conditions in social environments (places
where people live, learn, work, play, worship,
etc.) that affect health risks, health outcomes,
and quality of life outcomes.
ex. education, employment, housing, wealth, etc
How are “Social
Determinants of Health” and “Structural Inequities,” connected?
Structural inequities (racism, sexism, classism,
able-ism, xenophobia, homophobia, etc.)
use policy, law, and cultural norms to sort people
into social environments that are rich or poor in
the social determinants of health
What are 3 current examples of government provided (socialized) health care in US?
Can you identify what group is
served by each government provided health care?
Medicare (retired, over 65)
Medicaid (poor, diabled)
Tricare (veterans, service members)
Factors that contribute to unequal distribution of healthcare:
(a) imbalance of primary care and specialist physicians;
(b) health insurance attached to employment; (c) unequal
distribution by identity groups & region.
key issues that contribute to high cost of US healthcare.
The soaring costs of hospital care-
The rise in fees for the services of physicians
Medical Malpractice
Role of Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)
9 social determinants of health
education
employment
health systems and services'
housing
physical environment
public safety
social environment
transportaion
wealth
what place are we in the world health care systems?
37
Recognize the 8 practices that experts say would improve and help
reduce US healthcare cost (that do not involve changing who pays
for the healthcare)
emphasize primary care
stick to what works
emphasize prevention
IM efficiencies through IT]
manage chronic disease
import/negotiate for cheaper drugs
pay providers less
consumer-directed health care
What were the key provisions of the Massachusetts Plan?
private-market-based; all must have coverage; employers must help;
“broker” agencies will help match people to plans,
government will subsidize the poor in purchasing health care
What did Obamacare (Affordable Care Act) try to do for the whole
US BEYOND what the Massachusetts plan provided in its state?
Strengthen the Healthcare Workforce
Generally speaking, what did Pres.Trump and Pres. Biden do with
ACA? What was uninsured rate before ACA? Now?
Pres. Trump aimed to repeal and undermine the ACA, including cutting enrollment outreach, while Pres. Biden sought to restore and expand the ACA's provisions to DACA. The uninsured rate before the ACA was around 12%, which decreased to approximately 7-8% following its implementation.
Single Payer = the Canadian system = proposed US “Medicare for All.” Can you explain how a single payer system differs from the
current US system? How it differs from the English system?
canadian Single Payer: A healthcare system where the government gets the bill first, pays a large chunk, and sends a small amoutnt back to you and your private insurance to pay
England: In the UK, 90% of people are covered by a government owned hospitals, there are no bills because the government pays it. 10% use private healthcare
US: relies on public and private insurance.
Per Michele Wucker, what are the differences
between migrant-sending and migrant-receiving nations?
migrant sending: developing nations who export workers hoping they will send money home. offering these migrants dual citezenship is one way to retain their loyalty.
migrant receiving: developed nations with older populations who need to fill their work force and tax base.
offering these migrants voting rights is one way to reward their participation
What are “law of the soil” and “law of
blood”?
law of the soil: born here, your a citizen
Law of blood: citizenship inherited from parents
What were the major US policies about immigration from 1882-1986? (You can omit The Gentleman’s Agreement)
1882 chinese exclusion act
1921 national origin system
1965 Immigration and nationality act
1986 immigration reform and control act
Approximately what percent of the US population is currently foreign born? Is this at an all-time high?
just under 15%, no. high was in 1900
From what region is the highest percentage of
foreign-born Americans?
Mexico
From what region is the highest percentage of new immigrants to the US?
Asia (specifically china)
What is chain immigration?
