Respiratory System Autonomy
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What is the #1 function of the respiratory function?
Gas exchange
What are the 5 functions of the respiratory system?
Gas exchange
Receptors for smell
Filter, warm, and moisten incoming air
Produce sounds (phonation)
Eliminate some wastes other than CO2 (water vapor, alcohol, ketones)
What is respiration?
The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, the blood, and the body cells
What are the 3 basic processes of respiration?
pulmonary ventilation
external respiration
internal respiration
what respiration process involves inspiration (inhalation) and expiration (exhalation), allowing the lungs to exchange air with the surrounding environment
pulmonary ventilation
what respiration process is the exchange of gases between the air in the lungs' alveoli and the blood in the pulmonary capillaries.
external respiration
What respiration process is the exchange of gases between the blood in the systemic capillaries and the body's tissue cells.
internal respiration
Why do we need oxygen?
It is essential for cellular respiration
Internal respiration requires oxygen because it is the cellular process where cells use oxygen to convert nutrients into energy (ATP)
Outline the flow of air moving through the respiratory airways starting with the nasal cavity and ending with alveoli
Nasal cavity —> pharynx —> larynx —> trachea —> primary bronchi —> secondary bronchi —> tertiary bronchi —> bronchioles —> terminal bronchioles —> respiratory bronchioles —> alveolar ducts and sacs —> alveoli
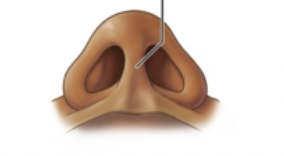
What is this?
Nasal septum
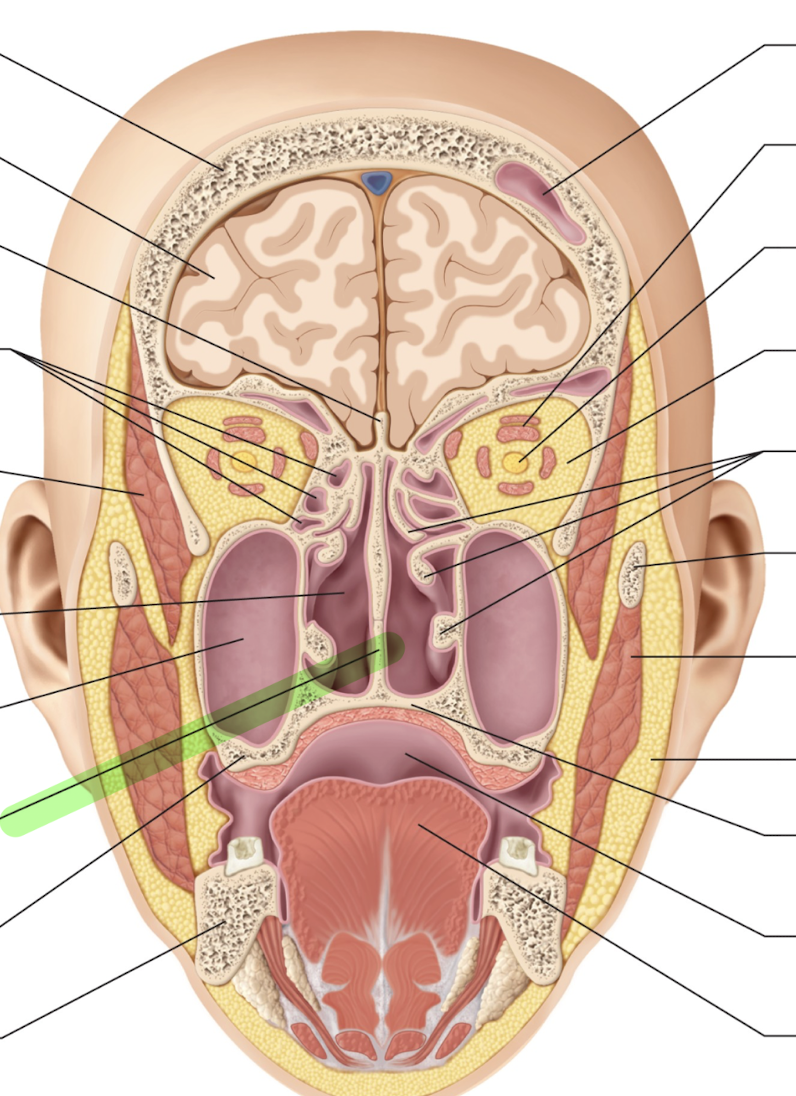
What is this and what is its purpose?
