Bio-psych quiz
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
action potential
the rapid, electrical discharge, or nerve impulse, that travels along the axon of a neuron to communicate with other neurons
Afferent Neuron
carries sensory information; sensory input
all-or-none response
principle stating that a nerve or muscle cell will either respond completely or not at all when stimulated
autonomic nervous system
controls internal organs and glands; involuntary bodily functions
agonist
a chemical substance that binds to a specific receptor and activates it
Central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
antagonist
a drug or chemical that blocks the effects of a neurotransmitter by binding to its receptor without stimulating it
efferent neuron
carries neural impulses away (output) from the central nervous system to muscles or glands, helping with motor
glial cells
non-neuronal cells in the nervous system that support and protect neurons
interneurons
a neuron which transmits impulses between other neurons
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that relay neural messages across the synapse
hormones
chemical messengers that are produced in one part of the body and travel to other parts
threshold
the minimum level of stimulation, intensity, or magnitude required for a stimulus to be detected by an organism
parasympathetic nervous system
relaxes your body after periods of stress or danger; calming
peripheral nervous system
the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord;
pituitary gland
master gland that produces hormones influencing the secretions of all other endocrine glands
refractory period
a period immediately following stimulation during which a nerve or muscle is unresponsive to further stimulation
reflex
an involuntary, automatic, and unconscious response to a stimulus that occurs without conscious thought
reuptake
neuron reabsorbs neurotransmitters after they have been released
somatic nervous system
sense organs and voluntary muscles
sympathetic nervous system
prepares the body for stressful or dangerous situations; arousing
synapse
the tiny junction in the nervous system where one neuron passes a signal to another
nerves
A bundle of fibers that receives and sends messages between the body and the brain
hereditary
nature
enviroment
nurture
dendrites
receive chemical and electrical signals from other neurons
cell body
the central part of a neuron that contains the nucleus
axon
transmits electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body to communicate with other neurons
axon terminal
ending of a neuron's axon that releases neurotransmitters
