9 Limits of Functions at Infinity (Theory)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Sign Analysis Test
Step 1: Plot your discontinuities
Step:2 Test numbers to the left and right of those points
Step 3: Limits exist when infinities go to the same direction, otherwise, limits do not exist
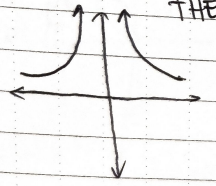
Does the limit exist?
Yes
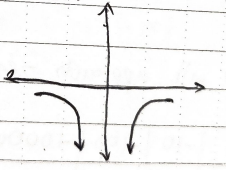
Does the limit exist?
Yes

Does the limit exist?
No
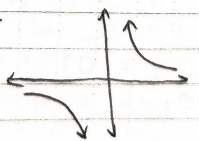
Does the limit exist?
No

What happens to the limit of this function as “x” approaches infinity?
(1) the limit will then get closer to zero
(2) imagine dividing 1 by a really large number, the number will get smaller and smaller
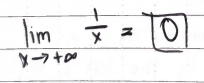
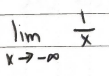
What happens to the limit of this function as “x” approaches infinity?
(1) the limit will approach zero
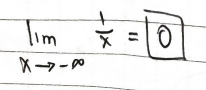
When do you get a horizontal asymptote?
(1) you get a horizontal asymptote when your function gets really close to a certain point as x approaches infinity
When f(x) gets really close to a certain number as “x” approaches infinity, then the limit _____(1)_____.
(1) exists
Horizontal Asymptote
(1) if the limit exists as x approaches infinity, then a horizontal asymptote happens?
Constant Divided by Infinity
0
Limit of Polynomials as “x” Approaches Infinity
Goes to ±∞ infinity itself
The limit of a polynomial will follow the behavior of the __(1)__ term.
(1) Leading
What is the limit of a polynomial?
(1) the limit of a polynomial as x—>±∞ goes to ±∞ itself
What is the limit of polynomials raised to even numbers?
x — ±∞ = +∞
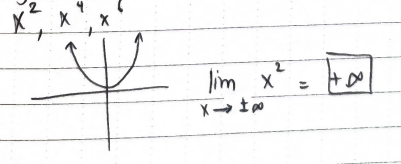
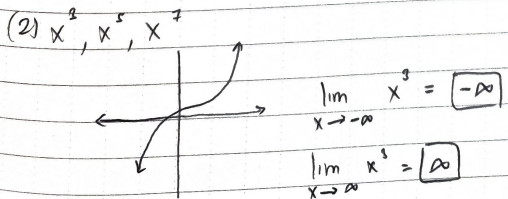
What is the limit of polynomials raised to odd numbers?
x —> -∞ = -∞
x —> ∞ = ∞
Steps for Finding Limits at Infinity for Rationals
Step 1: Observe the behavior of the leading term
Step 2: Divide every term in the numerator and denominator by the largest power of “x” in the denominator
Step 3: Simplify
Steps for Finding Limits at Infinity for Radicals
Method 1: Divide the radical by the largest power of x inside the radical, do the same for the numerator or denominator
Method 2: Rationalize, entire fraction by the largest power in the denominator to all the values outside of the radical; divide the radical by the largest power of the radical to the radical itself; simplify