Nasal septum; division between right and left nostril
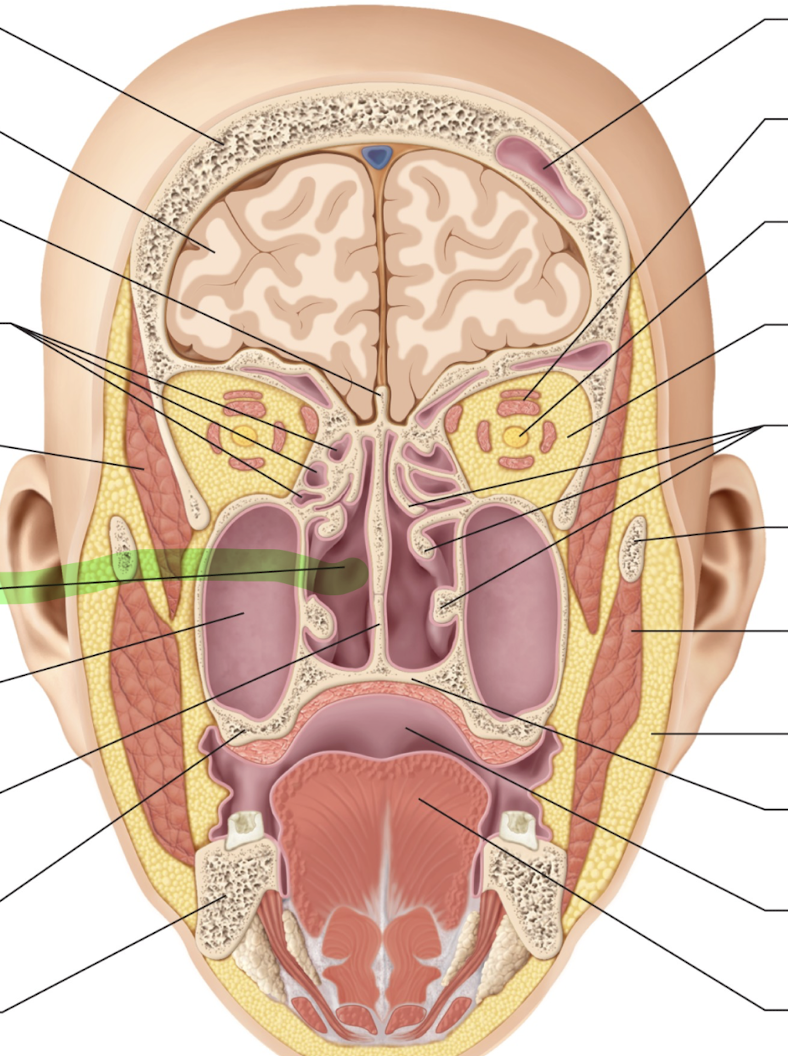
What is this?