Immigrants move based on stories from
relatives and friends who have gone
ahead
define: nativism
discrimination against the foreign born
define: xenophobia
fear of strangers. can be specific
define: sinophobia
fear of chinese.
define: Islamophobia
the fear of muslims
define: acculturation
acquire language and cultural fluency but retain key elements of the immigrant’s culture
What are the two approaches/goals of intransigent
nativism?
attempts to exclude (immigration laws)
forces assimilation (attejmpst to americanize as quickly as possible)
Why is intransigent nativism self-
defeating?
self defeating policies (border crossing becomes permanent because seasonal migration is made so difficult)
self fulfilling prophecies
Why does Zeke Hernandez argue immigration is a
plus?
immigration produces investments which creates jobs
skilled immigrants contribute to innovation
newcomers with less education make it possible for natives to upgrade skills and get better jobs
What are the three major issues about immigration
that are addressed in recent legislative attempts and
Presidential actions?
regularize undocumented immigrants
probelm: there’s kids and removing immigrants hurts economy
Improve legal immigration (emphasized by biden)
Enforcement (emphasized by trump)
workplace, border security, require social security number
Which of the three was
emphasized by Pres.Trump1?
Enforcement (emphasized by trump)
Which of the three
was emphasized by Pres. Biden?
Improve legal immigration (emphasized by biden)
What is going on
under Pres Trump2?
mass deportations
using military for immigration
workplace raids
expanding border wall
more border patrol
ending birthright citzenship
screenings for immigrants (muslims)
What is DREAMER and what is its current status
(‘23)?
individuals who were brought to the U.S. as children without legal status and are protected under the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) program.
No one new can enter the program, but those approved by daca can stay and work
What is DACA and what is its current status
(Fall 2022)?
deffered action for childhood arrivals: no deportation for those who came as minors and meet certain conditions.
It has been found unlawful and no new people can enter the program.
What are Zeke Hernandez’s key proposals for fixing
the system?
see immigration as economically and socially positive
expecially increase numbers related to US economic needs (but not narrow skill based)
increase the legal flow of immigration
continually update the system
What are the key proposals of other experts?
BE PRO IMMIGRATION!
avoid congressional gridlock by working with international organizations
make legal immigration easier
create legal pathways to permanent residence and citezenship
tie work visa numbers to skill needs
give immigrants who earn grad degrees here residency or citzenship
Johnson might ask:
How is the issue affected by or affecting culture?
2. How is the issue affected by or affecting structure?
3. How are paths of least resistance at work?
Key:
He talks about paths of least resistance, talks about systems and social structures
Marx might ask:
1. What are the material/economic dimensions of this
issue? Specifically, does class affect the issue?
2. Is one group dominating another group?
3. Are institutions (super structure) in some way helping the “bourgeoisie”?
Key:
He talks about bourgeouisie, proletariat, economy, superstructures, domination
Weber might ask:
1. Does “status” play a role in this issue?
2. Are cultural issues affecting this issue (especially religious ones?)
3. Is there an interplay between the material and the cultural?
4. Is “rationalization” involved? (increasing efficiency through math/science/logic)
Key:
He talks about religion, status, class, party, rationalization.
Durkheim might ask:
1. What function is being played by the various social phenomena associated with this issue?
2. Can we see “social facts” exerting an issue?
3. Is a group exerting influence on its members in some way?
4. Does the situation represent an equilibrium period or a period of change/evolution/dysfunction?
Key:
He talks about suicide, social groups, functionalism (a theoretical perspective that views society as a complex system where its various parts (like social institutions) work together to promote solidarity and stability), social isolation and integration
Mead might ask:
1. How is socialization at work in this issue?
2. What are the meanings associated with various social phenomena related to this issue? How
were they “constructed”? Do they need to be changed?
key:
he talks aobut social roles, identity, mental reflectivity (being able to reflect on ourselves), the self, I and me
Du Bois might ask:
1. How is the “color line” affecting this situation?
2. Is there some way in this situation that outside groups are unable to accurately perceive the
experience of Black people?
3. Is race in some way tied to class or class conflict in this issue?
key:
He talks about the veil, color line, black vs white, race, class, double conciousness, standpoint theory
Gilman might ask:
1. Are economic realities in some way distorting male-female relations in this situation?
2. Are women subordinate to men in this situation? If so, what is the result?
3. What actions might correct the problems in this situation?
Key:
She talks about women vs men A LOT, specifically the marital relationship between them. She talks about inequality between men and women, what rights women may not have, etc.