Biology- Mitosis and Cell division
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The primary purposes of mitosis are growth, repair, and replacement of cells, In a typical 24-hour eukaryotic cell cycle (such as in human somatic cells), mitosis and cytokinesis combined (the M phase) occupy a very short period, usually lasting only about 1 hour. The majority of the cell's time (roughly 23 hours or 95% of the cycle) is spent in interphase preparing for division.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Interphase
A cell spends 90% of its time, during the cell is busy taking in nutrients, replicating DNA and growing.
There are 3 stages: G1,S,G2
G1 stage
Cell grows and produces new proteins and organelles.
10-11 hours
S stage
DNA is replicated.
8 hours
G2 stage
Cell produces the organelles and structures needed for cell division.
3-4 hours
Chromatin
Relaxed/Uncoiled
Chromosome
Condensed and replicate form
Sister Chromatids
Replicated chromosomes consist of two of these.
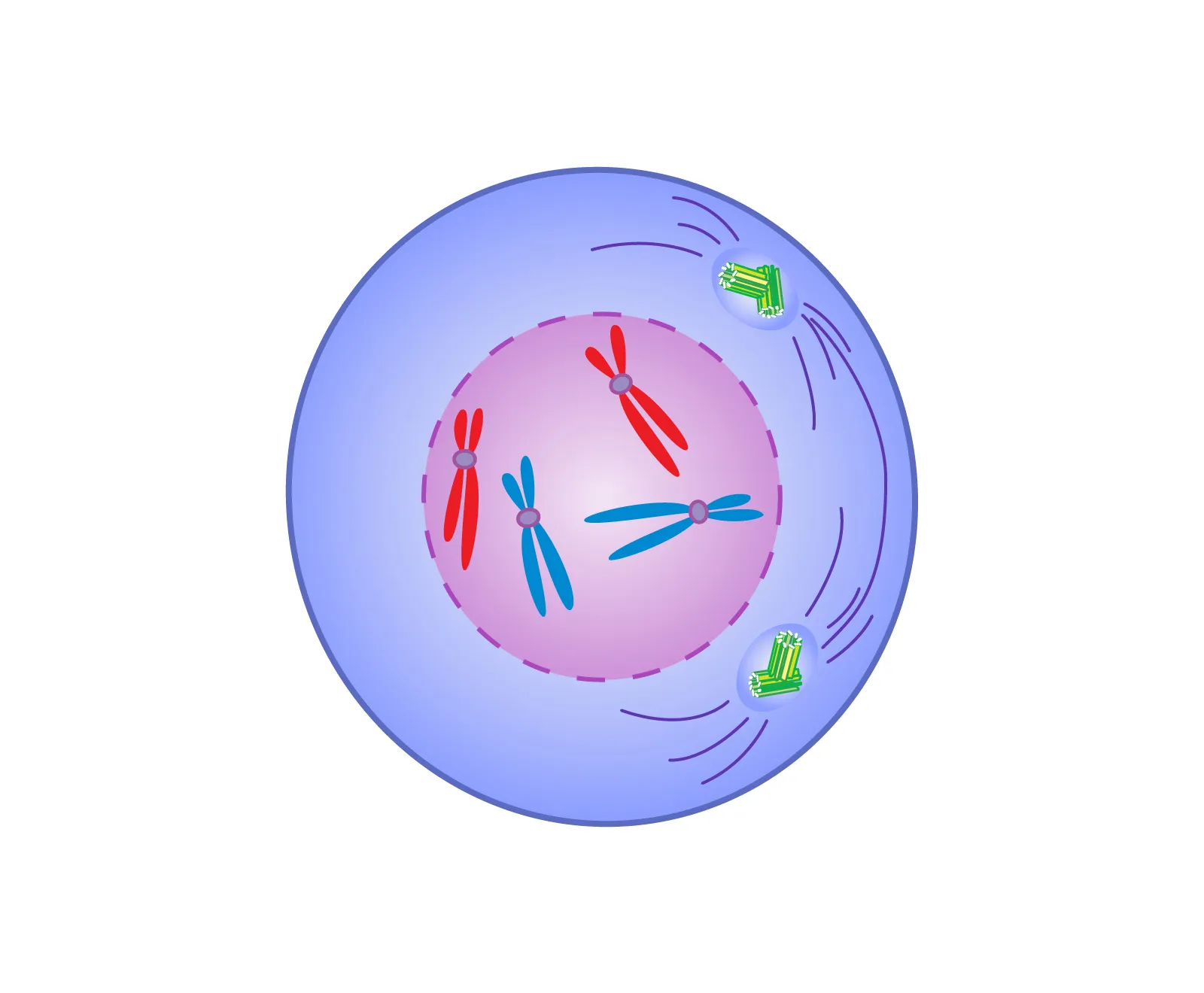
Prophase
Chromatin condenses to become chromosomes (2 sister chromatids)
Nuclear envelope disintegrates
Mitotic spindle/spindle fibers form
Centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell
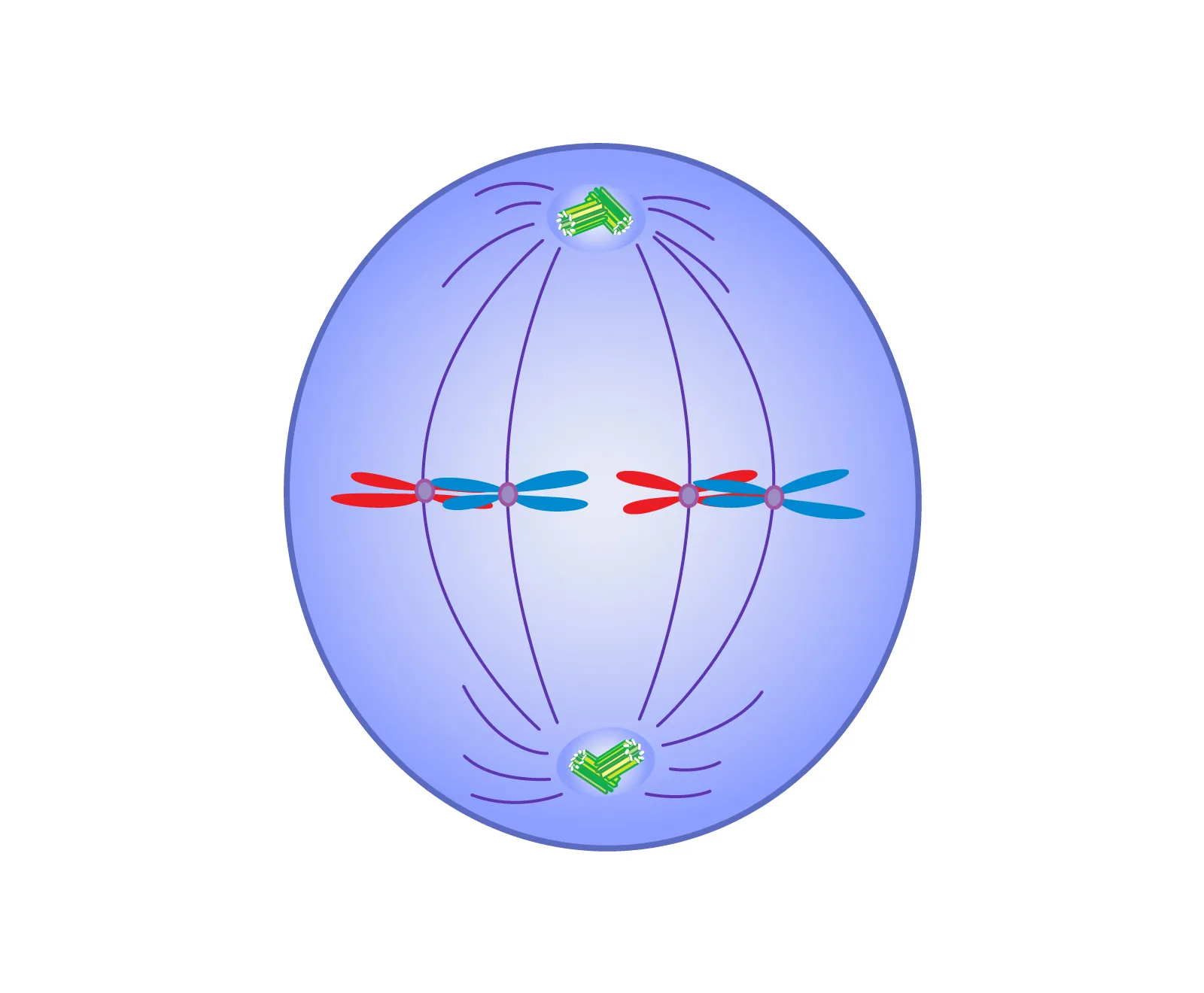