Nasal cavity
is the lining of the nasal cavity, the interior of the nose
Nasal mucosa
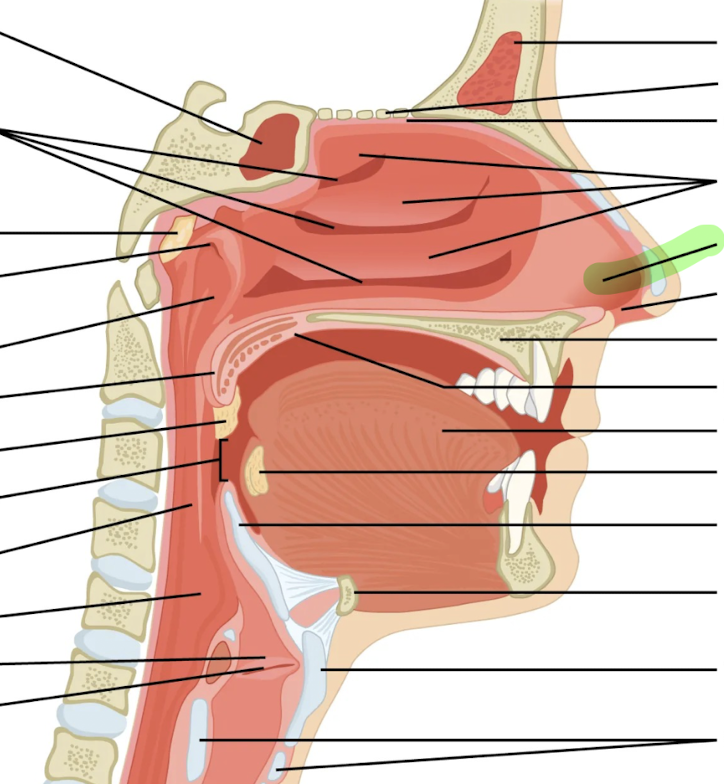
What is this?
Nasal vestibule
What is the mucosciliary escalator?
the respiratory system's primary defense mechanism, clearing inhaled particles like dust, smoke, and bacteria from the airways using a synchronized system of mucus and cilia
What cells produce mucin (mucus) and why are cilia necessary?
Goblet cells secrete mucin
Cilia propel the mucus upward out of the lungs towards the throat to be swallowed or coughed out
Moving down the respiratory system, what do we lose first? goblet cells or cila?
Goblet cells
What organs are in the conducting portion of the respiratory system?
Nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, primary bronchi, bronchi 2 and 3, bronchiole, terminal bronchiole
What organs are in the respiratory portion of the respiratory system?
Respiratory bronchioles
Alveolar ducts and sacs
Alveoli
What portion of the respiratory system moves air into and out of the lungs, warming, humidifying, and filtering it.
Conductive portion
What portion of the respiratory system exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide with the blood.
Respiratory portion
What is the larynx’s main function?
Voice production
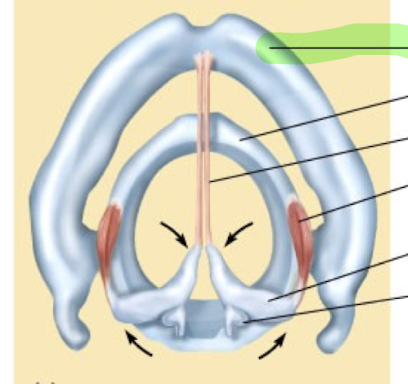
What is this structure?
Thyroid cartilage
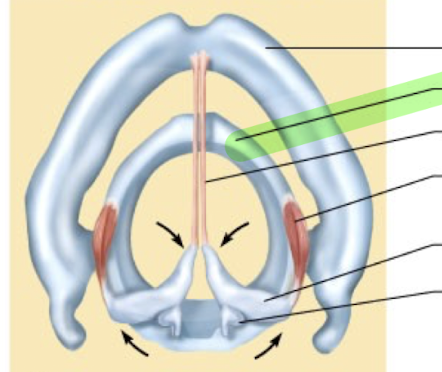
What is this structure?
Cricoid cartilage
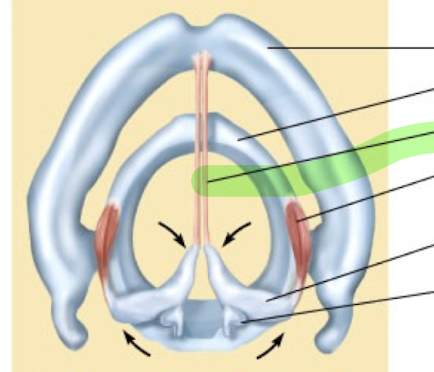
What is this structure?