Myelin Sheath
a protective, fatty layer that insulates and surrounds axons; speeds up movement of current
excitatory
increases the likelihood of a neuron firing an action potential,
inhibitory
a chemical messenger that decreases the likelihood of a neuron firing an action potential
Dopamine
pleasure/reward, voluntary action/movement
Serotonin
mood
Norepinephrine
fight or flight; brain’s adrenaline
gluatamate
gut; main excitatory
GABA
main inhibitory
endorphins
painkiller
substance P
pain
acetylcholine
memory/alzheimers
Adrenaline
during stress, it increases blood circulation and breathing; adrenal glands
Leptin
regulate appetite; adipose tissue
Ghrelin
“hunger hormone”
Melatonin
sleep; production and release is connected to time of day
Oxytocin
social bonding, sexual reprodcution, childbirth; hypothalamus
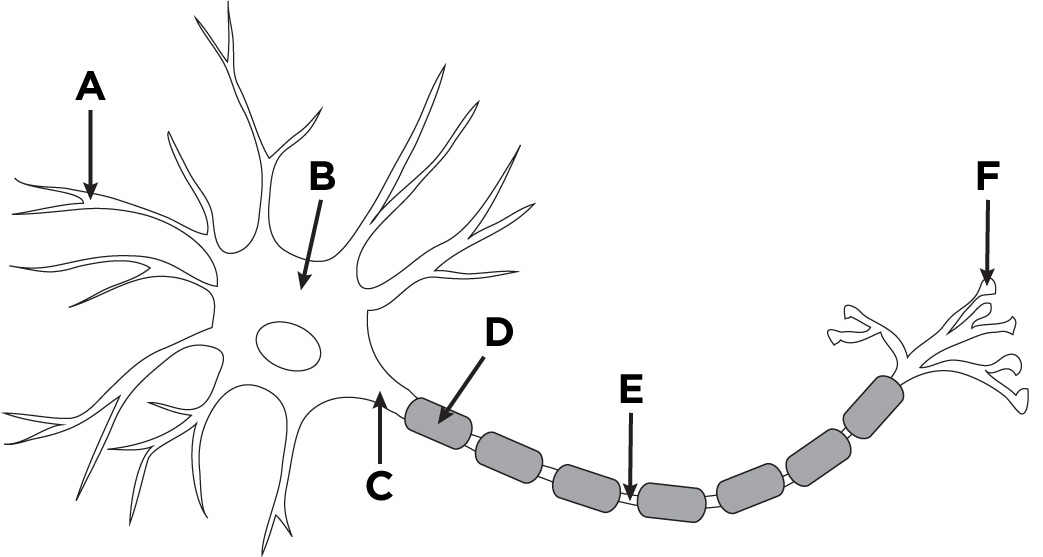
dendrites
A
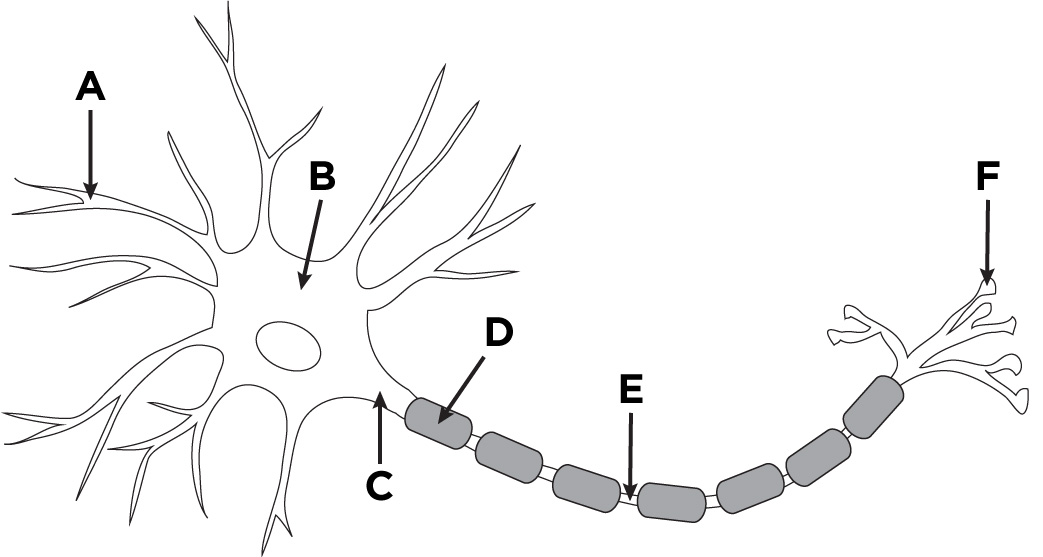
cell body
B
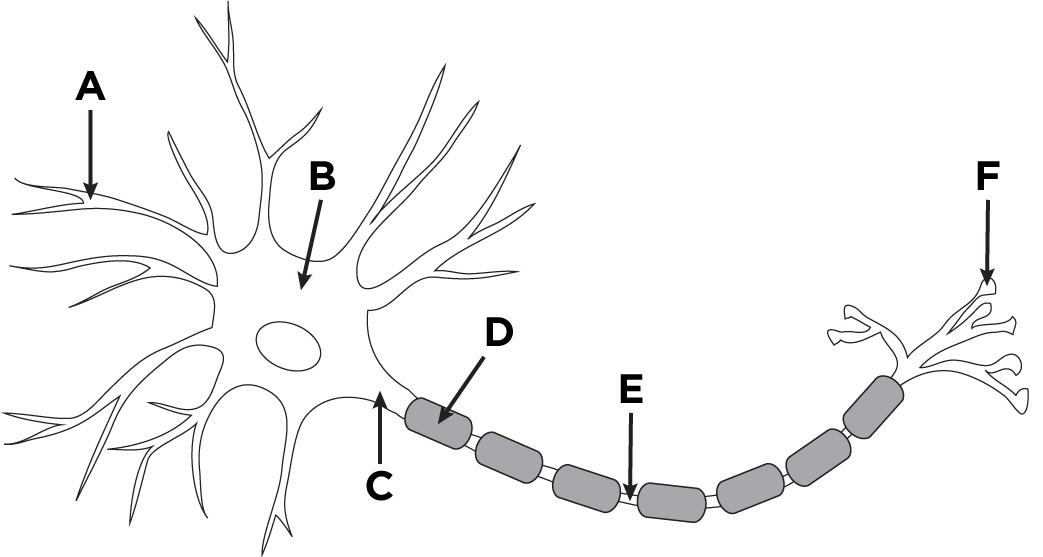
Axon
C
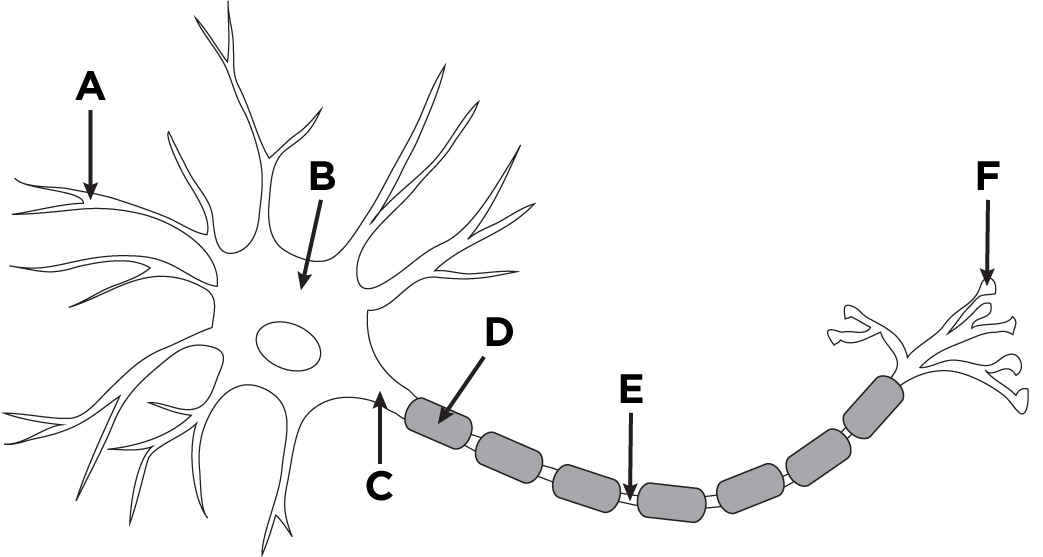
Myelin Sheath
D
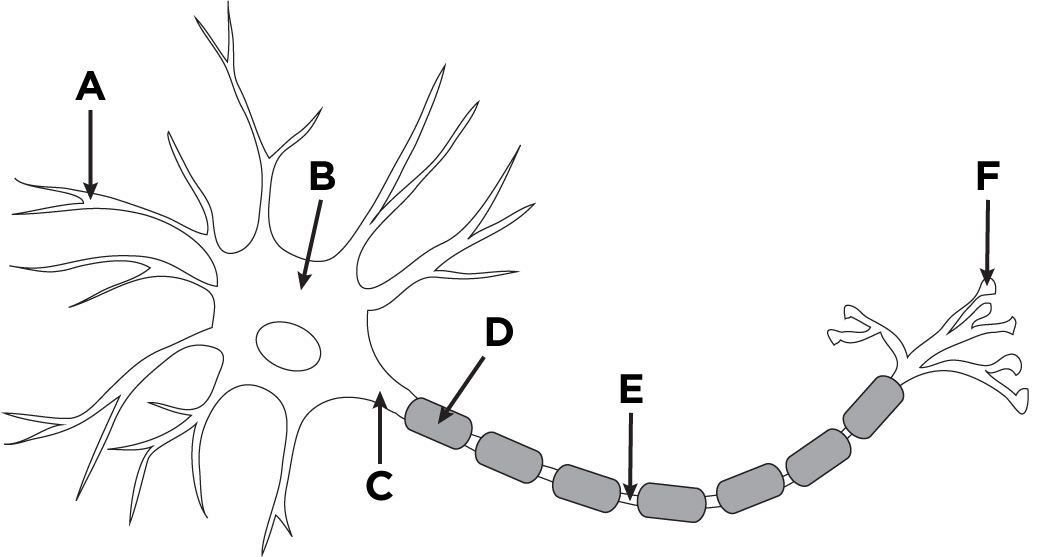
Axon terminal
F
reflex arc
the neural pathway through which a reflex action occurs
sensory neuron
a nerve cell that detects physical and chemical stimuli; controls senses
motor neuron
a nerve cell that controls voluntary and involuntary movements