Metaphase
Chromosomes move to the middle of the cell
Miotic spindles attach to the centromeres of the chromosome
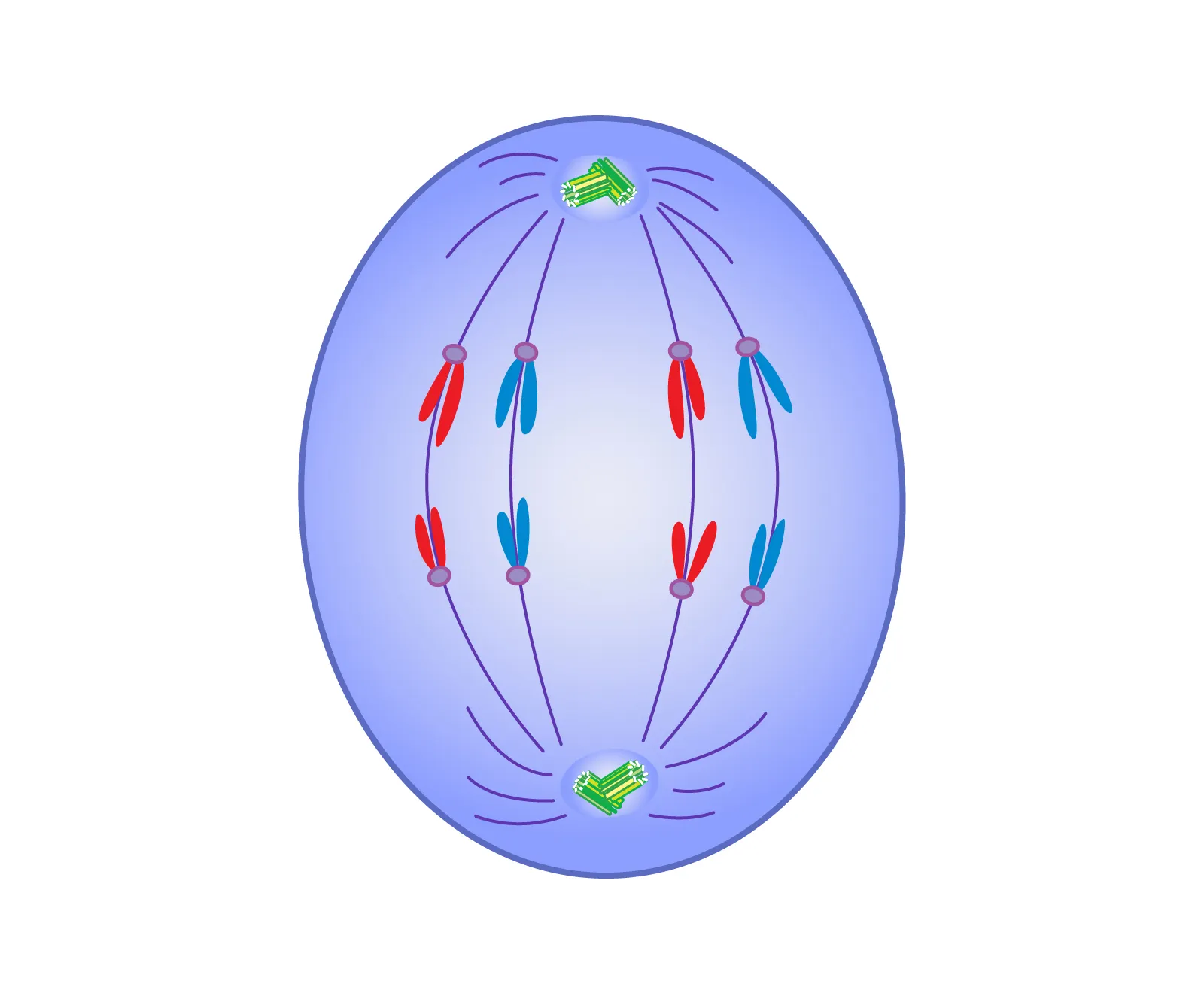
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate at the centromere
Pulled to opposite poles by the centriole
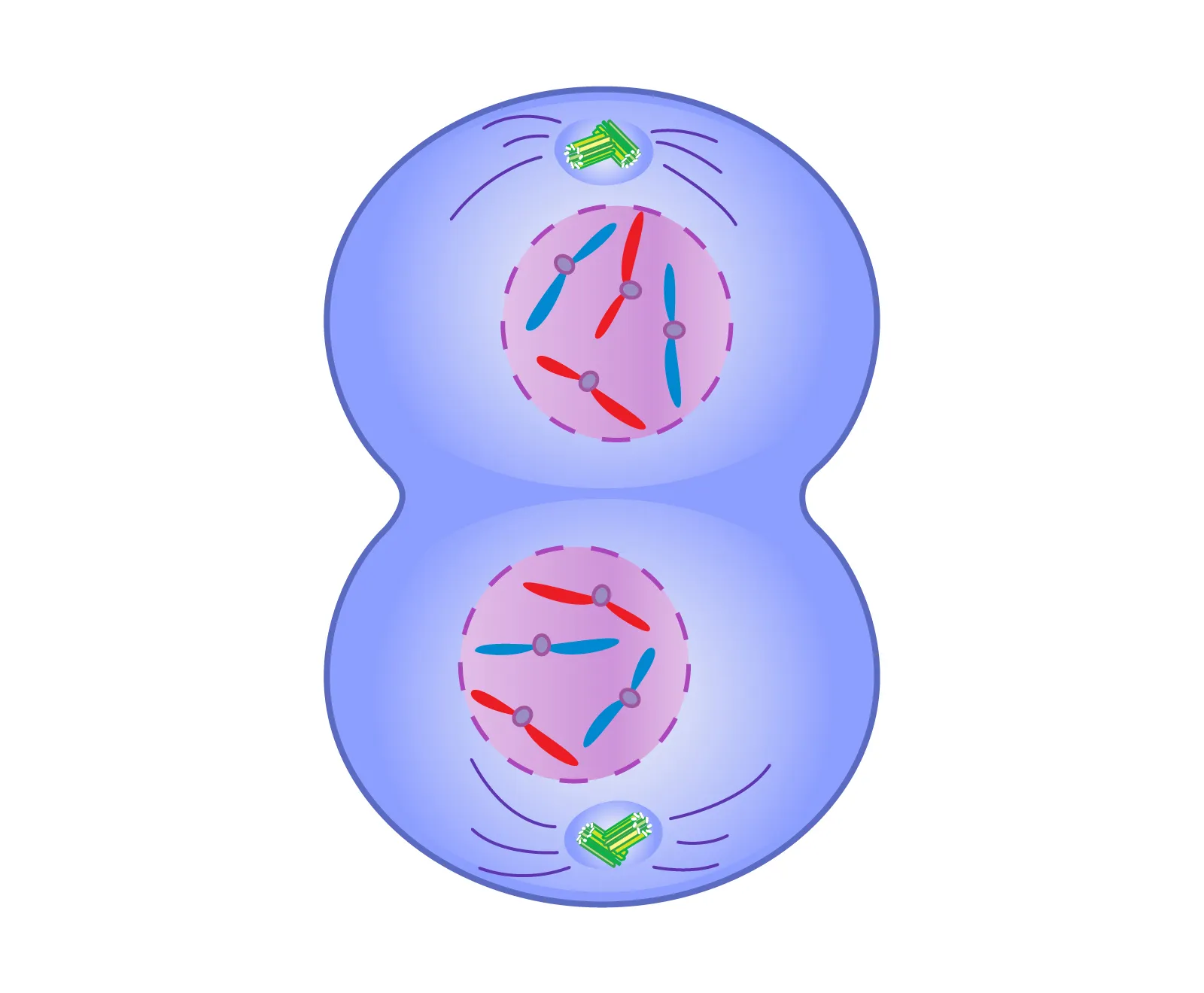
Telophase
Miotic spindle breaks down
Two new nuclei are formed