Vocal cord
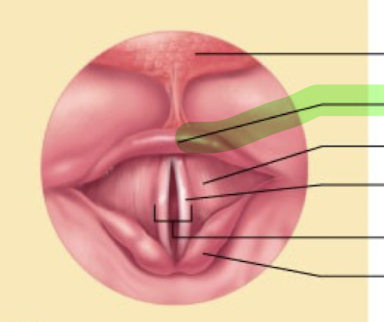
What is this structure
Epiglottis
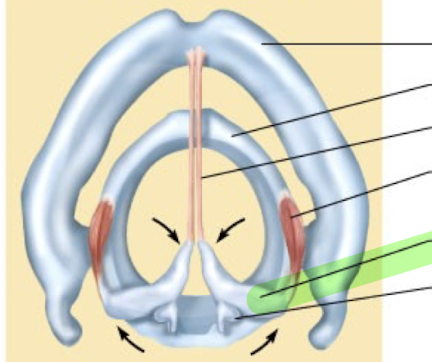
What is this structure?
Arytenoid cartilage
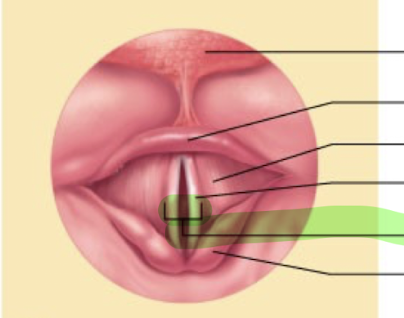
What is this structure?
Glottis
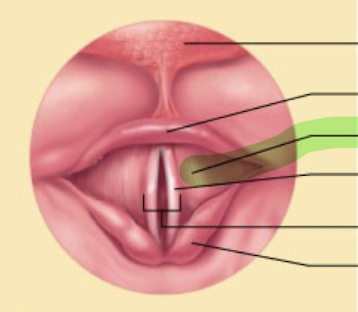
What is this structure?
Vestibular folds
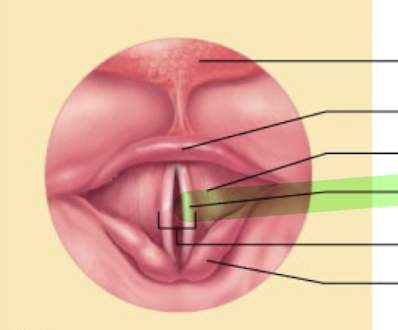
What is this structure?
Vocal cord
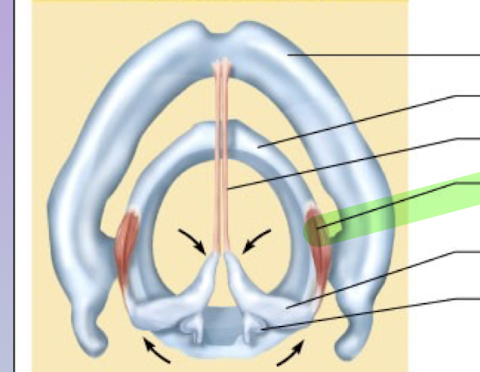
What is this structure?
Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
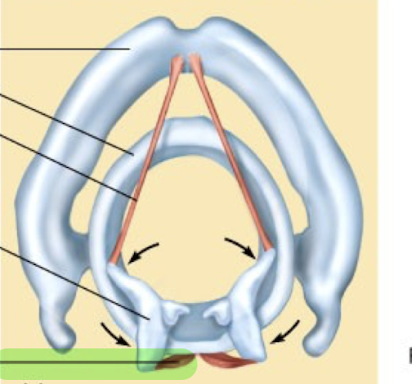
What is this structure?
Posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
Glottis muscles are contracting awkwardly; coughing
laryngospasm
The lengthening and thinning of the vocal leads to ____ pitches
Higher
The shortening and thickening of the vocal cords leads to ____ pitches
Lower
What type of epithelial cells are present in alveoli? and what is the function of each? (3)
Simple squamous epithelial cell (type I); primary cells responsible for the efficient exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air in the lungs and the blood
Septal cell (type II); produce surfactant = reduces surface tension, prevent from collapsing
Macrophage (dust cell) = protection; phagocytosis bacteria, inhaled particles, debris
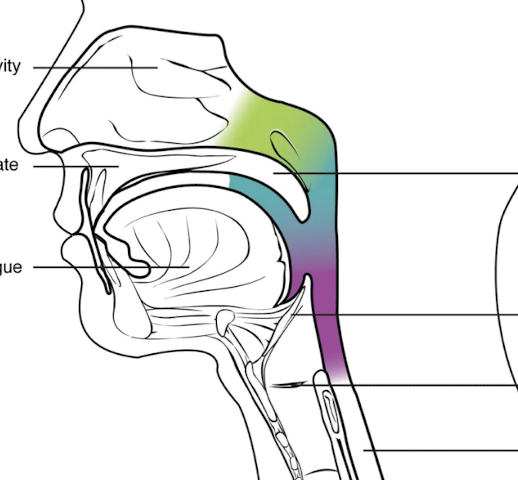
What is highlighted in green?
Nasopharynx
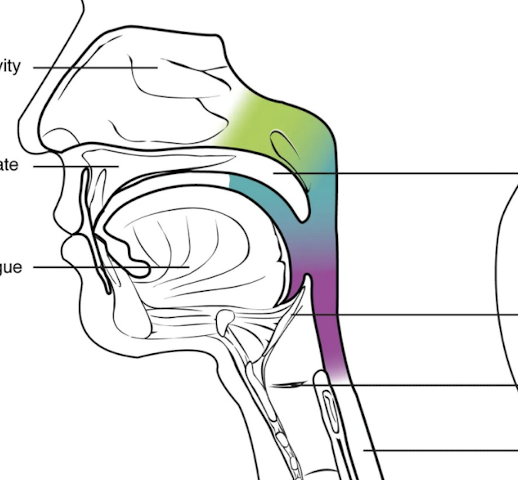
What is highlighted in blue?
Oropharynx
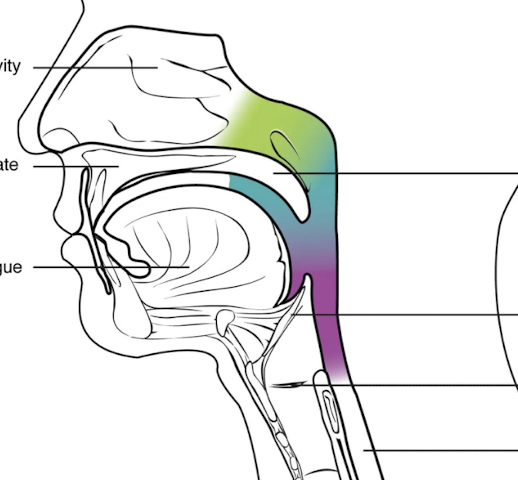
What is highlighted in purple?
