GI E1- Disorders of Small Intestine
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Which region of the small intestine is the shortest & retroperitoneal?
duodenum
Which region of the small intestine begins at the suspensory muscle of the duodenum (ligament of treitz)?
jejunum
Which region of the small intestine is the longest, paler, narrower, thinner, less vascular, fewer circular folds, and has more lymphatic nodules?
ileum
What are finger like mucosal projections that increase surface area for digestion and absorption?
villi
What are visible, mucosal/submucosal ridges that increase SA in the jejunum for absorption and cause spiraling of chem for efficient digestion?
circular folds
What are microscopic projections of apical membrane of absorptive cells (brush border)?
microvilli
Where does 90% of nutrient absorption occur?
small intestine
Which water soluble vitamin is NOT absorbed via simple diffusion, instead absorbed in the ileum by active transport in combo w/ intrinsic factor (IF)?
B12
A disruption of digestion and/or nutrient absorption is ______
malabsorption
What are the 3 phases of normal digestion?
intraluminal, mucosal, post-absorptive
What would a resection of the terminal ileum (TI) result in?
malabsorption of bile salts & vit B12
What are other names for celiac disease?
gluten enteropathy, celiac sprue, sprue
What condition?
autoimmune disorder caused by exposure to gluten
IgA abs against gliadin and tissue transglutaminase → diffuse damage to proximal SI mucosa → malabsorption
villous atrophy, flattening of SI villi; crypt elongation; lymphoid proliferation in laminated propria
can present any age; grossly underdiagnosed
celiac disease
What is a protein component of grains such as wheat, rye, and barley?
gluten
What condition?
malabsorption signs → loss of muscle mass or SC fat, pallor
sx: dermatitis herpetiformis, easy bruising, bone pain, non-specific GI sx, etc
dx: serology & bx, 24 hr stool (fecal fat > 7g), IgA tTG (most accurate), antigliadin abs, improvement after gluten free diet
Celiac disease
What should be considered in any patient presenting with unexplained deficiencies of iron, folate, vit B12 or undiagnosed non specific GI complaints?
Celiac Disease
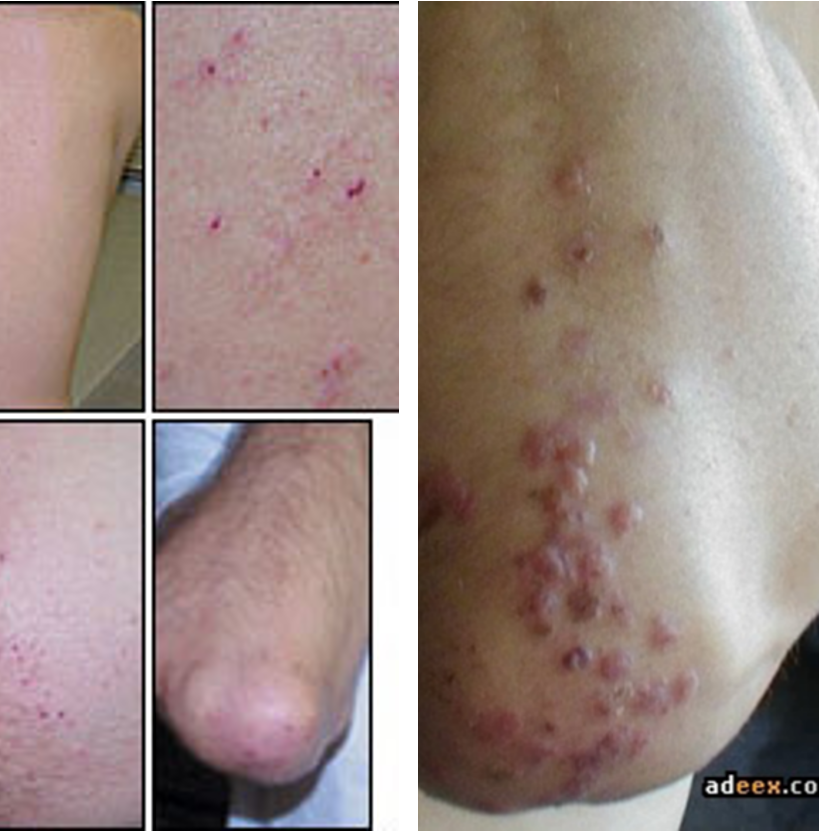
The intensely pruritic papulovesicular rash over extensor surfaces, trunk, scalp, and neck known as dermatitis herpetiformis is a characteristic rash of what condition?
Celiac disease
What is the treatment for celiac disease?
dietary consult & gluten free diet- avoid wheat, rye, barley
what conditions can celiac disease be associated with?
insulin dependent DM, autoimmune thyroid, IgA deficiency
Since the small intestine normally contains a sparse amount of bacteria, what can happen if there is a bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)?
direct damage to bowel mucosa → malabsorption
What condition?
diarrhea, flatulence, bloating, abd distension, fatigue, steatorrhea (RARE)
if severe malabsorption → wt loss
long standing cases (elderly) → B12 deficiency that mimics pernicious anemia
dx: breath test, stool collection, BA w/ SBFT, CT enterography
empiric abx trial for dx & tx
SIBO
What is the treatment for SIBO?
abx (diagnostic & therapeutic) → cipro, augmentin, norfloxacin, bactrim & metro combo, or rifaximin (fewer SE)
What broad spectrum antibiotic is used to treat E. coli associated with traveler’s diarrhea, IBS-D, SIBO, and has fewer SE?
