MCM-SV-Eicosanoids and Lipid Mediators-2 (2)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
which cells produce leukotrienes? Why are they called ‘trienes”? Which receptor do they act through and what do they do?
Leukocytes, mast cells, oesinophils and other immunocells; trienes = 3 double bond in succession; act through GPCR and has pro-inflammatory effects (including inflammatory effect in asthma); They also play a role in vasoconstriction, smooth muscle constriction, musocal secretion, and constriction of airways
Explain the biosynthesis pathway for leukotrienes. What are the three cysteinyl leukotrienes? What drug inhibit this synthesis? What chemical is an antagonist to leukotrienes?
AA —> LOX 5 —> LTA4 —> LTBCD4; LTB4, LTC4, LTD4 are the three cysteinyl leukotreins
zyflo (zileutron) inhibit this synthesis (asthma medicine)
singulair (montelukast) acts as an antagonist for leukotriene receptors
What are peptidoleukotrienes? What are SRS-A? What does SRS-A do? Where is it implicated?
leukotrienes that has some peptides attached. SRS-A are the Lts that triggers anaphylatic. SRS-A is released from lungs by immunological stress and causes smooth muscle contraction of bronchi.
Implicated by hypersensitivity reaction.
What are the functions of neutrophils? What does activated neutrophils secrete? What is this chemical’s function? How can neutrophils cause emphysema? What is PGP?
Neutrophils can created inflammation of the lungs. This inflammation can cause diseases such as COPD, cystic fibrosis,…
Activated neutrophils secrete ROS which is proinflammatory while inhibiting anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids
Neutrophils can cause emphysema by degrading elastin/collagin via:
secretion of elastase and proteinase-3 which degrades elastin and secrete mucus
secretion of MMP 8/9 which causes elastin and collagen degradation
PGP is the biproduct of elastin/collagen degradation by MMP8/9. It acts as a neutrophil attractang
What is the function of LTA4H and why does smoke inhibits its action?
LTA4H helps with the synthesis of LTB4 and also degrades PGP. Smoke causes acetylation of PGP which makes it harder for it to be degraded by LTA4H
Compare and Contrast the functions of LTB4 and LTC/D4
LTB4: Increase vasopermeability, increase IFN-gamma, increase IL1 and IL2, leukocyte aggregation, T-cell proliferation
LTC4/LTD4: Increase vasopermeability, increase IFN-gamma. bronchoconstriction
Which cells produce eicosanoids during inflammation? Discuss the role of eicosanoids during inflamation? How can PGs have contradictory inflammation roles? What eicosaonoids play a role in resolving inflammation
granucyte, macrophages, neutrophils, platelets, mast cells, endothial cells.
Role of eicossanoids in inflammation:
LTB4: chemoattractant
LTs: vasopermeability
cystein LTs: smooth muscle contract
TXA4: platelet aggregation
PGH2: proinflammatory
PGs’ effects is determined by the different EP receptors.
Lipoxins resolve inflammation
What is the relationship between leukotrienes and rheumatoid arthritis?
Leukotriens have found to develop rheumatoid arthritis, specifically LTB4
Describe the synthesis of lipoxins (LX). What are the two discovered Lipoxins? What do they do? How does Aspirin affect this?
AA —> LOX5 and LOX 15 —> LXA4 and LXB4;
They oppose some leukotriens function by:
They resolves inflammation
prevent platelet degranulation and chemotaxis
inhibit vasoconstriction by VD4
could be used to reduce constriction of airways
Aspirin creates 15-epi- LXA4 which inhibits inflammation and carcinogenesis.
Draw out the relationship between Cox1, Cox2, and cancer
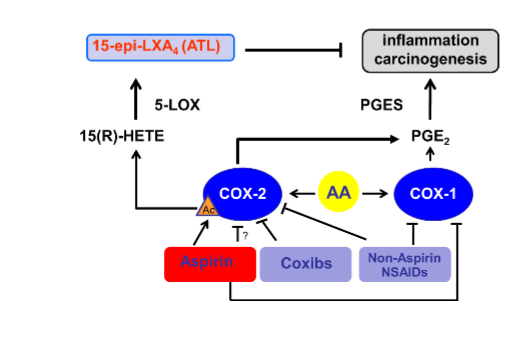
How does cox-2 derived PGE2 cause cancer?
through five ways
increases cell proliferation and angiogenesis
decreases apoptosis
increase cell invasiveness
decreases immune surveilence
inhibit function and differentiation of dendritic cells
What is anandamide? Describe how it is produced/degraded. explain one theory on why chocolate is so addictive
anadamide is an endogenous cannaboid binding receptor;
phosphotidylethanolamine is cleaved by TEA (transacyclase) which result in AA binding to ethanolamine. This is then cleaved by phospholipase D which results in AA + ethanolamine.
Anandamid promotes analgesic effects via CB1 (CNS) and CB2 (peripheral)
Chocolate is addictive because it has compounds that slow down anandamid degradation (fatty acid amide hydrolysis)
Describe the synthesis and function of isoprosteins? What lab test used this for? How can this have anti-cancer effects?
isoprosteins are produced via free radicals. PLA2 release these altered AAs which can covalently modify lots of stuff. This test is used to assess oxidative stress .
This can have anti-cancer effects if produced from DHA
What is hemostasis? What are the four phases?
hemostasis is clot formation
vascular phase
platelet phase
coagulation phase
fibrinolytic phase
What are the three ways in which endolithium cells have anti-thrombotic properties?
they have PGI2 which has anti platelet aggregation and stimulates smooth muscle relaxation
They have NO (aka EDRF, endolitheum derived relaxing factor)
Heparin sulfate and thrombomodulin
Describe how production of TXA2 is initiated when there is damage to blood vessels. How does TXA2 help with clot formation
damage to vessels —> collagin exposed —> platelet attaches —> PLA2 creates TXA2
TXA2 causes platelet aggregation, vasoconstriction, degranulation of platelets
What is platelet aggregation controlled by? How does aspirin and omega 3 help reduce platelet aggregation
controlled by levels of PGI2 and TXA2; aspirin inhibits COX 1 which means no production of TXA2;
OMEGA 3 slows down synthesis of TXA2 and reduce production of proinflammatory eicosanoids