Laryngopharynx
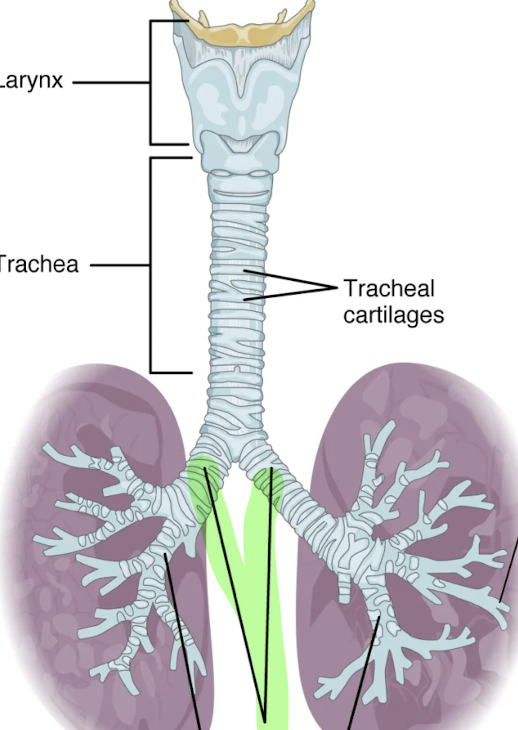
What is this structure?
Primary bronchi
What is the epithelium of the trachea, intrapulmonary bronchi, bronchioles, terminal bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles, alveoli?
Trachea = ciliated pseudostratified columnar
Intrapulmonary bronchi = ciliated pseudostratified columnar
Bronchiole = ciliated simple columnar
Terminal bronchiole = ciliated simple cuboidal
Respiratory bronchiole = ciliated simple cuboidal
Alveoli = simple squamous
What is this structure?
Hilus
The lungs consist of a ___ cavity; it has 2 layers, what are they called?
Pleural; parient and visceral layer
The pleural cavity consists of a fluid called…
Pleural fluidW
What does pleural fluid provide for the lungs?
Reduce friction
Create pressure gradient
Compartmentalize
Pulmonary ventiliation occurs in the….
Thoracic cavity
external respiration take place where?
across the alveolar membrane in the lungs
Where does internal respiration take place?
In the systemic capillaries throughout the body
This structure helps filter air; moisten and warm up; allow for voice to resonate
Paranasal air sinuses
Where is the location of the pharynx?
Posterior to nasal cavity, oral cavity and larynx
what is the muscular tube composition of the pharynx
Circular and longitudinal
The circular muscle tube of the pharynx does what?
constrictor muscles narrow the cavity to propel food downward (peristalsis)
The longitudinal muscle tube of the pharynx does what?
shorten and widen; elevate the pharynx to swallow
How does the bronchial tissue of an asthmatic patient differ from a healthy patient?
More mucus is produced
More leukocytes = increased swelling = airway gets narrower —> asthma attack
to act as a valve that covers the opening of the trachea (windpipe) during swallowing, preventing food and liquid from entering the lungs and ensuring they go down the esophagus
Epiglottis
Traveling down the respiratory tract, smooth muscle ___ as cartilage ___
increase, decreases
List the cartilage
Trachea -
Intrapulmonary bronchi -
bronchioles -
c-shaped cartilage
irregular plates of cartilage
cartilage = gone
a sheet of smooth muscle that connects the ends of the C-shaped cartilage rings at the back of the trachea
trachealis
explain the importance of the c-shaped cartilage to the structure of the trachea and areas surrounding it
With the esophagus being directly behind the trachea, the incomplete cartilage of the trachea allows for it to flatten and “move” with the movement of the esophagus when something is swallowed.
What is the functional unit of the bronchius tree?
Alveolus
What are the components of the respiratory membrane?
surfactant
type 1 alveolar epithelial cell
fused basement membrane
capillary endothelial cell
What is the surface area of each lung?
70 m²
The large surface area of the lungs is crucial for…
maximizing the efficiency of gas exchange
brings deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lung
pulmonary artery
brings oxygenated blood from left ventricle to bronchial tree
bronchial artery
takes oxygenated blood back to left atrium
pulmonary vein
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the tone of the _____ surrounding the airways, thereby controlling the diameter of the bronchioles and the amount of air moving in and out of the lungs
Smooth muscle
the parasympathetic nervous system sparks…
bronchoconstriction
The sympathetic nervous system sparks
bronchodilation