Rifaximin (Xifaxan)
What is a brush border enzyme that hydrolyzes lactose into glucose & galactose?
lactase
What happens to malabsorbed lactose?
fermented by intestinal bacteria → produce gas & organic acids → inc stool osmotic load → fluid loss
In lactase deficiency, how soon after ingestion of lactose might bloating, abdominal cramps, flatulence, diarrhea, and nausea appear?
30 min - 2 hr
How is a lactase deficiency diagnosed?
empiric trial of lactose elimination x 2 weeks (diagnostic & therapeutic); slowly reintroduce & assess for resolution of sx
hydrogen breath test
What is the treatment for a lactase deficiency?
restriction of dietary lactose, lactase enzyme supplementation (Lactaid), calcium supplementation
What meds might be hidden sources of lactose?
omeprazole, citalopram, senna, prednisolone
The dumping of stomach contents into the proximal SI that might occur after gastric surgery is _____
dumping syndrome
What condition?
undiluted chyme dumped into SI → fluid shifts from blood to SI to dilute contents
food rapidly digested/absorbed → hyperglycemia & inc insulin secretion → hypoglycemia 2-3 hrs later
hypovolemia occurs, SI distends
gastric emptying of liquids more rapid → dilution of enzymes & bile acid in duodenum → mismatch of chyme delivery & absorptive capacity
Dumping syndrome
What is the treatment for dumping syndrome?
smaller frequent meals (6-8/day), dec fatty food intake, restrict carb intake
What is neurogenic failure or loss of peristalsis in the intestine without mechanical obstruction?
acute paralytic ileus
What medications can cause acute paralytic ileus?
opioids and anticholinergics
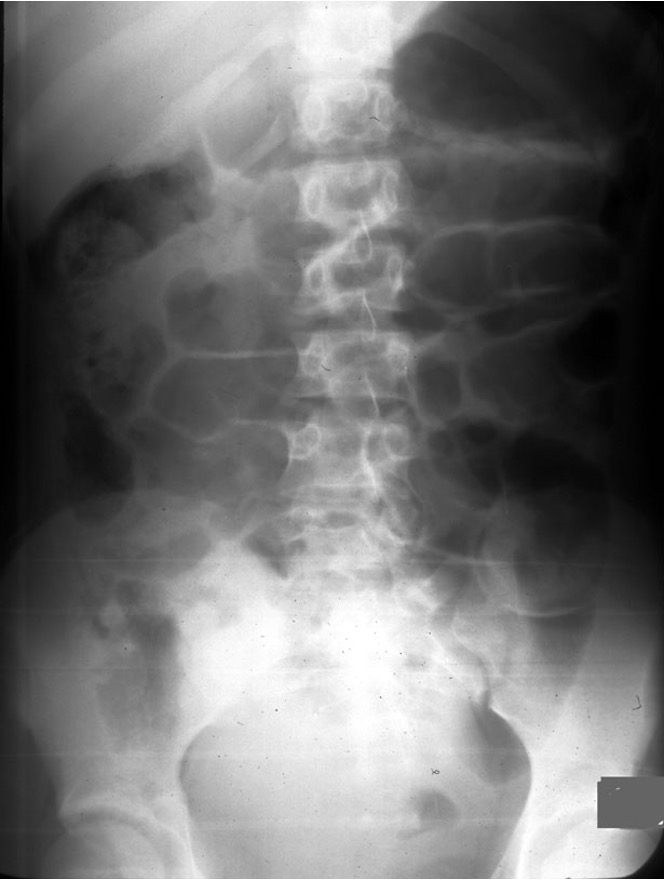
The following sx are seen with what condition?
mild-mod diffuse, continuous abd discomfort → steady & severe pain w/ strangulation
obstipation, N, V, distension
hyperactive high pitching “tinkling” bowel sounds; peristaltic “rushes”
xray: diffuse gas filled loops of small & large bowel +/- air fluid levels (no stack of coins or string of pearls)
acute paralytic ileus
paralytic ileus might be difficult to distinguish from what condition?
partial small bowel obstruction
What is the treatment for acute paralytic ileus?
correct underlying, IV fluids, NPO, NG tube( low intermittent suction), surgery
Is the following SBO functional or mechanical?
ileus → bowel not moving / contracting
functional
Is the following SBO functional or mechanical?
something physically blocking the contents from passing through
mechanical
what is the MCC of mechanical SBOs?
adhesions from prior surgeries
What condition?