Cell splits into two new daughter cells by pinching inwards
Cytoplasm divides= Cytokinesis
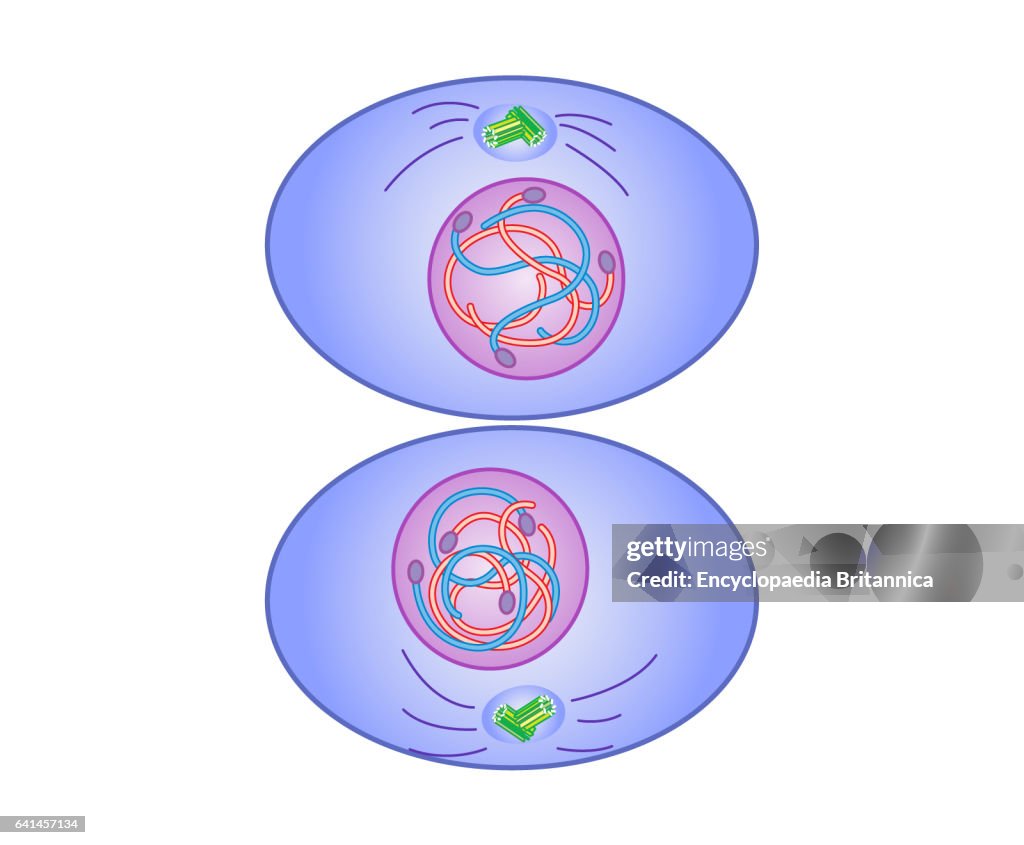
Cytokinesis
The actual splitting of the cytoplasm into two separate cells
Occurs differently in both plant and animal cells
Animal cells: Cleavage furrow pinches cell
Plant cellls: Cell plate forms in between
Two Daughter Cells: The primary outcome is two separate cells, each enclosed by its own plasma membrane.