abd pain, N, V, bloating, obstipation
high pitched tinkling & hypoactive bowel sounds, hyper resonance on percussion, listened abd, tachy, signs of dehydration
dx: plain film & CT → dilated loops of small bowel w/ air fluid levels, free air under diaphragm (indicates perforation)
SBO
what is the treatment for SBO?
emergent surgical consult, IV fluids, NPO, NG tube w/ suction for decompression if persistent N/V/abd distension
A sudden twisting of the bowel on itself causing obstruction and ischemic that can lead to gangrene, necrosis, and perforation is called ______
volvulus
what are the 2 most common sites for volvulus?
cecum and sigmoid colon
what is the treatment for volvulus?
endoscopic reduction & surgery
what causes volvulus?
idiopathic, anomaly of rotation, ingested FB, adhesions
What is telescoping or invagination of a portion of the bowel into a distal portion that can cause constriction, edema, and hemorrhages?
intussusception
What condition?
M > F, MC in infants
unknown cause, linked to some rotavirus vaccines
kids: severe colicky pain, currant jelly stools (blood & mucus), sausage like abd mass
BA enema diagnostic and therapeutic
adults: crampy abd pain
abd plain films, CT, & surgery
Intussusception
what is the MCC of bowel obstruction in children 6mo-36mo?
intussusception
what condition?
extreme dilation and immobility of colon; emergency
fever, abd cramps/pain/distension, rigid abd, systemic sx
MC sx is severe bloody diarrhea
emergency
toxic megacolon
what is toxic megacolon associated with?
ulcerative colitis (esp pancolitis), crohn’s, amoebic colitis, pseudomembranous colitis, infx (shigella, c diff)
what is the tx for toxic megacolon?
emergent→ colon decompression, IV fluids, surgical resection
what condition?
congenital absence of autonomic smooth muscle ganglia
aganglionic bowel segment contracts but needed relaxation does not occur → stasis of stool
can affect entire colon
M > F
coexist w/ other anomalies- down syndrome
commonly dx in kids and infants, underdx in adults
Hirschsprung Disease
how is Hirschsprung Disease dx?
abd xray, CT, colonic transit studies, sitz mark studies
what is the most common mucosal tumor?
adenocarcinoma
what tumor?
sx- anemia, bleeding, obstruction, jaundice
risk: FAP
most found near ampulla of vater
tx- segmental resection
adenocarcinoma
what tumor?
primary or secondary to disseminated dz
MC type: NHL B cell
MC site: distal small intestine
sx: abd pain, distention, wt loss, N, V< anemia, occult blood, fevers unusual
lymphoma
What are treatment options for lymphoma?
surgical resection, surgical debulking, chemo +/- radiation
what is the most common neuroendocrine tumor that’s most frequently in small intestine?
carcinoid tumor
what size carcinoid tumor has a high probability of metastasis?
> 2 cm
what syndrome?
results form hormones secreted by tumors
sx: D, abd pain, wheezing, flushing
may develop into crisis during surgery; somatostatin must be administered pre-op
carcinoid syndrome
how are carcinoid tumors dx?
imaging, 24 hr urine, blood test (CgA)
what is tx for carcinoid tumor
local excision if confined to SI
palliative tx for late dz
what is the most common abdominal surgical emergency?
appendicitis
What condition?
obstruction of appendix by fecalith, inflammation, etc
peak incidence: 10-19 yrs
generalized periumbilical pain → localized RLQ pain
mcburneys point rebound tenderness, + psoas & obturator signs
N, V, anorexia, fever, constipiation or diarrhea
Appendicitis
What is the workup for appendicitis?
abd CT > u/s
labs: CBC (mild leukocytosis), U/A (hematuria), CMP normal
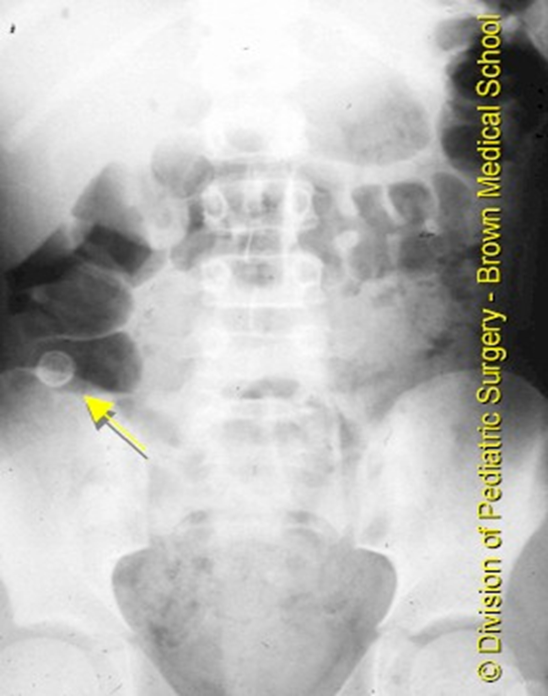
What happens if appendicitis left untreated?
gangrene and perforation w/in 36 hrs
What is the treatment for appendicitis?
surgical appendectomy - laparoscopic (MC) or laparotomy
IV abx